Suspension therapy
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
When do we use suspension therapy?
active assisted exercises to improve the ROM and muscle strength with minimized friction
It helps in positioning the patient in a gravity eliminated position (grade 2 )
What are the types of suspension?
static suspension: facilitates standing and walking functions. It decreases the effect of gravity on the lower limb and enables the child to control less body weight
Dynamic suspension - e.g. a suspension walker
Vestibular suspension - hammock
What is a Guthrie smith apparatus/ falcons frame?
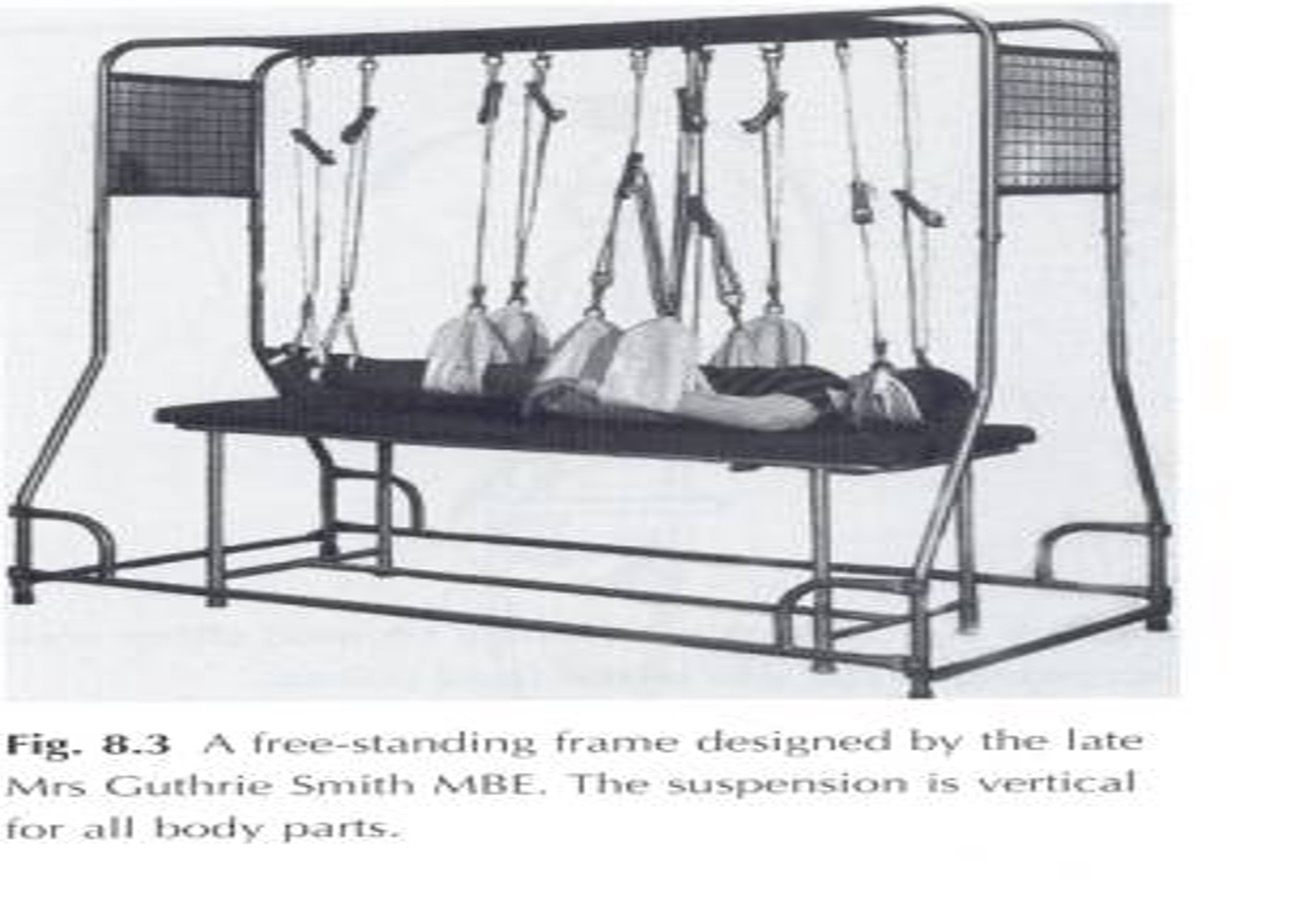
What are the benefits of suspension for rom exercises?
active participation of the patient is required to use the appropriate muscle for desired movement
Relaxation is promoted through secure support and smooth rhythmic motion
Little work is required from stabilizing muscles because the part is supported
Modification can be made to the system to provide grades of exercise resistance
What is the fixed point in suspension therapy?
It is made of stainless steel or plastic covered 5 cm metal mesh around the area of a plinth
It is 2m x 2m x 2m mesh cube (3 sides and a ceiling)
The sides of the frame allows lateral fixed points

What else is required for suspension therapy?
storage trolley
Suspension unit
what are the types of non-slippery supporting ropes?
A single rope
A pulley rope
A double rope
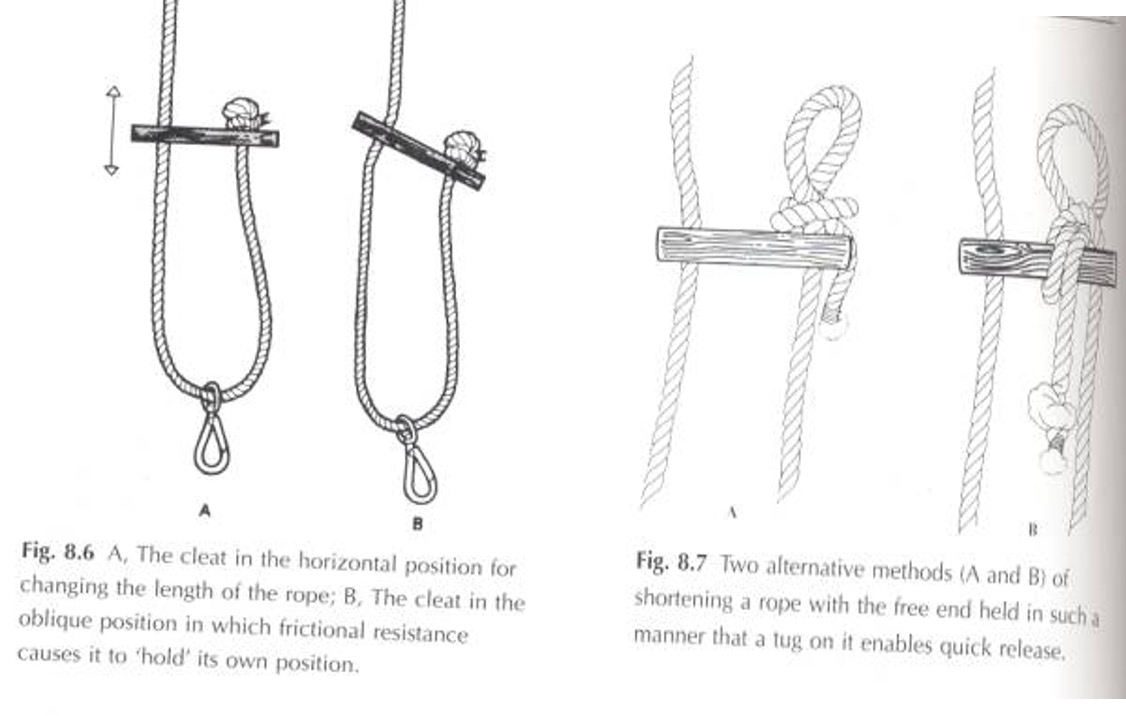
Describe single rope:
a single rope has a ring fixed at one end by which it is hung up, the other end passes through a wooden cleat then through the ring of a dog clip
The cleat is for altering the length of the rope and should be held horizontally for movement
The cleat should be pulled obliquely when supporting the rope as it holds on the cleat by friction
The total length of the rope is 1.5 m further shortening the rope may be brought by knotting the cleat
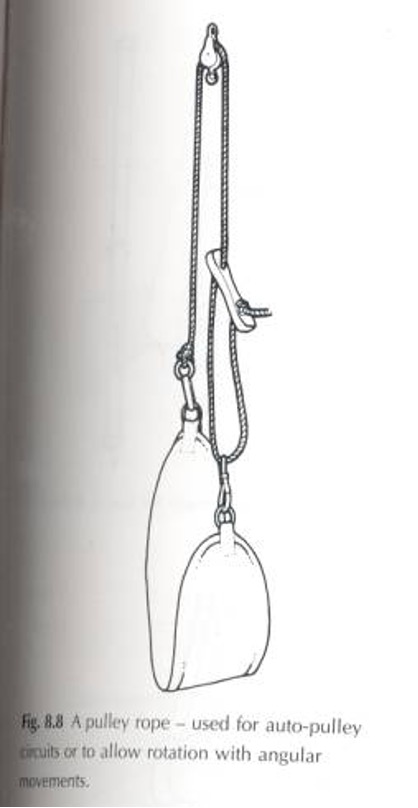
What is a pulley rope?
a pulley rope has a dog clip attached to one end which then passes over the wheel of a pulley. The rope then passes through the cleat and a second dog clip
The rope is 1.5 m long
This arrangement is used for reciprocal pulley circuits - with one sling supporting a limb and the ends of the sling attached to the 2 dog clips it is used for 3 dimensional movement of a limb
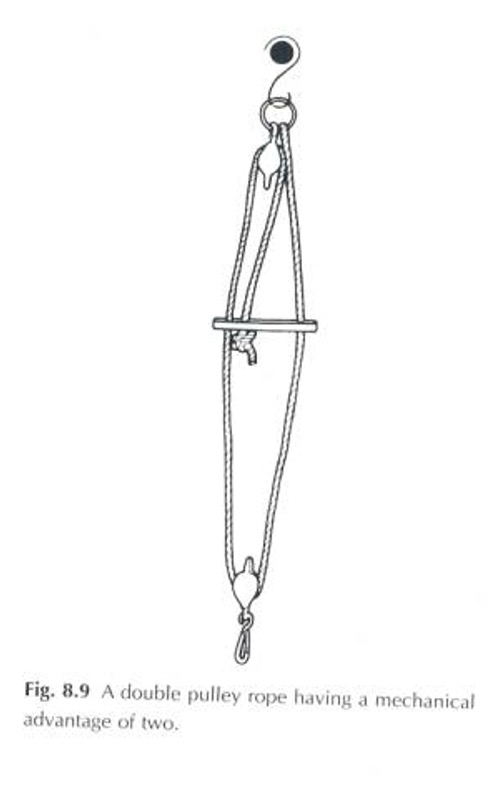
What is a double rope?
a double rope consists of a ring and clip from which the rope is hung to create a compensating device permitting a certain amount of swivel on the rope
This device gives mechanical advantage
It is used to suspend heavy parts of the body - the pelvis, thorax, or heavy thighs when these are to be supported together
What is an s hook?

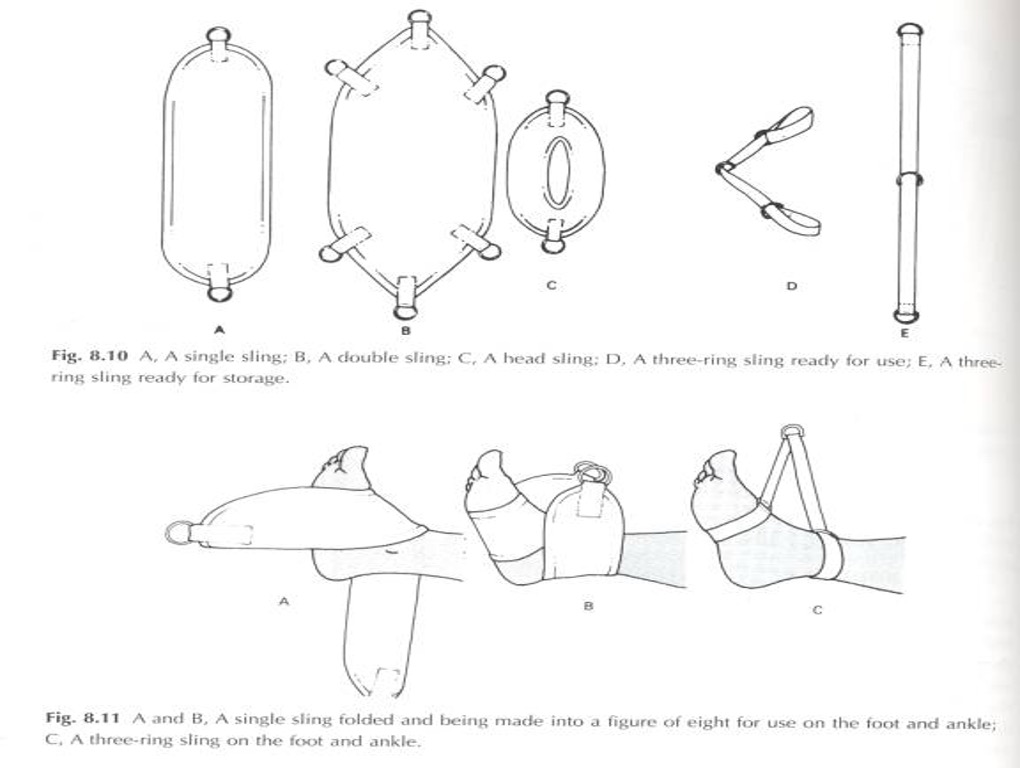
what are the types of slings?
single sling: made of canvas bound with soft webbing and with a D ring at each end, it supports the limbs
Can be folded in two and as a figure of 8 to support the hand and foot
They measure 68 cm long by 17 cm wide
double slings: broad (68 cm by 29 cm wide) with D rings at each end to support the pelvis, thorax or thighs together, support the wrist, hand, ankle and foot
three ring sling: webbing slings (71 cm long by 3-4 cm wide) with 3 D rings one fastened at each end and one free in the middle
The center ring is for attachment to a dog clip and the webbing is slipped through the end D rings to make 2 loops Which are used to support the wrist and hand or ankle and foot
Head sling: short, split sling with its two halves stitched together at an angle to create a central sling - allows the head to rest supported at the back under the lower and upper parts of the skill in the side lying position leaving the ear free
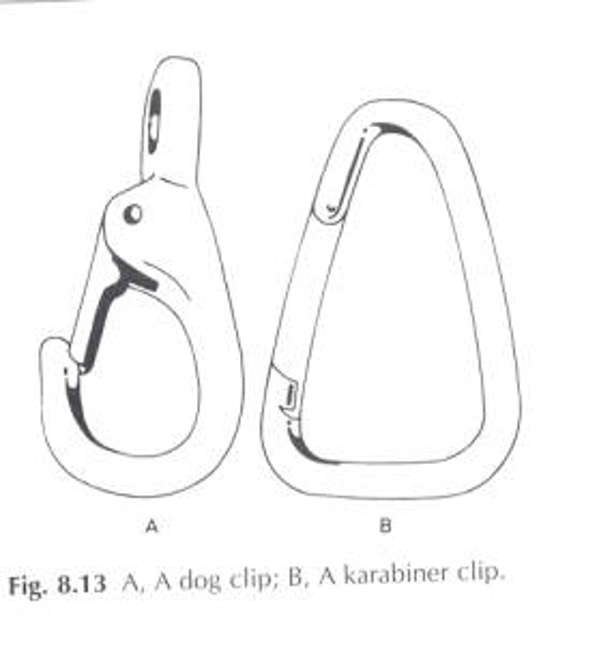
Describe the clips used in suspension therapy:
karabiner hooks of 70 mm or 100 mm provide a convenient alternative means of clipping 2 pieces of equipment together
What are the indications of suspension therapy:
To increase muscle power 2 according to MRC grading
Any post operative orthopedic conditions
Spastic limbs -rhythmic movements helps reduce spasticity
Degenerative joints
LMNL
To mobilize joints
Pressure sores
What are the contraindications of suspension therapy?
active joint infections
Skin infections
Recent fractures
Shoulder subluxation
What are the advantages?
more comfortable
Gravity eliminated
Friction free technique
The limb is completely supported And is made weightless
Provides rhythmic relaxation to the muscle
what are the disadvantages?
not applicable for smaller joints
Traction cannot be given
Cost effective
Time consuming
Patient effort is minimised
what is vertical suspension?
vertical fixation the rope is fixed vertically above the centre of gravity of the part to be suspended
It is primarily used for providing support and to find the centre of gravity
Provides general body relaxation and is effective for bed sores
describe axial suspension:
This provides all the ropes supporting the part attached to a S hook above the centre of the joint
The part will move of a flat pan parallel to the floor
This type of fixation allows to increase rom
What are the suspension points of the upper limb?
Joint | Movement | Position of pt. | Point |
Shoulder | Flexion & ext. | Side lying | Greater tubercle of the humerus |
Abduction & add. | Supine lying | Acromion process | |
Medial & lat. rotation | supine lying with 90* elbow and shoulder flexion | Olecranon process of ulna | |
Elbow | Flexion & ext. | Side lying | Lateral epicondyle of humerus |
What are the suspension points for the lower limb
Joint | Movement | Position of pt. | Point |
Hip | Flexion &ext. | Side lying | Greater trochanter |
Abduction & add. | Supine lying | ½ inch below the ASIS | |
Med.& lateral rotation | Supine with hip & knee flexed 90* | Apex of patella | |
Knee joint | Flexion & ext. | Side lying | Lateral condyle of femur |
Describe pendular suspension?
increases muscle strength
The suspension point (s hook) is shifted to the side opposite the muscle action
The muscle has to take effort to overcome the resistance by the gravitational force due to shifting of the suspension point