BBB - Week 5 - touch, temp, pain
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
definition of sensation?
the arriving info from the senses - specialised receptors dedicated to each sensation (transduce info)
definition of perception?
once info from senses is sent to the brain, this is where processing occurs
what is vestibulation?
vestibulation system made up of receptors in inner ear that respond to body position/tilting of the head - this info used alongside other senses in order to perceive what is happening → also important for balance
the vestibular organ, in the ear, consists of how many organs?
2
the vestibular organ, in the ear, consists of organs which are?
the semicircular canals, the otolith organ
what is the structure of the semicircular canals?
has 3 canals pointed in different directions, filled with fluid (endolymph) with hair cells in it
what is the function of the semicircular canals?
movement causes endolymph to move against hair, bending said hair (orientated on 3 planes - comparative stimulation gives brain info about movement of head)
what is the structure of otolith organs?
comprised of utricle and saccule - different orientations (similar to the endolymph but they are glutinous, movement due to gravity)
what is the function of otolith organs?
these sends messages about our position in 3D space, sensitive to acceleration/deceleration/direction changes
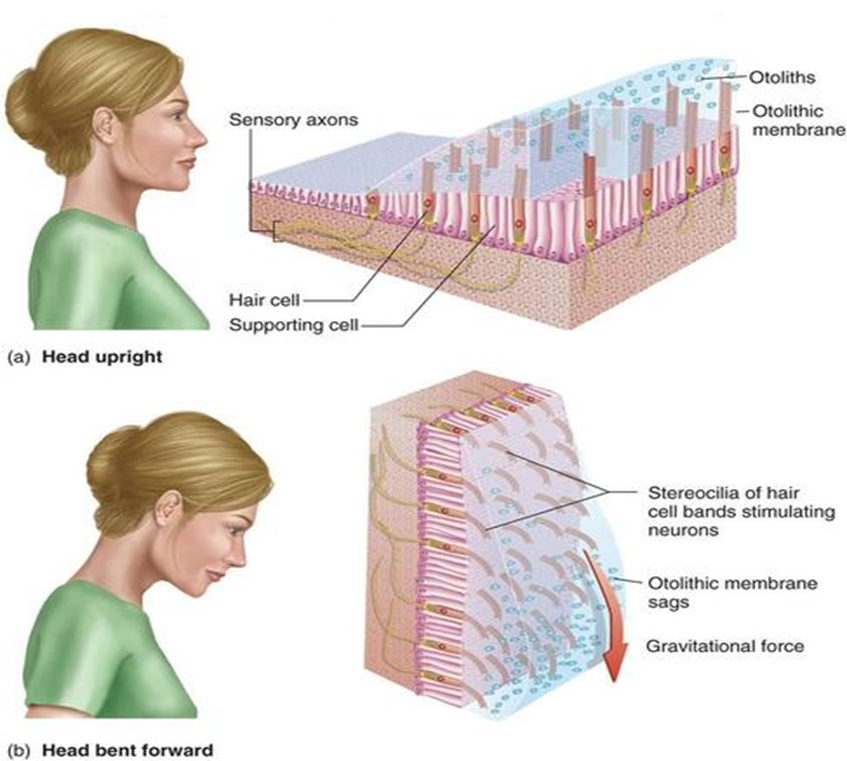
how do otoliths work?
otoliths have weight, so when we move our heads back or forward, the weight shifts and stimulates/bends the hair cells, which sends signals to the brain
what is somatosensation?
the sense of the body
what are some key aspects of somatosensation?
Hapsis, kinesthesis/vestibular, proprioception, temperature, pain
What is Hapsis?
fine touch/pressure
what is kinesthesis/vestibular?
movement, position and spatial orientation/balance
what is proprioception?
awareness of our body in space, walking/running, not falling over
there are 20 different types of receptors for touch, where/what are they?
sensory neurons, in all parts of the body (except brain), vary in density and sensitivity to stimuli
there are different varieties of receptors according to location, what are the ones where stimuli is inside the body?
Interoceptors, Proprioceptors
there are different varieties of receptors according to location, what are the ones where stimuli is outside the body?
Exteroceptors
what are the 2 types of skin on mammals?
hairy and glabrous
What is glabrous skin?
hairless, very sensitive because we use it to explore objects, specialised for discriminative touch to mediate things like grip control
what is the functions of skin overall?
protective function, prevents evaporation of bodily fluids, provides direct contact with the world →sensitivity of our skin varies by location and function
what does discriminative touch mean?
This is what we normally mean when we discuss touch, being able to determine stimuli from skin and body tissue → facilitated by specialised touch receptors with different structures
What are haptic receptors?
These are receptors on our skin which detect vibration and pressure, these are ‘touch receptors’, detecting fine touch/pressure
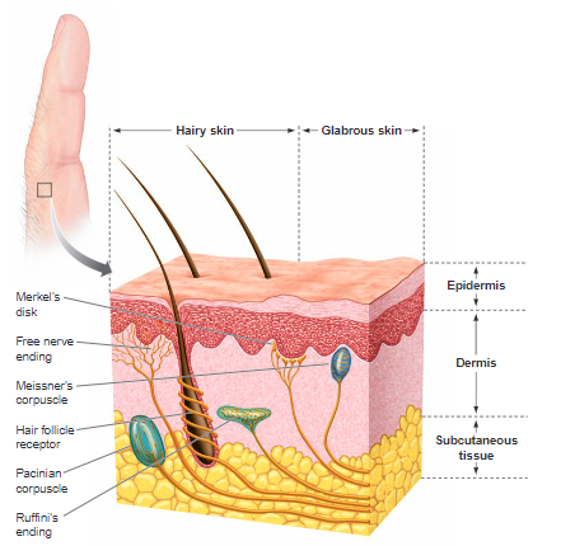
what is the epidermis (skin)?
Top layer of skin, contains cells that produce pigment and protect immune system
what is the dermis (skin)?
Contains much of our nerve endings, oil and sweat glands, and hair follicles
what is the subcutaneous tissue (skin)?
Fat, connective tissue, blood vessels, protecting underlying organs/muscles
function of hair receptors?
Dendrite attached to hair on your skin, as an object moves across skin, these hairs move, sending a nerve impulse → detects direction because specialised receptors for each direction
what are the 2 types of cutaneous receptors known to be found?
Encapsulated (surrounded by a capsule) and Unencapsulated (Includes free nerve endings)
what are properties to free nerve endings (unencapsulated)?
mostly common in skin (different forms), dendrite of sensory neuron, polymodal (meaning not specialised) so its sensitive to painful stimuli, hot and cold and to light touch, slow to adjust to a stimulus
what are the 4 primary tactile mechanoreceptors?
Pacinian Corpuscles, Ruffini’s Corpuscles, Merkel’s Disks, Meissner’s Corpuscles
properties of the Pacinian Corpuscle?
the specific capsule involved in pressure detection, important for detecting deep touch and vibration, rapidly-adapting (changing stimuli), thin layer structure, found in both hairy and glabrous skin
properties of Ruffini’s Corpuscle (AKA Ruffini’s ending)?
also found deep in dermis and subcutaneous tissue, also found in both glabrous and hairy skin →sensitive to stretching/sustained deep touch, slow adapting
properties of Merkel’s disk + nerve endings?
Unencapsulated, found in epidermis and deeper, found in both glabrous and hairy skin, tonic receptors (sustained light touch, slow adapting)
properties of Meissner’s Corpuscle (AKA Tactile Corpuscle)?
encapsulated receptor, found high within dermis, particularly found in glabrous skin and finger pads, rapidly adapting, sensitive to light touch (changing stimuli), sensitive to shape/textural changes in exploratory and discriminatory touch
what do nociceptors do?
They detect pain and temperature
what do thermoreceptors do (temperature receptors)?
Detects temperature, separates for hot and cold