redox and electrochemistry
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
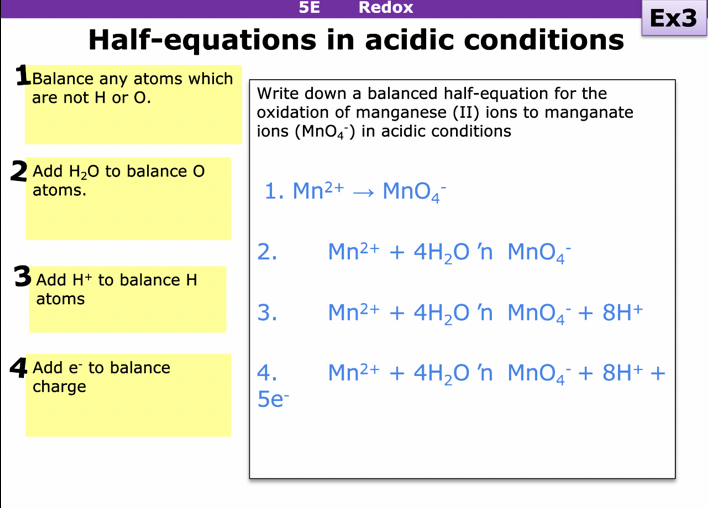
How do you write half equations in acidic conditions eg: oxidation of manganese to manganate ions
FEWH = Formula, Electrons, Water, Hydrogen
First balance any Atoms that are not H or O
Add e- to balance the charge (work out oxidation number of element at start and element at end)
Add H2O to balance O
Add H+ to balance H+ ions
What does oxidation mean
Increase in oxidation number
Gaining of oxygen
Loss of electrons
What is reduction
Gain of electrons
Decrease in oxidation number
Loss of oxygen
When determining oxidation states
What is oxidation state of a molecule?
Oxidation state of a compound?
Oxidation state of an ion
Molecule = 0
Compound depends on charge eg: NaCl Na= +1 Cl= -1
For an ion eg: SO4 2- Oxygen = -8 S= +6 = -2
Oxidation state of oxygen
Oxidation state of hydrogen
Oxidation state of fluorine
Oxygen = -2 except in H2O2 (-1) F2O (+2)
Hydrogen = +1 except NaH (-1)
F = -1
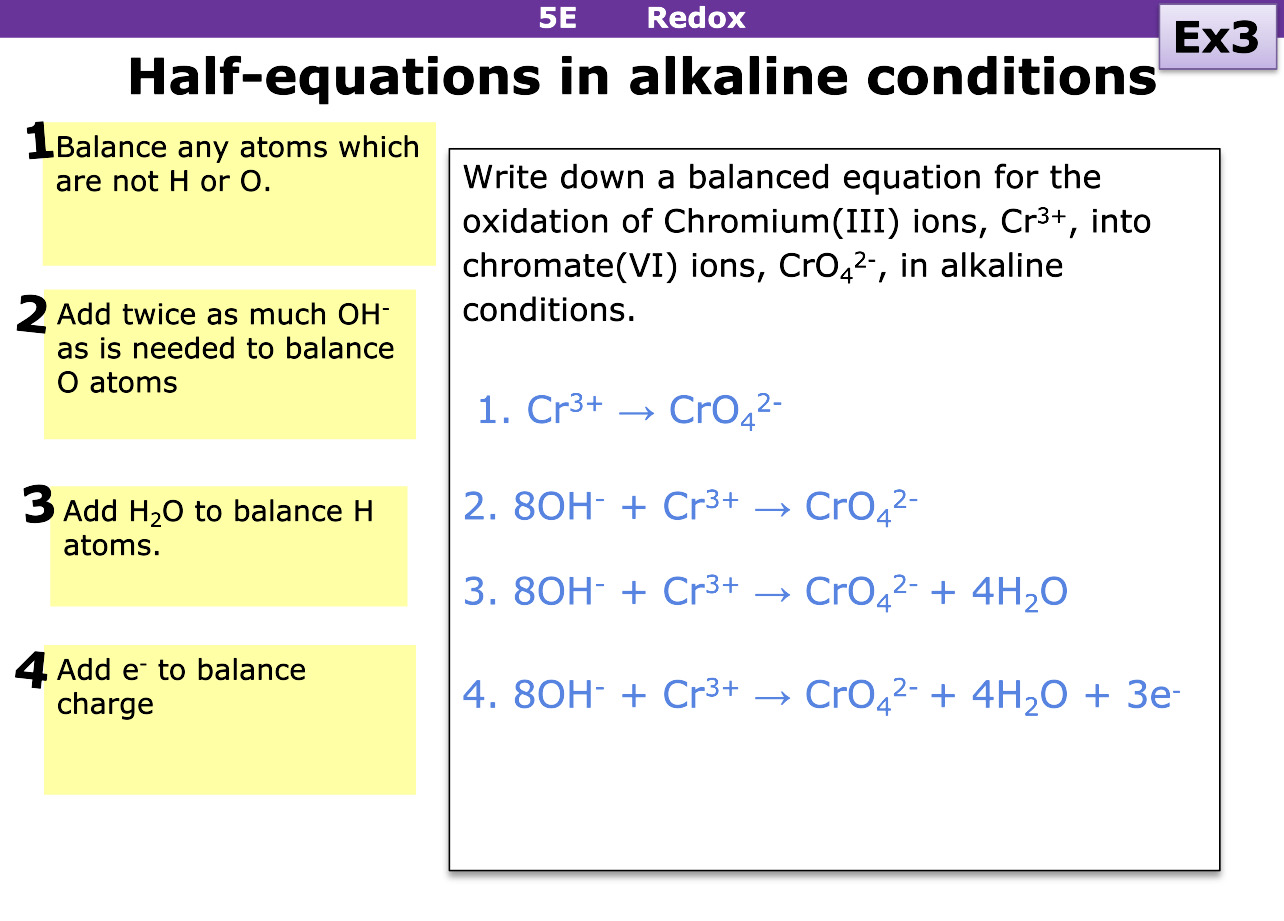
How do you write half questions for alkaline conditions
Balance atoms that are not H or O first
Add twice as much OH needed to balance O atoms
Add H2O to balance H atoms
Add e- to balance charge ( to work it out, work out oxidation number of element at start and end)
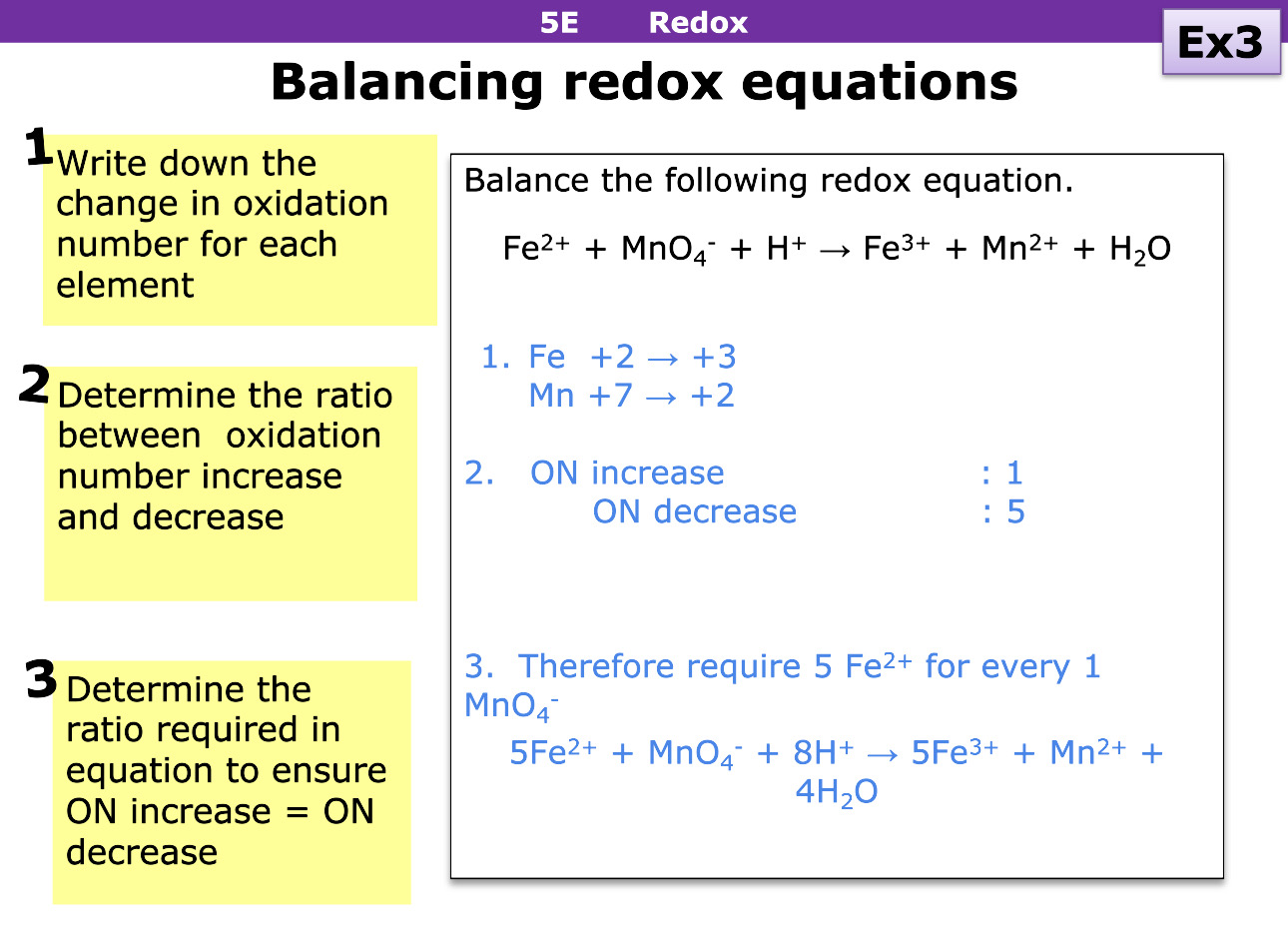
How do you balance redox equations
Write down the change of each oxidation number
Determine the ratio between oxidation number increase and decrease
Determine the ratio required for the elements
How to combine half equations
Write out two half equations
Multiply equations so number of electrons are same in both
Add 2 equations left side on left side and right side on right side and cancel electrons
when doing half equations are big numbers involved
yes
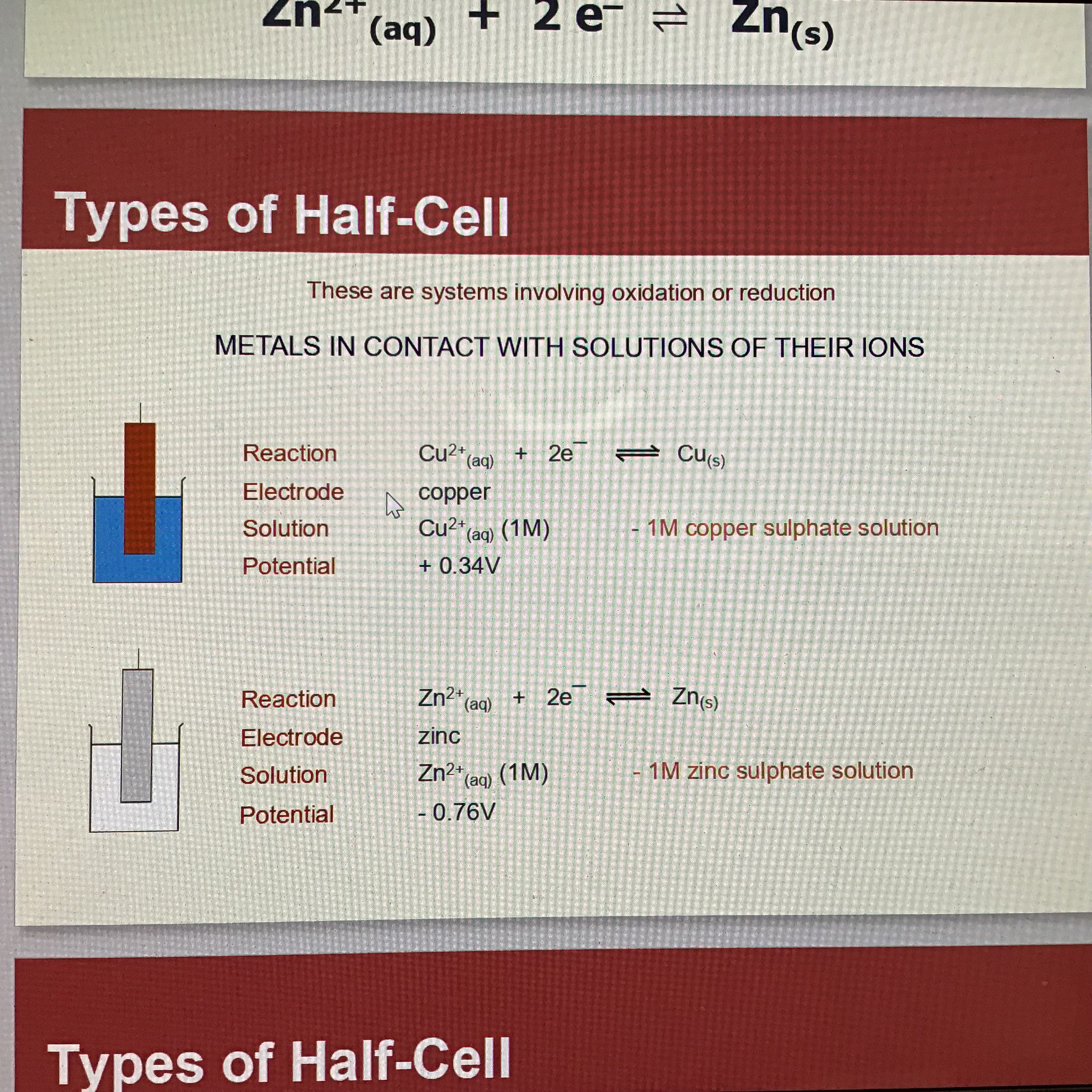
What is a half - cell/electrode
A metal dipping into a solution of its ions
1st of type of half cell
Metal in contact with solutions of its ions
Eg: Zn(s) electrode and Zn2+ (aq)
With the metal as the electrode
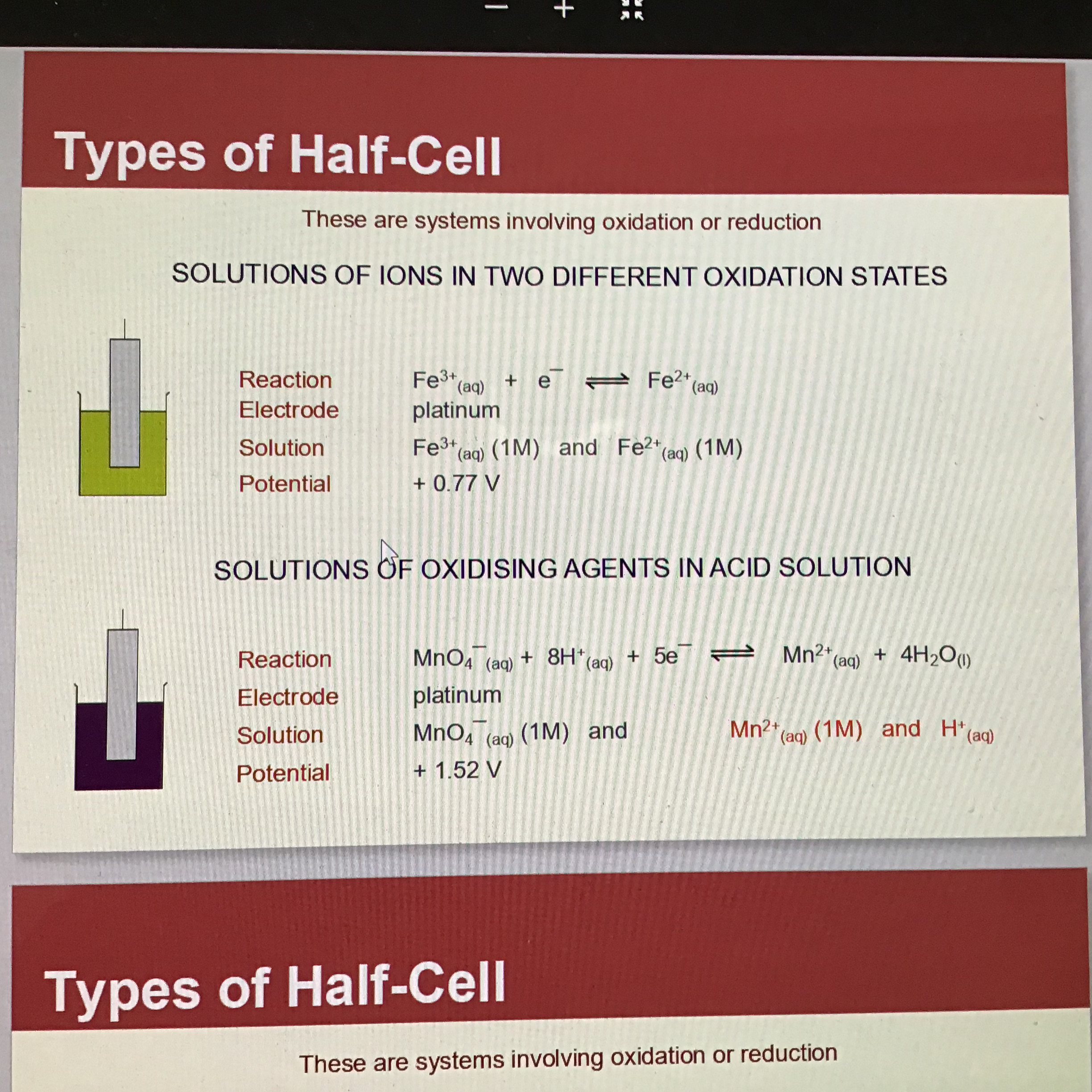
What is the second type of half cell
Solutions of ions in 2 different oxidation states
Eg: Fe3+ (aq) and Fe2+ (aq)
Electrode = platinum
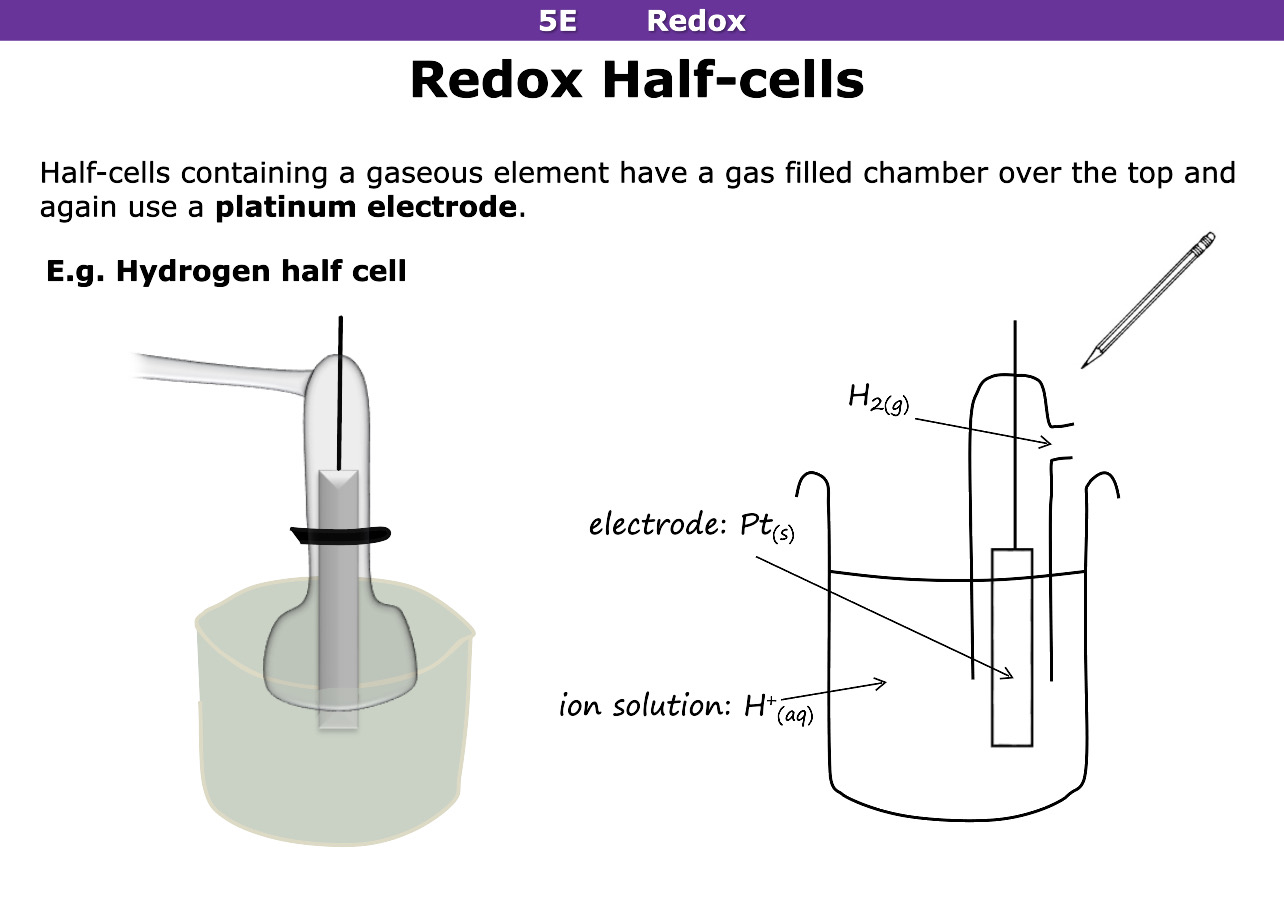
What is the third type of half cell
Gases in contact with solutions of their ions
Eg: 2H+ (aq) —> H2(g)
Electrode = platinum

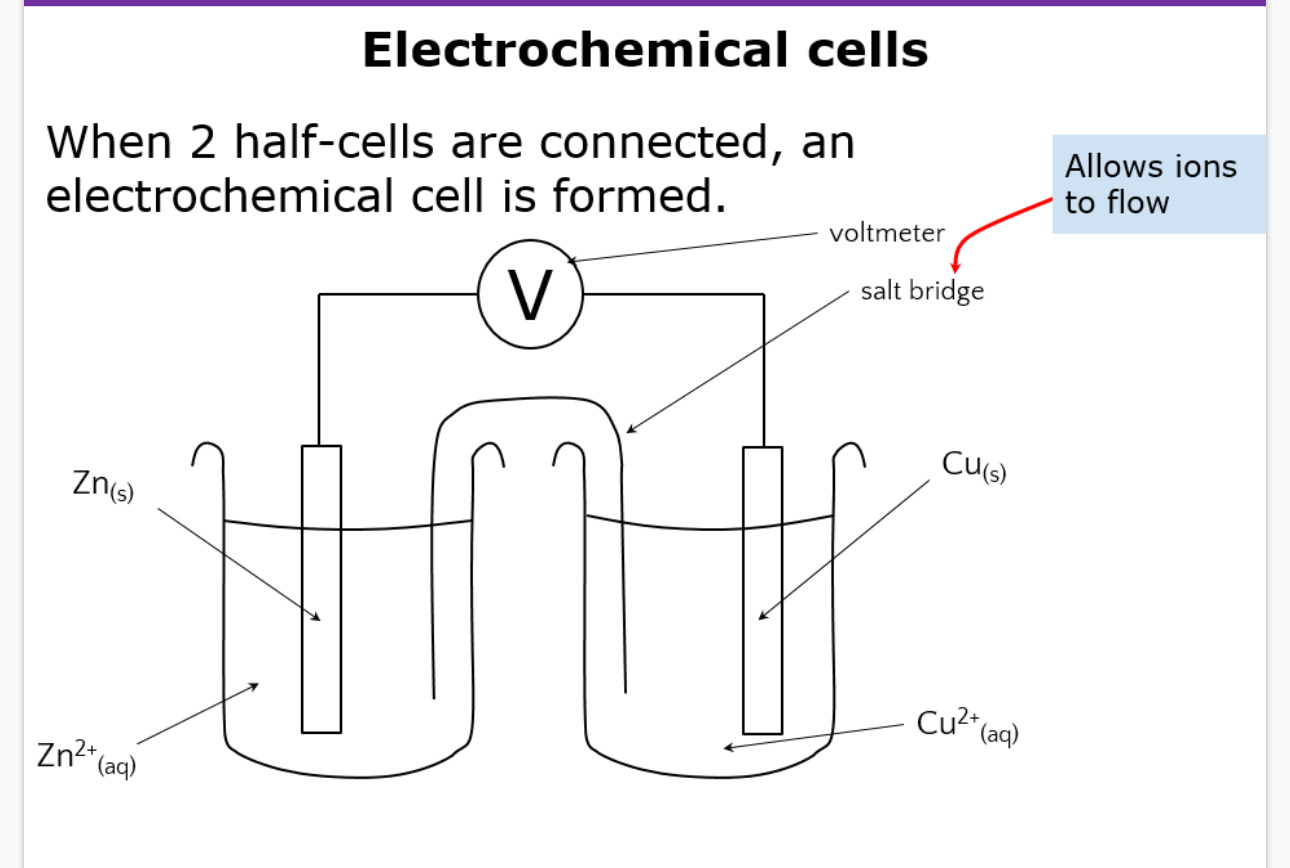
How do you draw an electrochemical cell
What are the conditions
298k
100kpa (1atm)
1moldm^-3
Half cells that have a gaseous element have what over the top of platinum electrode
Gas filled chamber
What is standard electrode potential under standard conditions
0.00v
why is electrode potential 0
universal reference point for electrode potential measurements
why is platinum acting as an electrode
it is inert and doesnt react with solutions
why are the half equations written as equilibrium reactions
oxidation and reduction is happening simultaneously
rate of oxidation and reduction are equal
until combined with another half cell there is no driving force to alter the equilibrium
If a half cell is oxidised (loses electrons) when connected to standard hydrogen half cell what happens to electrode potential
Becomes negative
If a half cell is reduced (gains electrons) when connected to standard hydrogen half cell what happens to electrode potential
Becomes positive
In electrode potential the half equation with the more negative electrode potential will undergo what reaction
In electrode potential the half equation with the more positive electrode potential will undergo what reaction
Oxidation
Reduction
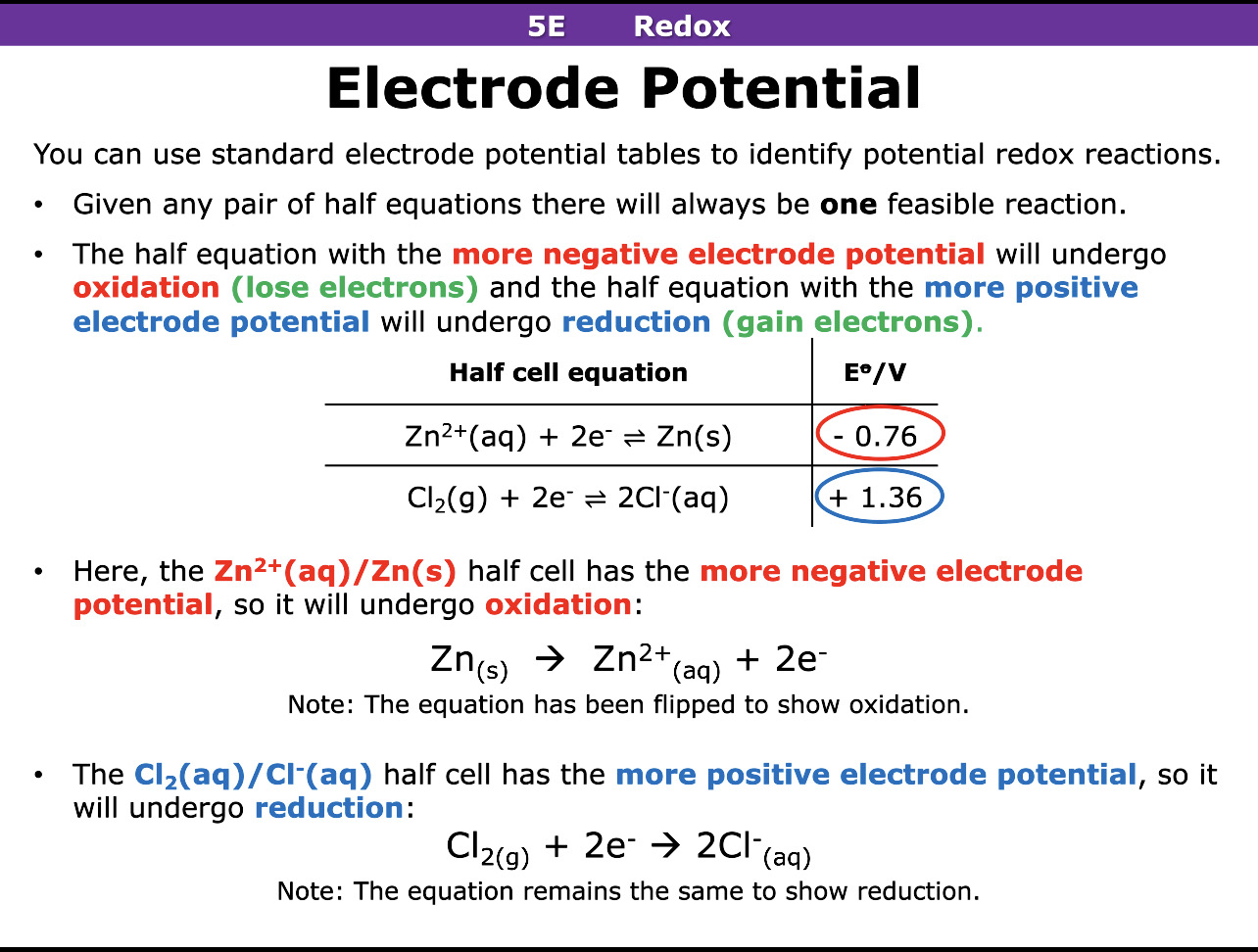
How do you calculate E cell
Value of reduction - value of oxidation
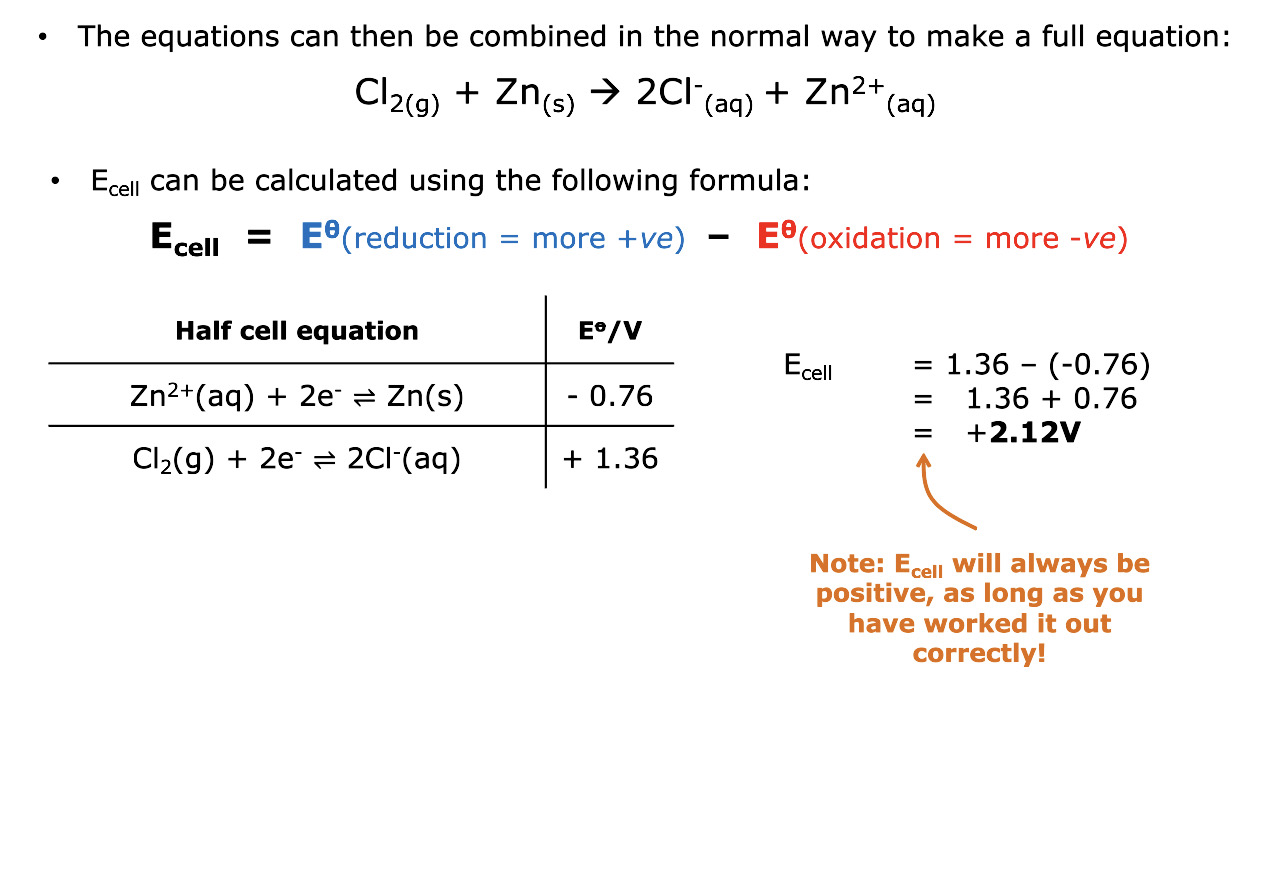
the value of E cell is always what
Positive
The reaction with the more negative value will go where
Right to left
The reaction with the more positive value will go where
Left to right
Is the cathode the positive or negative terminal and what reaction occurs there
positive, reduction
Is the anode the positive or negative terminal and what reaction occurs there
negative, oxidation
How do you write redox half equations
Eg: 2 reactions
Zn2+ + 2e- —> Zn
Cu 2+ +2e- —> Cu
Equation = Cu2+ + Zn —> Cu + Zn2+
Cu2+ goes to Cu so is reduced as it gains electrons
Zn goes to Zn2+ so is oxidised as it loses electrons
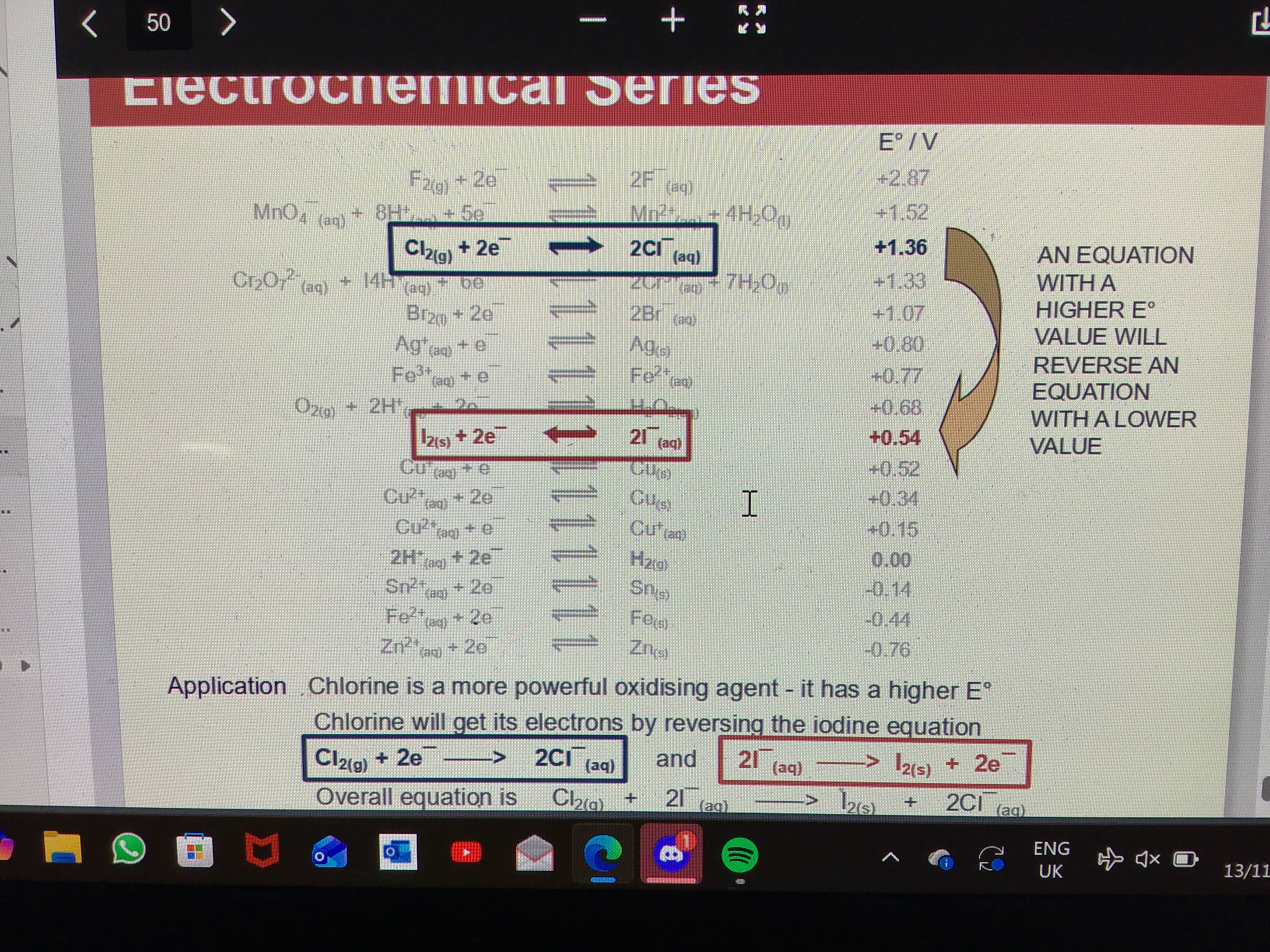
When writing half equations in electrochemical series what does the equation with the higher E value do the the equation with the lower E value
It reverses its reaction
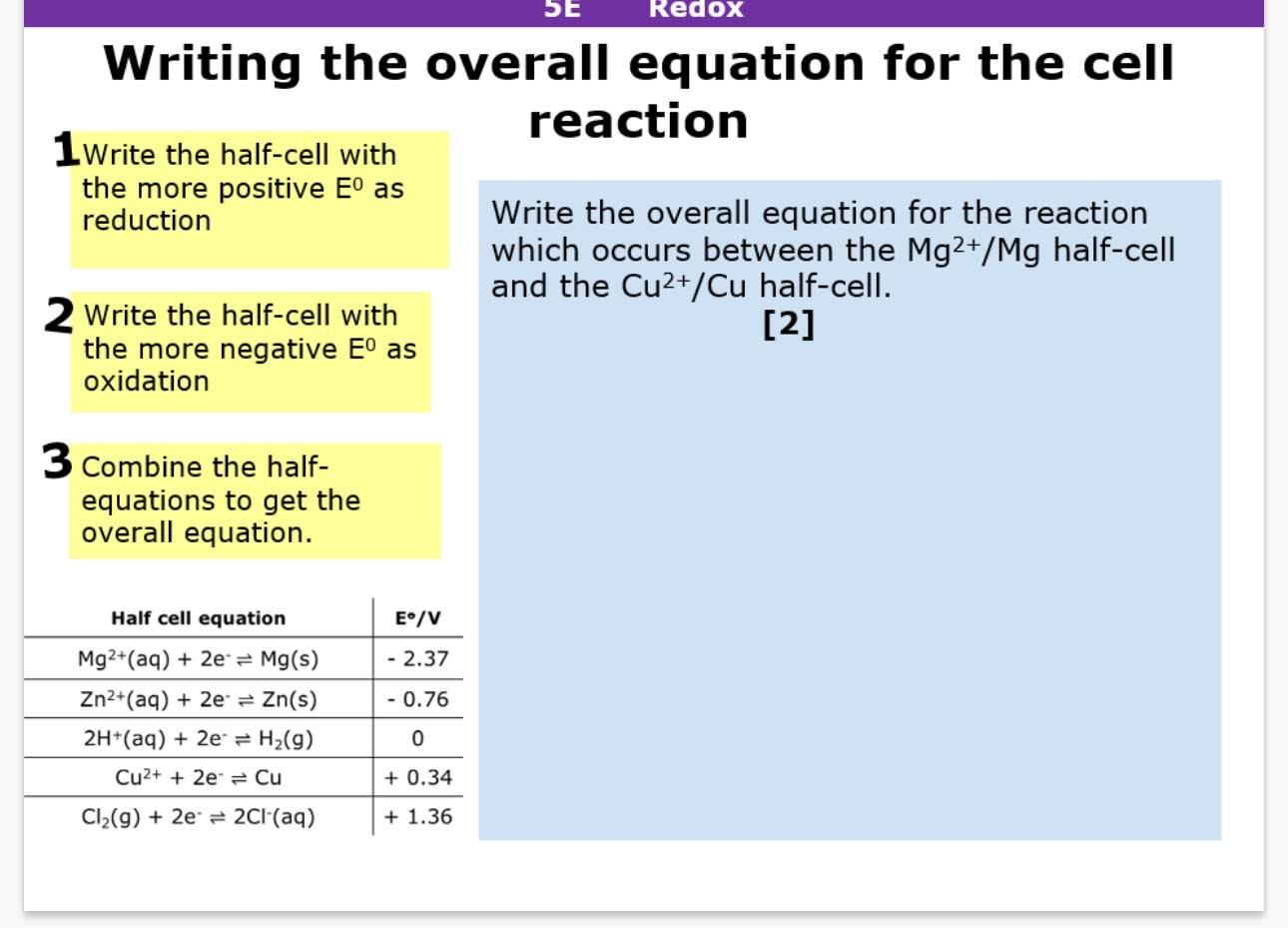
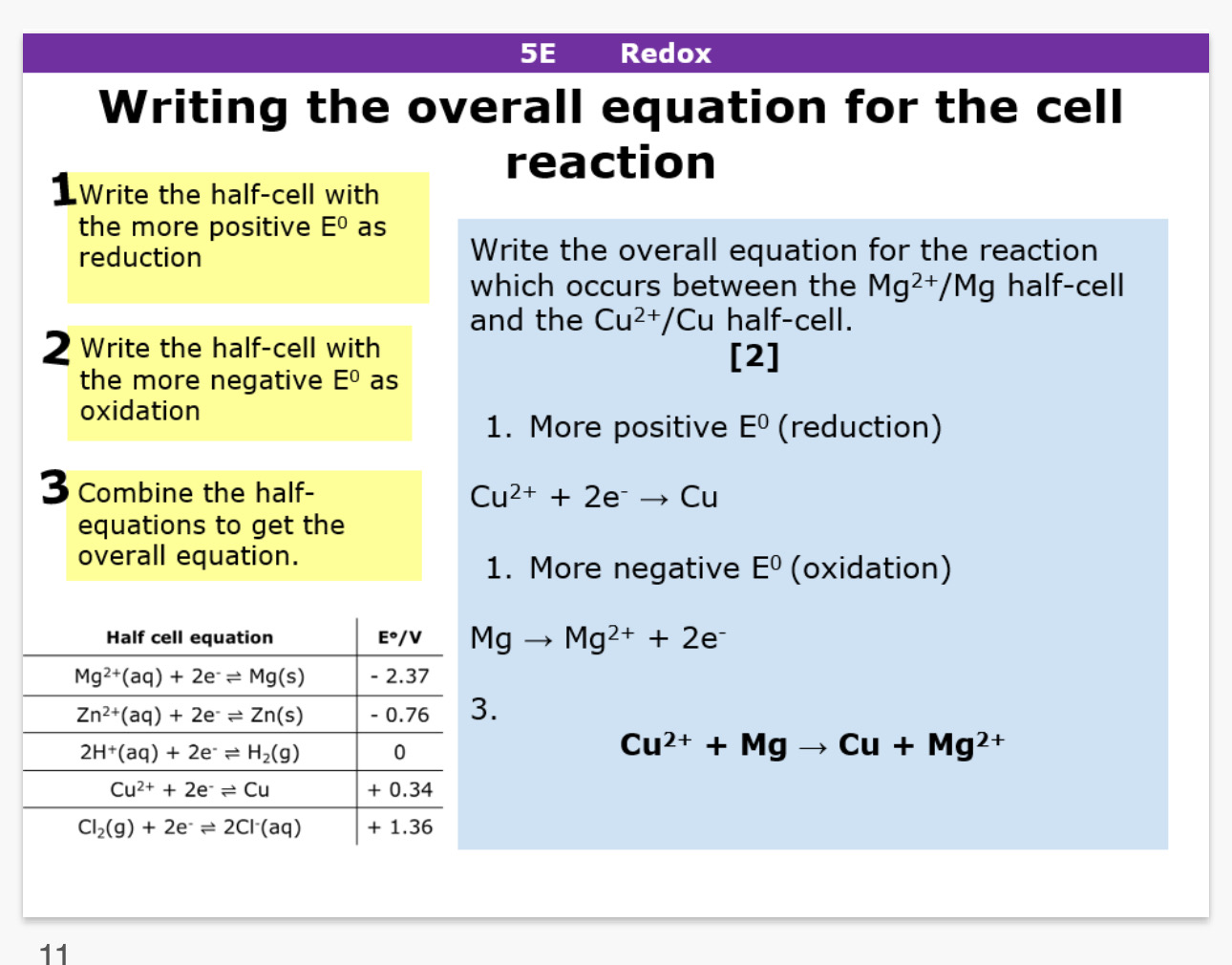
How to write the overall equation for a cell reaction
Write the half cell with the more positive E value as reduction
Write the half cell with the more negative E value as oxidation
Combine the half equations to get an overall equation
In redox half equations how do you know if a reaction is feasible
If the oxidising agent (thing being reduced) is more positive than the reducing agent (thing being oxidised)
A feasible reaction will have the E cell greater than E > 0
The E cell value that is more positive reverses reaction of less positive one
If it doesn’t match the equation not feasible
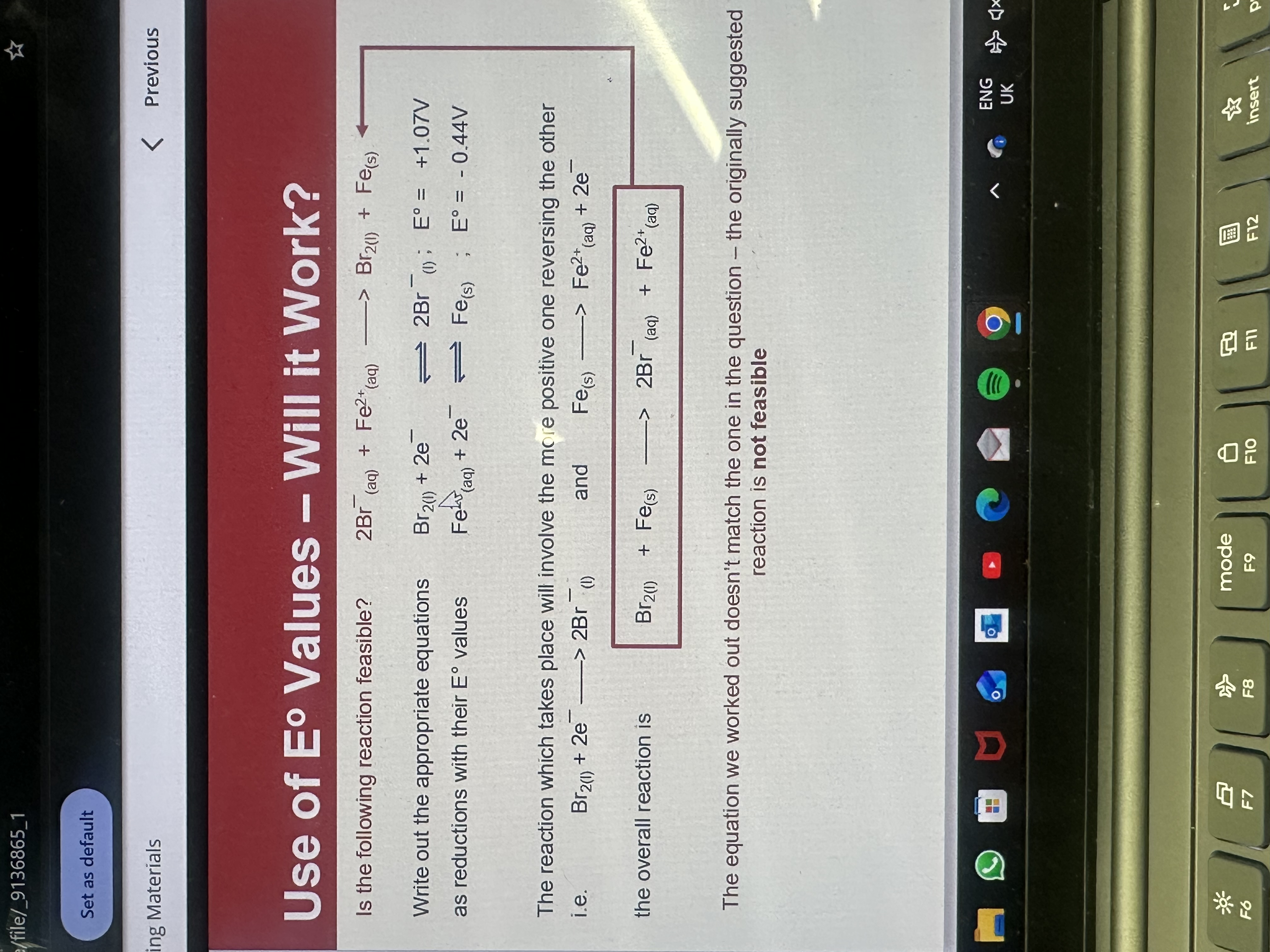
Feasibility question example
Since Br equation is more positive the Fe equation reverses so the reaction is not feasible
What are the observations of oxidation with half cells
Metal dissolves
Made into ions
Changes colour( in some cases)
What are the observations of reduction in half cells
Metal is deposited on electrode
Decrease in metal ions
Colour fades or disappears( in some cases)