Acid Base Titrations
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Titrations and Titration Curves
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What reaction occurs when a base / alkali is added to an acid?
Neutralisation reaction- forms a salt and water.
What happens to pH when a base / alkali is added to an acid?
pH increases.
What is a titration curve?
Titration curves shows the pH against the volume of base added from titration.
Titration curves show the different combinations of weak and strong acids and bases.
What are the different combinations of weak / strong acids and bases?
Strong acid / strong base
Strong acid / weak base
Weak acid/ strong base
Weak acid / weak base
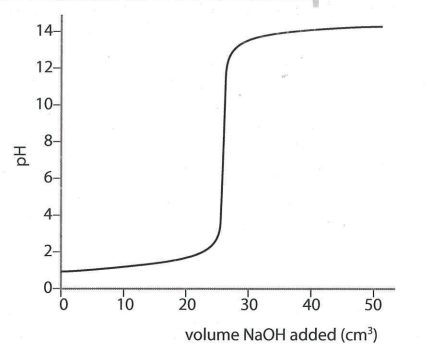
Titration curve for a strong acid / strong base reaction.
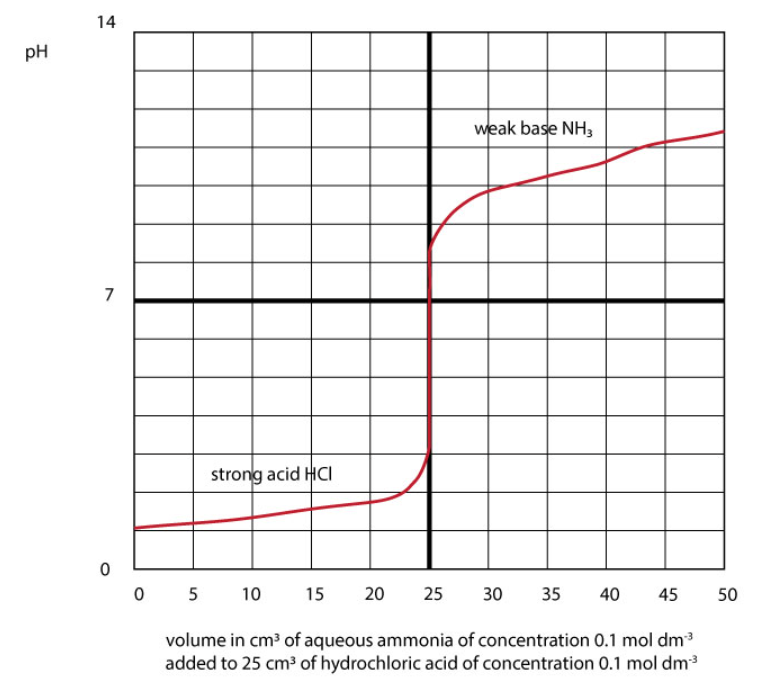
Titration curve for a strong acid / weak base reaction.
Titration curve for weak acid / strong base reaction.

What is the equivalence point?
This is the point where the acid has been fully neutralised by the base.
The pH of this solution is the mid-point of the vertical part of the titration curve e.g. for strong acid / strong base reaction the pH is 7 (neutral).
What is the half neutralisation point?
This is the point halfway between 0 and the equivalence point.
What is the significance of the half neutralisation point?
When an acid is half-neutralised, the concentration of the acid is equal to the concentration of the salt.
[HA] = [A-]
Ka= [H+]
taking -log on both sides
-logKa= -log[H+] i.e. pKa = pH