Chapter 5: Electric Forces and Fields
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Last updated 12:51 AM on 3/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
basic components of atoms
protons, neutrons, and electrons
2
New cards
Two varieties of electric charge
Protons (positively charged) & Electrons (negatively charged)
3
New cards
Ionization
the removal or addition of electrons
4
New cards
Elementary charge
the magnitude of charge on an electron (and therefore on a proton) is denoted e, the basic unit of electric charge
5
New cards
Uniform Electric Field
Having a uniform field means having a constant force (and therefore a constant acceleration).
6
New cards
Examples of Conductors
metals and aqueous solutions that contain dissolved electrolytes (such as salt water)
7
New cards
Example of Insulators
glass, wood, rubber, and plastic
8
New cards
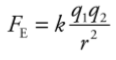
Coulomb’s Law
9
New cards
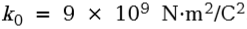
Coulomb’s constant
10
New cards
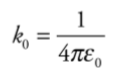
Permittivity of free space
11
New cards
Electric Field formula
\
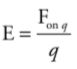
12
New cards
**electromagnetic force**
one of the most powerful forces in nature
13
New cards
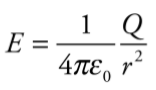
Electric field in the space surrounding for a point charge
14
New cards
**electric dipole**
two equal but opposite charges, form a pair
15
New cards
A charge *q* = +3.0 nC is placed at a location at which the electric field strength is 400 N/C. Find the force felt by the charge *q*.
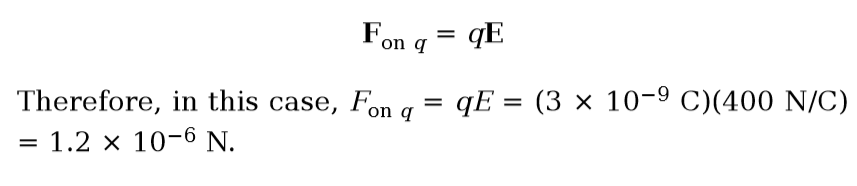
16
New cards
**Dipole-induced forces**
are caused by a shifting of the electron cloud of a neutral molecule toward positively charged ions or away from a negatively charged ion; in either case, the resulting force between the ion and the atom is attractive
17
New cards
the electric field is always ____________ to the surface, no matter what shape the surface may be
**perpendicular**