biochem meow meow meow
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
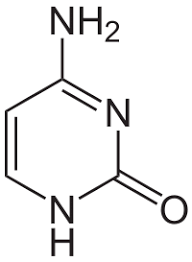
cytosine
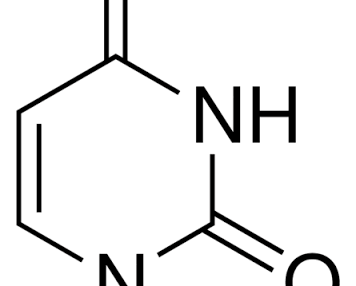
uracil baby
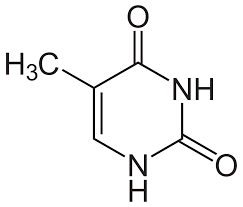
thymineee with that methyl group aye
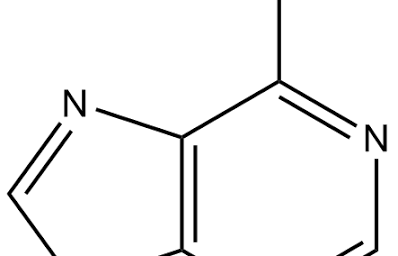
adedeninee
guanine
dna structures orders levels
linear nucleotides 5 to 3’
base pairings!, cruciform (double stranded four way junction, two closed hairpin, occurs in palindromic regions of dna); helixes forms a, b, z, h
3-d folding, circular dna (supercoils- roles in gene expression) trna
nucleosomes bead on string histone, fibers, loops, mini bands, sister chromatids, chromosome
nucleosides
base with pentose sugar beta N1/9 glycosidic bond
nucletides
phosphate acid esterfied at 5’ sugar - strong acid
high energy- phosphoric anhydrides link extra phosphates
nucleic acids
3 to 5’ phosphodiester bridges forms that phosphate sugar backbone
dna
two antiparallel polynucleotides in double helix with base pair interchain h bonds and stacking, elextrostatic phosphate repulsions, recognizes and replaces uracil with cytosine
greater resistance to alkaline hydrolysis, strong base may denature but dna won’t cleave the phosphodiester bond
transcribed to rna
types of dna
A: short fat dehydrated right duplex (double strand), most common for double stranded RNA, no common in vivo
B: right duplex rings stack, most common physiological DNA
Z: left duplex, interchanges with B with methylation of cytosine bases; CG rich, may be physiologically relevant in dna expression regulation
H: triple helix, 1 purine 2 pyrimidine
rna
single strand, more flexible, less stable under alkaline conditions and promotes alkaline hydrolysis
rna structure levels
nucleotides
stems, loops, bulges (mismatches), multi branched junctions (intrastrand base pairing), hairpin are stem loop from imperfect base pairs,
psuedoknots ( single strand with hairpin loop) formed by coaxial stacking
ribosome RNA and their proteins
mRNA
carries genetic info from dna to ribosomes for pan synthesis
eukaryotes have splicing and polyadenylation intron removal
tRNA
reads mRNA, translates, AA attaches to invariant 3 CAA
cloverleaf: acceptor stem, anticodon loop, D loop, TPC loop
3D L shape
rRNA
forms ribosomes for translation, synthesizes proteins, has large and small subunits
structure and functional core of ribosomes
catalytic power
how fast enzyme reaction occurs vs uncatalyzed
competitive inhibitors
increase Km max constant
uncompetitive
same factor decrease of km and vmax
noncompetitive
km constant, vmax decrease
proteolytic activation
zymogens need proteolytic cleavage to activate, irreversible and only as needed, to prevent premature enzyme activity that could harm tissues or cells
Ex: chymotrypsinogen activates to chymotrpysin to help digest ptns in small intestines
covalent NA catalysis
ES bind together, E nucleophile residue (ser, cys, lys, his) attacks and covalent bonds S electrophilic center, transition state reactive high energy, E stabilizes with H bond and lower Ea increases reaction rate, chymotrypsin cleaves carboxyl of large hydrophobic aa (phe, met, tyr, trp) to form EP complex, another nucleophile like water then NA and forms P
acid base catalysis
nucleophile attacks base, proton transfer stabilizes transition state, product forms
metal ion catalysis
enzyme cofactor that interacts with S, stabilizes transition state, orients S for run, leaving group leaves
water acitivated
thermolysis- endoprotease with catalystic Zn that stabilizes negative charges on peptide carbonyl oxygen as Glu deprotonates water, promotes attack on carbonyl carbon
active sites
small 3d pockets on E where catalysis happens, enforces S specificity and stereoselectivity, oreients R, stabilizes transition state, regulates E activity, perform chemical reactions
atp hydrolyssis not required for ES bind but can modulate ES affinity
yas queen now repeat what I just said
irreversible inhibitiors
lower vmax
active site or other
permanently covalent bonds (aspirin acetylation of ser, penicillin inhibits cell wall synthesis)
taq polymerase
thermos aquatics functions at 72 degrees
MM
hyperbolic shape
holoenzyme
fully assembled, catalytically active form of E that has coenzyme or metal ion bound
without is called apo enzyme
Glycogen phosphorylase
active site and allosteric site regulation,
covalent modification- hormone converts inactive GP to active
cleaves glucose from nonreducing ends of glycogen through phosphorolysis reaction to convert to cellular fuel, glucose 1 phosphate
allosteric activators AMP (signals low energy)
inhibitors ATP and glucose 6 P
pyridoxal 5 phosphate acid base catalyst
5 phosphate (acid) protonates and weakens bond of glycosidic oxygen of glucose, (base) help attack inorganic phosphate on C1 glucose, promotes cleavage of glycosidic bond, forms G1P!
phosphofructokinase 1 PFK1
active site and allosteric site regulation
commits glucose to glycolysis by forming fructose 1, 6 biphosphate
activators AMP ADP fructose 26 biphosphate
inhibitors ATP citrate
absolute specificity favors binding of one substrate
aspartate transcarbamoylase ATCase
catalytic and regulatory subunits with allosteric sites (regulates and cooperatively)
activated by ATP
inhibitor CTP (end product)
HEMOGLOBINNN
tetramer a2b2 four prosthetic heme group
sigmoidal cooperative (essentially for efficient o2 transport)
oxygen binding: shifts F helix because iron is pulled into the heme plane, one ab rotates 15 degrees (t to R aye) break salt bridges
CO2 hydration and glycolosis make protons which increase o2 dissociation
bicarbonate dehydration consumes protons, decrease o2 dissociation, binds o2, releases CO2
BPG allosteric effecter ionic bonds in central cavity has negative charges with 8 positive charges (2lys, 4 his, 2 n term)
fetal hemoglobin
a2y2, His instead of Ser in 143, higher affinity to oxygen than BPG, lacks 2(+) charges binds loosely, hyperbolic curve, depends on mother for o2 and gas exchange
sickle cell disease
Glu6 turned to Val in B globin, causes deoxyHbS polymerization which distorts rbcs to sickle cell shape under lower oxygen or acidic conditions.
rigidity and aggregations leads to blockage of capillaries, circulation impairment, tissue damage, and premature rbc death (anemia)m
myoglobin
metalloprotein with one heme group
stores o2 in muscle tissues
hyperbolic noncooperative binding
local structural changes with o2 bind
higher affinity to o2 than hb
unaffected by pH or pressure
transferases
phosphate from ATP to substrate
Kinases: hexokinase- transfers phosphate from ATP to glucose to form glucose 6 phosphate (group specificity)
tyrosine kinase phosphorylates tyrosine with phosphate from ATP to make ADP
ligases
joins two substrates together with ATP breaking down to release energy
catalyzes phosphodiester bonds of two DNA strands
DNA ligase- covalent bond of 3 hydroxyl and 5 phosphate terminal
oxireductase
adds molecular oxygen to single substrate, movement of electrons
alcohol dehydrogenase catalyses conversion of primary or secondary alcohol to aldehydes or ketones and reduces NAD+ to NADHp
isomerases
intramolecular group transfer, epimerication, racemization of chiral carbon
converts carotenoid double bond from cis to trans
lyases
add or remove groups from double bond without h2o
decarboxylase aldolases
hydrolases
hydrolysis (cleave bond with h20)
proteases ptns to peptides or AA
lipases - lipid substrate hydrolyzed to components (glycerol and FA), ester bond cleaved
lactase- hydrolyzes lactose to glucose and galactose
relazed confomation
binds to activator and increase S binding pr
protoporphyrin IX
uses four pyrites N atoms to bind to iron, and also a proximal histidine
BPG
allosteric effector shifts o2 bind curve to the right decrease Hb affinity for o2, stabilizes t state, promotes o2 release
bohr effect
increase co2, decrease pH decrease Hb affinity for o2