Genetic Principles: Codominance, Epistasis, and Mapping
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
What is codominance in genetics?
The phenotype of the heterozygote simultaneously expresses the phenotypes of both homozygotes.
What is the ABO blood group system determined by?
The presence of three alleles: IA, IB, and i.
What does allele IA code for in the ABO blood group system?
The production of antigen A on the surface of red blood cells.
What does allele IB code for in the ABO blood group system?
The production of antigen B on the surface of red blood cells.
What is the phenotype and antibody presence for blood group A?
Has antigen A in RBCs and will have Anti-B antibodies in plasma.
What is the phenotype and antibody presence for blood group B?
Has antigen B in RBCs and will have Anti-A antibodies in plasma.
What is the phenotype and antibody presence for blood group AB?
Has both antigen A and B in RBCs and has no antibodies in plasma.
What is the phenotype and antibody presence for blood group O?
No antigens in RBCs and has both Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies in plasma.
What is the dominance relationship between IA, IB, and i?
IA and IB are codominant, while both are dominant over i.
What are the genotypes and corresponding phenotypes for the ABO blood group system?
IA/IA is A, IB/IB is B, IA/IB is AB, and i/i is O.
What is the level of dominance determined by?
The investigative level of analysis: macroscopic, cellular, or molecular.
What is an example of complete dominance?
Hb^A is dominant over Hb^S at the macroscopic level.
What is an example of incomplete dominance?
Sickle cell anemia shows incomplete dominance at the cellular level.
What is codominance at the molecular level in sickle cell anemia?
Both HbA and HbS are expressed in heterozygotes, showing migration for both bands A and S.
What is penetrance in genetics?
The percentage of individuals with a particular genotype that expresses the expected phenotype.
What is expressivity in genetics?
The degree to which a character is expressed in individuals with the same genotype.
What is an example of incomplete penetrance?
In a population with the allele for polydactyly, only 38 out of 42 individuals express the phenotype. 38/42 = 0.9 = 90% individuals with polydactyly
What does variability in expressivity mean?
Individuals with the same genotype can show different phenotypes, such as varying degrees of polydactyly.
What environmental factors can affect gene expression?
Environmental factors can modify genes, impacting the expression of traits.
What is the probability of a child being homozygous for long fingers if both parents are heterozygous?
The probability is 25% (from Ll x Ll mating). Ll x Ll gives LL Ll Ll ll, 25% are ll.
What is the formula to calculate the percentage of individuals who have a specific phenotype given a genotype frequency?
Multiply the genotype frequency by the percentage of individuals that actually have the genotype. For example, .25 x .8 = 0.2, which equals 20%.
What does the term 'locus' refer to in genetics?
A locus (plural: loci) refers to the specific physical location of a gene or DNA sequence on a chromosome.
What is gene interaction in genetics?
Gene interaction occurs when the effects of genes at one locus depend on the presence of genes at other loci, influencing a single phenotype.
What is the gene interaction of Rr/Yy in pea plants?
The R and r alleles affect seed shape but have no effect on seed color (Y and y) and vise versa
What is epistasis in genetics?
Epistasis is a form of gene interaction where one gene masks the effect of another gene.
What are the two types of epistasis?
Recessive epistasis and dominant epistasis.
Describe the F2 generation phenotype ratios in summer squash. What does the 9:3:4 ratio represent?
From parents of AaBb x AaBb: In the F2 generation, the phenotypic ratio is 9:6:1, representing disc, sphere, and long shapes respectively. 9/16 will be A_B_, 3/16 will be A_Bb, 3/16 will be aaB_, and 1/16 will be aabb, hence the 9:6:1 (9 disc, 6 sphere, 1 long)
What is the significance of the 6/16 probability in the F2 generation of summer squash?
The 6/16 probability indicates that 6 out of 16 offspring will exhibit the sphere phenotype due to the interaction of two genes.
What happens when the achondroplasia allele is homozygous?
The recessive allele for achondroplasia is lethal when homozygous.
What is the difference between a dominant lethal allele and a dominant allele that is lethal?
A dominant lethal allele would cause all heterozygotes to die, while a dominant allele that is lethal does not necessarily lead to death.
What does variable expressivity mean in the context of cystic fibrosis?
Variable expressivity refers to the variation in severity of symptoms of cystic fibrosis among different patients.
In the context of recessive epistasis, what do the alleles B and b represent?
B is the dominant allele that encodes black pigment, while b is the recessive allele that encodes brown pigment. Alleles at one locus determining a pigment
What do the alleles E and e affect in the context of dog coat color?
E is the dominant allele that allows for the deposition of dark pigment, while e is the recessive allele that prevents deposition. Alleles at another locus affecting pigment
What is the genotype of a black dog in this genetic model?
A black dog can have the genotype Bb or BB, along with EE or Ee (B_E_).
What is the genotype of a brown dog?
A brown dog has the genotype bb and E_.
What is the genotype of a yellow dog?
A yellow dog can have the genotype B_ ee or bb ee.
Why can yellow dogs produce pigments but not deposit them in their hair shafts?
Yellow dogs have the ability to produce pigments but lack the correct genes to deposit them into the hair shafts due to the recessive e allele.
What is the phenotypic ratio for black, brown, and yellow dogs?
The phenotypic ratio is 9:3:4 for black, brown, and yellow dogs.
What is the genotypic ratio for black, brown, and yellow dogs?
9:3:3:1 (two of which (the second 3 and 1) produce yellow)
What does the term 'phenotypic ratio' refer to?
The phenotypic ratio refers to the relative frequencies of different phenotypes produced in a genetic cross.
What is a potential phenotype for dogs with a pink nose and lips?
Pink nose and lips may indicate a lack of dark pigment deposition, similar to yellow dogs.
What are sex-linked characteristics?
Characteristics determined by genes located on the sex chromosomes.
What are sex-influenced characteristics?
Characteristics determined by autosomal genes but expressed differently in males and females.
How are sex-influenced characteristics inherited?
According to Mendel's principles, but expression differs between sexes.
Give an example of sex-influenced characteristics in goats.
The presence of a beard is influenced by the autosomal gene BP.
What is the genotype for beardless males and females in goats?
B+B+.
What is the genotype for bearded males and beardless females in goats?
B+Bb.
What is the genotype for bearded males and females in goats?
BbBb.
What is the Bb effect?
The effect that Bb is dominant in males but recessive in females
What are sex-limited characteristics?
Characteristics encoded by autosomal genes but expressed in only one sex.
Give an example of sex-limited characteristics in chickens.
Cock feathering is limited to males.

What are the genotypes for hen feathering in chickens?
HH and Hh.
What is the genotype for cock feathering in males?
hh.
What is cytoplasmic inheritance?
Inheritance of characteristics encoded by genes located in the cytoplasm, such as chloroplast and mitochondrial genes.
What is the mitochondrial genome's size and its function?
Contains about 15,000 nucleotides encoding 37 protein-coding genes.
What is the nuclear DNAs size and its function?
3 billion nucleotides encoding 20,000-25,000 protein-coding genes
How is mitochondrial DNA inherited?
Typically inherited from the maternal parent due to higher mitochondrial content in eggs.
What is stochastic segregation of mtDNA?
The random distribution of mitochondria to daughter cells during cell division.
How does the proportion of mutant mtDNA affect an organism?
This process can result in different cells containing different proportions of mutant and wild-type mtDNA.
The severity of conditions may depend on the proportion of mutant mtDNA within the cell.
What did Carl Corrents recognize in 1909?
Cytoplasmic inheritance.
What are the color variations observed in the 4 o'clock plant?
White, green, and variegated colors.
What is the significance of reciprocal crosses in cytoplasmic inheritance?
They can yield different results due to maternal inheritance patterns.
Why do characteristics exhibit extensive phenotypic variation within a single family?
Due to more mutations occurring after numerous cell divisions.
What causes variegation in certain plants?
A defective gene in the chloroplast DNA (cDNA) leads to a failure to produce the green pigment chlorophyll.
What types of chloroplasts are found in cells from white plants?
Cells from white plants contain only abnormal chloroplasts.
What types of chloroplasts are found in cells from green plants?
Cells from green plants contain only normal chloroplasts.
What types of chloroplasts are found in cells from variegated plants?
Cells from variegated plants contain both normal and abnormal chloroplasts.
What is the key difference between genetic maternal effect and cytoplasmic inheritance?
In genetic maternal effect, genes are inherited from both parents, and the phenotype of offspring is determined by the genotype of their mother, not their own genotype, while in cytoplasmic inheritance, genes are inherited from only one parent.
Where are nuclear genes located?
Nuclear genes are located on the chromosomes in the nucleus.
What is the phenotype of the F1 progeny when a dextral coiling snail (S+S+) is crossed with a sinistral coiling snail (ss)?
The genotype of the F1 progeny is S+s (heterozygote), and the phenotype is sinistral, determined by the mother's genotype.
What is the expected genotype ratio in the F2 generation from self-fertilization of S+S snails?
The expected genotype ratio is ¼ S+S+, ½ S+s, ¼ ss.
Why are all F2 snails dextral when the mother has the genotype S+S+?
All F2 snails are dextral because the mother in the F1 generation was S+S, and the dominant allele S+ determines the dextral phenotype.
What does the S+ allele encode in snail coiling?
The S+ allele encodes for the right-handed (dextral) coil.
What does the s allele encode in snail coiling?
The s allele encodes for the left-handed (sinistral) coil.
What is the maternal effect in the context of the snail coiling trait?
The maternal effect means that the phenotype of the offspring is determined by the genotype of the mother, regardless of the offspring's own genotype.
What types of maternal parents are mentioned in the notes regarding branch color?
Maternal parents with white branches, green branches, and variegated branches.
What determines the phenotype of the offspring in relation to the mother?
The genotype of the mother determines the phenotype, not the maternal phenotype.
What is genomic imprinting?
Genomic imprinting is the differential expression of genomic material depending on whether it is inherited from the male or female parent.
What can disruptions in normal imprinting patterns lead to?
Specific diseases, known as imprinting disorders, can arise from disruptions in normal imprinting patterns.
Name two imprinting disorders.
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) and Russell-Silver Syndrome (RSS).
How does lack of genomic imprinting affect cancer development?
Lack of imprinting can lead to inappropriate activation of oncogenes or silencing of tumor suppressor genes.
What is an example of a gene involved in cancer that is affected by genomic imprinting?
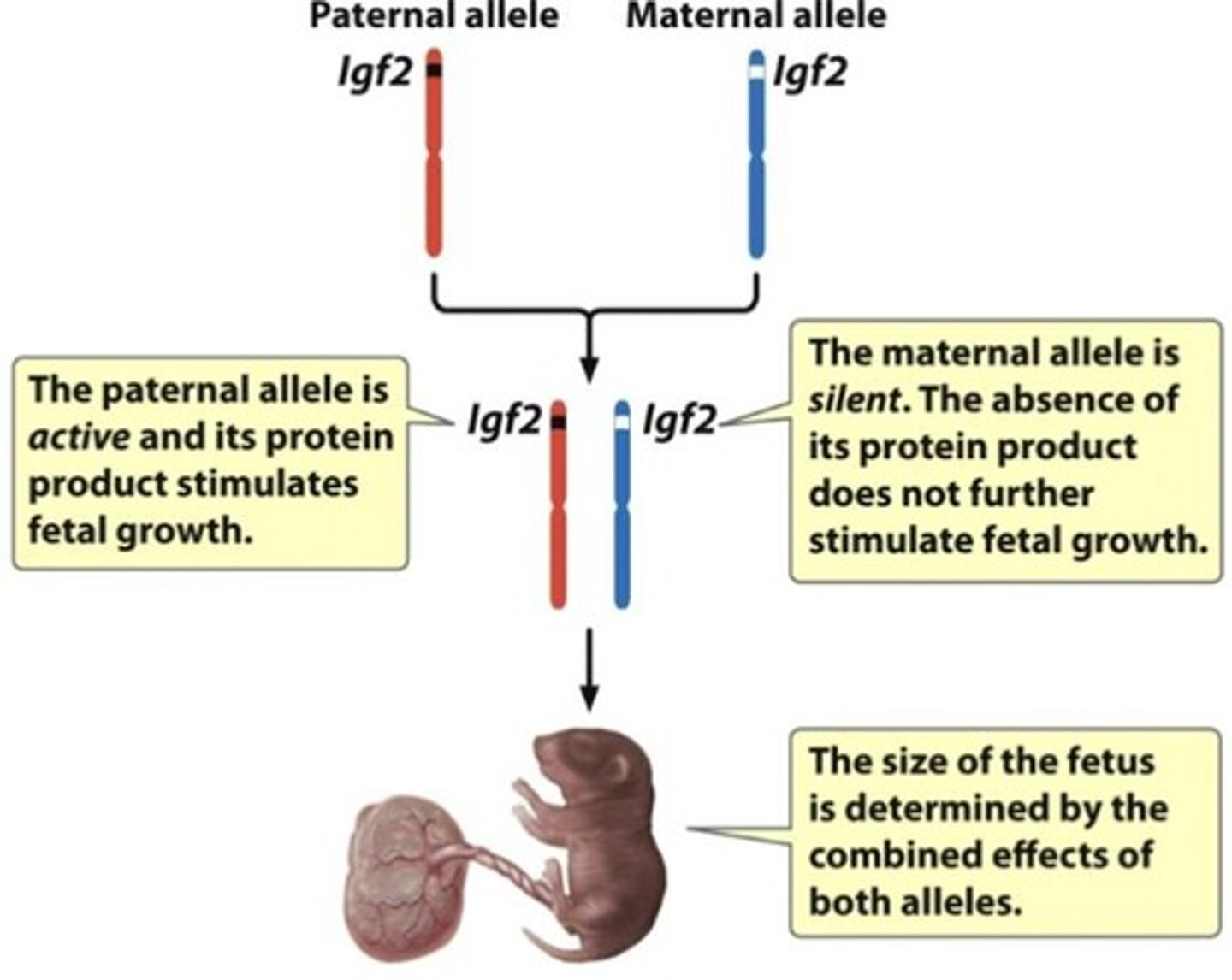
The IGF2 (insulin growth factor) gene, which is involved in growth and located on chromosome 11.
What is the expression pattern of the IGF2 gene from parental alleles?
The paternal allele is active and stimulates growth, while the maternal allele is not active (silenced)
Why does genomic imprinting occur in mammals?
It is related to genetic conflict, where genes that are imprinted affect fetal and early embryonic growth, with paternal alleles promoting more growth.
How does genomic imprinting differ in birds compared to mammals?
In birds, there is no paternal allele, so imprinting does not occur as males do not influence resource allocation within the egg.
What is a temperature-sensitive allele?
An allele whose product is functional only at certain temperatures.
Give an example of an environmental effect on phenotype.
The Himalayan allele in rabbits, which results in a white coat with black extremities at lower temperatures and all white at higher temperatures.
What are continuous characteristics in genetics?
Continuous characteristics show a continuous distribution of phenotypes and are often polygenic, meaning they are influenced by multiple genes.
What is pleiotropy?
Pleiotropy is when one gene affects multiple characteristics.
What are lethal alleles?
Lethal alleles are alleles that can cause the death of an organism when expressed.
What is the principle of Mendel's dihybrid cross?
Alleles of different genes assort independently during gamete formation.
What happens when genes for multiple traits are located on the same chromosome?
It can impact the expected ratios of offspring phenotypes compared to when the genes are on different chromosomes.
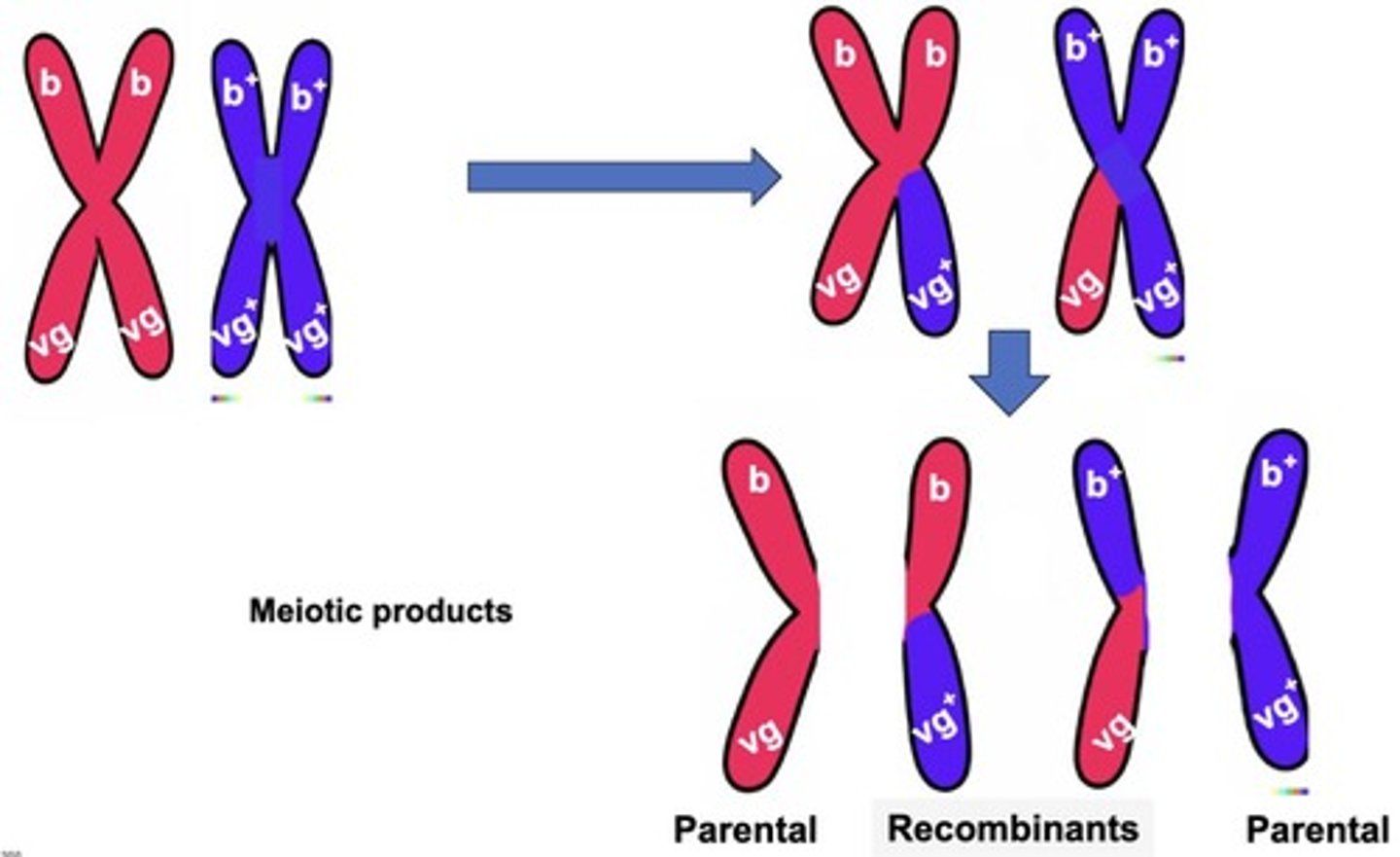
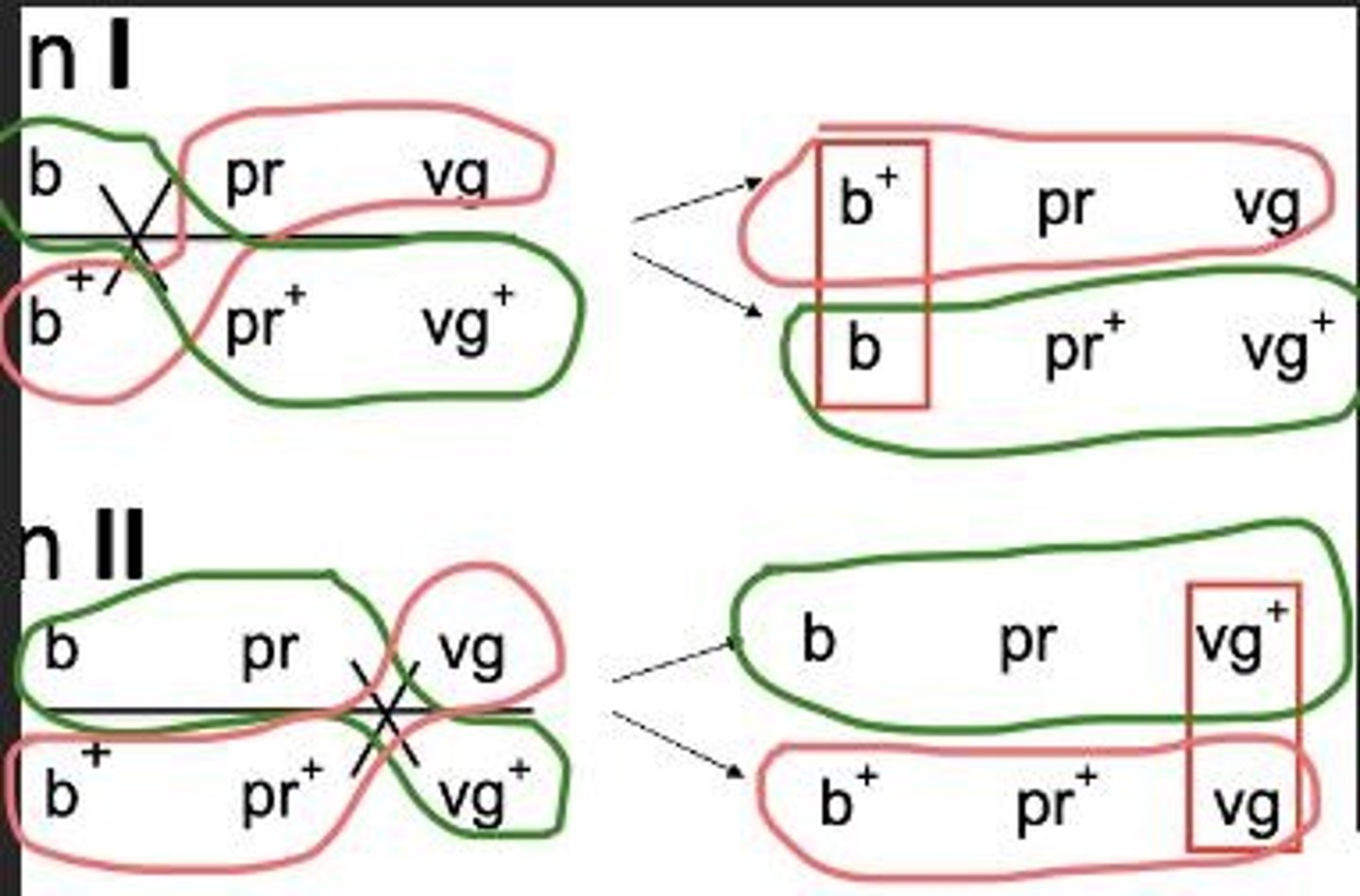
What is the difference between linkage and recombination?
Linkage refers to genes that are inherited together due to their proximity on the same chromosome, while recombination occurs when linked genes are shuffled during meiosis.
What is the impact of environmental influences on gene expression?
Environmental factors can affect how genes are expressed, potentially altering phenotypes.
What is epistasis?
Epistasis is the interaction between genes where the expression of one gene is affected by one or more other genes.
What is the significance of recombinant frequencies in genetics?
Recombinant frequencies can indicate whether genes are linked or assort independently.
How does the maternal imprinting affect progeny phenotype in a reciprocal cross?
In a reciprocal cross, maternal imprinting results in the maternal allele being silent, leading to different phenotypes depending on which parent the allele is inherited from.
What is the role of the paternal allele in the expression of phenotypes in genomic imprinting?
The paternal allele is typically active and can express traits, while the maternal allele may be silent.
What occurs when two genes are on different chromosome pairs?
They assort independently, producing 50% recombinants.
What is the result of pairing gametes from parents in genetics?
It creates F1 offspring, which are heterozygous meiotic diploids.