cells
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
description of a light microscope :
small and inexpensive
max magnification is x1500
cannot see viruses, atoms or molecules because they are smaller than a wave of visible light
maximum resolution is 0.2 um
description of a laser scanning confocal microscope :
creates a 3D image
cells are tagged with fluorescent dye
the laser causes the dye to give off light
light focused through a pinhole onto a detector
computer will generate an image
high resolution
description of a transmission electron microscope (TEM) :
large
electrons are smaller than photons so can see very small atoms
produces a 2D image
artificial colour
maximum resolution is 0.0002 um
magnification can be more than x1000000
can see interior
description of a scanning electron microscope (SEM) :
replicates the surface of cells
specimen must be in a vacuum therefore no living organism
3D
can see detailed structure of organelles
maximum magnification is x500000
can see small atoms
maximum resolution is 0.002 um
expensive
preparing slides takes high level of skill
definition of resolution :
how well a microscope can distinguish between two separate points that are close together
magnification =
image size / object size
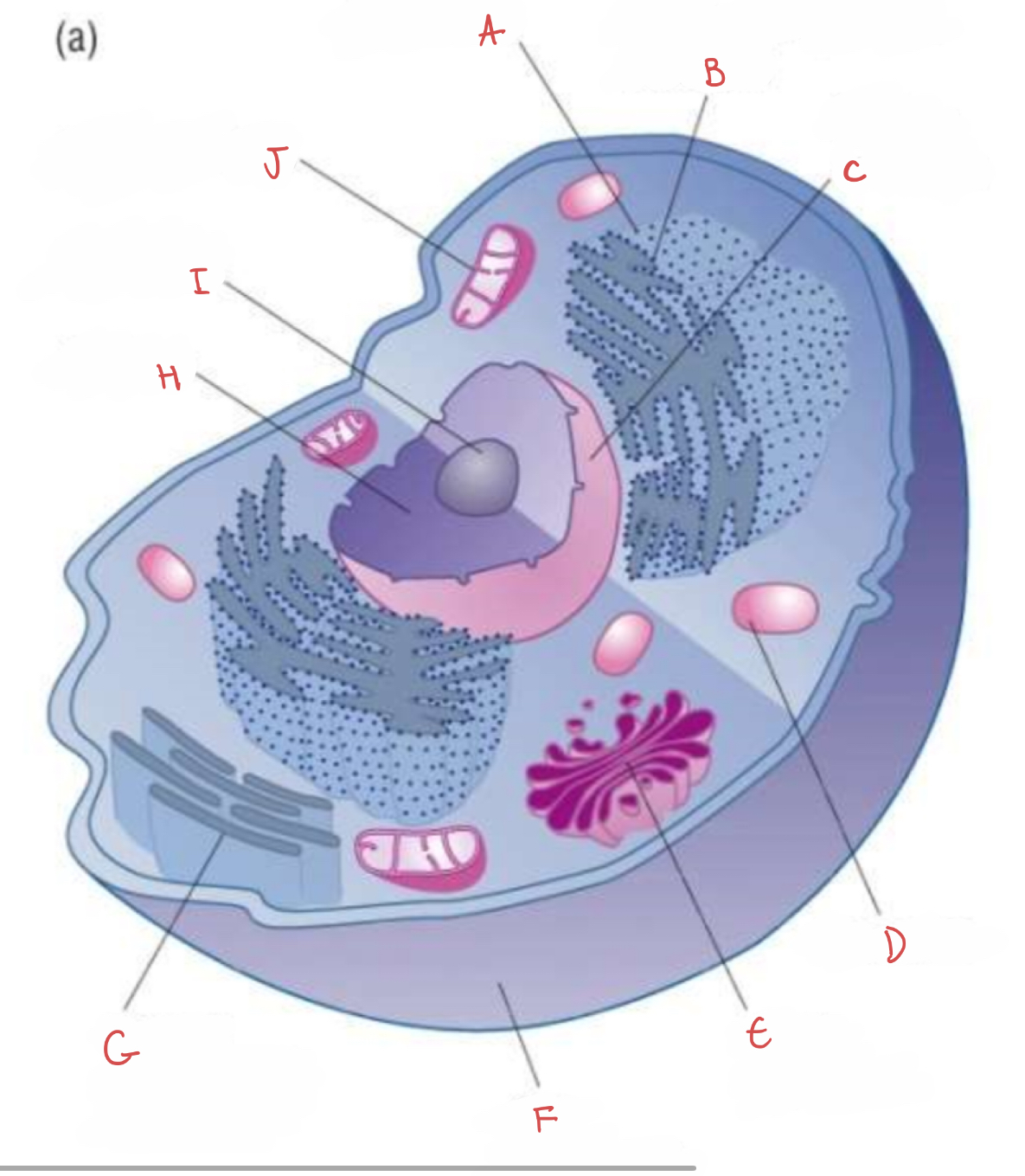
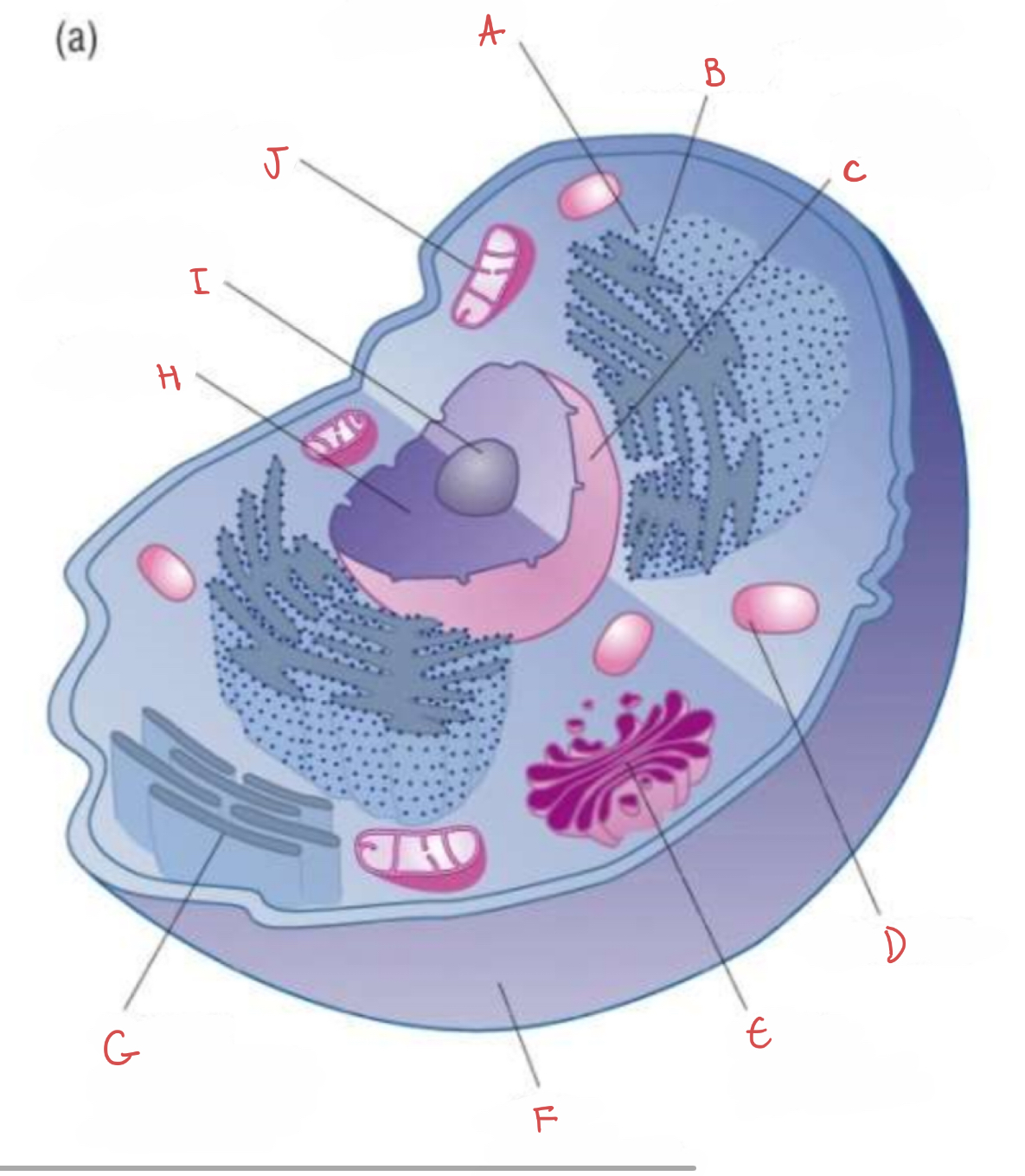
what is A?
ribosome
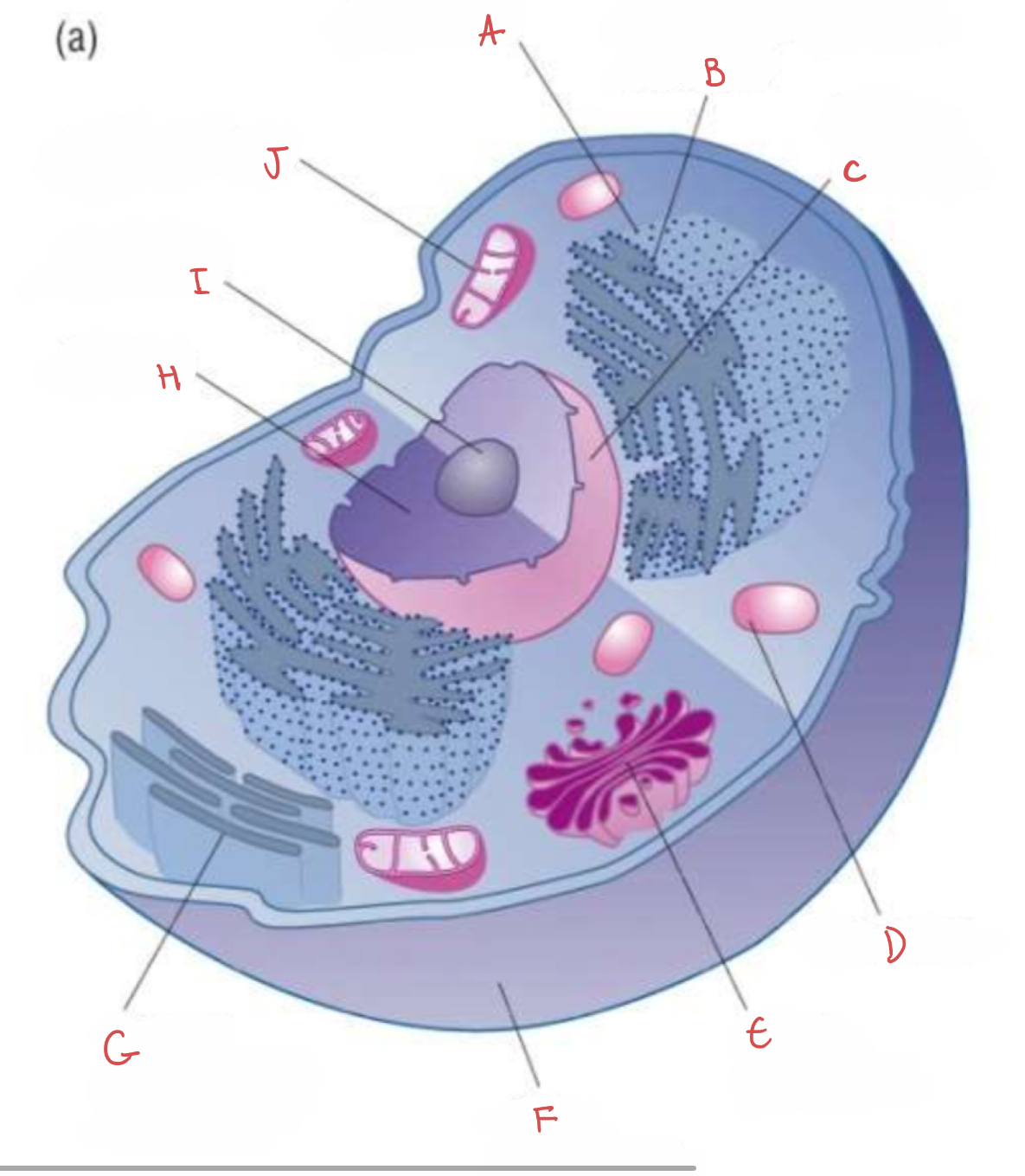
what is B?
rough endoplasmic reticulum
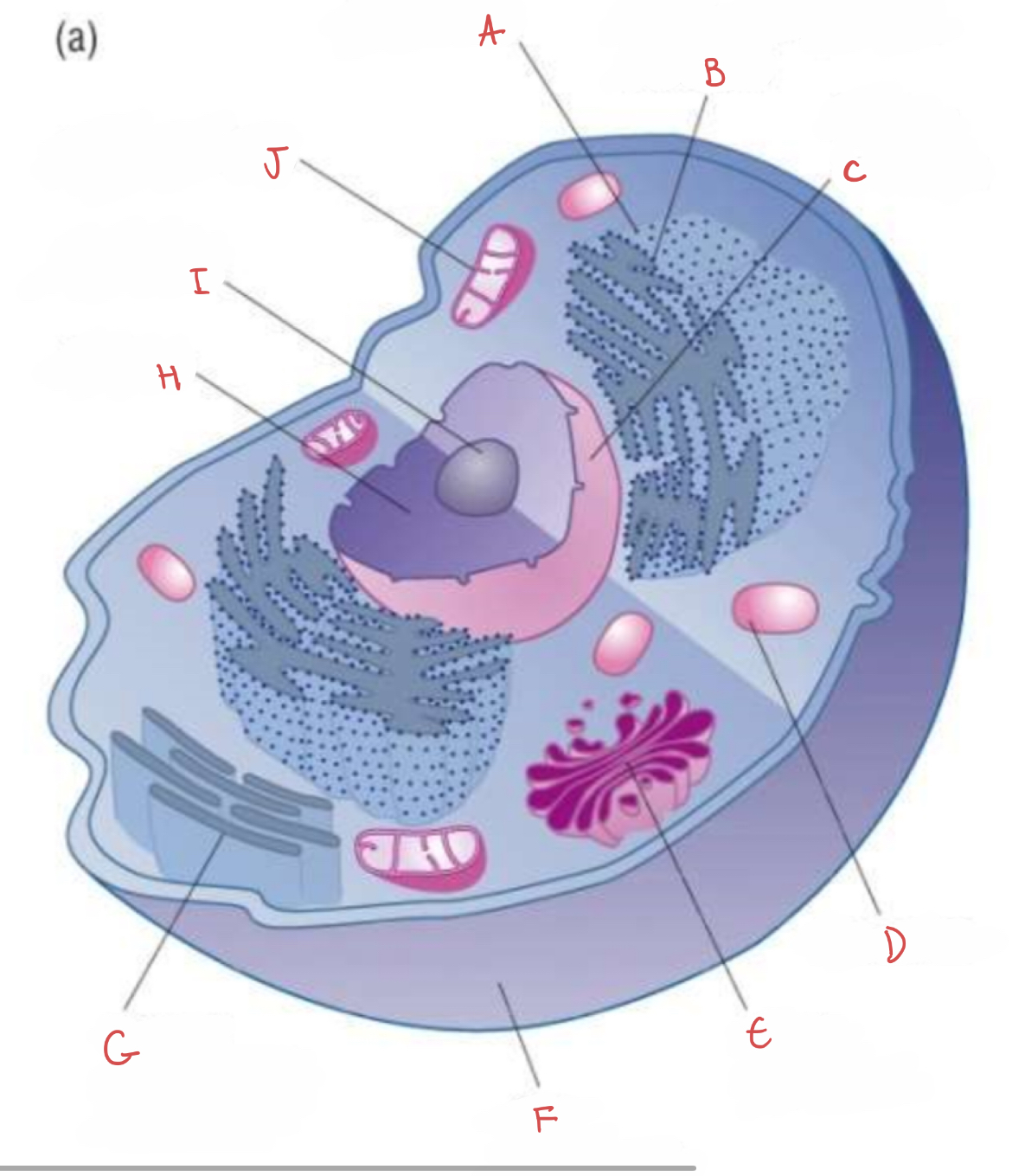
what is C?
nuclear envelope
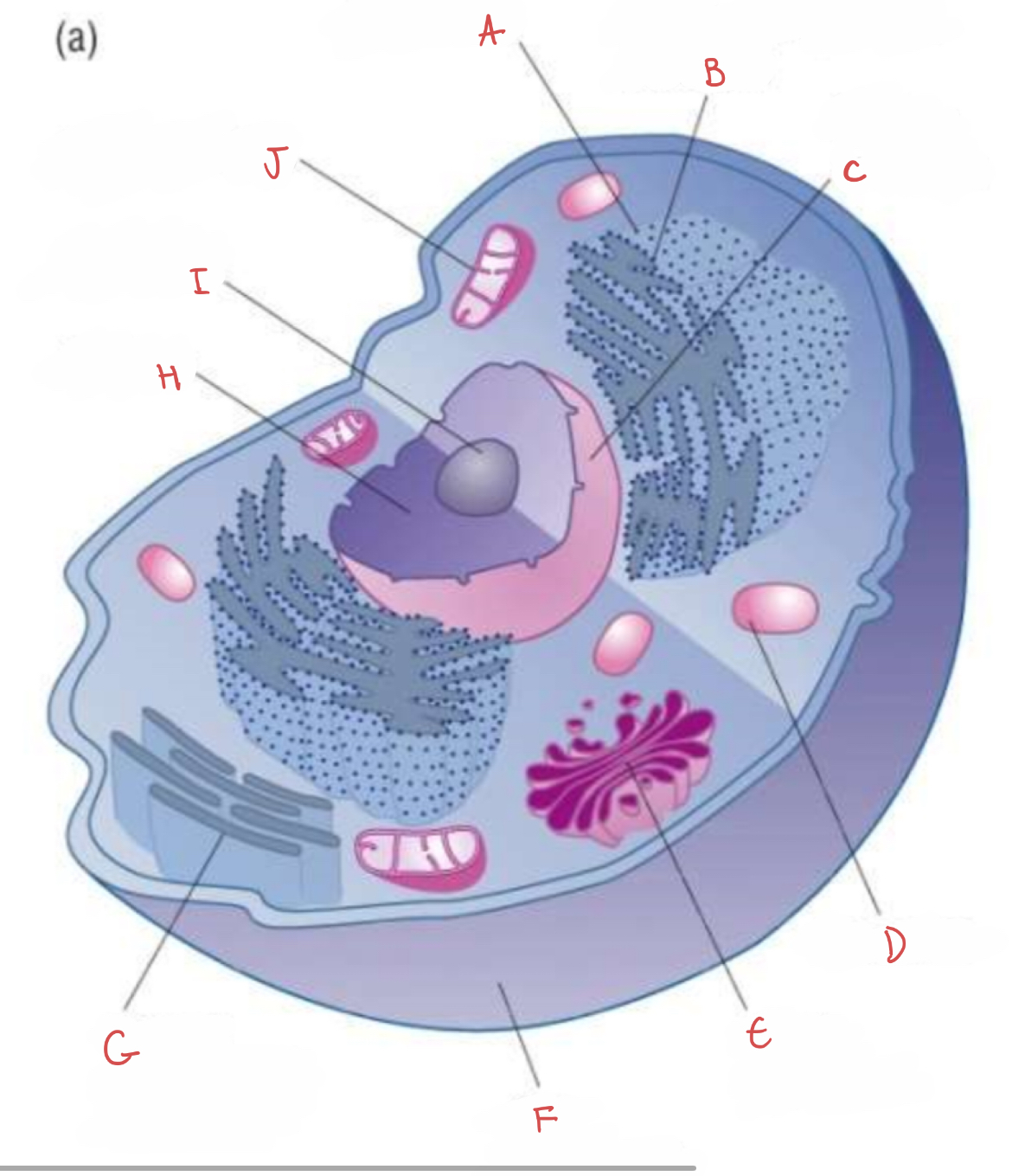
what is D?
lysosome
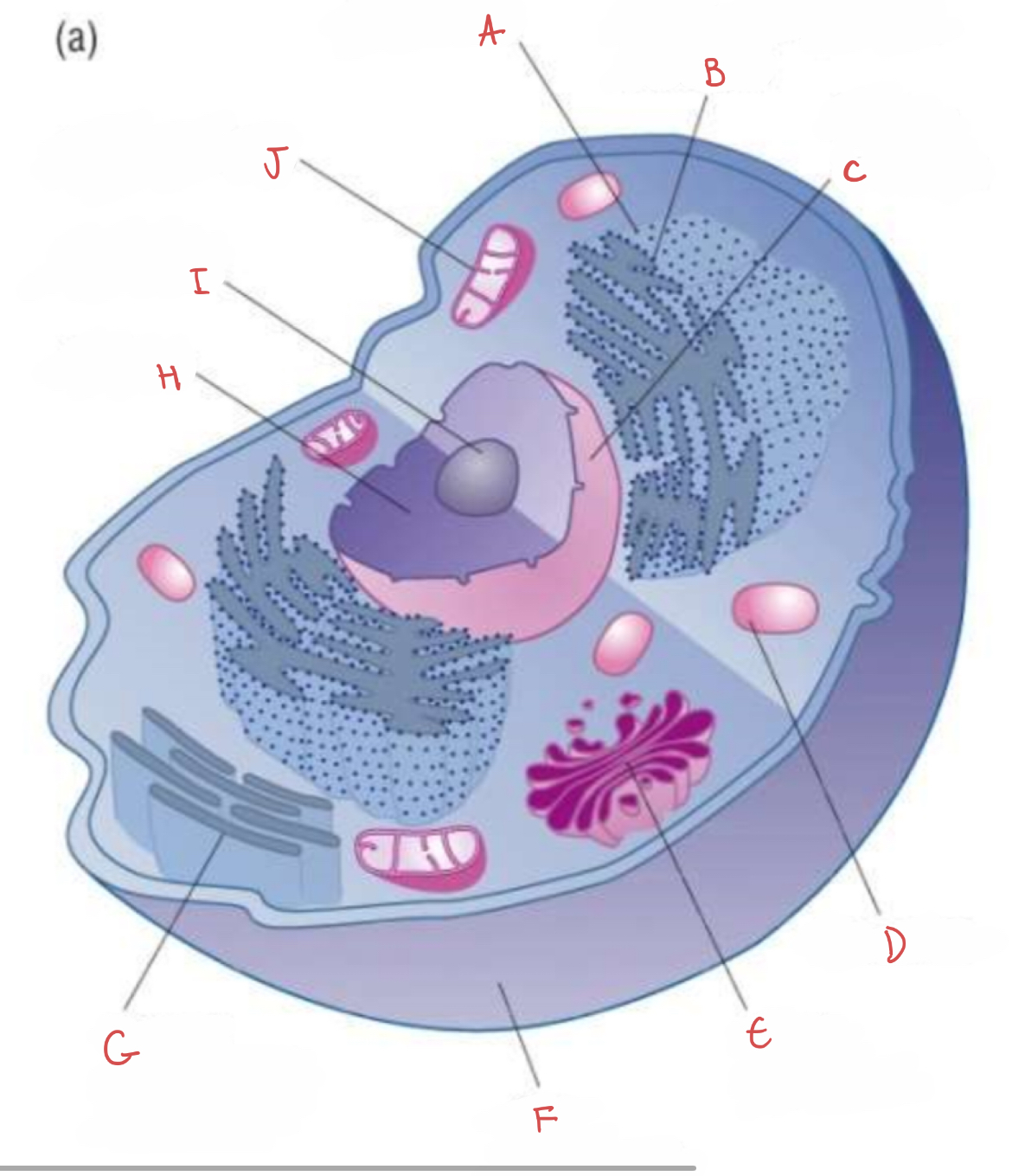
what is E?
golgi apparatus
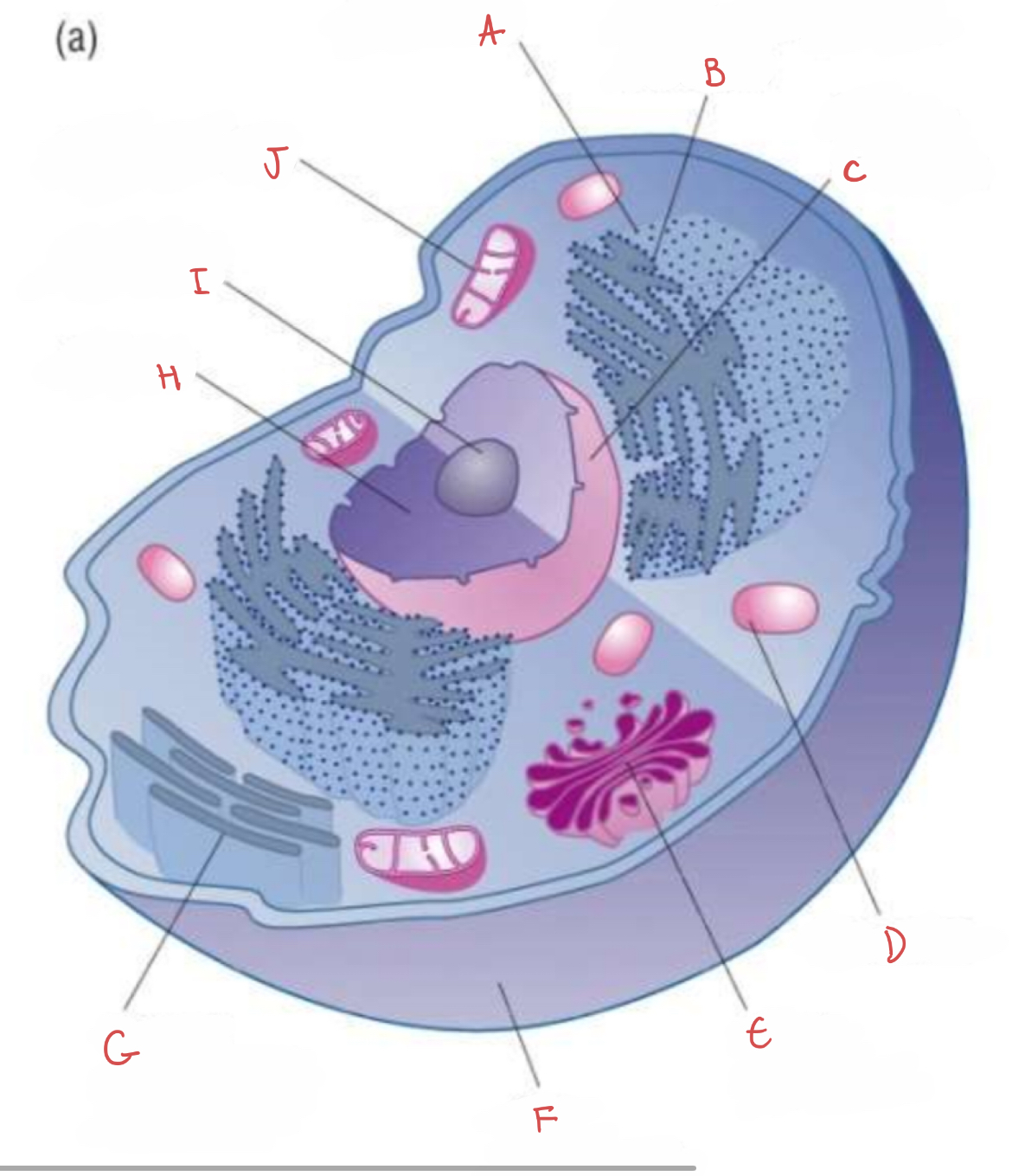
what is F?
cell membrane
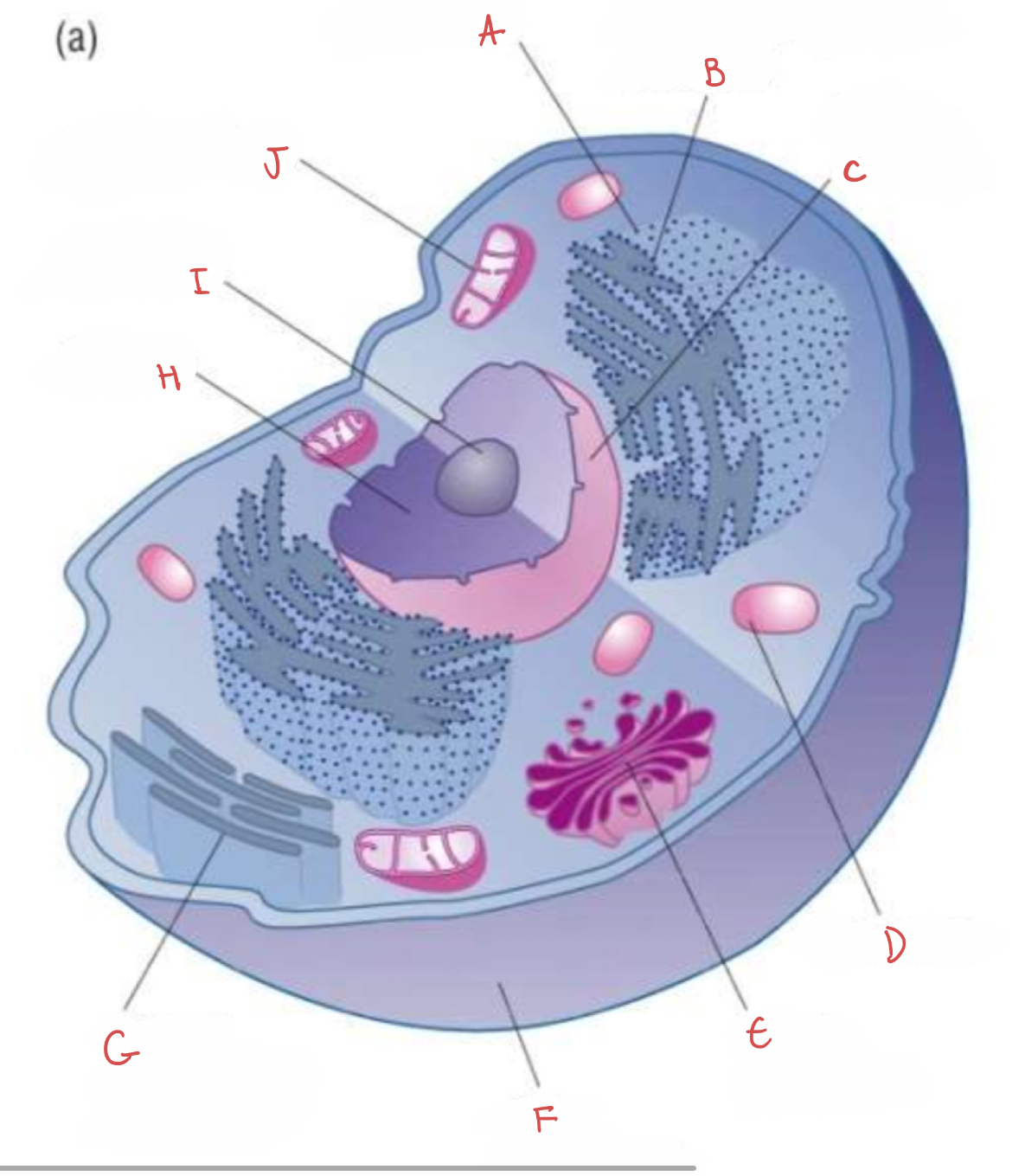
what is G?
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
what is H?
nucleus
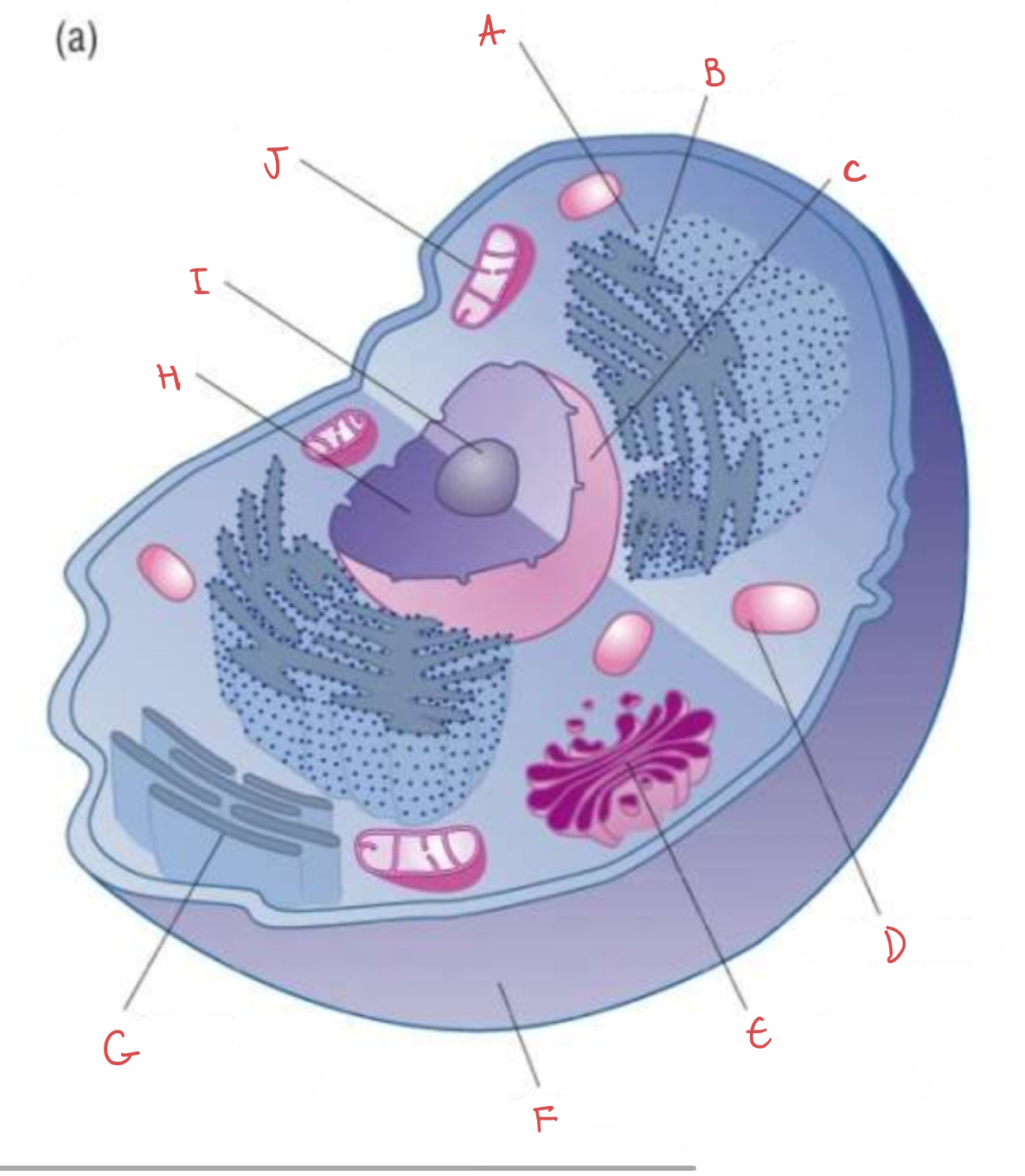
what is I?
nucleolus
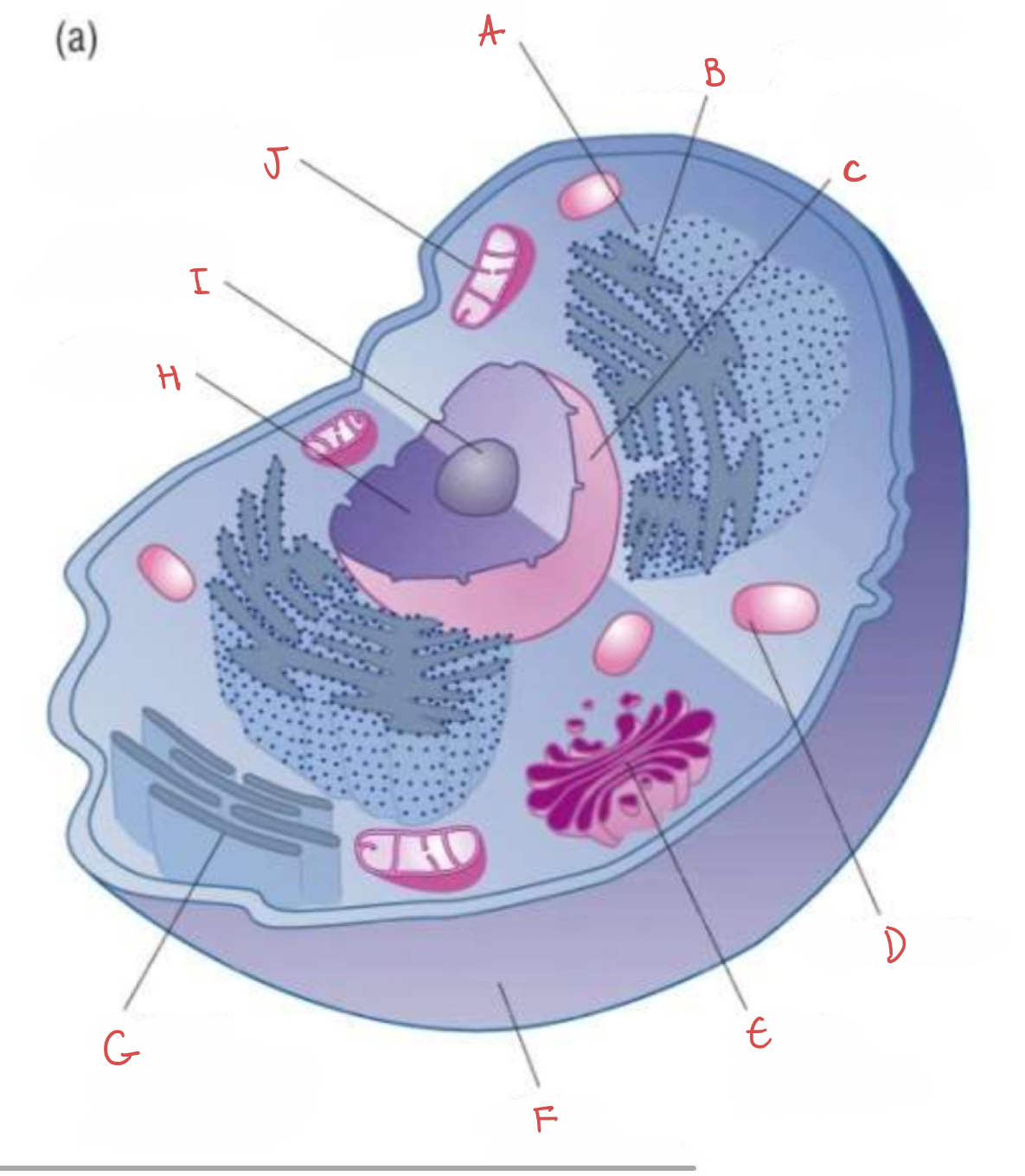
what is J?
mitochondrion
what is a eukaryote?
any organism consisting of one or more cells that contain DNA in a membrane bound nucleus separate to the cytoplasm
animals
plants
fungi
protoctists
nucleus :
contains all the cells genetic material
chromatin :
made of DNA and proteins
nucleolus :
makes RNA which is made into ribosomes
nuclear envelope :
dense, spherical structure
surrounds nucleolus
made of inner and outer membrane with fluid in between
has nuclear pores to allow molecules to pass through
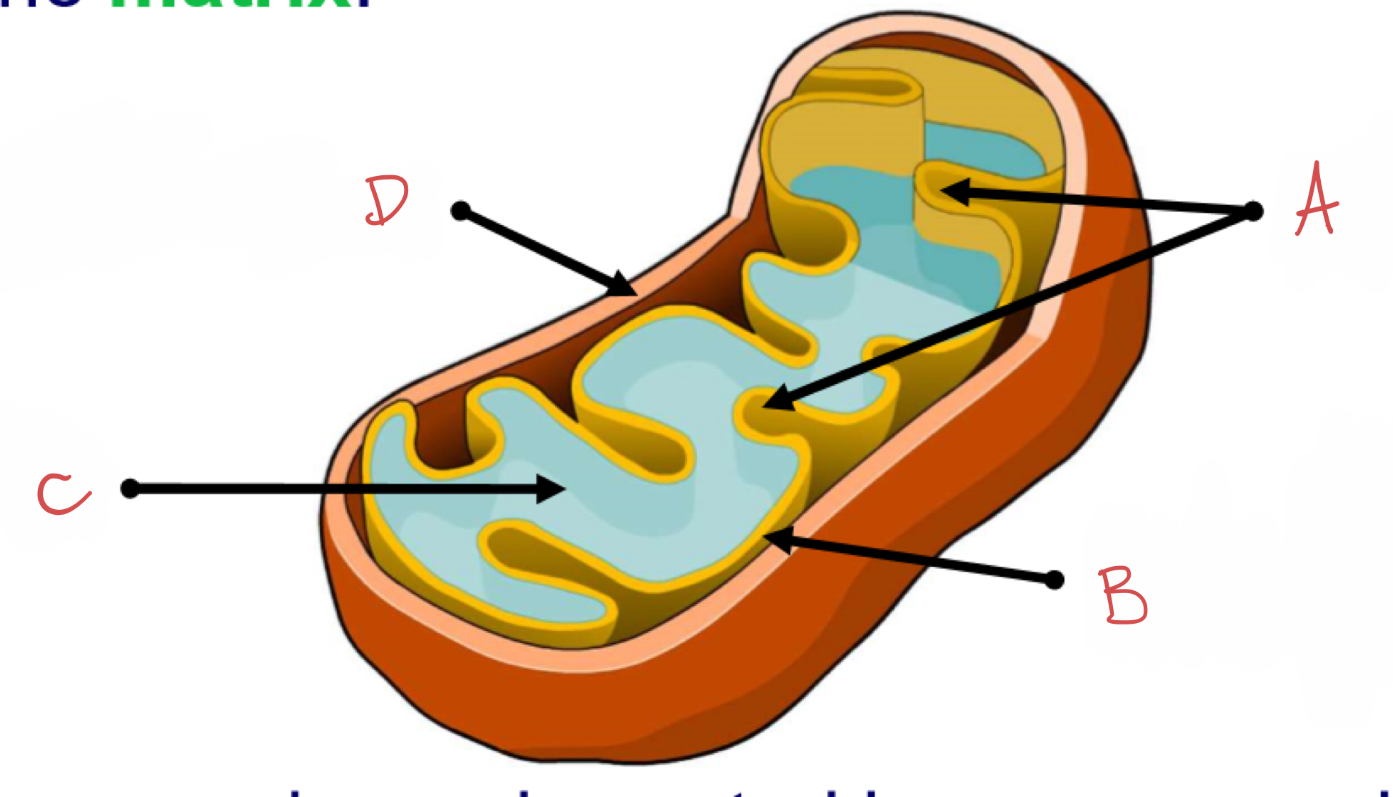
what is A?
cristae
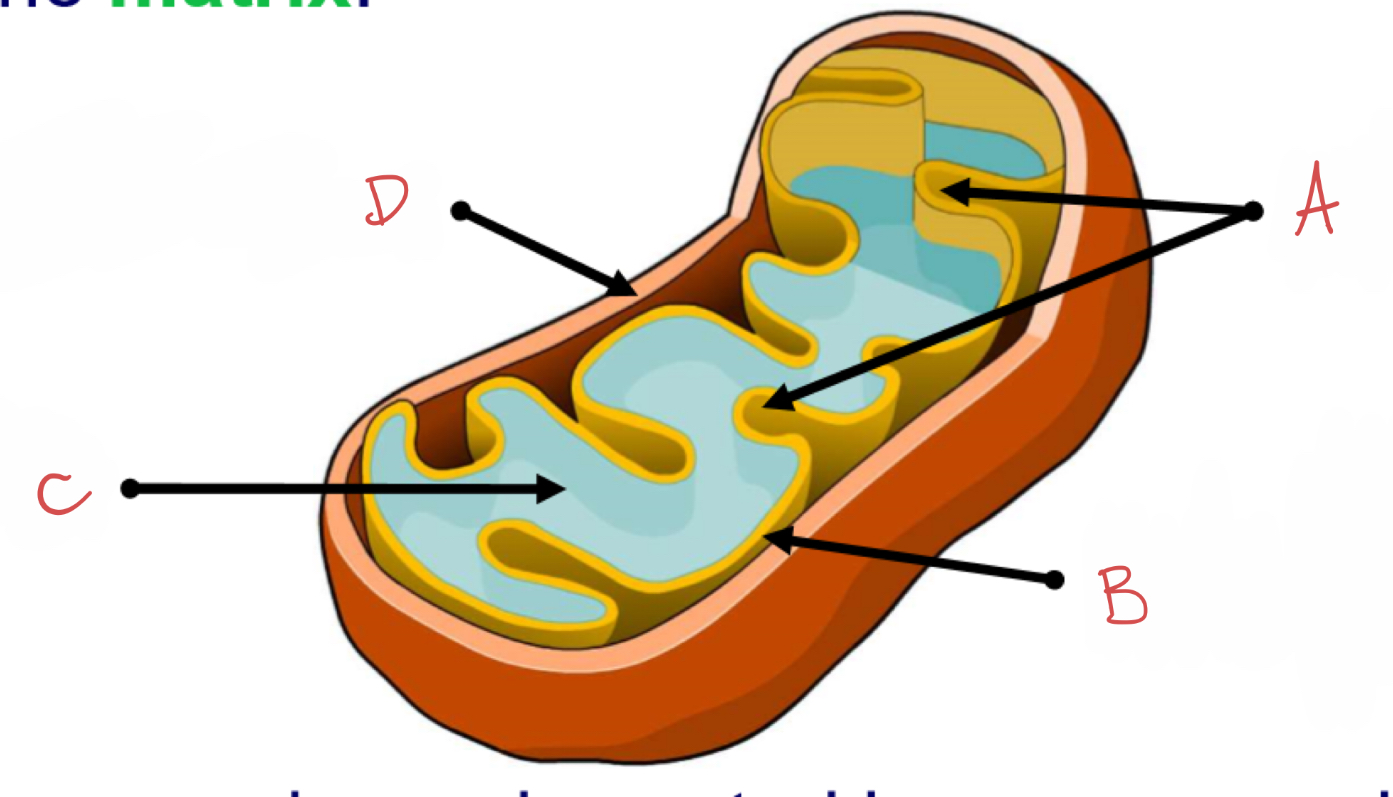
what is B?
inner membrane coated in enzymes which catalyse reactions for aerobic respiration to produce ATP energy
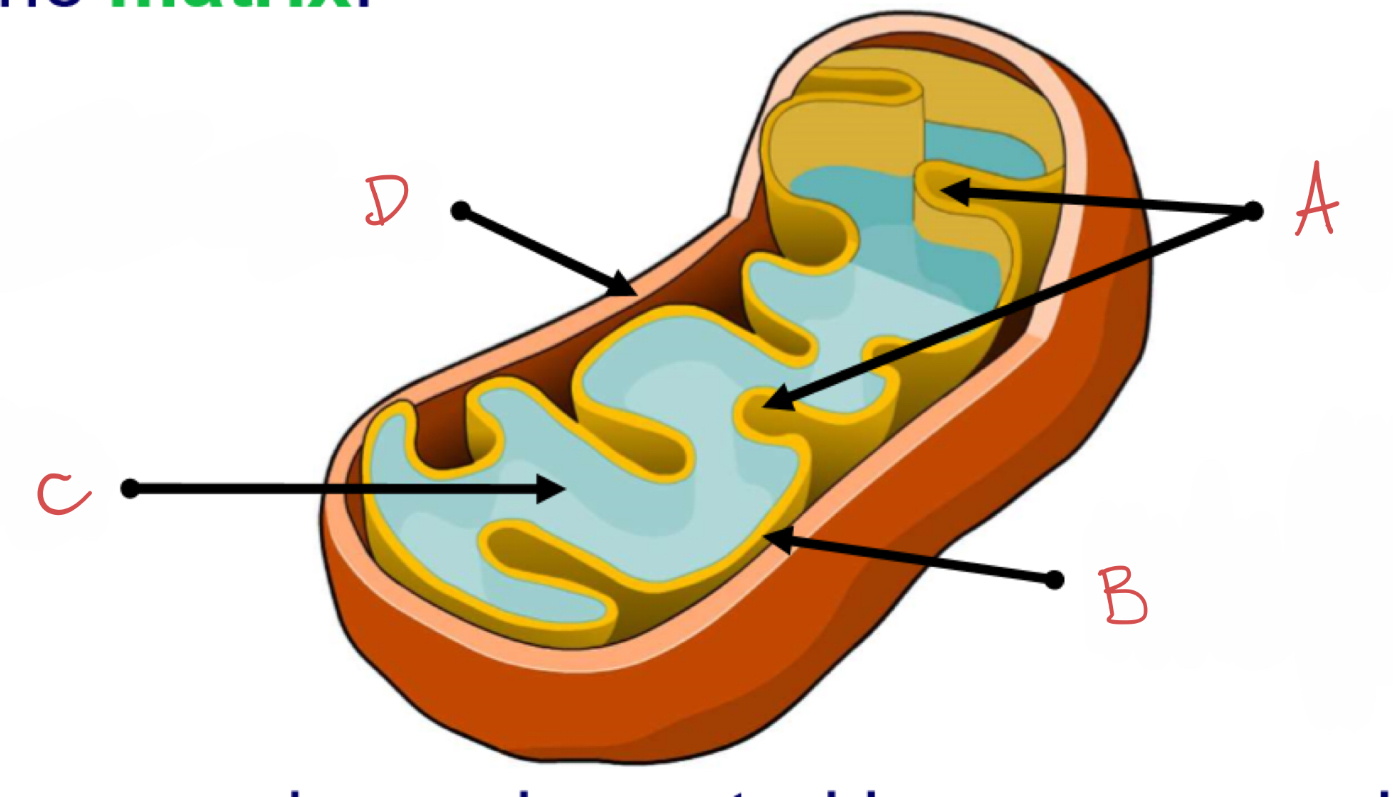
what is C?
matrix
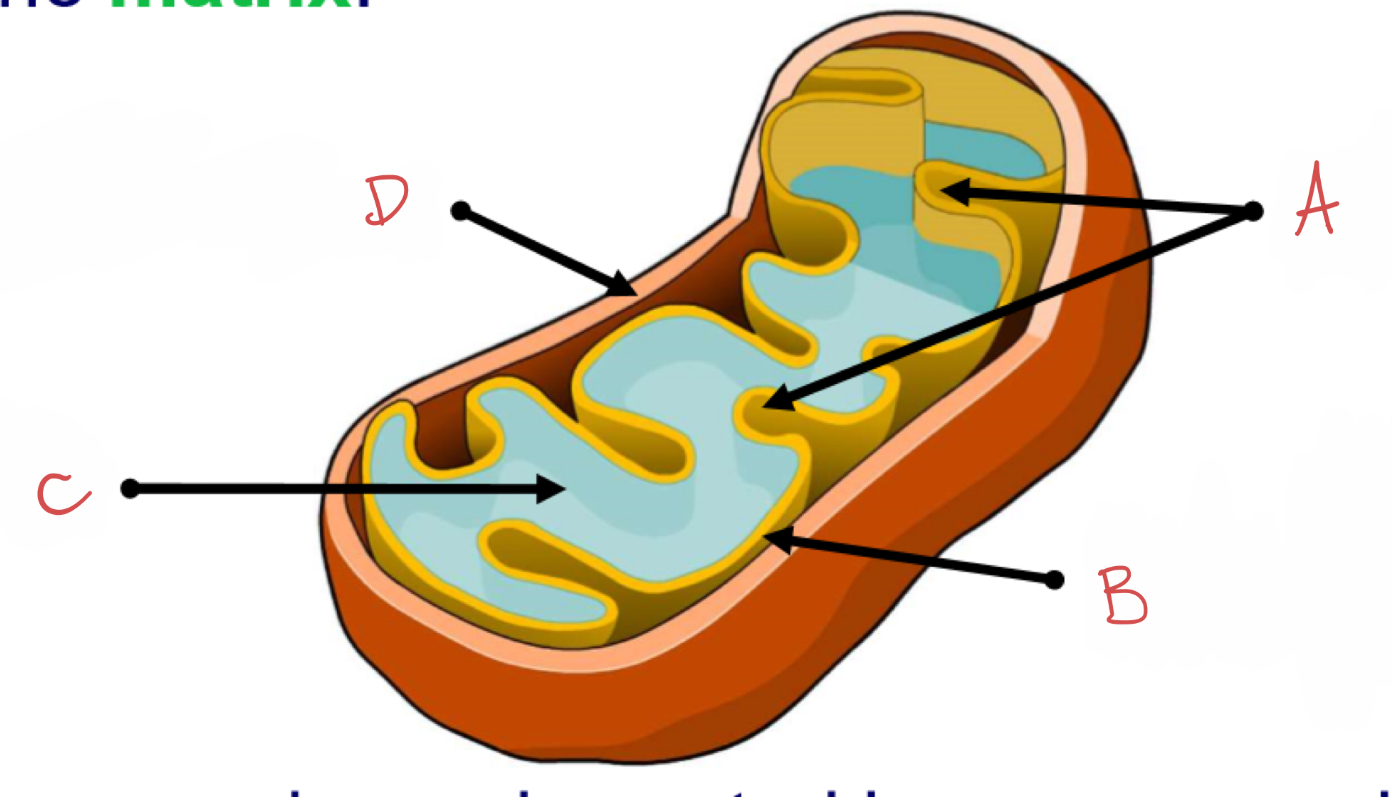
what is D?
outer membrane
mitochondrion :
energy generating organelle
why do mitochondria have their own DNA?
evolved from bacteria with a different genetic code
golgi apparatus - structure :
stack of membrane bound flattened sacs
single membrane has two layers
membrane surrounds an area of fluid where complex molecules are stored and changed
golgi apparatus - function :
receives proteins from the ER and modifies them
packages modified proteins into vesicles to be transported
rough endoplasmic reticulum :
made of cisternae
studded with ribosomes
transports proteins made on the attached ribosomes
some will be secreted or placed on the cell membrane
smooth endoplasmic reticulum :
same structure as rough but without ribosomes
involved in making lipids
lysosomes :
spherical sacs surrounded by a membrane
specialised vesicles
contain digestive enzymes which break down pathogens
ribosomes :
site of protein synthesis
acts as an assembly line for coded information from the nucleus
used to make proteins from amino acids
centrioles :
self replicating organelles made of nine bundles of microtubules
help organise cell division
cilia and flagella :
essential for locomotion of individual organisms
move fluid or materials past an immobile cell
production of a protein :
hormone instructions found in DNA in the nucleus
nucleus copies instructions into mRNA
mRNA leaves nucleus through nuclear pore
attaches to a ribosome
ribosome carries out protein synthesis
assembled protein is pinched off in a vesicle
golgi modifies and packages the protein
excreted by exocytosis
function of the cytoskeleton :
supports organelles
strengthen and maintain shape of cell
allow movement of materials
cell movement with flagellas and cilia
structure of the cytoskeleton :
microfilaments
microtubules
intermediate fibres
microfilaments :
small strands of actin that contract during cytokinesis helping new membranes form
microtubules :
tiny protein cylinders made of tubulin involved in cell movement
intermediate fibres :
provide mechanical strength to cells
what happens in the thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts?
it is the site of photosynthesis
structure of a vacuole :
membrane called tonoplast filled with a cell sap
function of a vacuole :
keeps cells turgid
structure of cell wall :
made of polysaccharide cellulose with plasmodesmata
function of the cell wall :
enable exchange and transport of materials and act as a carbohydrate store
dry mount sample preparation :
thinly cut solid specimen put on a slide
wet mount sample preparation :
specimens suspended in a liquid and cover slip placed at an angle
squash slides sample preparation :
wet mount but sample is squashed between two slides
smear slides sample preparation :
use an edge of a slide to smear a thin coating onto slide
why is staining necessary when preparing samples?
makes cell components more visible
definition of resolution :
ability to distinguish between two close together objects
actual size =
image size / magnification
definition of a prokaryote :
single celled organism that does not have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles
definition of eukaryote :
have membrane and complex organelles that are part of a multicellular organism performing a function
prokaryotes :
smaller circular DNA
no nucleus
cell wall made of polysaccharide
flagella made by protein flagellin in a helix
small ribosomes
eukaryotes :
larger
linear DNA
nucleus
cellulose and chitin cell walls
flagella made of microtubules
larger ribosomes
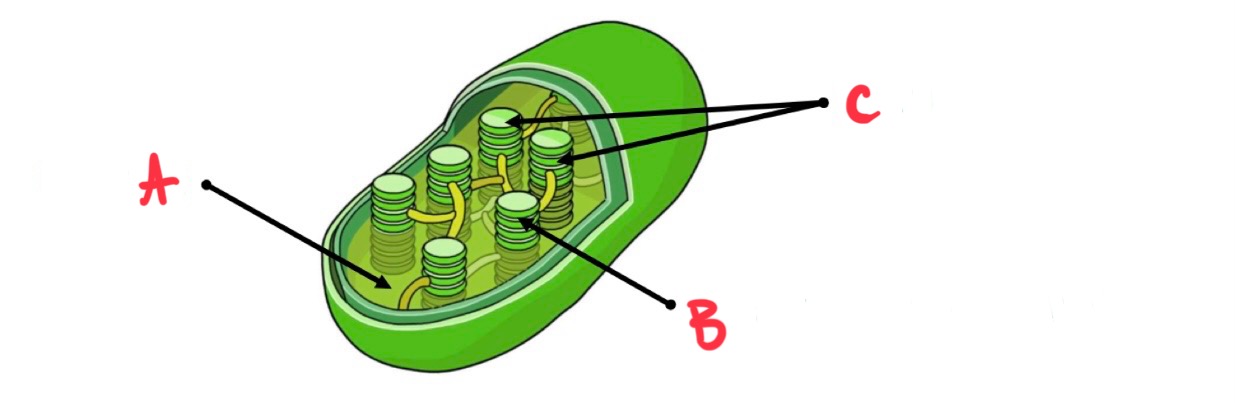
what is a?
stroma
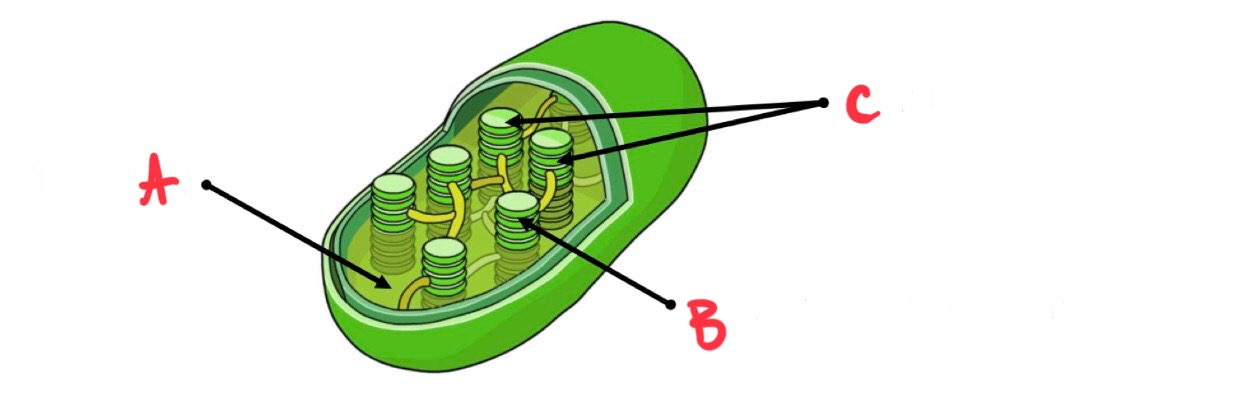
what is b?
thylakoid membrane
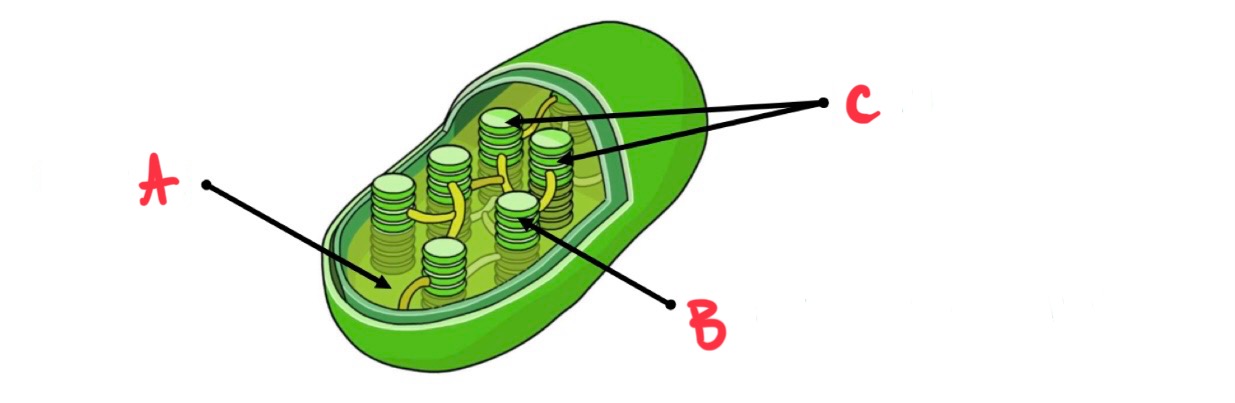
what is c?
grana