IGCSE - Unit 5.1 (Sources of Finance) and 5.2 (Cash Flow)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Captial expenditure
Investment spending on fixed assets such as the purchase of land and buildings.
Revenue expenditure
Expenditure on the day-to-day running of a business, such as rent, wages, and utility bills.
Retained profit
The amount of net profit after interest and tax that the business keeps to use within the business rather than paying out as dividends to its shareholders.
Owners funds
The money invested in an unincorporated business by their owners
Sale of Assets
An internal source of finance involving the sale of fixed assets that the business no longer needs
Share Capital
Share capital refers to the money raised from selling shares in a limited liability company
Loan Capital
Money borrowed from a bank via bank loans. Loans are paid back in monthly payments over an agreed period of time plus interest
Overdraft
A short-term source of external finance, which involves a deficit in a bank account that is caused by drawing more money than the account holds.
Trade Credit
A short-term source of external finance involving an arrangement to buy goods and/or services on credit, without making immediate cash or cheque payments. Invoices are usually payable within 30, 60 or 90 days.
Grant
A sum of money given by a government or other organization for a particular purpose. An application must be made to prove that specific criterion has been met.
Subsidy
A sum of money granted by the government to assist an industry or business so that the price of a commodity or service may remain low or competitive.
Debt-factoring
An external, short-term source of finance which involves a business raising cash by selling their outstanding sales invoices (receivables) to a third party (a factoring company) at a discount.
Leasing
An external source of finance that allows a business to use an asset over a fixed period, in return for regular payments. Ownership of the asset remains with the lessor.
Hire Purchase
An external source of finance used for buying certain fixed assets. An initial down payment is made and the balance (plus interest) is paid in monthly installments over an agreed period of time. Transfer of ownership of the asset is only made once all payments have been finalised.
Venture Capital
A form of long-term external finance whereby investment banks and other financial institutions provide funds to startup companies and small businesses that are believed to have long-term growth potential, in return for equity in the business.
Business Angels
Wealthy and entrepreneurial investors who risk their money by investing in small to medium-sized businesses that have high growth potential. In addition to their financial investment, they can also provide mentoring, support and access to key contacts.
Revenue
The money that a business receives from the sale of its goods and services.
Profit
The financial benefit that is gained when revenue exceeds total costs. It can be calculated by the formula: Revenue - Total costs
Working Capital
The amount of available capital that a business can readily use for day-to-day operations. It can be calculated by the formula: Current Assets - Current Liabilities
Cash flow forecast
A document that shows a projection of an organisation's future financial position based on the anticipated amounts, and timing of cash inflows and outflows
Cash inflow
Cash received by an organization in a particular period of time as a result of its operating activities, investment activities, and financing activities.
Cash outflow
Cash paid out by an organization in a particular period as a result of its operating activities, investment activities, and financing activities.
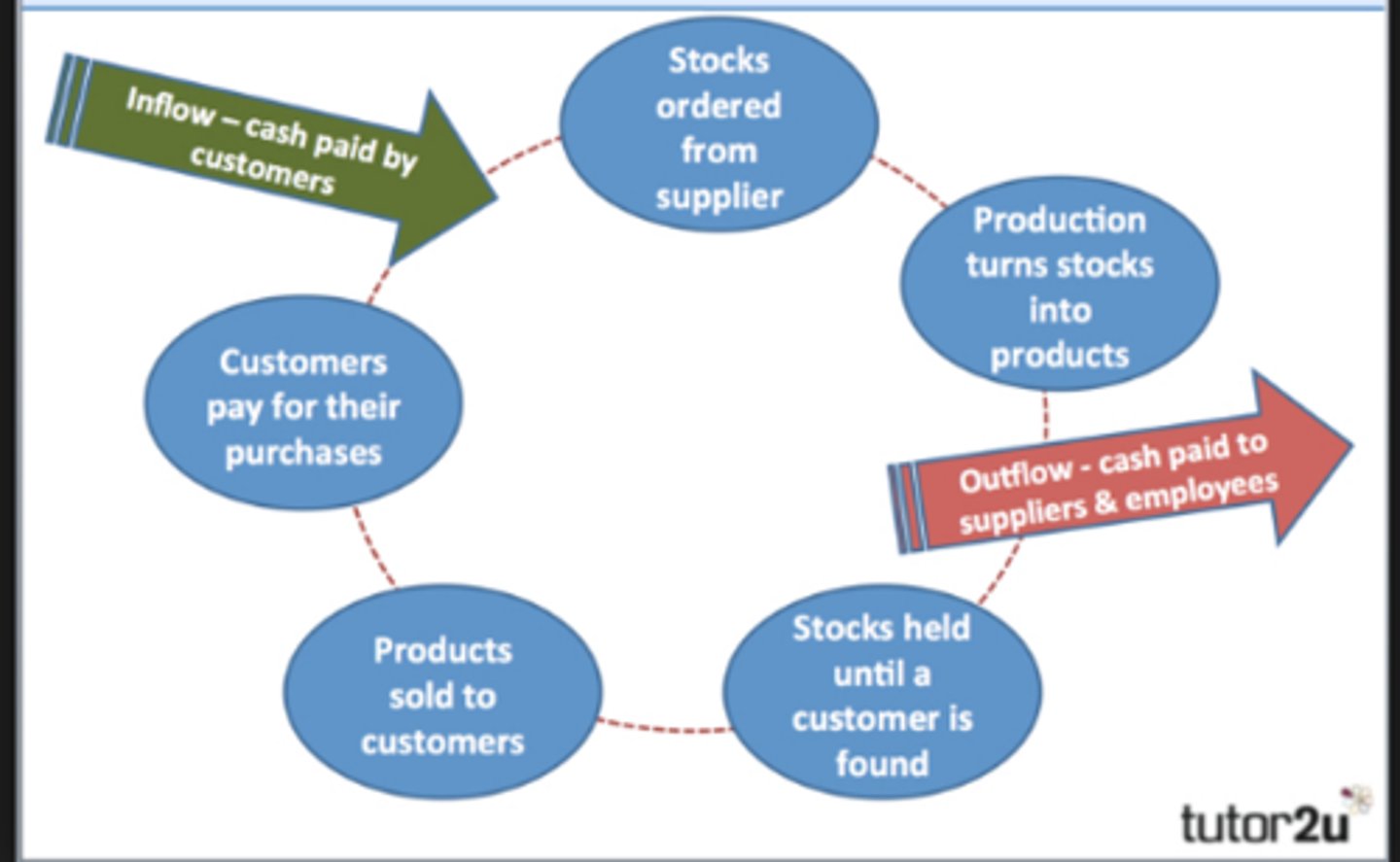
Working capital cycle
The period of time between spending cash on the materials needed for the production process and receiving cash payments from customers.
Net cash flow
Total inflows - total outflows for a given period of time
Closing balance
The amount of money a business has at the end of a time period. Calculated by the formula: opening balance + net cashflow
Opening balance
The amount of money a business has at the start of the time period. It is always equal to the closing balance from the previous time period.
Negative net cash flow
When total outflows are greater than total inflows for a particular time period. This will result in a reduction in the cash balance of the business
Positive net cash flow
When total inflows are greater than total outflows for a particular time period. This will result in an increase in the cash balance of the business