AP Biology Unit 2
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Ribosomes
composed of ribosomal RNA and protein. They help to synthesize proteins. All forms of life have ribosomes, which demonstrates common ancestry
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
provides mechanical support and plays a role in intracellular transport. There are two kinds of ER, rough and smooth.
Rough ER
helps to compartmentalize the cell and helps to carry out protein synthesis in the ribosomes.
Smooth ER
helps in detoxification and lipid production, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Golgi Complex
a membrane-bound organelle that is composed of several flattened membrane sacs called cisternae. The Golgi is vital in the final stages of preparing a protein. A newly made protein will get help in correctly folding and modifying as needed. The Golgi also helps in packaging proteins and sorting them before transport.
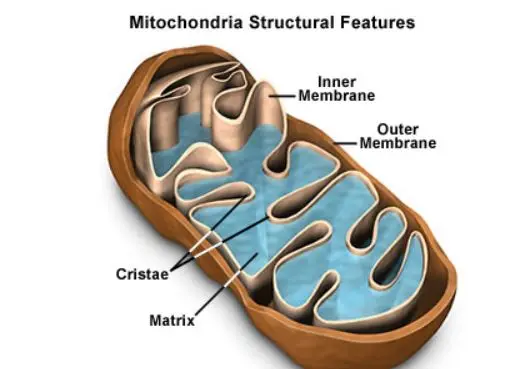
Mitochondria
helps with ATP production. It has a small set of its own DNA and is a double membrane organelle. The outer membrane is a smooth phospholipid bilayer. The inner membrane is highly convoluted, meaning it is highly folded, which increases the surface area for a growing number of electron transport chains. The increase in surface area facilitates the production of ATP.
The mitochondria is the site where cellular respiration occurs. Glycolysis is the first step in cell respiration and occurs with or without oxygen present and shows common ancestry. After the completion of glycolysis, the rest of cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria, given that oxygen is present. The Citric Acid/Kreb’s Cycle happens in the matrix of the mitochondria, and oxidative phosphorylation, with the help of the electron transport chain, occurs in the inner membrane.
Lysosomes
membrane-enclosed sacs that contain hydrolytic enzymes. These enzymes are digestive enzymes that help to break down excess or worn-out cell parts. The lysosomes also help with programmed cell death, known as apoptosis.
Vacuole
a membrane-bound sac that has many different roles, including storage and release of macromolecules and waste . Plants have a specialized large central vacuole that also serves many functions. The primary function of the large central vacuole is water retention. Water retention is important in turgor pressure, which helps to maintain the rigidity and function of plant cells.
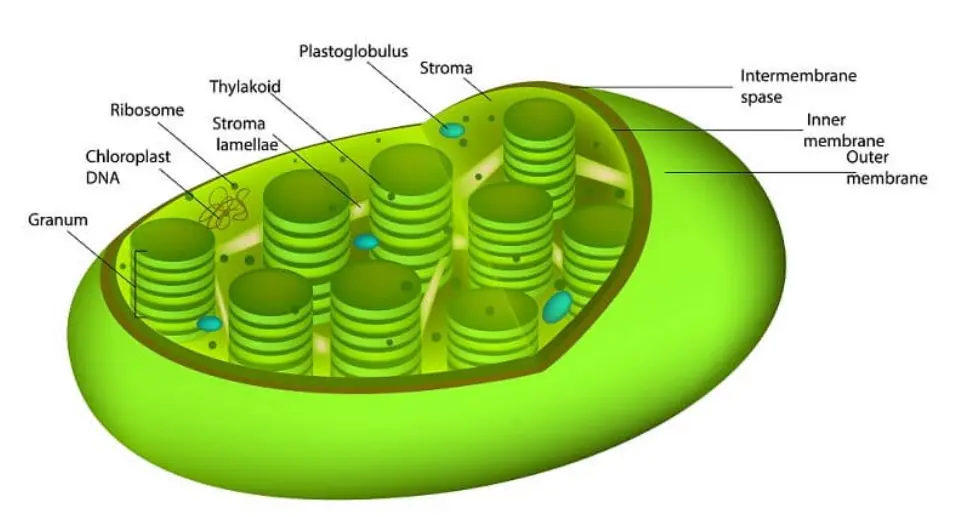
Chloroplasts
photosynthetic algae and plants contain these specialized organelles that can photosynthesize and make simple sugars. Chloroplasts have a double membrane and thylakoids that are flattened sacs with a phospholipid bilayer.
Chloroplasts are the site where photosynthesis occurs. The light-dependent reaction occurs in the grana and produces the ATP and NADPH necessary for the light-independent reaction. The light-independent reaction is where the Calvin-Benson cycle takes place and carbon is fixed to make simple sugars.
Cell Size
As cell size increases, the volume grows faster than the surface area, making it less efficient for the cell to transport materials. Greater surface area to volume ratio = most efficient.
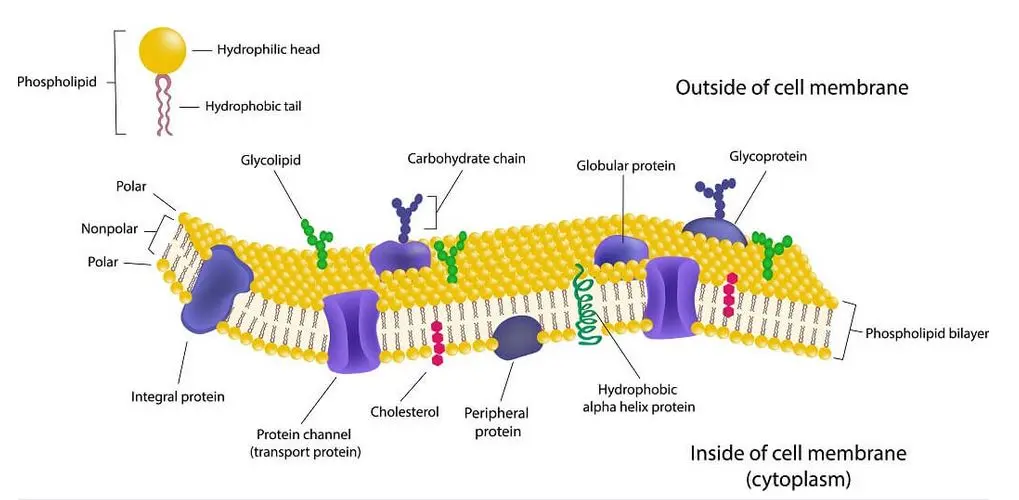
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is a flexible, double layer of phospholipids that controls what enters and leaves the cell. Small nonpolar molecules pass through easily, while larger or charged ones need help from proteins. Membrane proteins also aid in communication, transport, and structure.
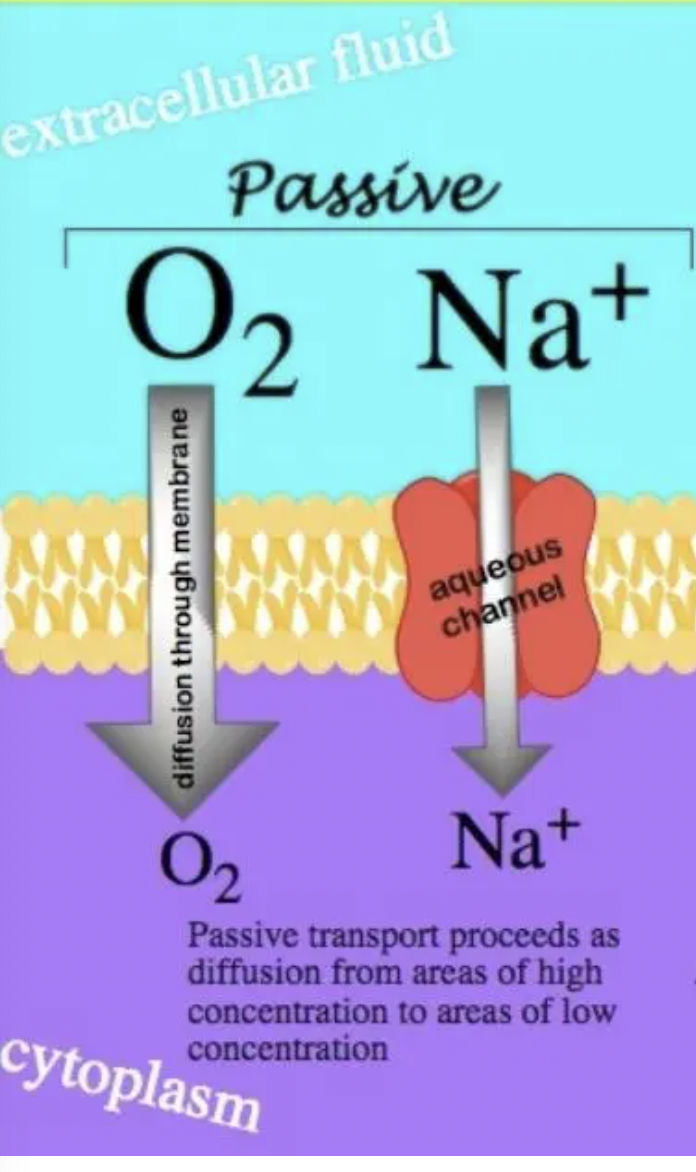
Passive Transport
molecules are moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Energy is not required in passive transport. ⚡️
Facilitated Diffusion
a type of passive transport that allows substances to cross cell membranes with the help of special transport proteins.
Active Transport
molecules are moving from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration and will require energy use.
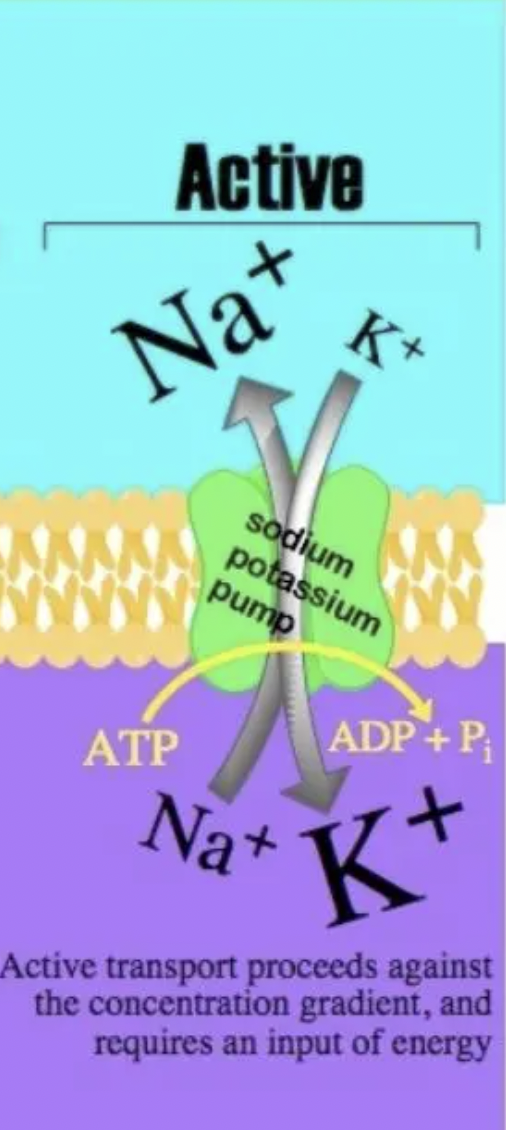
Secondary Active Transport
A method of transporting molecules across the cell membrane where the transport of one molecule depends on the gradient created by primary active transport.
Endocytosis
the process of taking bulk material into the cell.
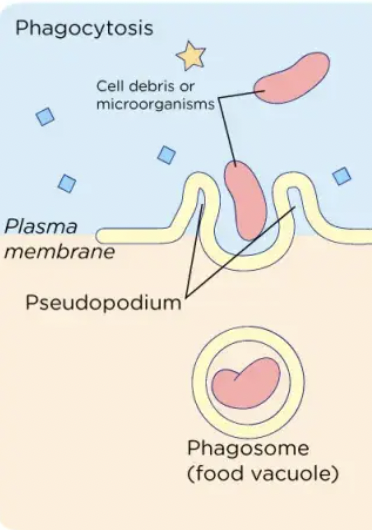
Phagocytosis
the process by which a cell takes in solid particles, such as bacteria or cell debris, by enclosing them in a vesicle called a phagosome. Phagocytosis is carried out by specialized cells called phagocytes, which are found in tissues such as the skin and the immune system.
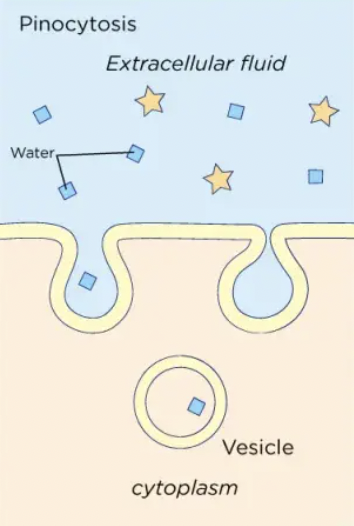
Pinocytosis
This is the process by which a cell takes in liquids, such as extracellular fluid or dissolved substances, by enclosing them in small vesicles called pinocytotic vesicles. Pinocytosis is also known as "cell drinking" and is often referred to as a type of "non-specific" endocytosis.
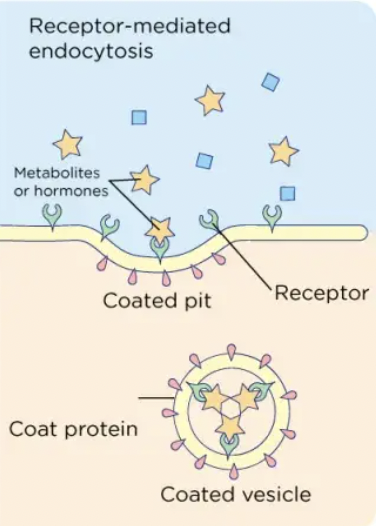
Receptor-mediated Endocytosis
This is a specific type of endocytosis that involves the internalization of specific molecules or substances by binding to specific receptors on the cell surface. The receptors and the bound substances are then internalized in a vesicle called an endosome. Receptor-mediated endocytosis plays a key role in the uptake of large molecules, such as hormones and growth factors, as well as in the immune system.
Exocytosis
the process of removing bulk material out of the cell.
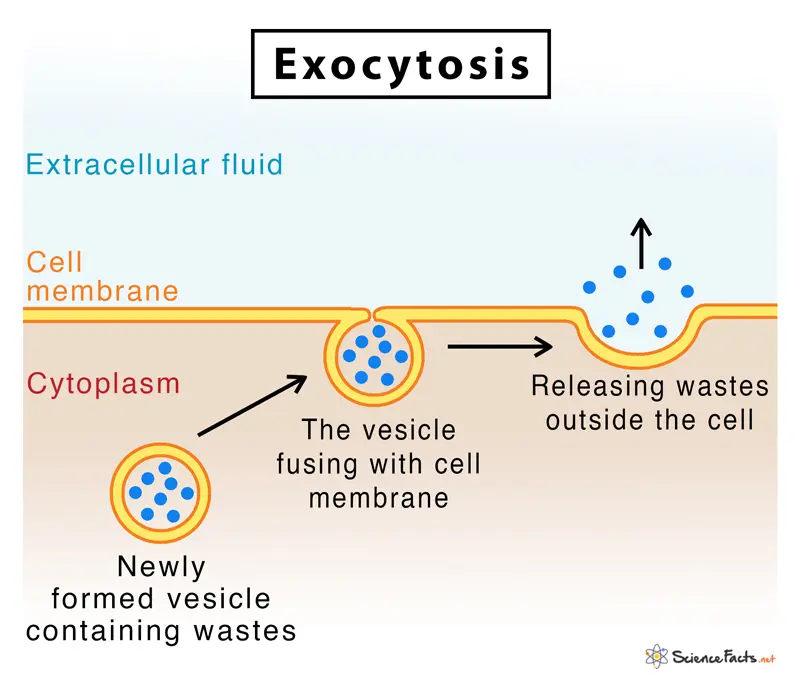
SNAREs (Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive Factor Attachment Protein Receptors)
SNARE proteins are essential components of the machinery that drives fusion of membranes during exocytosis and endocytosis - basically they help transport materials in and out of cells.
Water Potential
likelihood water will diffuse in or out of a cell. Water potential = solute concentration + pressure. Water moves from higher water potential to lower water potential.

Tonicity
the relative concentration of solutes between a cell and its surrounding solution, specifically concerning the movement of water across the cell membrane.
osmosis
the net movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. This movement essentially aims to equalize solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
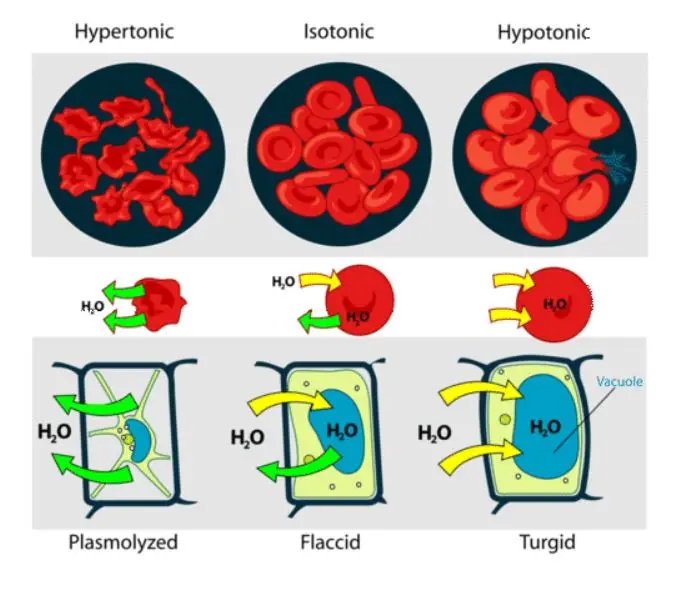
Osmoregulation
maintains water balance and allows organisms to control the internal environment.
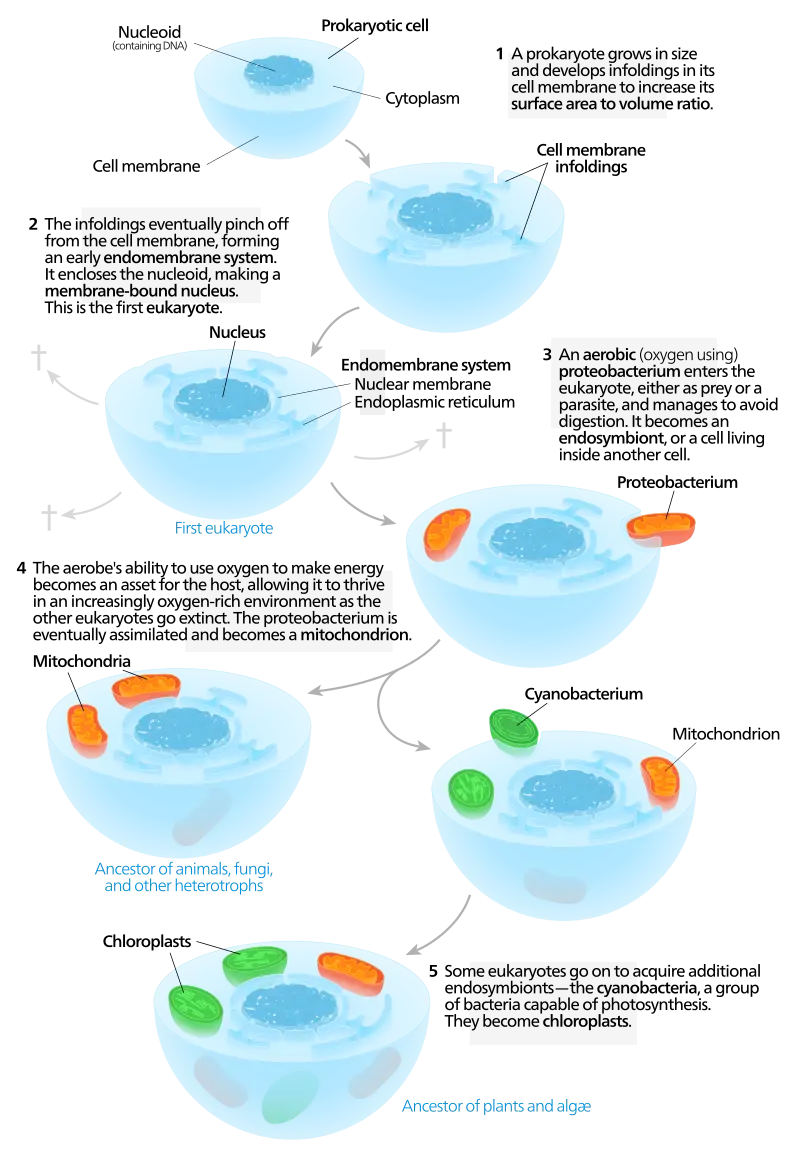
Endosymbiotic Theory
organelles that were once free-living prokaryotic cells became engulfed and serve a purpose now inside the cell.
Integral Proteins
Proteins that are permanently attached within the plasma membrane. They perform various functions including transporting ions or molecules across the membrane.
Peripheral Proteins
Proteins that bind to the surface of the cell membrane, rather than being embedded within it. They often serve as enzymes or in signal transduction
Cotransporters
Proteins in the cell membrane that move two or more molecules through the membrane in the same direction at once.
Exchangers (antiporters)
Proteins that transport two or more ions or molecules in opposite directions across a membrane