Veterinary Parasitology CH7 - Trematodes
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study material for Chapter 7 of Diagnostic Parasitology for Veterinary Technicians. For class BIO225 at MWCC.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What shape are trematodes/flukes?
Dorsoventrally flattened, unsegmented, leaf-like
What are the two subclasses of trematodes/flukes?
Monogenea: Ectoparasites of fish, amphibians and reptiles
Digenea: Associated with wild and domestic animals and humans
Subclass Monogenea
Attach to gills, skin, fins or mouth
Posterior adhesive organ: suckers, hooks or clamps
Usually only diagnosed in specialty practices that do saltwater or freshwater fish or fish farming
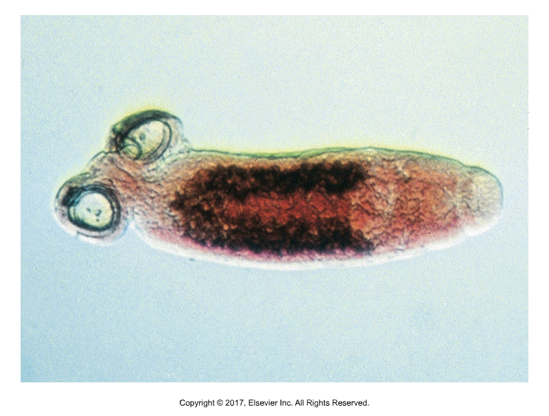
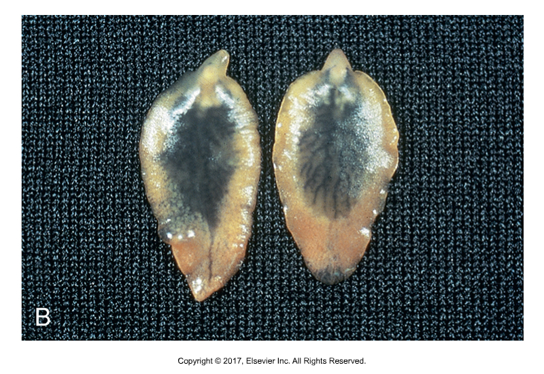
Subclass Digenea
Flukes are endoparasites of domestic and wild animals and sometimes humans
Most are flat and broad, although a few are thicker and fleshier like Fascioloides magna
Schistosomas can be long thin and wormlike, more resembling nematodes
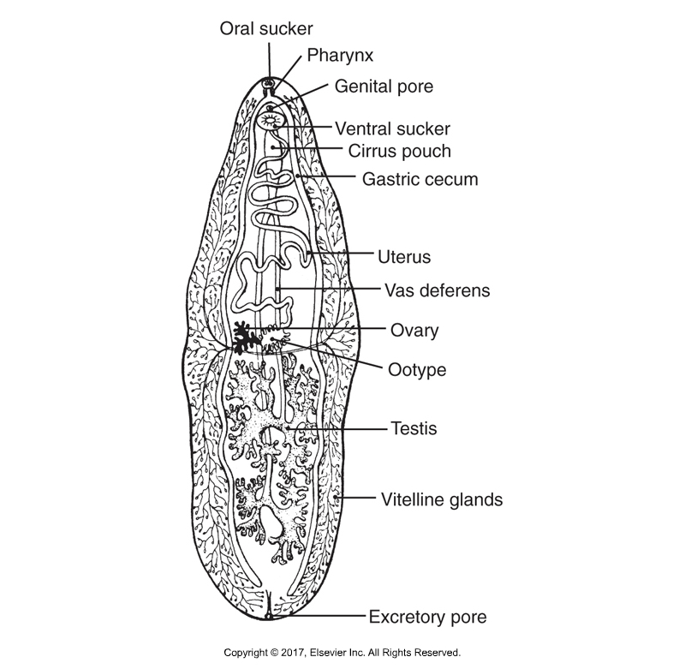
Trematode/fluke morphology
Near anterior end is oral sucker, used to eat
Connects to pharynx and esophagus, bifurcates into two blind ceca
No anus; regurgitate contents of ceca into tissues or organs of host animal they infect
Can be seen in histological sections as fluke puke
Also contain an acetabulum or ventral sucker used to attach to host
Most flukes are hermaphrataditic (Exception is blood flukes or Schistosomes that have male and female)
Self-fertilization is most common but cross-fertilization between two adult flukes can happen
Trematode/fluke lifecycle
Female produces operculated eggs stored in the uterus
Pass out the genital pore to external environment, usually in host feces
Eggs embryonate in external environment and hatch into motile ciliated miracidium
Swims in aquatic environment, penetrates skin of snail 1st intermediate host
Develops into sporocyst. Inside sporocyst, many rediae develop.
Within each redia, many cercariae develop, often with a tail
List the three possible fates of the cercariae
Penetrate skin of definitive host
Attach to vegetation, lose tail, encyst and develop into metacercaria — definitive host eats vegetation
Lose tail, penetrate 2nd intermediate host, encyst and develop into metacercaria—definitive host ingests 2nd intermediate host
Most trematodes/flukes migrate to…
The digestive system
Which trematodes/flukes don’t migrate to the digestive system?
Paragonimus kellicotti (lung fluke) and Schistosomes (blood flukes)
List the stages of trematodes/flukes in order
Egg
Miracidium
Sporocyst
Rediae
Cercaria
Metacercaria