Bacteriology 1: skin pathogens
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
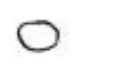
What type of bacteria does this image show?
single cocci
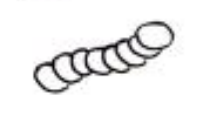
What type of bacteria does this image show?
cocci chains
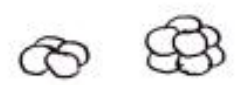
What type of bacteria does this image show?
4’s and 8’s cocci

What type of bacteria does this imag eshow?
pairs of cocci (diplococci)

What type of bacteria does this image show?
cocci clusters
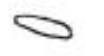
What type of bacteria does this image show?
single rods
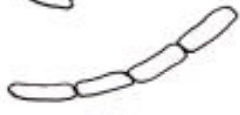
What type of bacteria does this image show?
rod chains

What type of bacteria does this image show?
curved rods

What type of bacteria does this image show?
club-shaped rods

What type of bacteria does this image show?
filamentous rods

What type of bacteria does this image show?
rod pairs
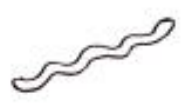
What type of bacteria does this image show?
helical rods
What kind of DNA do bacteria have?
nucleoid
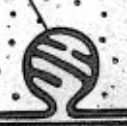
What is this part of bacteria?
mesosome
What does a gram positive cell wall contain?
simple phospholipid bilayer
peptidoglycan with teichoic acids

What does this image show?
gram positive cell wall
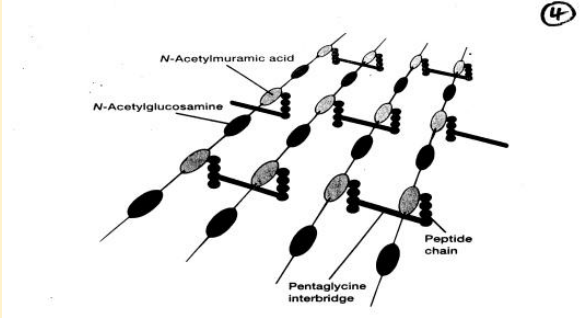
What does this image show?
peptidoglycan
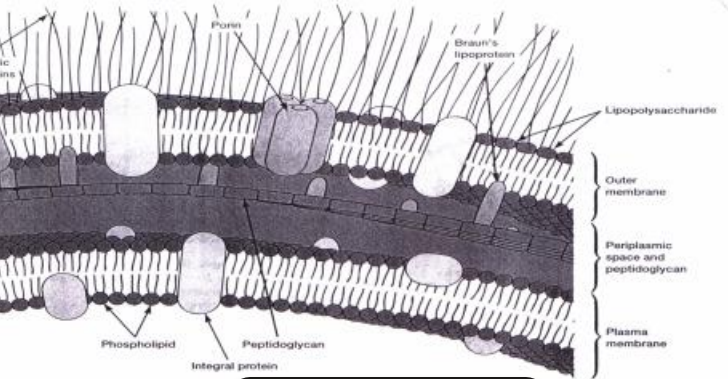
What does this image show?
gram negative cell wall
What does the gram negative cell wall contain?
2 layers of polysaccharides
peptidoglycan holds together & gives shape
lipopolysaccharides
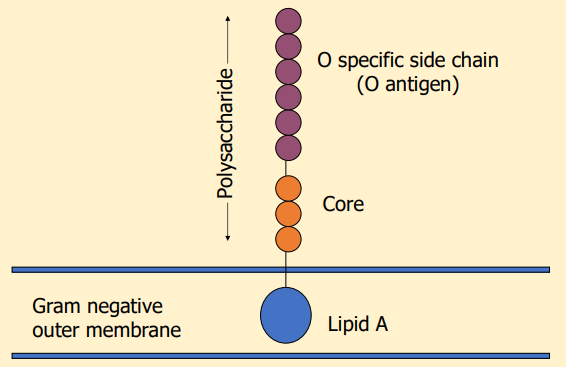
What does this image show?
lipopolysaccharide structure
Do gram positive or gram negative bacteria change colour in the heated fixed smear/crystal violet/iodine/alcohol/dilute fuschin test?
gram negative
In the test for bacteria, what colours to gram negative bacteria change to with alcohol?
white
In the test for bacteria, what colours to gram negative bacteria change to with dilute fuchsin?
pink
What internal structures does this image show?
glycocalyx
What is the glycocalyx?
capsules
slime layers
Name 4 gram positive cocci
staphylococcus
streptococcus
enterococcus
micrococcus
What do staphylococcus cause?
localised lesions (often peripheral - skin infections, mastitis)
What does streptococcus cause?
generalised lesions (deeper - strangles, mastitis, endocarditis)
What does enterococcus cause?
rarely pathogenic (found in the intestine, can cause wound infections)
Which type of gram positive cocci are very small?
micrococcus
Are micrococcus pathogenic or non-pathogenic?
non-pathogenic
What are the cellular arrangements of staphylococci?
irregular planes of division & sticky
What are the cellular arrangements of micrococci?
more regular planes of division & sticky
What are the cellular arrangements of streptococci and enterococci?
1 plane of division & some sticky
What are the habitats of staphylococcus/micrococcus?
worldwide
environment
animal/human skin
animal/human mucous membranes
Which mucous membranes are staphylococci found in?
upper respiratory & digestive tracts
Which mucous membranes are micrococcus found in?
mammary gland
Which staphylococcal species are of importance?
staph. aureus
staph. pseudintermedius (intermedius)
Which species is staph. pseudintermedius (intermedius) found in?
JUST DOGS
What do staph. aureus and staph. pseudintermedius (intermedius) cause?
mastitis
skin infections
soft tissue infections
surgical site infections
What are the rare opportunistic staphylococcal species?
staph. epidermidis
staph. saprophyticus

What does this image show?
human strain of staph. aureus

What does this image show?
dog strain of staph. aureus
What colour is staph. aureus?
golden yellow
What does this image show?
haemolytic staph. aureus
What does Staph aureus alpha-haemolysin cause?
disrupts leucocytes
necrosis/constriction of smooth muscle in blood vessel walls
What laboratory tests for Staph aureus alpha-haemolysin can you do?
complete red blood cell lysis (narrow, clear zone)
How does Staph aureus alpha-haemolysin affect rabbits?
necrotic (ears)
lethal
What are characteristics of Staph aureus beta-haemolysin?
phospholipase C
potent
unique to animal strains
role in pathogenesis unknown
partial RBC lysis
What are general types of disease associated with staphylococci?
pyogenic (suppurative) skin infections
systemic infections
What is seen with pyogenic (suppurative) skin infections associated with staphylococci?
dermatitis
pyoderma
abscesses
What is seen with systemic infections associated with staphylococci?
septicaemia & deposition/localised damage
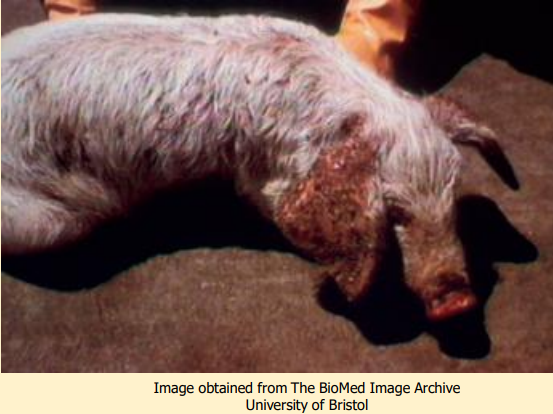
What does this image show?
greasy pig disease (staph. hyicus)
What does staph. hyicus cause in pigs?
ear necrosis
How can you treat staphylococcal infections?
wound drainage and cleaning (remove body of infection)
Why is it challenging to treat staphylococcal infections?
resistance genes common/widespread (e.g. MRSA)
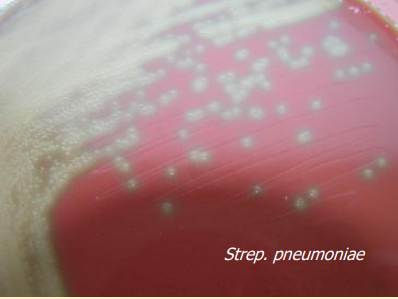
What does this image show?
alpha-haemolysin & greening of strep. pneumoniae
What are the habitats of lactococci?
milk/products
What is the habitat of enterococci?
gut
What are the habitats of streptococci?
skin/mucosal membranes
upper respiratory tract
upper GI tract
lower urogenital tract
What are the main disease patterns of streptococci?
upper respiratory tract infections & lymphadenitis
neonatal septicaemic infections
secondary pneumonia
urogenital tract infections
mastitis
What does strep zooepidemicus cause in pigs?
suppurative arthritis in piglets
How does strep zooepidemicus cause suppurative arthritis in piglets?
sow flora → umbilical cord → septicaemia → chronic lameness or death
What does strep porcinus cause in pigs?
strangles-like disease in piglets
What are the characteristics of strep porcinus?
highly contagious
seen mainly in young animals
commensal organism
What streptococci cause mastitis in cattle?
strep uberis
strep dysgalactiae
strep agalactiae
strep zooepidemicus
Features of strep uberis
commensal
most common
acute
mild
economically significant
Features of strep dysgalactiae
commensal
less common
acute
severe
often in summer with A.pyogenes
Features of strep agalactiae
obligate pathogen
less common
chronic
economically significant
zoonotic
Features of strep zooepidemicus
least common
from horses
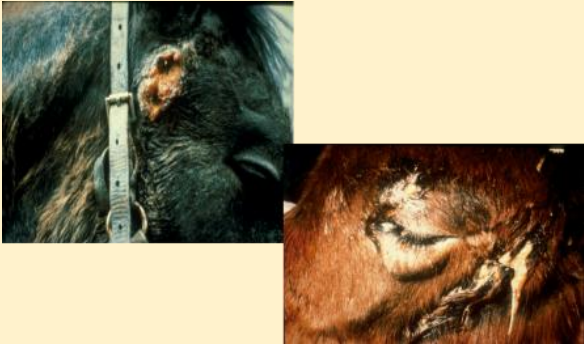
What do these images show?
streptococcus equi (strangles)
How can you control streptococcal infections?
antibiotics
disinfectants
vaccines
Is resistance more of a problem in streptococcal or staphylococcal infections?
staphylococcal
Why are antibiotics used in the control of streptococcal infections?
help prevent local infection becoming systemic
Where should you use disinfectants for control of streptococcal infections?
milking machinery
stables
troughs
Why are vaccines such an important part of controlling streptococcal infections?
for prevention of wound infections in the first place