Unit 2: The Periodic Table and Atoms
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Who was Dmitri Mendeleev?
Creator of the version of the periodic table we use today
How is the periodic table organized?
in periods and groups and by increasing atomic number
What does the periodic table of elements look like, what does it consist of?
It has periods and groups, and groups of different types of elements
Alkali metals
high reactivity, especially with water
very soft and malleable
low melting and boiling points
Alkaline Earth Metals
reactive, but not as reactive as alkali metals
higher melting points than alkali metals
metallic luster
easily conduct heat and electricity
Transition metals
very good conductor of heat and electricity
form colorful compounds
very high melting and boiling points
often magnetic
Metalloids
semiconductive
brittle
can behave like metals or nonmetals in chemical reactions
Halogens
non-metal
high reactivity
brittle
solid, liquid, and gas at room temperature
Noble Gasses
non-reactive
gas at room temperature
colorless, odorless, tasteless
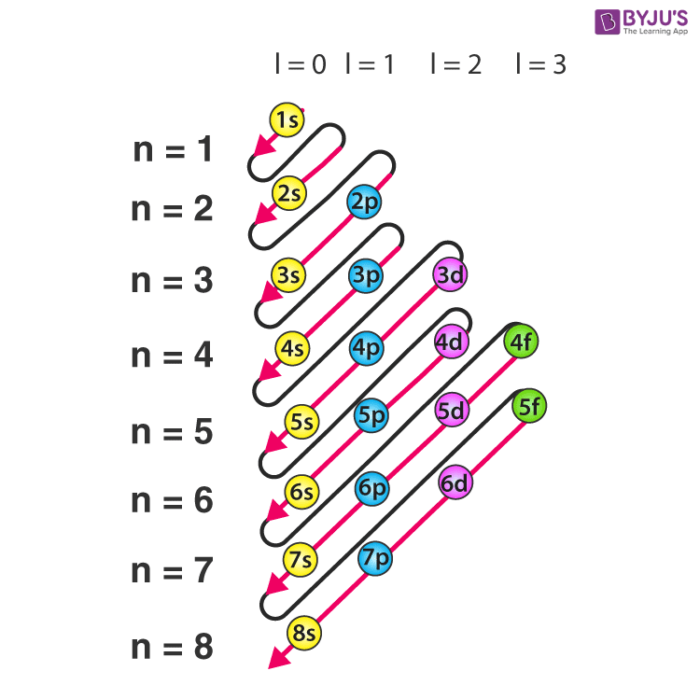
Electron configuration
Calcium: 1s² 2s² 2p^6 3s² 3p^6 4s²
Metals
luster, and malleable, and most easily conduct electricity and heat
Metalloids
aren’t as good as a conductor as metals but are better than non-metals and they fall between metals and non-metals in the periodic table
Non-metals
non-metals are very poor conductors of electricity and are brittle if solid
periodic table trends
changes in the periodic table
Atomic radius
The distance from the nucleus to the outermost shell, or how large the electron energy levels are
DIFFERENT than the others (decreases across periods, increases down groups)
Half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms
Ionic Radius
Similar to atomic radius but gets larger or smaller when the atom becomes an ion
More electrons = larger ionic radius
Mg -2 > Mg
Electronegativity
An atom’s tendency to attract other electrons
Increases across periods, decreases down groups
Ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell
Anions
negative ions that have gained one or more electrons
Cations
positive ions that have lost one or more electrons
Electron Affinity
the neutral atom’s likelihood of gaining an electron
Timeline of the atom
Democritus
Dalton
JJ Thompson
Rutherford
Bohr
Schrodinger
Dalton’s atomic theory
All matter if made of atoms, atoms of the same element are identical, atoms are combine in more than one ratio, during a chemical reaction atoms can rearrange but cannot but changed or destroyed
Bohr’s atomic model
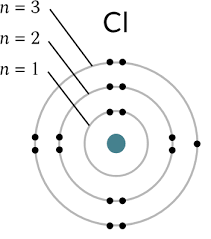
protons
positive particles in the nucleus (p+)
neutrons
neutral particles in the nucleus (n o)
electrons
negative particles in shells moving around the nucleus (e-)
atomic number
number of protons (same as number of electrons)
atomic mass
number of protons + neutrons
wavelength
Distance between the identical points, or wave peaks) on successive waves
Symbol: λ
Formula: c/f
Unit: meters
frequency
The number of complete wave cycles that pass a given point in one second
Symbol: f
Unit: Hertz
speed of light
3 × 10^8 m/s
Symbol: c
frequency formula
f= c/λ
wavelength formula
λ=c/f
Energy of atoms
E = h x f
h= Planck’s constant (6.63 x 10^-34J x s)
Quantum energy
Quantum energy is the energy in discrete packets called "quanta." It indicates that energy changes happen in specific amounts rather than continuously, like when an electron jumps between energy levels in an atom. This concept helps explain the behavior of particles at the quantum level
small discrete units of energy
Formula for maximum number of electrons in an energy level
n=1: 2(1²) = 2 electrons
n=2: 2(2²) = 8 electrons
n=3: 2(3²) = 18 electrons