Human Physiology Final exam
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
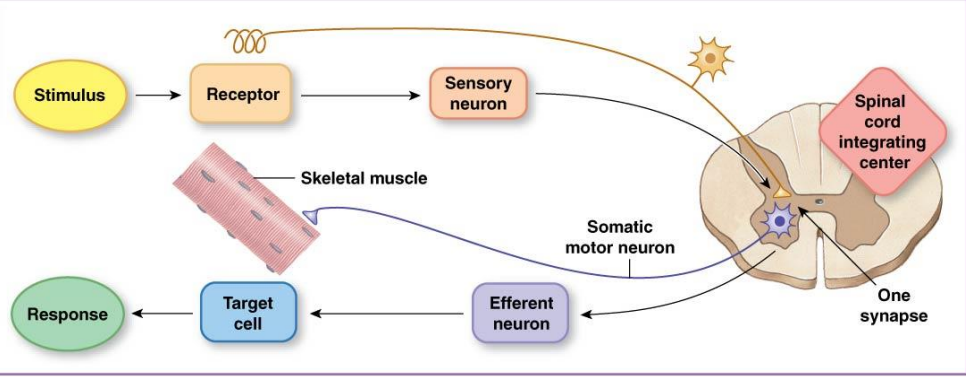
Monosynaptic reflex
has a single synapses between the afferent and efferent neurons
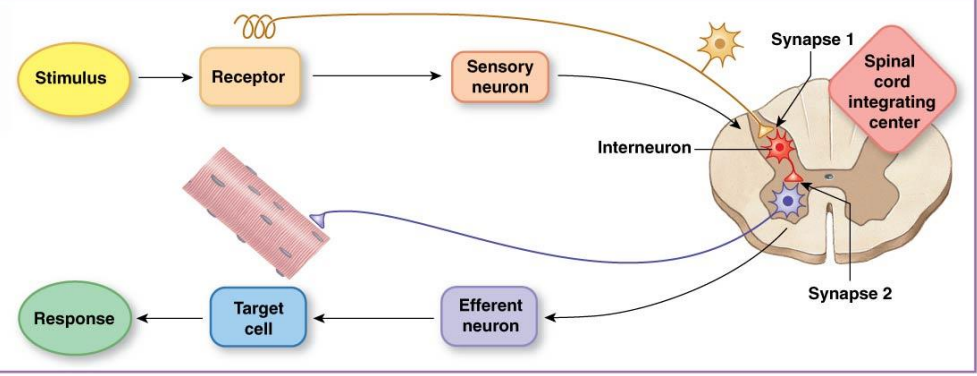
Polysynaptic reflexes
have two or more synapses. This somatic motor reflex has both synapses in the CNS
Proprioceptors
are located in skeletal muscle. joint capsules and ligaments
Somatic motor neurons carry ______ signal.
output
Effectors
are contractile skeletal muscle fibers, or extrafusal muscle fibers
CNS integrates _____ signal.
input
The three types of proprioceptors are
Joint receptors, golgi tendon organ, and muscle spindle
Golgi tendon organ and muscle spindle are found in _____
Skeletal muscle
Joint receptors are found in ______
Capsules and ligaments around joints
______ senses the changes of joints.
Joint recpetors
With joint receptors the sensory information is integrated in _______
the cerebellum
Golgi tendons organs respond to
Muscle tension
Golgi tendon organ is surrounded by ______ fibers and in between the extrafusal muscle fibers and the tendon.
collagen
Myotatic unit
the collection of the pathways controlling a single joint
Reciprocal inhibition
antagonist muscles must relax as the prime mover muscles contract
Reflex
integrated at the spinal cord or brain stem
Rhythmic
integrated in the spinal cord with higher center input required
Voluntary
integrated in cerebral cortex
The two sets of heart valves ensure one-way flow
Atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves
During ventricular contraction, the _______ remain closed to prevent blood flow backward into the atria
AV valves
The _____________ prevent blood that has entered the arteries from flowing back into the ventricles during ventricular relaxation
semilunar valves
Contractile cells
Striated fibers organized into sarcomeres
Autorhythmic cells
Pacemakers, set heartbeat rate and DO NOT have organized sarcomeres
Desmosomes
allow force to be transfered
Gap junctions
provide electrical connection
______ starts with the heart pacemaker cells
Action potential
Action potentials
Voltage-gated L-type ____ channels in the cell membrane open (extracellular calcium contributes 10%)
_______ receptors open in the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
_______ binds to troponin
_________ cycle as in skeletal muscle
Ca2+
Ryanodine
Calcium
Crossbridge
During relaxation, _____ is removed from cytoplasm: back into the SR with Ca2+ ______ and out of the cell through the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger
calcium
ATPase
Force generated is proportional to _____________, which is determined by how much ______ is bound to troponin.
number of active crossbridges, calcium
Sarcomere length affects ________
force of contraction
Myocardial contractile cells
– Depolarization due to ______.
– Repolarization due to ______.
– Long action potential (plateau) due to ______
Na+ entry, K+ exit, and Ca2+ entry
Myocardial autorhythmic cells
– Unstable membrane potential called _______
– Depolarization is due to _______
pacemaker potential, Ca2+ channels opening
Sinoatrial node (SA)
Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm
AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25–40 bpm) can act as _______under some conditions
pacemakers
Internodal pathway from SA to atrioventricular (AV) node
– Routes the direction of electrical signals so the heart contracts from______.
– AV node delay allows the atria to complete their contraction before _______ contraction begins
apex to base
ventricular
__________ transmit electric signals down the atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His) to left and right bundle branches.
Purkinje fibers
______: atrial depolarization
_______: conduction through AV node and AV bundle
_________: ventricular depolarization
______: ventricular repolarization
P wave
P-R segment
QRS complex
T wave
EKG analysis
______: time between two P waves or two Q waves
Heart rate
EKG analysis
_____: regular or irregular ?
Rhythm
EKG analysis
______ analysis: presence and shape
Waves
Cardiac cycle:
a single contraction-relaxation cycle.
Diastole:
cardiac muscle relaxes
Systole:
cardiac muscle contracts
The _______: atrial and ventricular late diastole
– The atria are filling with blood from the veins.
– AV valves open → _________
heart at rest, ventricles fill
_______: completion of ventricular filling
Atrial systole
Ventricular contraction
– Isometric ventricular contraction: both __________ valve are closed.
– Ventricular ejection: ventricles finish contracting, pushing semilunar valves open and blood is ejected into ______.
AV valve and semilunar, arteries
Ventricular diastole
– Ventricular relaxation and pressure _____, arterial blood flows back pushing semilunar valves shut.
– Isovolumic ventricular relaxation: volume of blood in ventricles ______.
– AV valves open when ventricular pressure drops ________.
drops, not changing, below atrial pressure
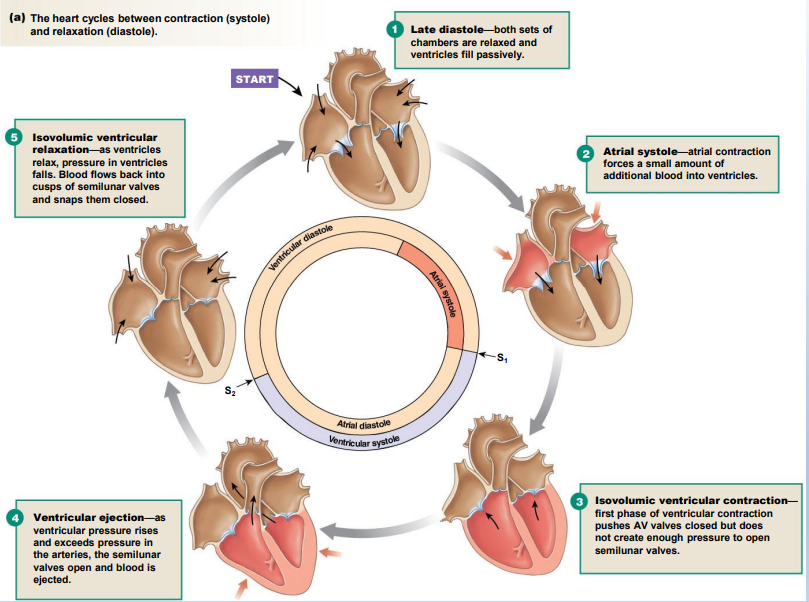
Note the steps and cylces
1
Atrial contraction starts at the end of _____
P wave
_________ signal goes through AV node and AV bundle
P-R segment
___________ starts at the end of Q wave and continues through T wave
Ventricular contraction
First heart sound
– Vibrations following the closure of the ______
– “Lub”
AV valves
Second heart sound
– Vibrations created by closing of _______
– “Dup”
semilunar valve
Auscultation
is listening to the heart through the chest wall through a stethoscope
End diastolic volume (EDV)
– The ventricle volume at the end of ____
diastole
End systolic volume (ESV)
– The ventricle volume at the end of
systole
Stroke volume
– Amount of blood pumped by one _____ during a contraction
– Volume of blood ____ contraction-volume of blood _____ contraction = stroke volume
– EDV – ESV = _____ volume
– Average = ___ mL
ventricle
before, after
stroke
70
Cardiac output (CO)
– Volume of blood pumped by one _____ in a given period of time
– Cardiac output = heart rate * stroke volume
– Average = __ L/min
• CO is a measurement of ________.
ventricle
5
cardiac performance
The parasympathetic neurotransmitter __________ slows heart rate
acetylcholine (ACh)
The sympathetic neurotransmitter ____________________ increases heart rate
norepinephrine and epinephrine
Tonic control of heart rate is dominated by the _______ branch.
parasympathetic
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and digitalis have _____ inotropic effects
positive
Chemicals with _____ inotropic effects decrease contractility
negative
Afterload
is the resistance against which the heart must work to eject blood during systole
Ejection fraction (EF) is the percentage of EDV ejected with one contraction,
i.e., (Stroke volume/EDV)x 100%