PSIO Lab 1A & 1B
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What two lobes make up the pituitary gland? What are they made of?
Posterior pituitary (embryonic tissue)
Anterior pituitary (glandular tissue)
What are the major hormones of the posterior pituitary gland?
Oxytocin
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
What does oxytocin target, and what are its effects?
Uterus, mammary glands
Uterine contraction and milk ejection
What do antidiuretic hormones (ADH) target, and what are their effects?
Kidneys
Water reabsorption
What are the major hormones of the anterior pituitary gland?
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Growth hormone (GH)
*Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone
(think FLAT PiGM)
What do follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH) target, and what are their effects?
Gonads (testes & ovaries)
Female: Growth of ovarian follicles and estrogen secretion
Male: Sperm production
What do luteinizing hormones (LH) target, and what are their effects?
Gonads (testes & ovaries)
Female: ovulation, maintenance of corpus luteum
Male: testosterone secretion
What do adrenocorticoid hormones do/target?
Target: kidneys
Do: produce and release glucocorticoids
What do thryoid-stimulating hormones (TSH) target, and what are their effects?
Thyroid gland
Thyroid hormone production and release
What does prolactin (PRL) target, and what are its effects?
Mammary glands
Milk production
What do growth hormones (GH) target, and what are their effects?
Most body tissues
Growth of tissues, blood sugar regulation
Where can you find the thyroid?
Anterior aspect of the larynx
What connects the right and left lobe of the thyroid?
Isthmus
What is the thyroid gland composed of?
Follicles: round structures where thyroid hormones are synthesized and released
What substance are found in the follicles? What is it rich in?
Colloid; iodine
Thryoxine is produced by the thyroid (as well as triiodothyronine and calcitonin). What does it do?
Targets: most body cells, increases metabolism
Where can you find the parathyroid glands?
Posterior aspect of the thyroid gland
Where can you find adrenal glands?
Superior aspect of each kidney
What are the two distinct regions of the adrenal glands?
Outer adrenal cortex
Inner adrenal medulla
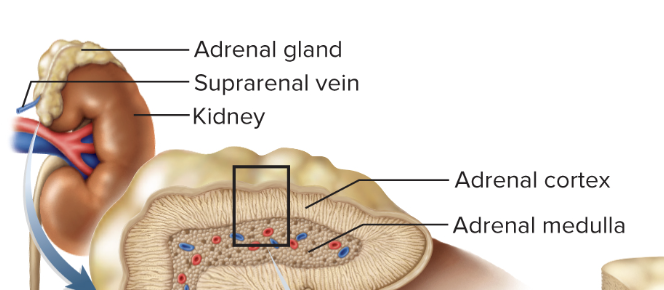
List the layers of the adrenal cortex from superficial to deep
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata
Zona reticularis
(Adrenal Medulla)
What are the functions of the adrenal cortex layers?
Glomerulosa: Outermost, secretes aldosterone (H2O + sugar absorption)
Fasiculata: Secretes cortisol
Reticularis: Secretes androgens (s3x hormones)
What is the function of the adrenal medulla?
Composed of nervous tissue
Produces epinephrine and norepinephrine
Where can you find the pancreas?
Posterior to the stomach
What are the functions of the pancreas?
Exocrine: Synthesizing digestive juices secreted into the small intestine
Endocrine: secretes insulin (decrease blood glucose) and glucagon (increase blood glucose) through pancreatic islets
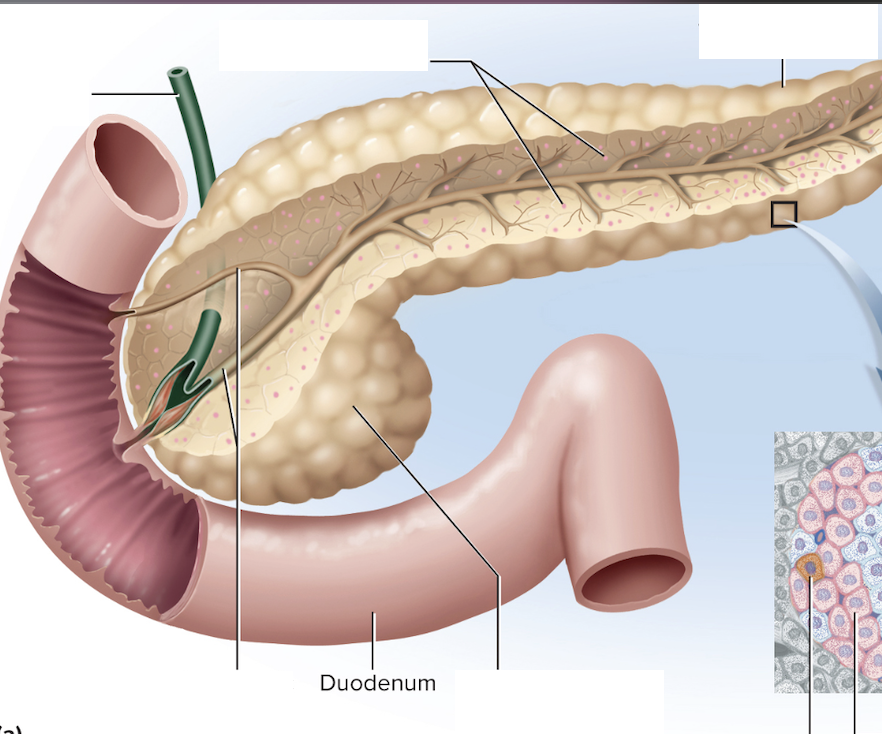
Label this diagram of the pancreas
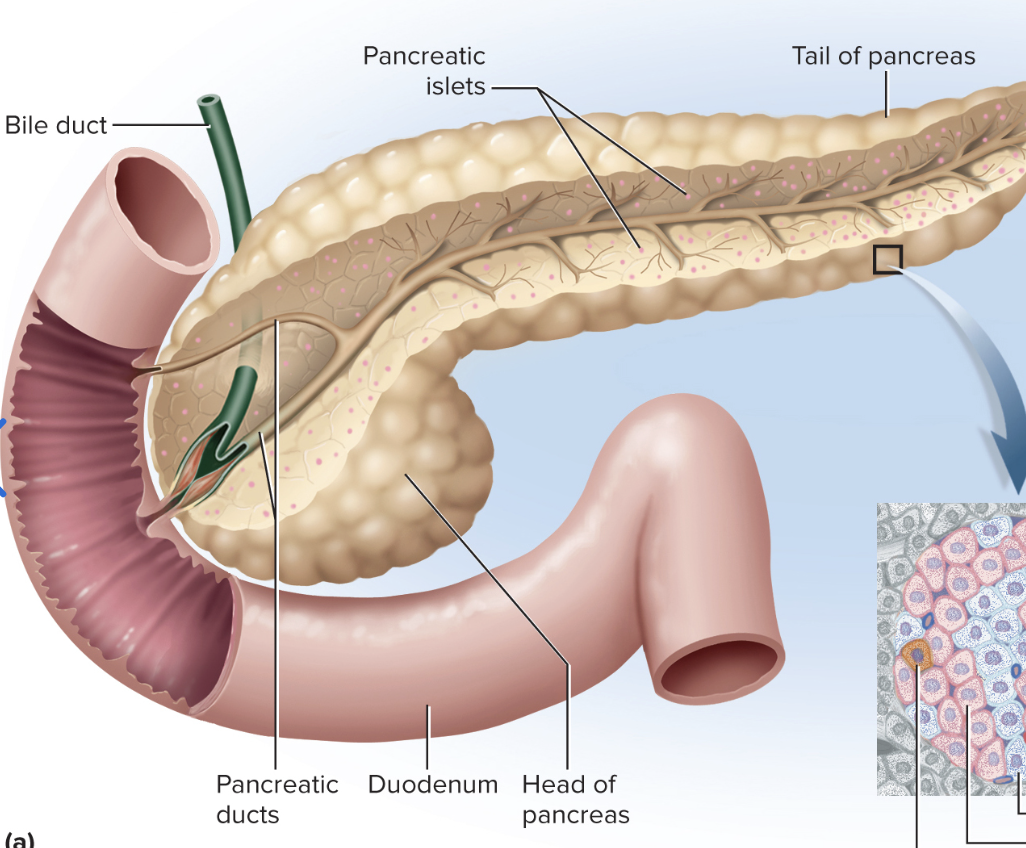
What is the function of the gonads?
Male testes: produce sperm, secrete testosterone
Female ovaries: produce oocytes, secrete estrogen and progesterone
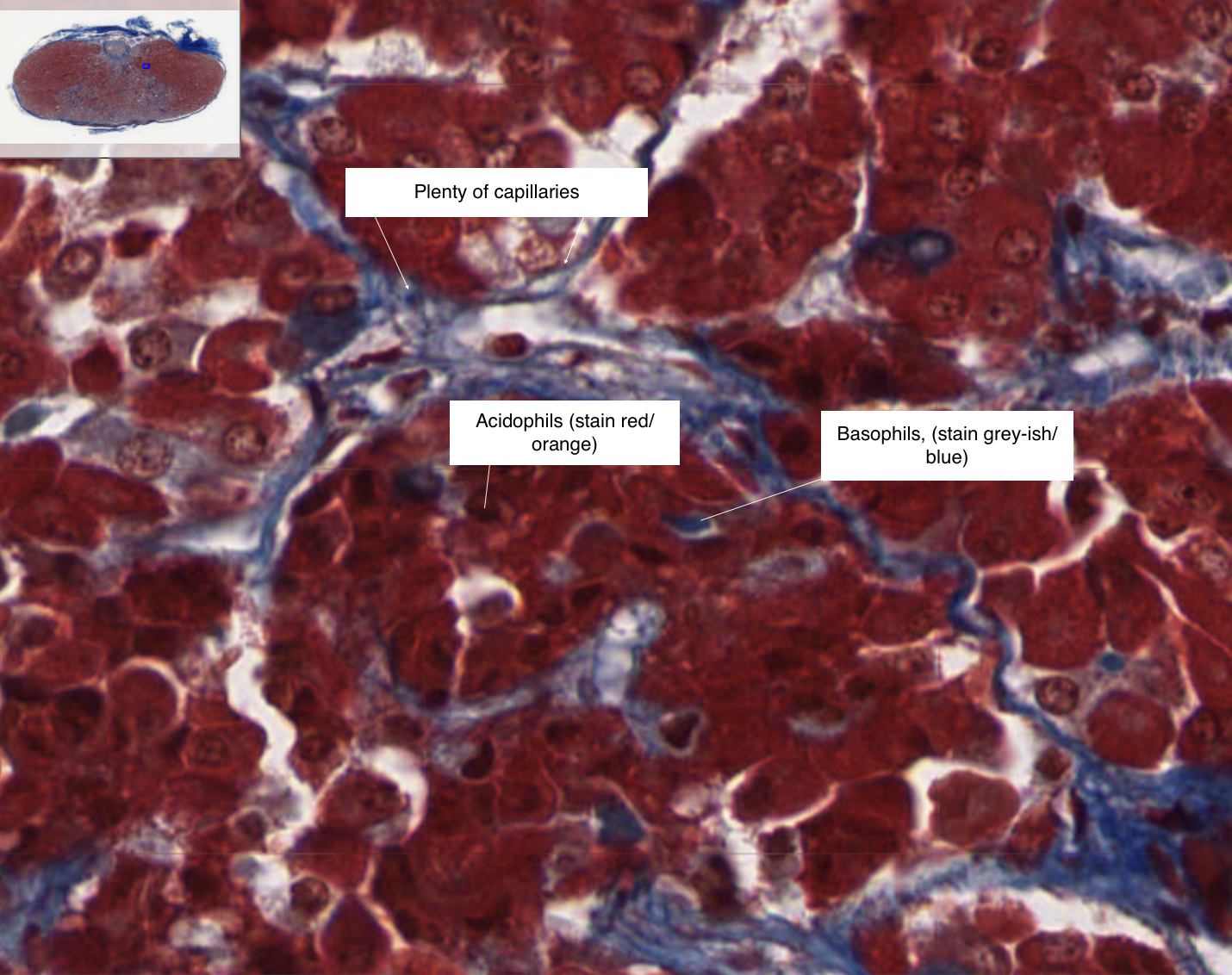
How can you identify the pituitary gland on a slide?
Identifying acidophils, basophils, and capillaries
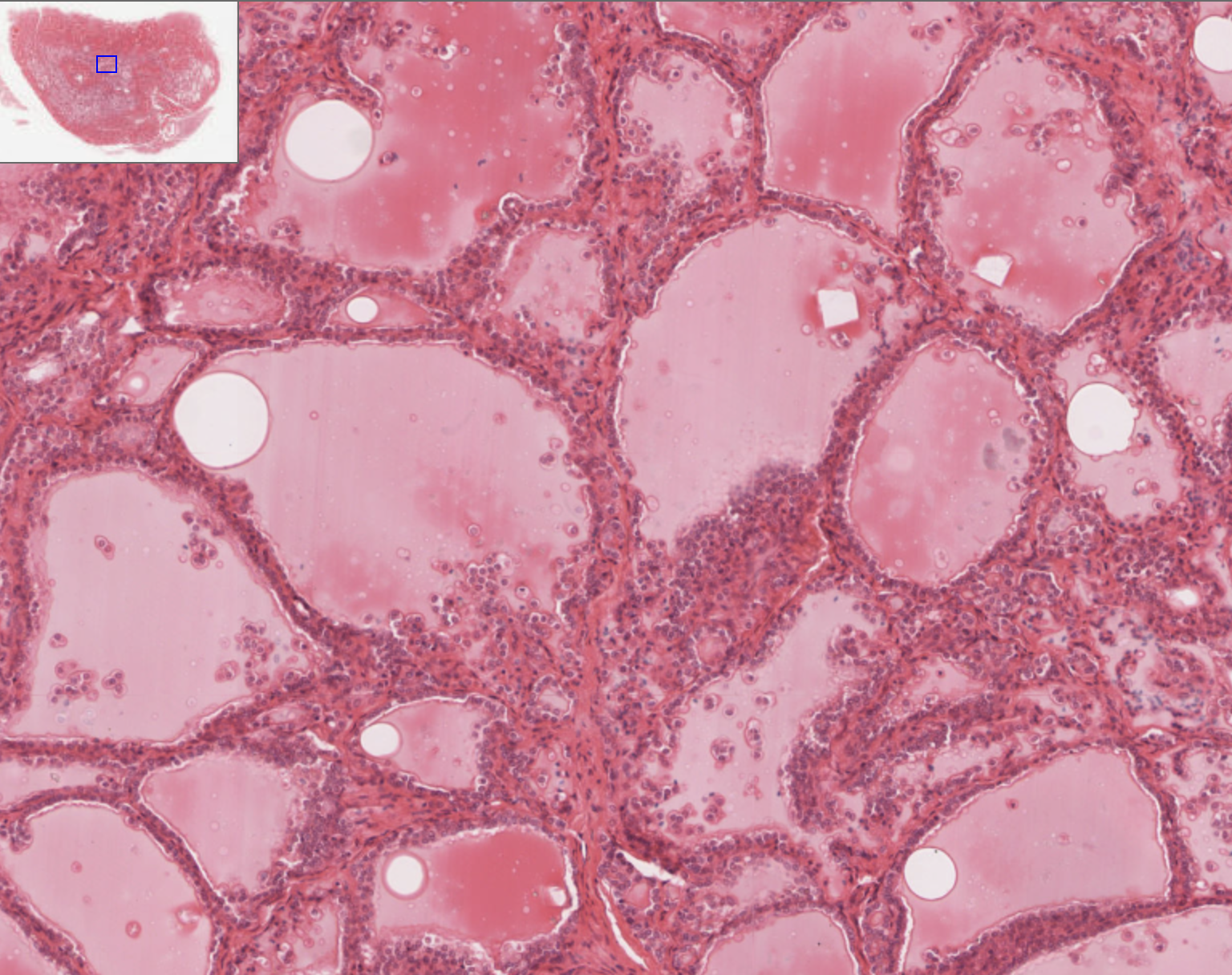
How can you identify the thyroid gland on a slide?
Identify follicles, colloid, and follicular cells (?)
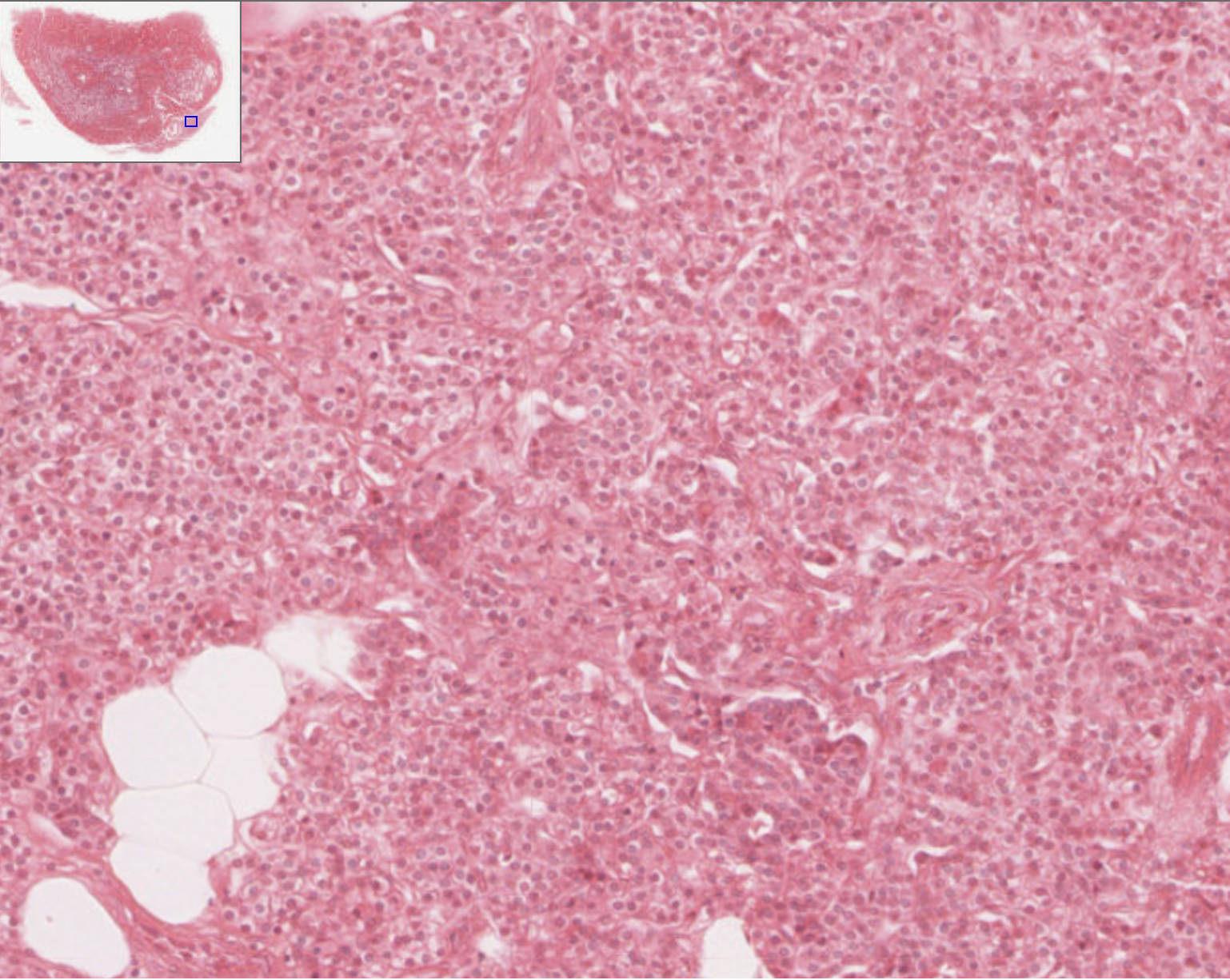
How can you identify the parathyroid gland on a slide?
chief cells..?
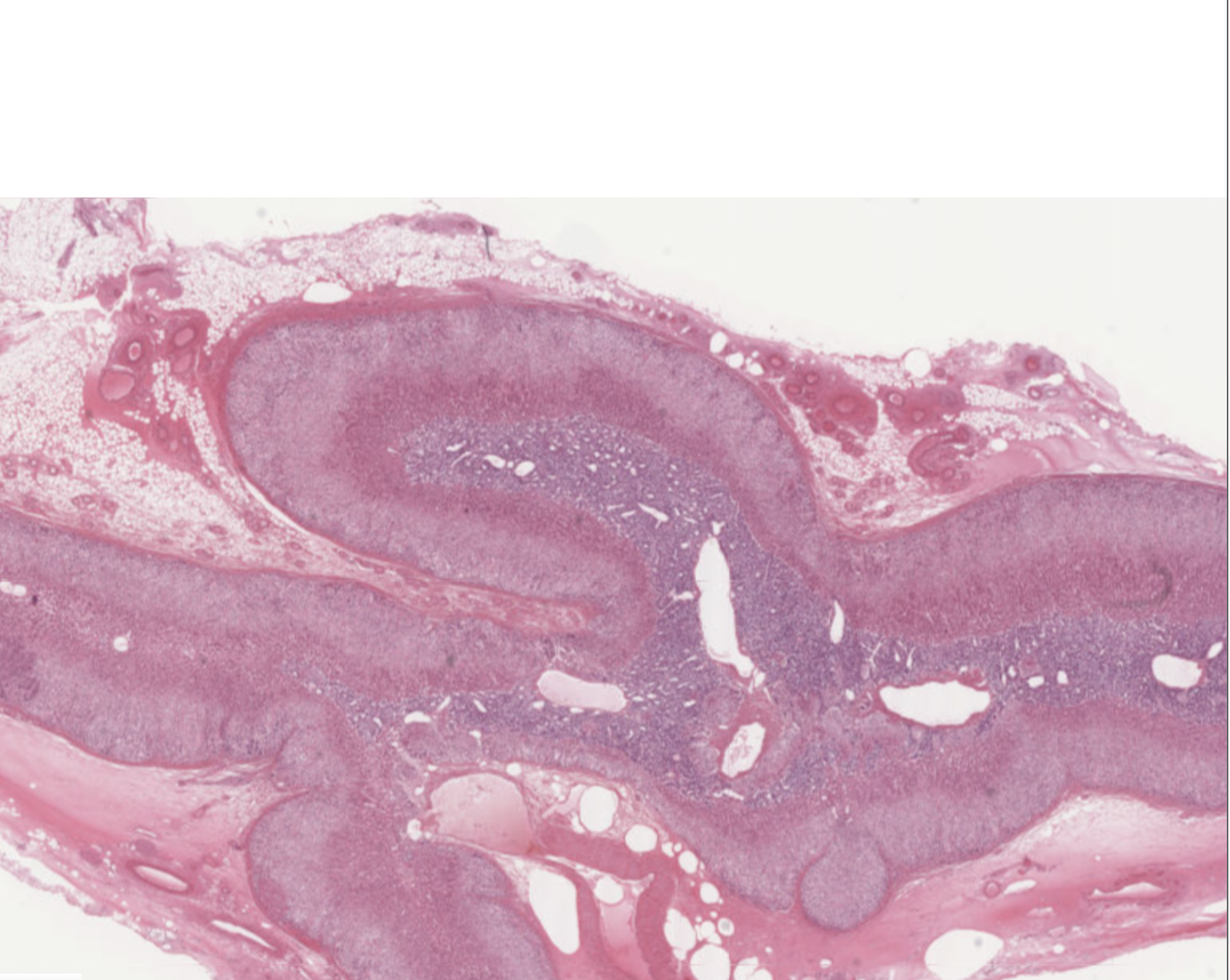
How can you identify the adrenal glands on a slide?
(adrenal cortex)
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciata
Zona reticularis
(adrenal medulla)
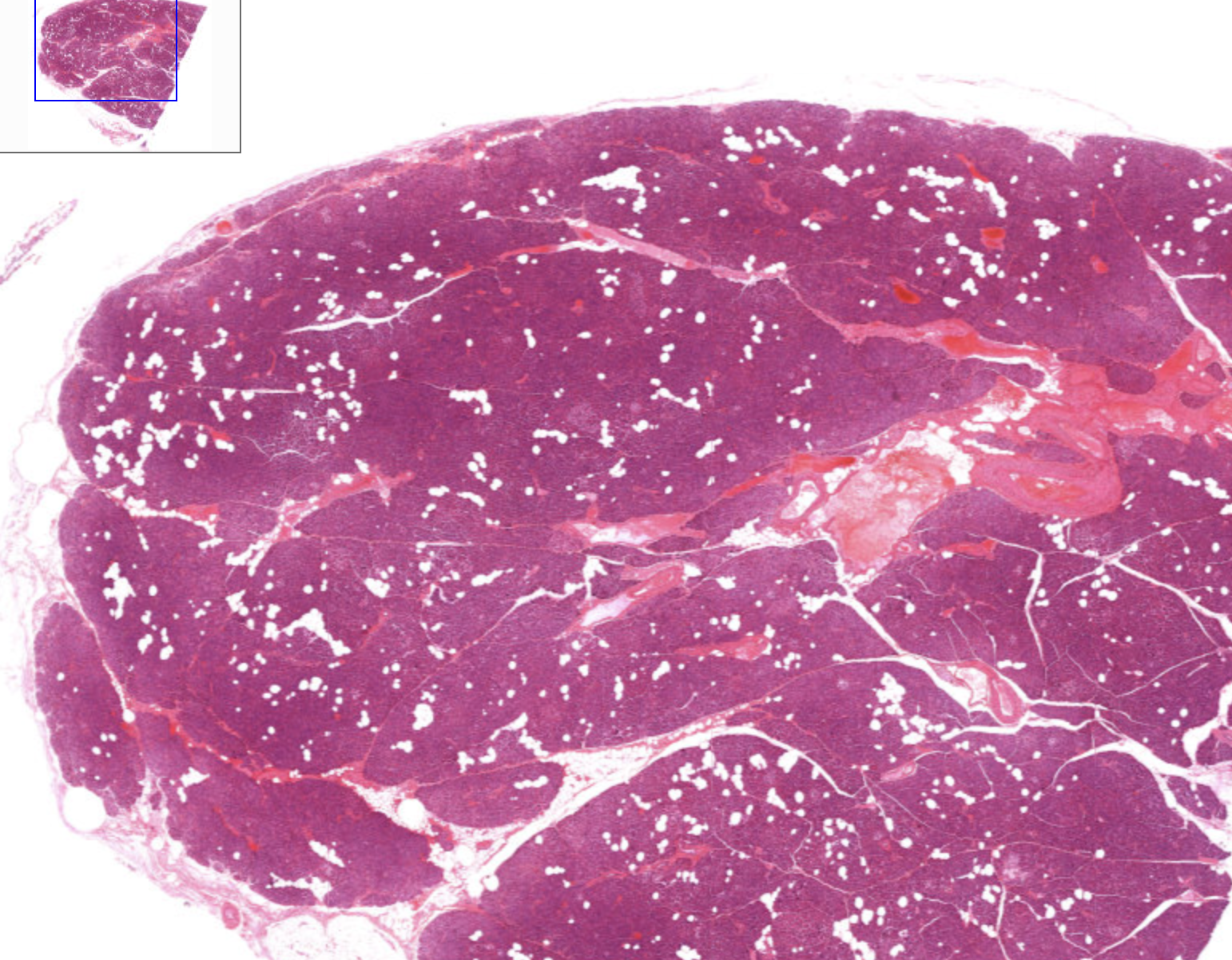
How can you identify the pancreas on a slide?
pancreatic islets
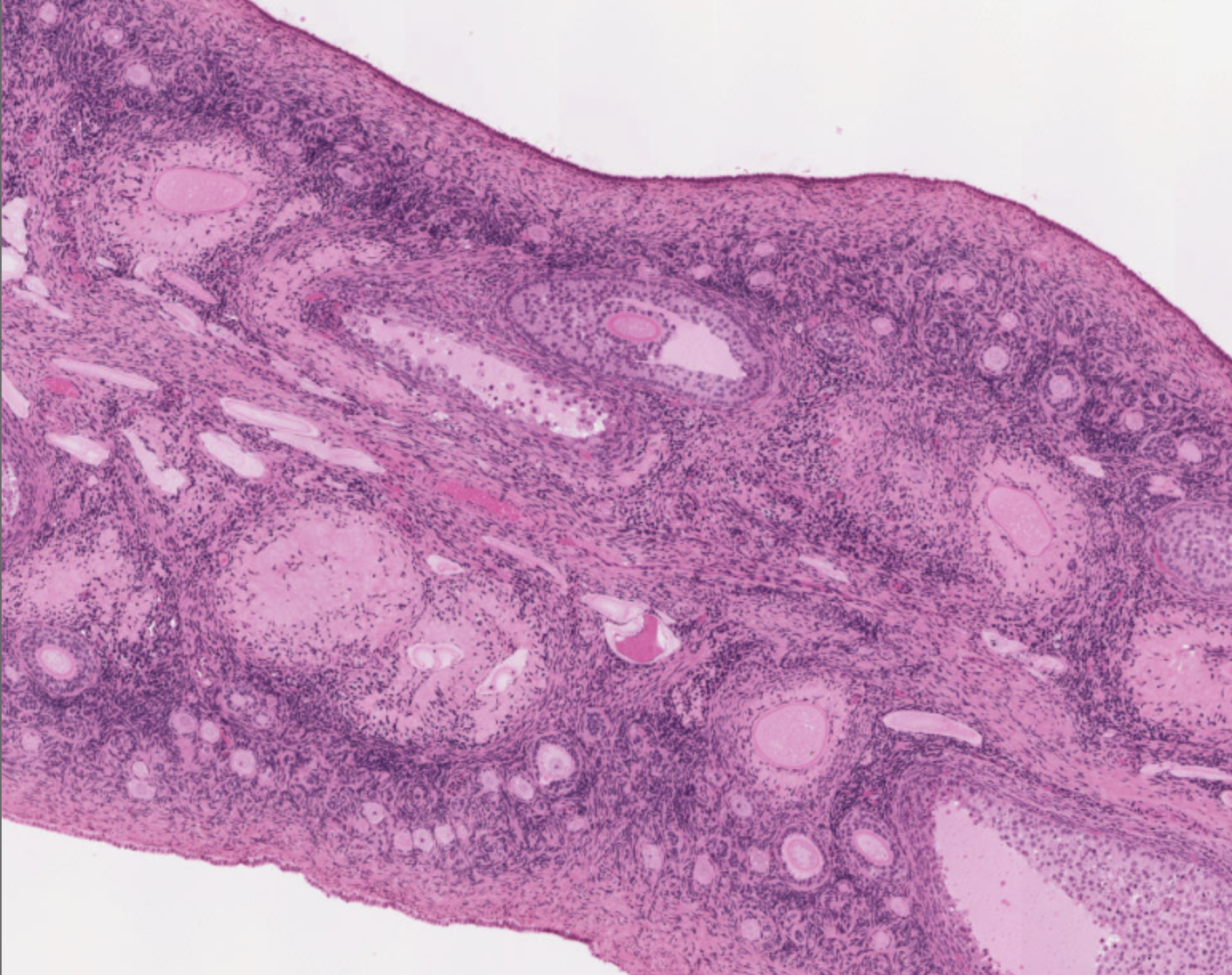
How can you identify an ovary on a slide?
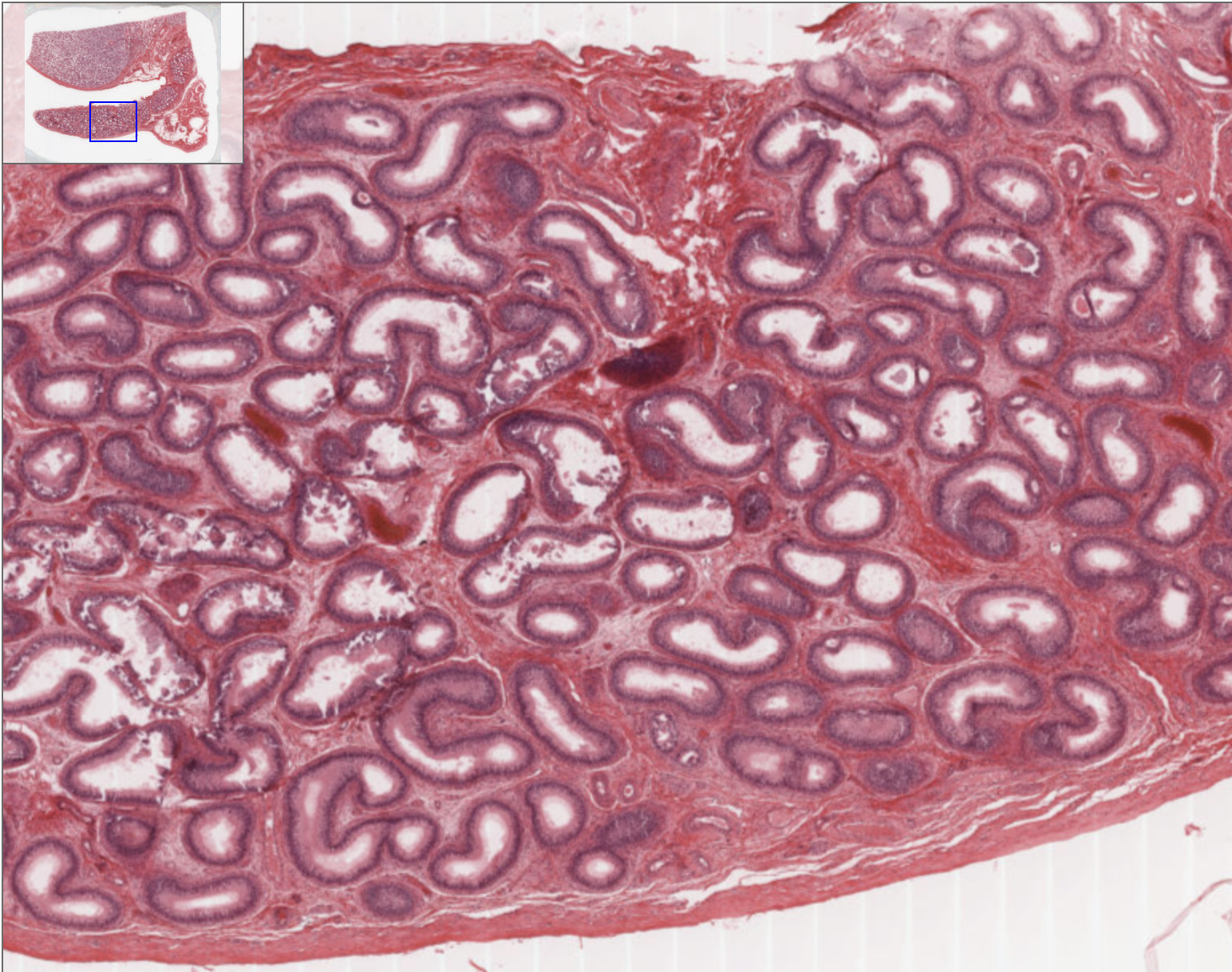
How can you identify a testis on a slide?
Where is the heart located?
In between the lungs in the mediastinum
What membrane separates the heart from other mediastinal structures?
The pericardium
What are the two layers of the pericardium?
Outer fibrous pericardium
Inner serous pericardium
What are the two layers of the inner serous pericardium?
Parietal pericardium
Visceral pericardium/epicardium
List the layers of the internal heart from superficial to deep
Epicardium (outermost layer of the external heart)
Myocardium
Endocardium
What is the myocardium made up of?
Cardiac muscle cells
collagenous fibers
blood vessels
Which valve sits in between the right atrium and the right ventricle?
Tricuspid valve
What are the flaps of a valve connected to?
Connected by chordae tendinae, which connect to papillary muscles to anchor them to the heart walls
True or false: There are no papillary muscles or chordae tendinae associated with the pulmonary valve
True
Which valve sits between the left atrium and the left ventricle?
Mitral valve
**Which blood vessels carry blood TOWARD the heart?
Veins
**Which blood vessels carry blood AWAY FROM the heart?
arteries
What is the function of coronary arteries?
To supply blood to the myocardium (first portion of the aorta)
Describe the function of the coronary vein, coronary sulcus, and coronary sinus
Coronary vein drains the heart of deoxygenated blood, goes through gas exchange, then comes back along the coronary sulcus/sinus
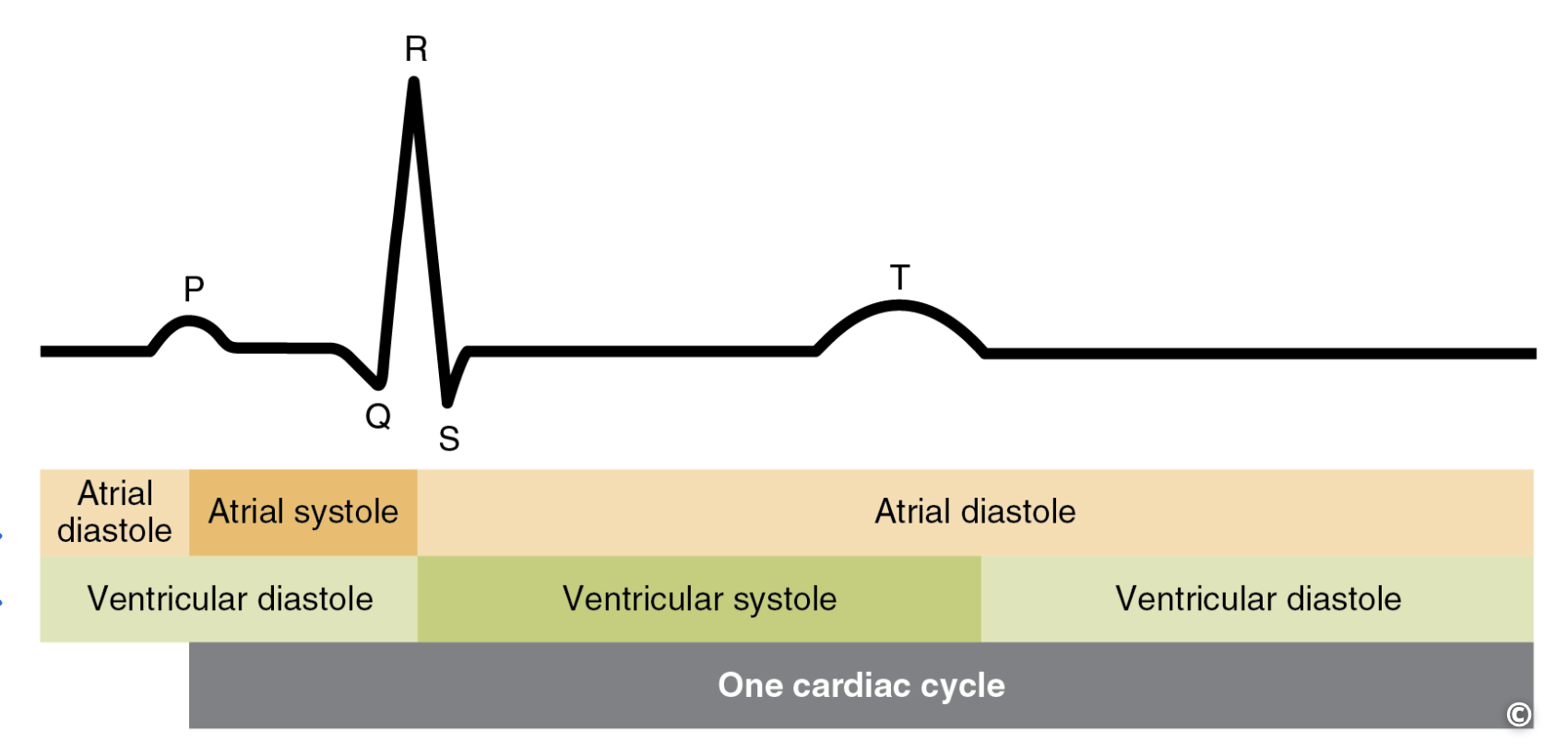
Systole
Contraction
Diastole
Relaxation
End-Diastolic Volume (EDV)
Volume of blood in ventricle before ejection
Diastole
Relaxation
Cardiac Output
Blood output per min
Stroke volume
Volume of blood pumped out per systole
End-systolic volume (ESV)
Volume of blood left in ventricle after systole
Tachycardia
Abnormally fast heart rate
Bradycardia
Abnormally slow heart rate
Describe the conduction system of the heart, listing the structures in order.
Sinoatrial node (SA)
Atrioventricular node (AV)
AV Bundle of His (down the interventricular septum)
Left/Right bundle (at the apex)
Purkinje fibers
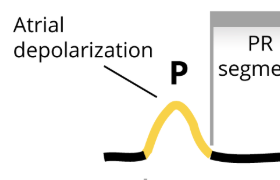
What produces the P-wave?
Atrial depolarization
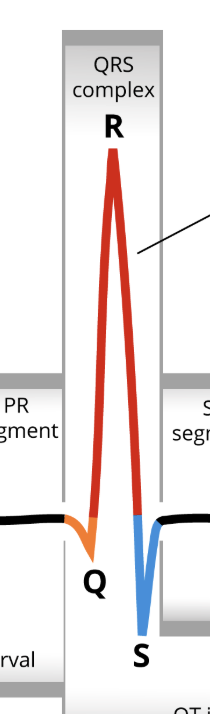
What produces the QRS complex?
Ventricular depolarization; atrial repolarization
What produces the T wave?
Ventricular repolarization
Describe the heart’s Mechanical Activity
Atrial systole (atrial muscles contract)
Early ventricular systole (ventricle muscles contract)
Late ventricular systole (blood passes through pulmonary/aortic valve)
Early ventricular diastole (blood refills atria)
Late ventricular diastole (blood begins leaking into ventricles)
what makes the “lub” and “dub” sound of your heart beat?
lub: closure of atrioventricular values
dub: closure of pulmonary valves
Where is the brachiocephalic trunk?
The first branch (on the right) of the aorta
What is the “hole” in a fetus/baby’s heart called? What does it turn into?
Foramen ovale; fossa ovalis
What attaches the aorta to the pulmonary artery? What was it called as a fetus?
Ligamentum arteriosum; ductus arteriosus
what hormone does thymus release? what does it do?
Thymosin; promotes T-cell maturation