Economics- chapter 3-6
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is elasticity of demand?
is a measure of how much the demand for a product changes when there is a change in one of the factors of demand.
What is price elasticity of demand?
measure of how mcuh the quantity demanded of a product changes when there is a change in price of the product.
What is the equation for PED
percentage change in quantity demanded of a product/percentage change in price of a product
What do you do if the equation of PED gives us a negative value?
It is usually ignored and the answer is given as a positive figure
what does it mean when the PED value is zero and how does it happen?
it means that the change in price of a product will have no effect on the quantity demanded
it happens when the percentage change in quantity demanded is 0
what does it mean when a product is perfectly inelastic and how would the graph look?
It means that the quantity demanded of a product is completely unresponsive to the price change.
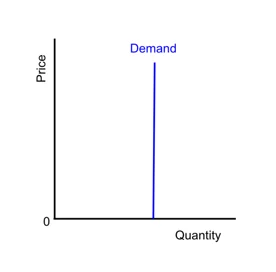
inelastic demand meaning and what is the range of PED value.
means that the change in the proce of the product leads to a proportionally smaller change in the quantity demanded of it
an example value is 0.5 less than 1 greater than 0
What does it mean for the demand when a product is inelastic.
It means that if the price of the product rises, the quantity demanded of the product will not fall by much in proportion.
elastic demand value range and what does it mean
When the value of PED is greater than one and less than infinity
this means that if the price is raised, quantity demanded will fall by more in proportion.
unit elastic demand value range and what does it mean
when PED=1
a change in price of a product leads to a proportionate, opposite, change in quantity demanded.
it means if the price is raised by a certain percentage, then the quantity demanded will fall by the same percentage
determinants of PED
number of substitutes
proportion of income spent on good
time period
necessity of product
Explain the determinant “number of substitutes”
The more substitutes here are for a product, the more elastic the demand for it will be. the closer the substitutes are available the more elastic the demand will be.
Explain the determinant “proportion of income spent on good”
If the product is cheap and suddenly changes in price by a certain amount, it is less likely to effect the consumers choice therefor is inelastic, especially if the consumers income is stable.
Explain the determinant “time period”
as the price of a product changes, it takes time for the consumers to change their buying and consumption habits
PED tends to be more inelastic in the short run and more elastic in a longer time period.
Explain the determinant “necessity of product”
When a product is required for living like food, then it is automatically very inelastic.
the products would need to be very necessary or addictive such as alchohol and cigarettes.
Why is knowledge about the PED important for firms?
It is a very useful tool for predicting the effects of their pricing decisions on the quantity demanded and also the total revenue.
Why is knowledge about the PED important for governments?
gives them an awareness of the possible consequences on a number of economic variables when they impose sales taxes.
if there is less demand for a product, there is a smaller amount of workers necessary meaning here will be an increase in unemployment which directly effects the government.
What is YED?
a measure of how much the demand for a product changes when there is a change in a consumers income.
What does the sign mean in the YED value?
if its a + it means the good is a normal good
if its a - it means the good is an inferior good
necessity goods…
have low income elasticity
he demand will change very little if income rises because people are already buying the goods before the income change.
value of YED in between 0 and 1
superior goods…
have high income elasticity
the demand for them changes significantly when income rises because they begin to purchase non essential products at a higher rate
value of YED is greater than 1
inferier goods…
demand decreases as income increases
people switch their expenditure from inferior goods to the superior goods which they can now afford
value of YED is negative
what is supply?
Quantity of a good or service that producers have the willingness and ability to supply at different prices at a given time.
effective supply
the idea that producers are not only willing to supply a product but also able to
non-price determinants of supply
costs of factors of production
price of related goods
competitive supply
joint supply
government intervention
expectations of future prices
changes in technology
explain the determinant of “costs of factors of production”
if there is an increase in a factor of production eg. wages for workers, the quantity that can be supplied will be less
a fall in factors of production will enable firms to increase their supply.
explain the determinant of “joint supply”
sometimes when one good is produced, another good is produced at the same time
the increase of one will lead to the ic
explain the determinant of “government intervention”
indirect taxes
taxes on goods and services which is added to the price of the product.
explain the determinant of “expectations of future prices”
when demand is expected to be higher, supply is also expected to increase.
producers can also with hold their expenditure so that they can supply more when demand is at it’s peak.
explain the determinant of “changes in technology”
improvements in the state of technology in a firm or industry should lead to an increase in supply.
What is PES?
a measure of how much the supply of a product changes when there is a change in price of the product.
What does it mean when PES is equal to zero.
it means that the change in price of a product will have no effect on the quantity supply
perfectly inelastic supply+an example
means hat no matter how much price changes, the quantity supplied will remain the same.
eg. concerts, football matches, movie tickets
Inelastic supply
value of PES is less than one and greater than 0
a change in price of the product leads to a less than proportionate change in the quantity supplied of it
elastic supply
the value of PES is greater than one and less than infinity
then a change in price of a product will lead to a greater than proportionate change in unity supplied of it.
any line which starts at the y axis
unit elastic supply
Value of PES is one
it means that the change in price of a product will lead to a proportional change in the quantity supplied of it
passes through the origin
determinants of PES
Existence of unused capacity
Mobility of factors of production
time period
Time period considered
In the long run supply can be elastic but because firms are not able to change their production patterns right away, initially supply seems to be inelastic.
Existence of unused capacity
If a firm has a lot of unused supply, they will be able to increase their output easily seeing as they have the products already at hand without great cost increases. In this case supply is elastic
If a firm is producing at capacity, it is difficult to increase supply without it being expensive, therefor in this case PES is inelastic
the ability to store stock
if a company is able to store high elvels of stock, they are able to react to price increases with swift supply increases, in this case PES for the product is elastic.