Organisms and their environment.
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
* plants use light energy from the sun to make their own food, storing energy in their cells
* animals eat the plants, gaining energy from them
* this chemical energy is passed on when animals are eaten by other animals
* eventually energy is returned to the environment through decomposition
Advantages of using a pyramid of biomass rather than a pyramid of numbers to represent a food chain:
pyramid of biomass is pyramid shaped whereas a pyramid of numbers is not always
biomass is an indicator of the energy available and how much food is left
it shows how much energy is passed through per meter square
Takes account of size/ mass of organisms.
a pyramid of numbers shown one large individual the same as one tiny individual
(For understanding: Pyramids of numbers count the number of organisms at each trophic level. One large producer (e.g., an oak tree) still counts as “1,” just like a single small producer (e.g., a blade of grass).
Advantages of using a pyramid of energy rather than pyramids of numbers or biomass to represent a food chain:
it shows how much energy is available
it shows the flow of energy at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
More accurate.
Takes into account seasonal differences.
Why are pyramids of biomass pyramid shaped?
Producers have a larger biomass than primary consumers
So, one producer provides food for many crabs.
Energy is lost at each trophic level.
Secondary consumers needs to eat many primary consumers.
Total primary consumer biomass is greater than total secondary consumer biomass.
explain, in terms of energy loss, why food chains usually have fewer than five trophic levels
Energy is lost due to movement, respiration, excretion and not all parts of the food can be digested. 90% of energy is lost at each level.
Energy transfer in a food chain is inefficient. Energy to decomposer. Not enough energy to support another trophic level.
* animals obtain carbon by consuming plants and other organisms.
* carbon dioxide is released back to the atmosphere when plants and animals respire
* decomposition also releases CO2 back into the atmosphere.
* the combustion of fossil fuels leads to the release of large amounts of carbon dioxide to be released back into the atmosphere.
nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in root nodules convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia.
This is nitrogen fixation.
Nitrogen fixation can also occur through lightning. Atmospheric lightning is converted into nitrates.
Nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites. Then nitrites are converted into nitrates. This is nitrification.
Plants can absorb and use nitrates to make amino acids and proteins.
Animals get their nitrogen by feeding on plants or other animals.
Decomposers such as bacteria and fungi break down the proteins in dead plants or animals into amino acids using proteases.
The amino acids are converted into ammonia by deamination.
Denitrifying bacteria take the nitrates out of the soil and convert them back into N2 gas. This is denitrification. They are found in poorly aerated soil.
community
all of the populations of different species in an ecosystem
Identify and state the factors affecting the rate of population growth for a population of an organism,
to food supply, competition for resources and food, predation and disease
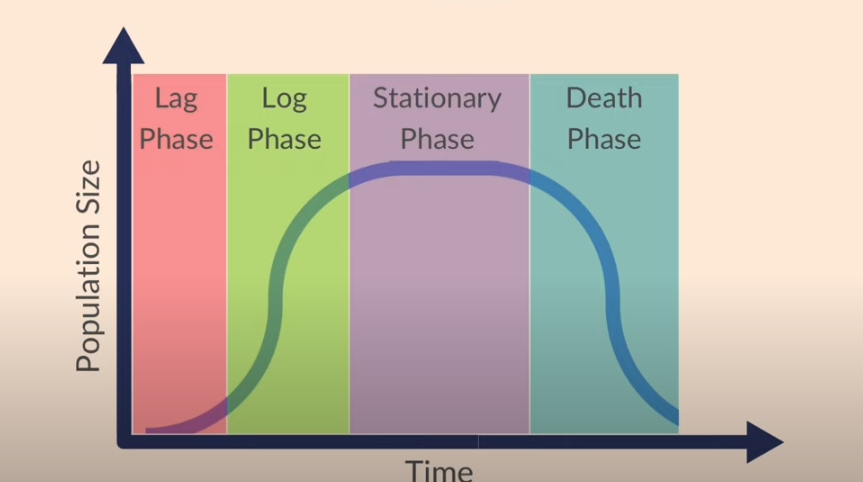
Describe a sigmoid curve
Lag phase - At first, the population grows slowly as it adapts to the environment.
Exponential (or log phase) - Then, it starts growing rapidly resources become more available. Birth rate is fast and death rate is low in this phase. No competition and plenty of resources.
• Stationary phase - The population becomes stable as the birth and death rates reach a balance, resulting in a relatively constant population size. (This may happen due to resources becoming limited and competition increasing)
• Death phase - The population declines as the death rate exceeds the birth rate, leading to a decrease in population size. Population numbers can decrease due to inadequate food supply and other resources or the spread of disease within the population. pH not favourable - for bacteria. Resources, such as food used up.