Chapter 4 Part II
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the five key causes of brain damage
Tumors
Infections
Exposure to toxic substances and radiation
Degenerative diseases
Close head injuries
Exposure to toxic substances and radiation
Degenerative diseases
Close head injuries
Lead poisoning
Alzeimers
A brain injury caused by impact to the head that does not crack the skull or puncture the brain
Three facts about plasticity after brain damage
Almost all survivors of brain damage show behavioural recovery to some degree.
Some recovery relies on the growth of new branches of axons and dendrites.
Babies and young children recover the quickest
What are the two key types of strokes
Ischemia
Hemorrhages
Ischemia
Hemmorage
An obstruction. The most common type of stroke, where neurons lose their glucose and oxygen supply
A rupture. Neurons are flooded with excess blood, calcium, oxygen, and other chemicals
Two negative after-effects of strokes
Edema: fluid build-up—if someone has a stroke early on, that can increase the risk of a future stroke.
Disruption of the sodium–potassium pump leading to the accumulation of potassium ions inside neurons, causing excessive depolorization
Five-central immediate post-stroke treatments
Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)
Blocking glutamine synapses
Blocking calcium entry
Cooling the brain
Cannabinoids
Acronym for spotting a stroke
BEFAST
B - Balance
E - Eyes
F - Face
A - Arms
S - Speech
T - Time
Three reasons tissue doesn’t grown back in the CNS
Scar tissue makes a mechanical barrier to axon growth
Neurons on the two sides of the cut pull apart.
Glia cells that react to CNS damage release chemicals that inhibit axon growth
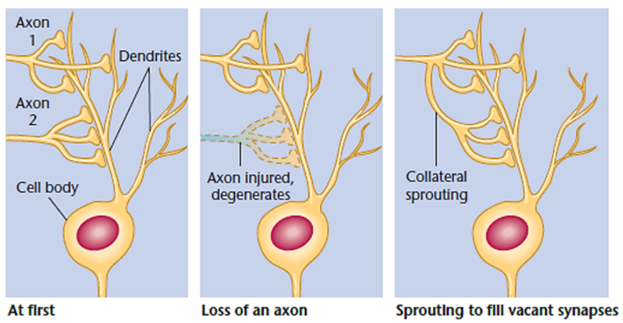
Axon collateral sprouts
New branches formed by other non-damaged axons that attach to vacant receptors.
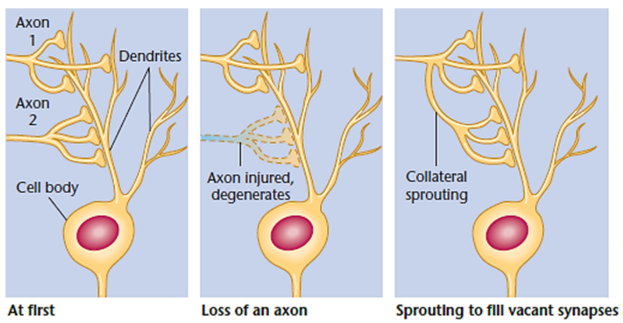
Neurotrophins
Proteins that attract collateral sprouts to the desired area
Cortical reorganization
The brain's ability to adapt by changing the functional role of its neural pathways
EX. If you touch the face of someone who has lost an arm, they may feel that arm, because the cortex face area is close to the hand area, and parts of the face area move into the area of the former arm