Reproduction viruses
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Infectious bovine Rhinotracheitis
virus: bovine alphaherpesvirus 1 (herpesviridae)
abortion storms, typically mid-late gestation, also pustular vulvovaginitis (IPV), key cue: abortions following respiratory disease outbreak in a naive or under vaccinated herd (fetal hepatic necrosis)
males: infectious balanoposthitis (IBP) painful penile/preputial lesions
veneral transmission; usually shed in genital secretions/semen
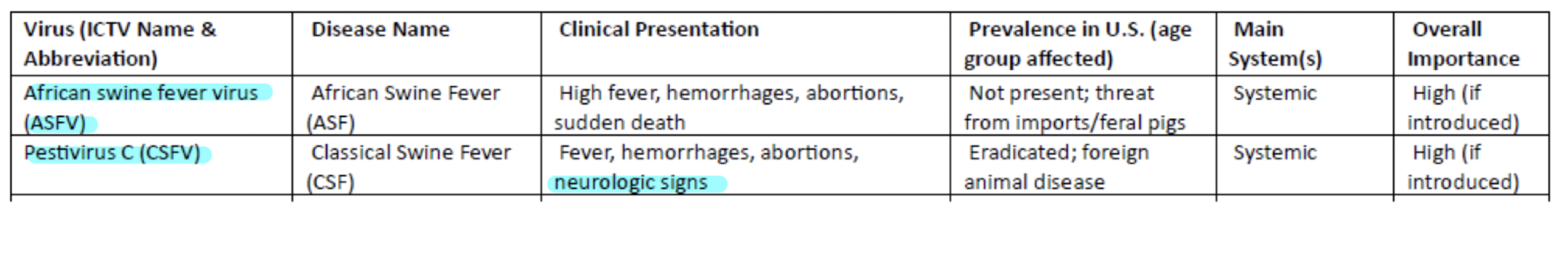
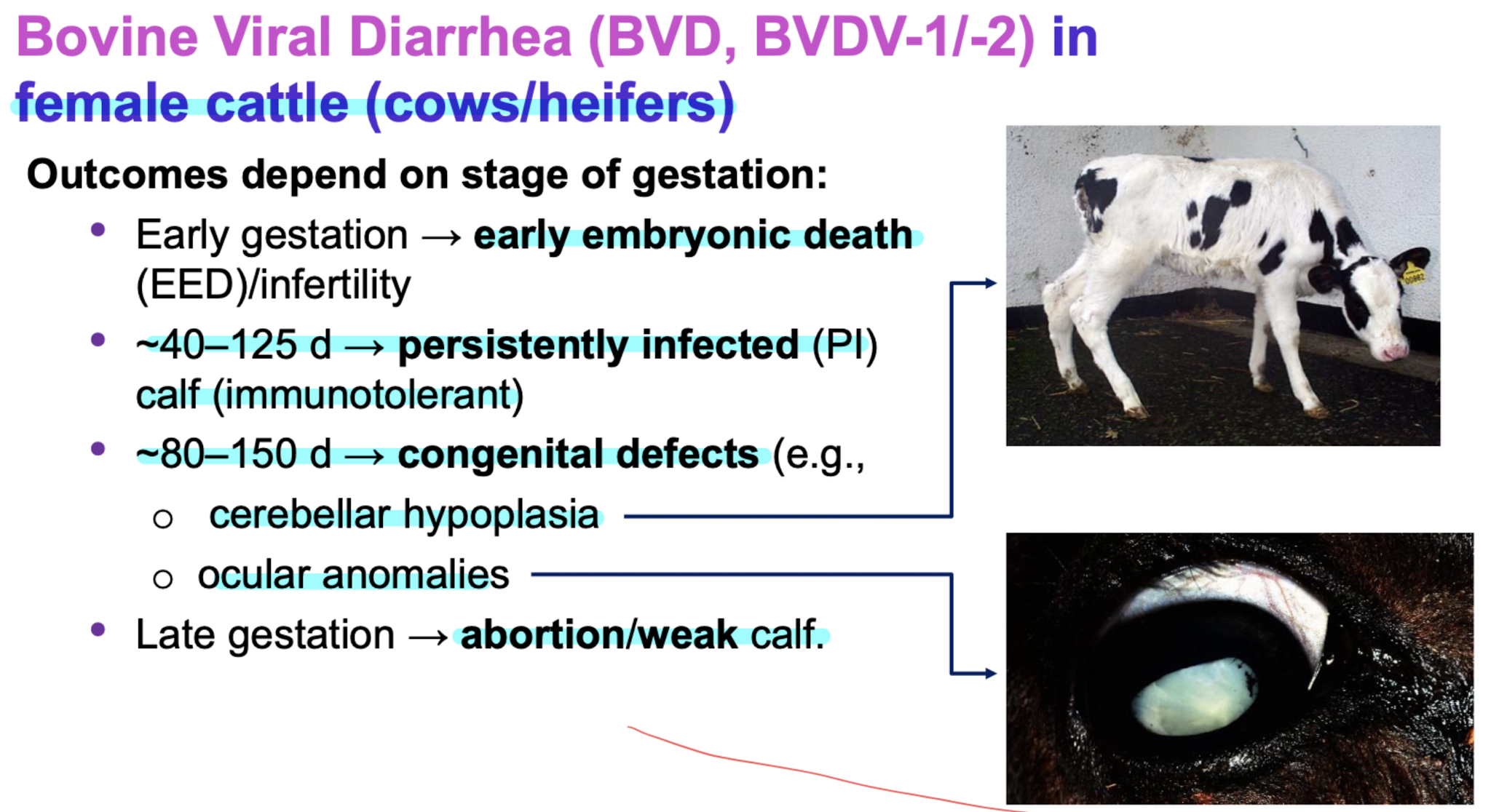
Bovine Viral Diarrhea
Pestivirus A and Pestivirus B (Flaviviridae)
clinical signs: inapparent infection to fever, depresssion, decreased milk production, abortion, diarrhea, death
NOt secifically affect the digestive tract but immune suppression as a hallmark sign
Muscoal disease high fatal form of BVD in persistently infected when superinfected with cytopathic BVDV
bulls:semen risk BVDV shed in semen, PI bulls chronically shed despite high antibodies→ test all breeding bulls
pre breeding vaccination to prevent fetal infection Ai only from screen bulls
Bluetongue cattle
Bluetongue virus (sedoreoviridae)
mild respiratory, integumentary system, reproductive impact much less frequent but can happen
Bluetongue Sheep
Bluetongue virus (sedoreoviridae)
female: culicoides-borne, non-contagious; abortions or malformed lambs if infected during gestation
classic defects= hyranencephaly/porencephaly→ blin/ataxic neonates
testing: RT-qPCR for virus(acute), ELISA/AGID for antibodies (exposure)
control: vector management, vaccination where available, movement/biosecurity controls
male: BTV RNA detectable in semen and transiently reduced semen quality
sexual transmission is not a major route at the population level but donor screening is standard
Border Disease
virus: Pestivirus Ovis

males: PI shedding rams transmit venerally in semen/secretions, screen rams before breeding season
Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS)
virus: Betaarterivirus suid 1 & 2 (arteriviviridae)
most costly disease in swine, pigs of all ages, common in winter and spring
transmission: virus shed in all secretions and excretions
clinical signs: depend on virulence of virs strain and immune status
initial sign: anorexia, fever, lethargy
hyperpneic, dyspneic, transient hyperemia or cynosis of extremities (blue ear dz) blue discoloration of ears, snout, vulva
nursery pigs: roughened hair coats, reduced growth rates, increased mortality

males: virus harbors in lymph nodes, tonsils, and male repro tract long after virus is cleared from other tissues, can continue to shed virus in semen for prolonged periods of time
control: herd closure, population level with ai and air filtration
porcine parvovirus
virus: protoparvovirus ungulate 1 (parvoviviridae)
enzootic, most important infectious agents causing infertility, NO SIGNS IN ADULT PIGS, NO DIARRHEA, virus is extremely stable in environement
females: intro to naive herd= extreme loss, gilts naturally infected have immunity and protect fetus, in neonates maternal antibodies can persist up to 6 months preventing active immunization
SMEDI, NO abortion

males: shed in semen, qPCR for screening semen
VAccinate all breeding stock (gilt, sows, boars) before breeding with KIlled PPV virus
Porcine Circocvirus associated disease
virus: porcine circovirus 2 (circoviridae) and 3
transmission: oronasal via direct contact and fomaties, virus shed in feces, respiratory secretions, urine, vertical transmission (maternal antibodies protect piglets againts infection)

Dx: traid clinical signs, lesions, viral detection in lesions

control: vax effective in reducing viral load and subsequent shedding, reduce occurrence of PCVADs and mortality
Bovine Respiratory disease complex shipping fever pneumonia
pathology: starts with immunocompromised animal (stress) then gets viral infection and secondary bacterial infection from commensal bacteria leading to broncho-pneumonia (which colonize in the cranioventral lung tissue)



Resp. dz
Bovine coronavirus infection (BCoV)
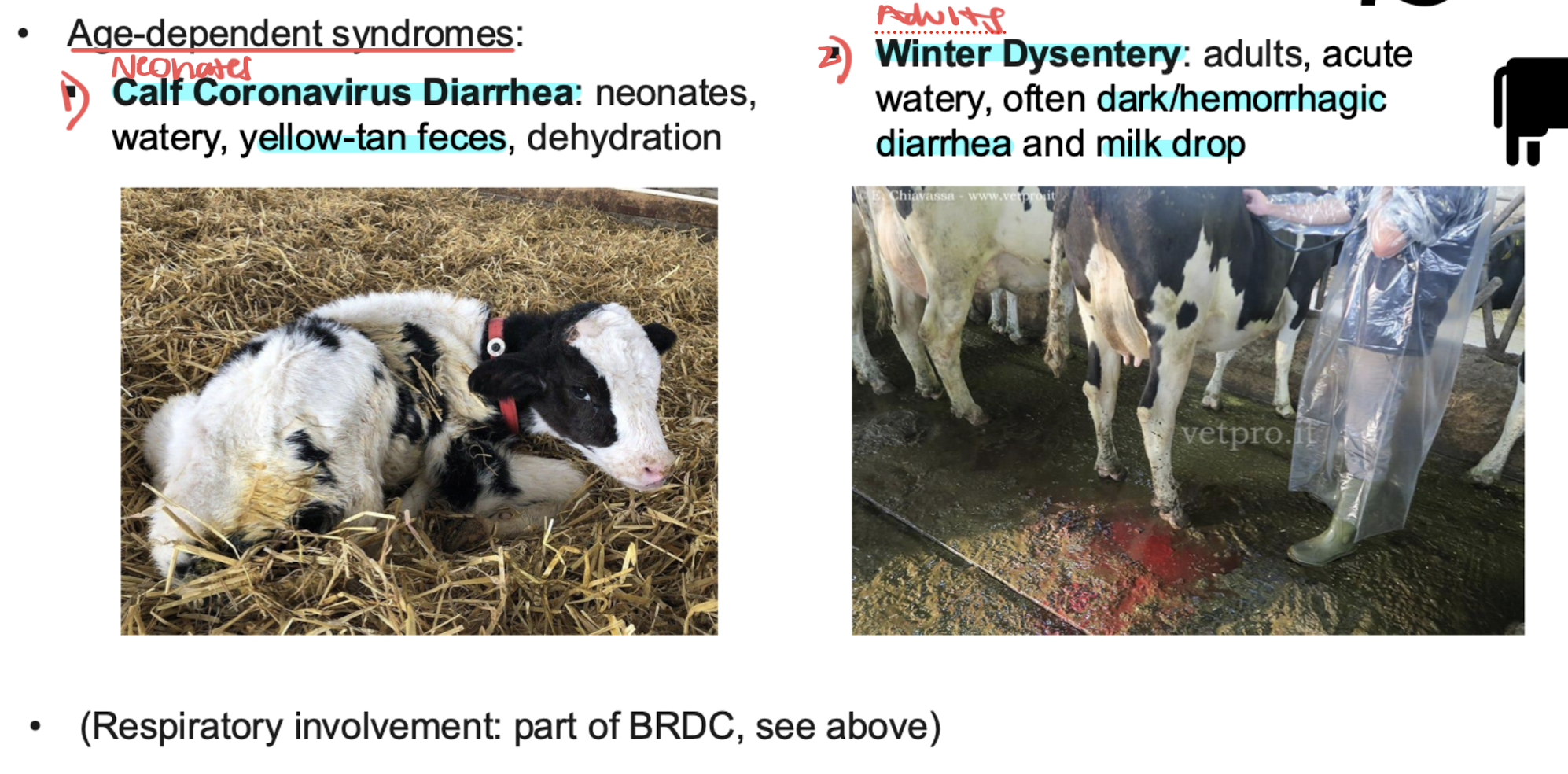
GI dz
Calf Rotaviral Diarrhea (rotavirus a)
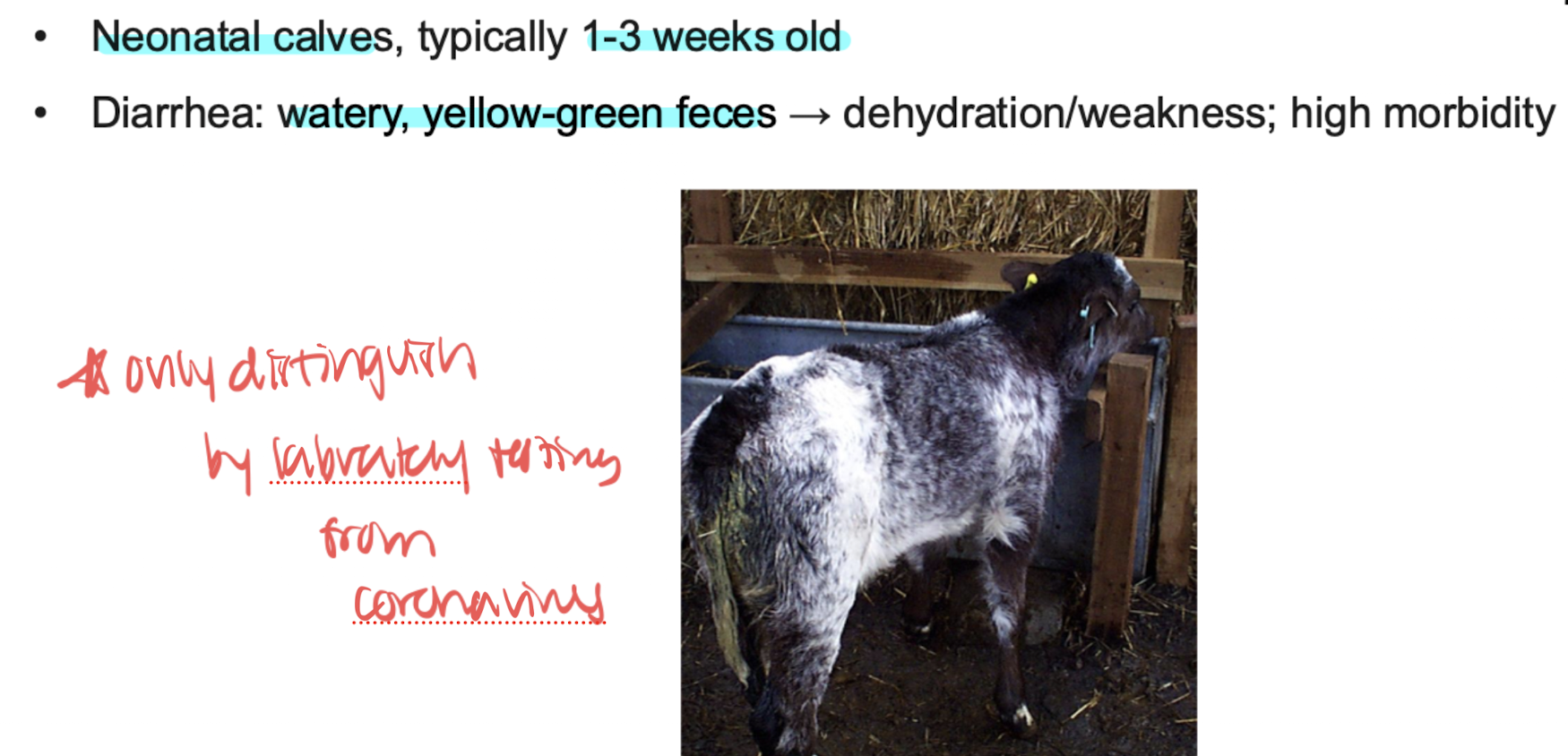
GI dz
Enzootic bovine leukosis
virus: bovine leukemia virus; systemic dz
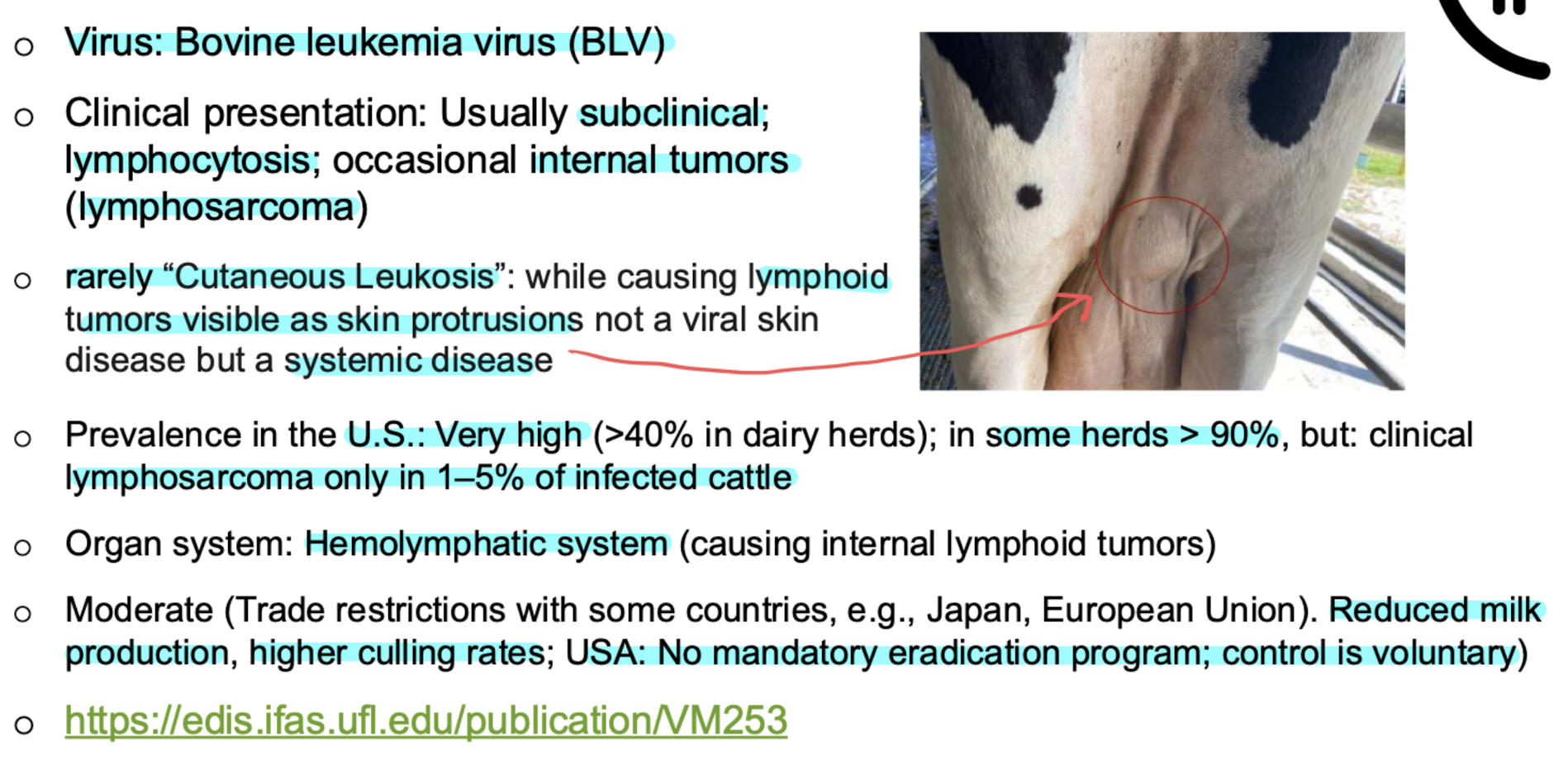
systemic dz
Ovine progressive pneumonia (Maedi-Visna virus)

Resp. dz
ovine pulmonary adenocarcinoma (Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus)

Resp. dz
Peste de Petite Ruminants virus (PPRV)
viral GI dz- small ruminats; causes severe GI (respiratory and reproductive signs not in US)
Carpine Arthritis Encephalitis
Retrovirus (hard udder but no respiratory dz (differentiate from OPP))

systemic dz
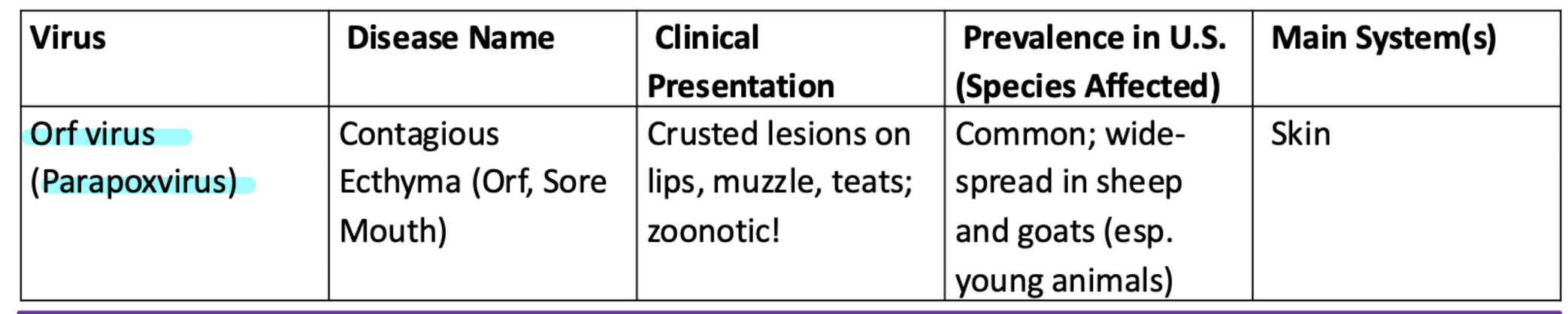
Contagious ecthyma (orc, sore mouth)
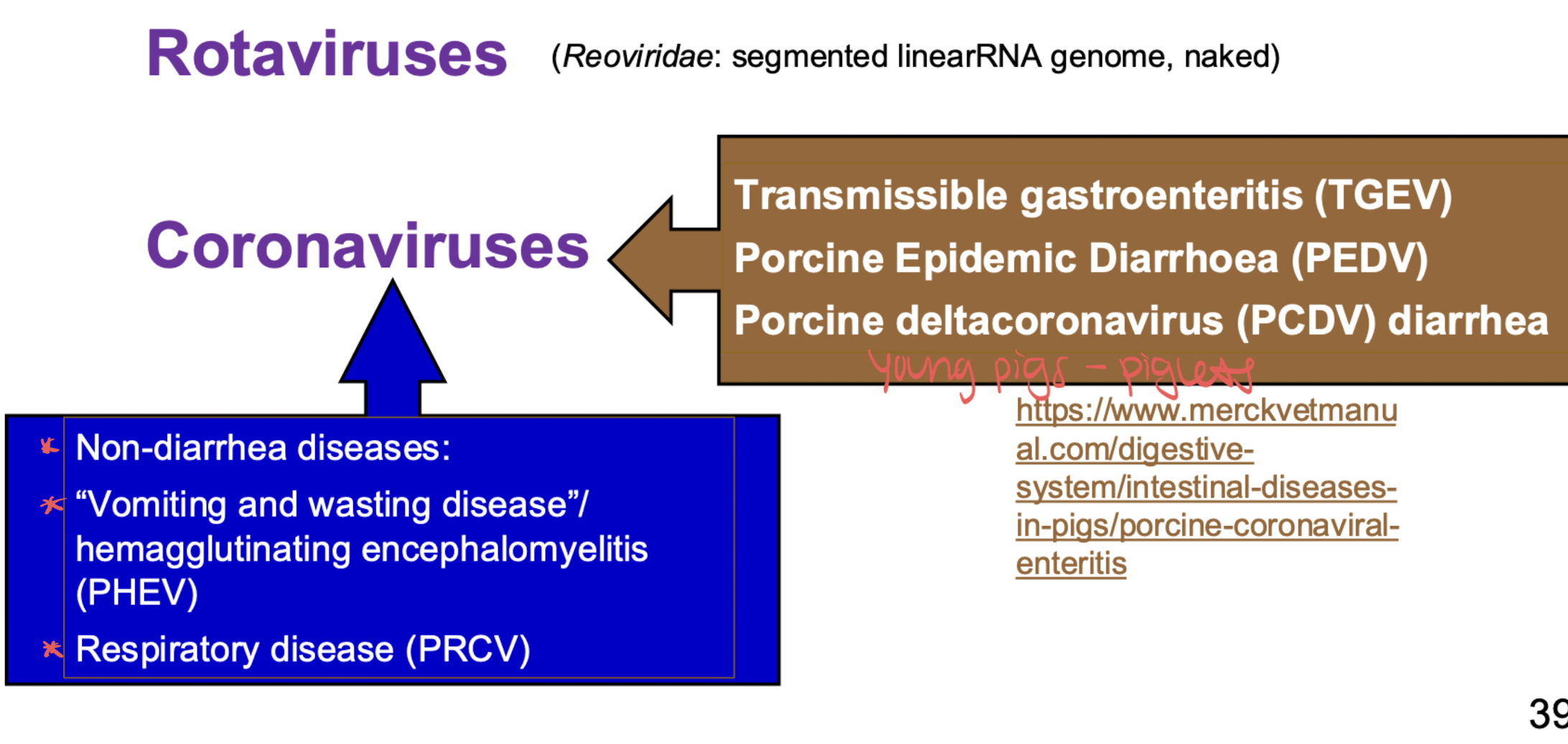
viral diarrheas in piglets
rotaviruses and coronaviruses
common systemic dz in swine: african swine fever and classical swine fever