Specify the Functions of the Skin & Skin Accessory Structures
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
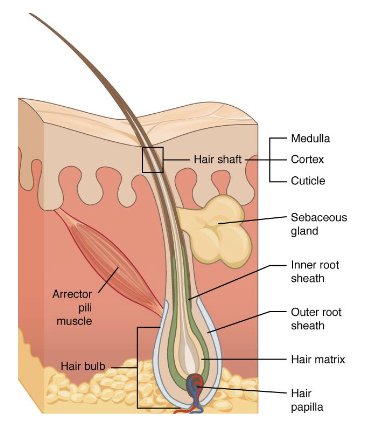
What is the location and function of Hair & what is it made up of?
Hair
Aids in sensation, protection against dust and insects, and temperature regulation
Made up of dead, keratinized cells produced in a hair follicle located in the dermis of the skin
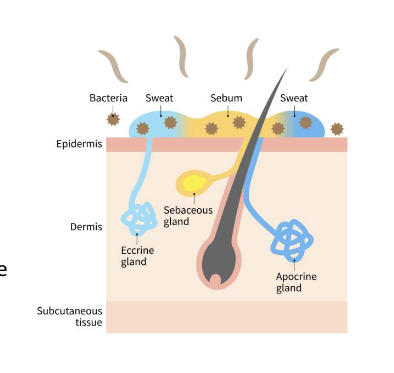
What are the functions of Glands?
There are two types of sudoriferous (sweat) glands:
Apocrine glands: Associated with the hair follicle, produces sweat, and found in the armpits & groin
Eccrine: Produces sweat and are distributed throughout the skin
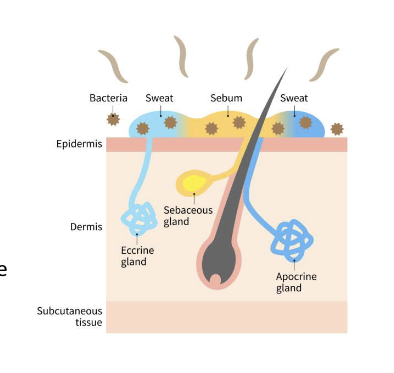
What are the functions of Glands? pt. 2
Sebaceous (oil) glands:
Secretes oily substance (sebum) which coats surface of hairs, preventing it from drying out and becoming brittle
Sebaceous glands contain anti-microbial substances
Ceruminous (wax) glands:
Secretes wax (cerumen) in the ear canal
Wax protects against dust & insects as well as containing anti-microbial properties
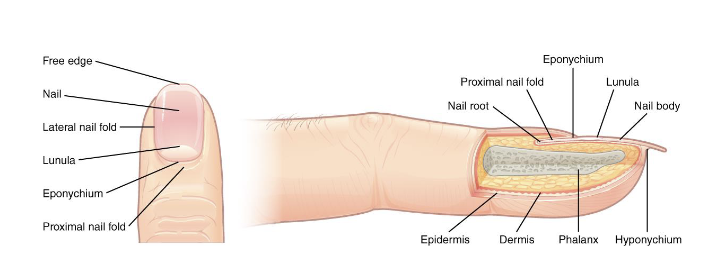
What are the functions of Nails?
Nails
Made up of compacted, keratin filled, dead epithelial cells
Protects the tips of fingers & toes and aids in the ability of scratching, digging, and defense
What are the General Functions of the Skin?
Skin Functions
Mechanical protection in the form of keratin in the epidermis
Prevention of dehydration from cells and glands secreting lipids
UV radiation protection due to the melanin in melanocytes and keratinocytes which absorb UV radiation
Antimicrobial effect from Langerhans cells and macrophages activating the immune response when encountering a pathogen
What are the General Functions of the Skin? pt. 2
Skin Functions
Body temperature regulation from sudoriforous (sweat) gland producing sweat to cool body down
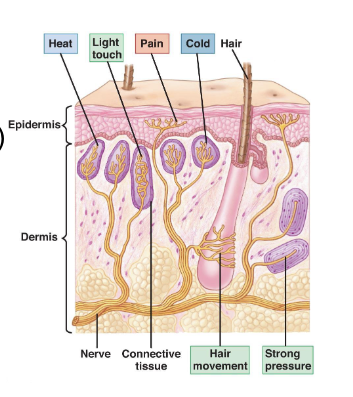
Sensation due to various receptors that detect stimuli (Mechanoreptors, Nociceptors, Thermoreceptors)
What are the General Functions of the Skin? pt. 3
Skin Functions
Excretion by removing small amounts of chemical waste from sweating
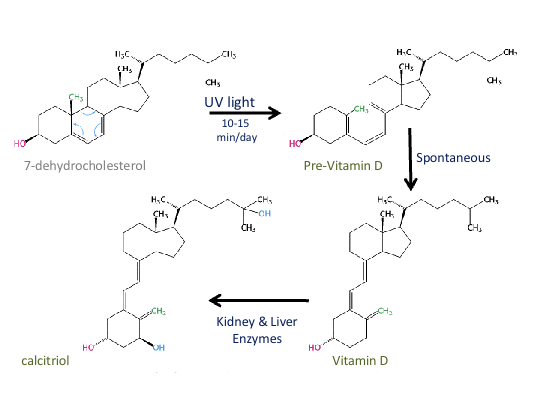
Synthesis of Vitamin D due to UV radiation from the sun