Microbiology Unit 2 Review
1/203
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 27, 7, 8, and 12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
204 Terms
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD)
A metric used to evaluate or gauge metabolic activity. Microbial oxygen consumption creates a biochemical oxygen demand.
The amount of O2 removed from the environment by aerobic respiration and a way to see how active microbes are at breaking down material.
More organic matter concentration means more oxygen consumption and therefore…
a higher BOD
Less organis matter means less oxygen consumption, therefore…
a lower BOD
Eutrophication
results in high levels of aerobic, bacterial decomposition of organic matter
Occurs from an influx of excess nutrients that trigger hypoxic zones in water
What is the purpose of wastewater treatment plants?
Produce a clear, outgoing stream, possessing minimal levels of organic solutes
Wastewater treatment
decreases the BOD and the level of human pathogens before water is returned to local rivers
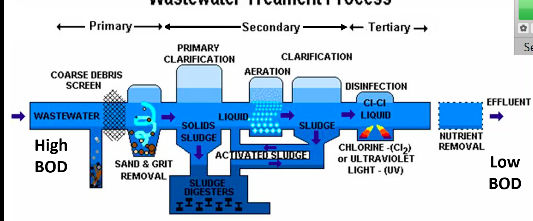
Wastewater treatment is made up of
Preliminary, primary, secondary, and tertiary (advanced) treatment
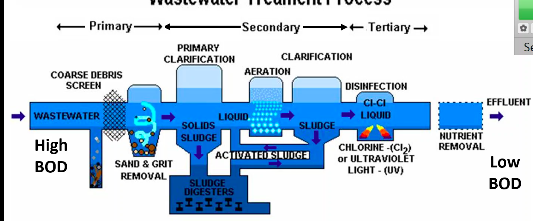
Preliminary treatment
removes solid debris
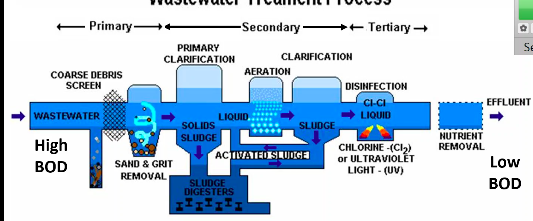
Primary treatment
uses fine screens and sedimentation tanks in order to remove small debris and insoluble particles EX: sediments
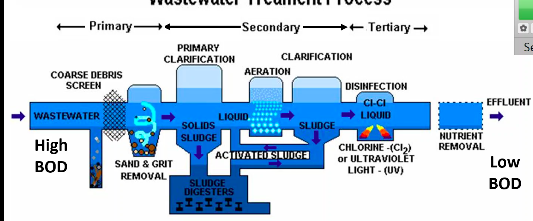
Secondary treatment
microbial decomposition of organic content
Tertiary (advanced) treatment
chlorination or other chemical application to eliminate pathogens
Clarification
goal is to knock down high BOD along with the removing organic matter that’s causing the high BOD → the organic matter removed is recycled into activated sludge which is then used to help lower high BOD
Activated sludge
a process for treating wastewater using air and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa
Healthy sludge
a brown floc, largely composed of saprotrophic bacteria
saprotrophic
feed on decayed matter
Flocculation
promoting growth of filliamented organisms in the wastewater which will then create a mesh network and produce substances that will allow the particles in the wastewater to settle
Floc formation is
critical in promoting settling of bacteria and associated microbes from the treatment process
Denitrification
The conversation of nitrate (NO3-) to N2
Ammonia/ammonium ion (NH3/NH4+) would be the end product of which processes?
nitrogen fixation and ammonification
Nitrogen cycles cannot exist without
prokaryotes
Nitrogen fixation
brings back the nitrogen lost from denitrification and turns it into ammonia
Ammonification
decomposing plants and animals turn into ammonia which is then inserted into nitrification
Lithotrophy/nitrification (assimilation)
ammonia is turned into nitrates
Denitrification (dissimilation)
Results in N2 which is released into the air
Artificial nitrogen fixation is accomplished by why?
Haber process
Haber procecss
generates fertilizers for agriculture
how you fix nin ammonia artificially
uses high pressure and catalysts. very energy consuming
N2 → NH3 → NH4+
Nitrogen fixation
What is used to catalyze nitrogen fixation?
nitrogenase
What is responsible for nitrogen fixation in certain cyanobacteria?
heterocysts
heterocysts
strictly used for nitrogen fixation
compartmentalizes N2 fixation in cyanobacteria in oceans and freshwater
NH4+ → NO2- → NO3-
Nitrification/lithotrophy
Nitrification
Ammonia or reduced nitrogen is transformed into oxidized nitrogen/nitrate which plants will then be able to use for growth
NO3- → NO2- → NO → N2O → N2
Denitrification
Denitrification
represents anaerobic respiration
leads to loss of nitrogen
reducing nitrogen
Sterilization
removal/destruction of ALL living microbes and spores and viruses
Disinfection
Killing of vegetative pathogens on a surface (inanimate object); usually with chemicals
Antisepsis
reduction of pathogens from living tissues (sepsis/asepsis)
Degerming
removal of transient microbes from skin by mechanical cleansing or by an antiseptic. Think washing your hands. Difference from antisepsis is that it’s meant to reduce the # of microbes temporarily rather than completely removing them or preventing infection.
Sanitation
related to hygienic practices; reduction in overall total microbial numbers to safe levels in places
total cell count
how many total cells there are, dead or alive
Viable cell count
the cell count of the sample that are alive
Bacteriostatic
growth inhibitory; no killing of cells. The addition of a treatment that prevents growth, not killing them. Key: STATIC
Bacteriocidal
Killing of cells. ONly viable cell count decreases because the cell body is still there
Bacteriolytic
killing of cells but also causes cells to lyse or break apart. Both total and viable cell count decreases because the cell is destroyed
D-value
time for an agent to kill 90% or one log of the population
Use-dilution test
Metals rings are dipped in test bacteria and then dried → The dried rings/culture are placed in disinfectant for a time at a specific temp (10 min @ 20ºC) → Rings are transferred to culture media to determine whether bacteria survived treatment (incubate 24 hr, check for growth)
Disk diffusion method
Filter disks soaked in chemical agent are placed on plate inoculated w/ bacteria. Analyze zones of inhibition → proportional to effectiveness of disinfection
is the area under and around the filter disks growing bacteria or not?
Agents can target one or a combination of what parts
Plasma membrane - dissolved
proteins - denaturing or break down of protein to reduce or eliminate functionality
nucleic acids - break down, denature, or chemical alteration
Standard conditions of an autoclave
15 psi/121ºC at 15 min
It’s a sterilization method which kills endospores
High temp & pressure as physical agents of control
Boiling: 10 min @ 100ºC
Steam under pressure
Autoclave
Dry heat sterilization
incineration or hot air
sterilizes at 170ºC for 2 hr
Pasteurization
mild heat and used for food/beverages
Cold temperatures
slows down microbial growth
Filtration
used for aqueous solutions & air
Irridation
used to sterilize food & non-biologicals. uses the wavelengths of light. The shorter the wavelengths the higher the energy and lower wavelengths have lower energy
Two different types:
Ionizing and Non-ionizing r
Non-ionizing radiation
UV rays. Best for surface disinfection because it does not penetrate well
Ionizing radiation
X, rays, gamma rays, electron beams
Ionizes water to release OH, penetrating radiation and can break and fragment nucleic acids
Phenolic
An example of chemical control.
Disrupts lipids of plasma membrane and denatures proteins. Can remain active on surface after application
Halogen
Another example of chemical control
alters protein synthesis and membranes
Alcohols
require water; denature proteins and dissolve lipids
Heavy metals
can denature proteins and can be toxic at high levels so often used at low concentrations
Surface active agents (surfactants)
mimic phospholipid structure and disrupt plasma membrane integrity
Chemical preservatives
control molds/bacteria in foods/cosmetics
Gaseous Sterilants
denature and modify proteins. Usually for heat sensitive materials such as plastics
Resistance when it comes to disinfection
Concentration of disinfectant is key
When is resistance to disinfectants more likely
At lower concentrations
Why is resistance more likely at lower concentrations of disinfectant
They are more likely to affect single targets compared to higher concentration which have multiple targets. This makes it easier to counteract the effects because there’s a less mutations needed to become resistant.
Why is resistance harder at higher concentrations of disinfectants?
Disinfectants have multiple targets at the proper concentration. This makes it more difficult to gain a resistance because it’s difficult to evolve multiple mutations to counteract all effects
What are the two aspects of microbial genetics
Genotype and phenotype
Genotype
genes inherited
Phenotype
expression of genes inherited
Microbial phenotype or observable traits are determined by what?
The function of proteins encoded by the genotype (genetic makeup)
The relationship between genotype and phenotype
Genotypes contain the genetic material that make up genes which code for proteins. These proteins make up the phenotypes that are expressed.
Genotypes hold the formula for the proteins needed for phenotypes to be expressed.
Flow of information
DNA → RNA → protein
Central dogma
theory that explains how genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to proteins
Characteristics of prokaryote genome
Single circular chromosome + any plasmids
Inheritance is through vertical and horizontal transmission of genes
vertical transimission
Think parent to child
Horizontal transmission
combination of genes from others in the population; acquiring different cells from neighboring cells and its environment
Semiconservative replication
DNA is unzipped into two separate strands before being filled in by its complementary nucleotide. Half of the old ladder or DNA is kept while the other is replaced, giving you two new ladders
DNA replication is done through
semiconservative replication
Order of prokaryotic genetics
Genome (DNA) → chromosome, plasmids → genes → proteins
Steps of Gene Expression
Retrieval of info → Transcription → Translation
Often times transcription and translation happen together
Polysome formation
multiple ribosome on a transcript because transcription and translation happen together
Retrieval of info
Signals within or outside the cell tell it to retrieve information needed in order to fulfill a specific function or need. → This will trigger it access the genetic information encoded in the DNA for use in building proteins and to will employ different RNAs to start the next steps
Transcription
The step of creating multiple copies of DNA into RNA version or into a messenger molecule (mRNA)
RNA Polymerase binds into a promoter on the Nucleotide base sequence and makes a copy of the DNA into a molecule of mRNA (messenger RNA) with the complimenting RNA nucleotides → after it reaches the end of the gene, the mRNA strand is released and transported to a ribosome while the DNA re-zips itself.
Translation
Translation of the mRNA sequence into a protein
The mRNA carries the RNA strand into the ribosome where the ribosome reads the mRNA codons and assembles the proteins. Transfer RNA bring in the amino acids needed for the proteins to be created
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
specific to carry the amino acids and can read the transcripts/RNA codons
Sense strand
used for coding
5’——-3’
identical to the mRNA sense strand except for the T/U substitutes
Antisense strand
3’——5’
The template strand. Used in transcription to create the complementary mRNA strand
Mutations
permanent alterations of the DNA bases sequences
Spontaneous mutation
random mistakes during replication
What are the base point mutations
Missense, Nonsense, and Frameshift
Missense mutations
when a single nucleotide is changed in the DNA sequence resulting in an amino acid substitution.
Nonsense mutation
When a single nucleotide is changed in the DNA sequence and changes a normal codon into a stop codon
Since the stop codon forms prematurely, it ends the translation process making it lethal for the cell or organism for the most part
Frameshift
Insertion or deletion of a single base nucleotide
Typically lethal since it causes a change in the amino acid sequence following the insertion or deletion site
What is the protein that mediates recombination between cells?
RecA protein
RecA protein
mediats recombination between donor/recipient
What are the benefits of recombination in DNA transfer
Allows cell to gain new functions, repair defective genes or damaged DNA, and contributes to genetic diversity of population
What are the different ways of horizontal transmission?
Transformation, conjugation, transduction, transposition
transformation
uptake of DNA from the environment (naked DNA)