SHS 300 - Phonatory System (Larynx)
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
biological functions of the larynx
prevents air from escaping the lungs when valving is needed (valving = closing the vocal folds)
prevents foreign substances from entering the lungs
expels foreign substances that threaten the trachea (through coughing)
non-biological functions of the larynx
sound generation
cartilages that are important for voice production
thyroid, cricoid, and arytenoid
cartilage that is crucial for airway protection during swallowing
epiglottis
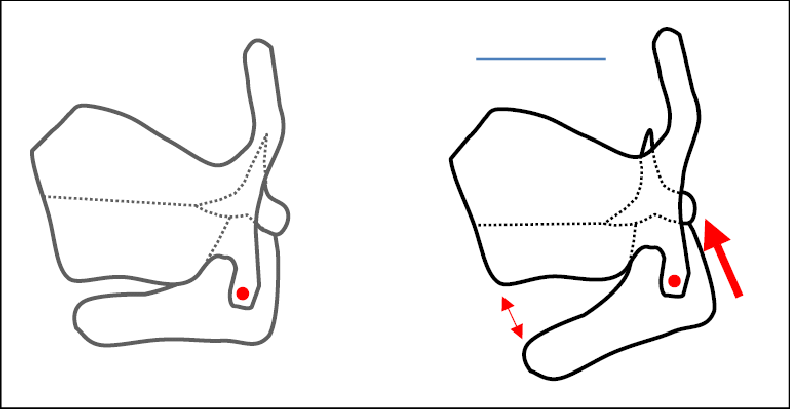
movement of the cricothyroid joints - how does this change the vocal folds?
movement: rotation
thyroid cartilage moves forward and downward
cricoid cartilage moves backward and upward
result: elongates the vocal folds which increases the pitch of the voice
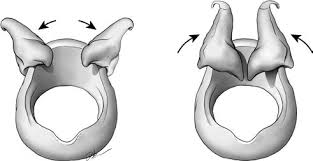
movement of the cricoarytenoid joints - how does this change the vocal folds?
movement: rocking
arytenoids move upward and outward (ABDUCTION - opening - of vocal folds)
arytenoids move downward and inward (ADDUCTION - closing - of vocal folds)
result: abduction or adduction of the vocal folds
thyroid cartilage
cricoid cartilage
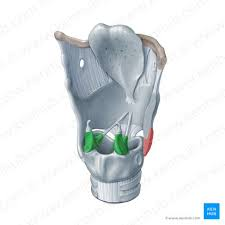
arytenoid cartilage

epiglottis cartilage
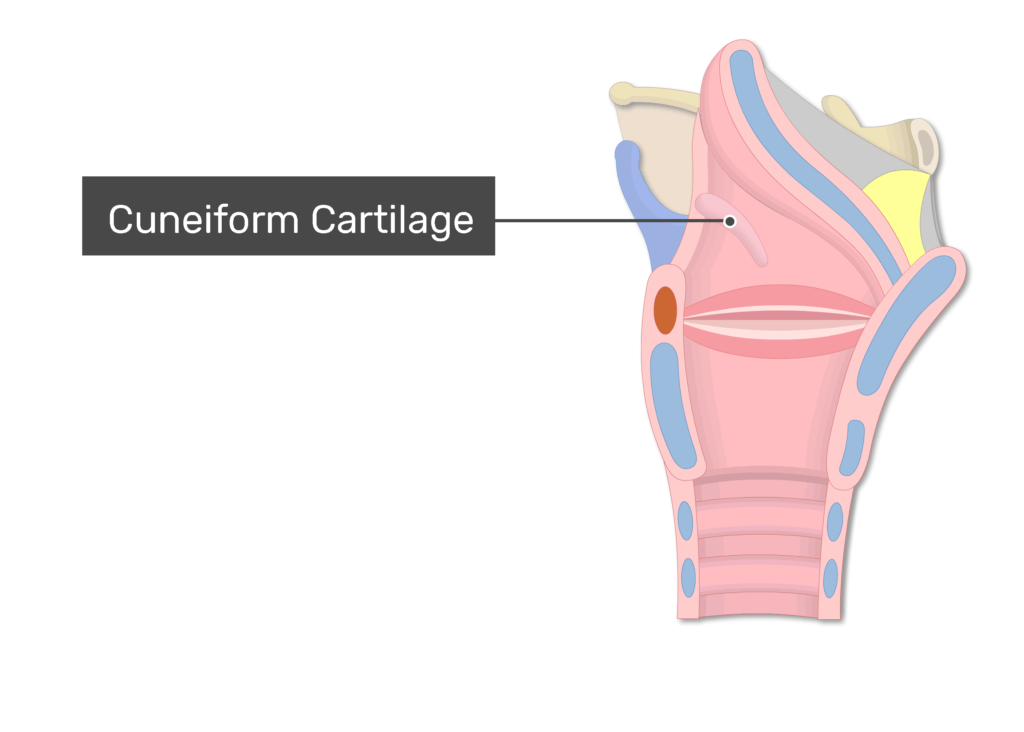
cuneiform cartilage
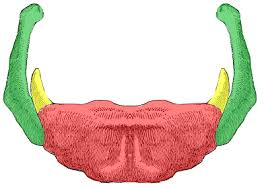
label red
corpus/body of hyoid bone
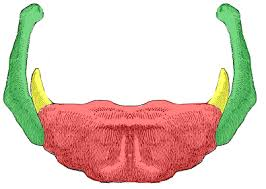
label green
greater horn of hyoid bone
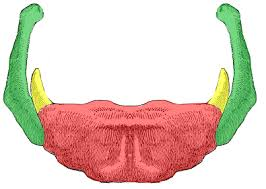
label yellow
lesser horn of hyoid bone
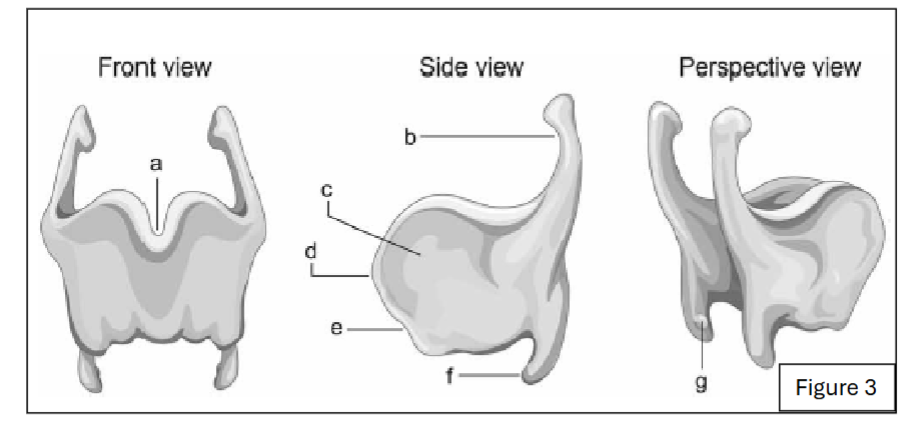
label c
thyroid lamina
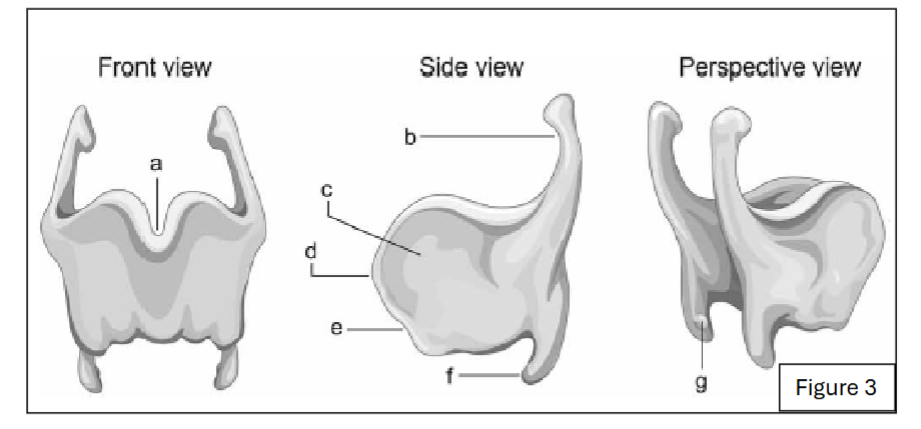
label e
angle of thyroid
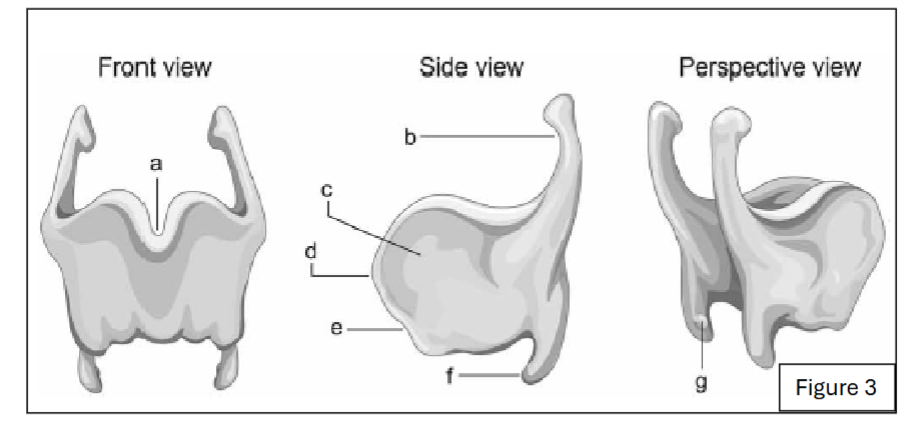
label a
thyroid notch
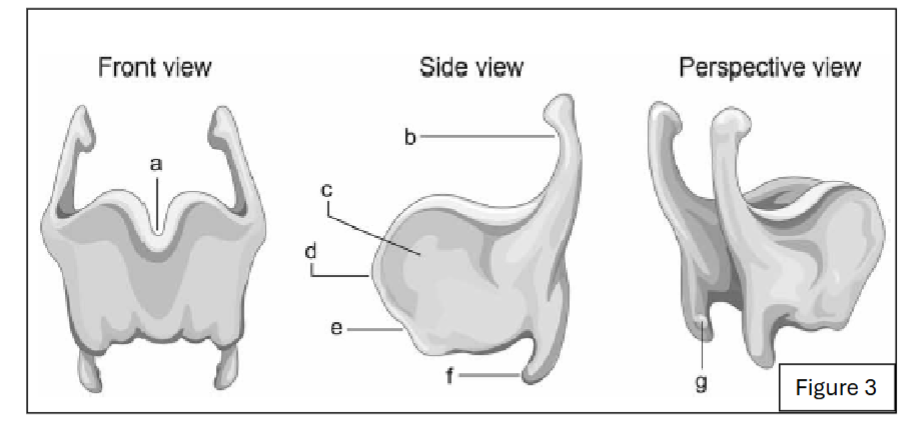
label d
laryngeal prominence
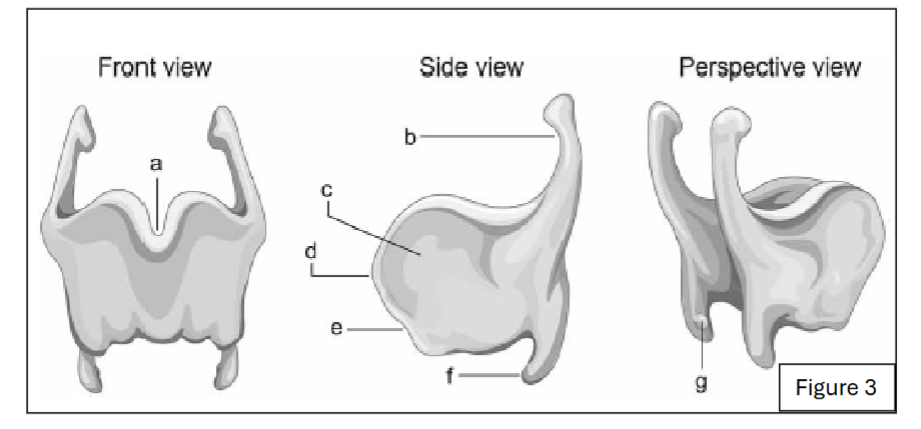
label b
superior horn of thyroid cartilage
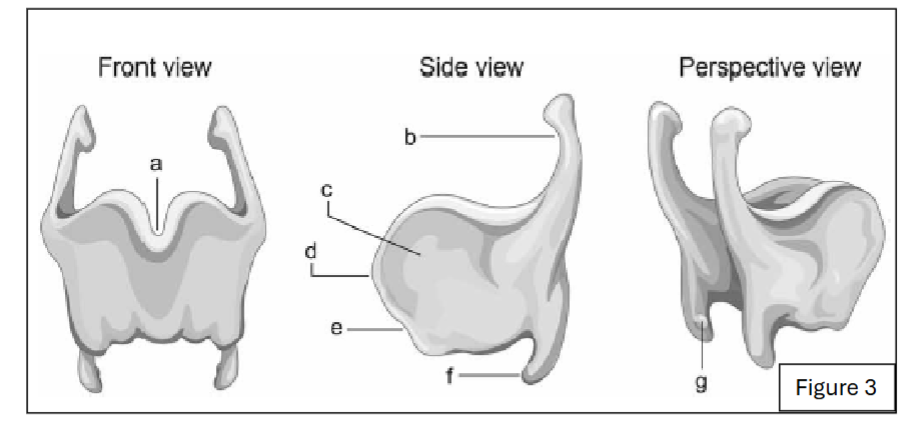
label f
inferior horn of thyroid cartilage
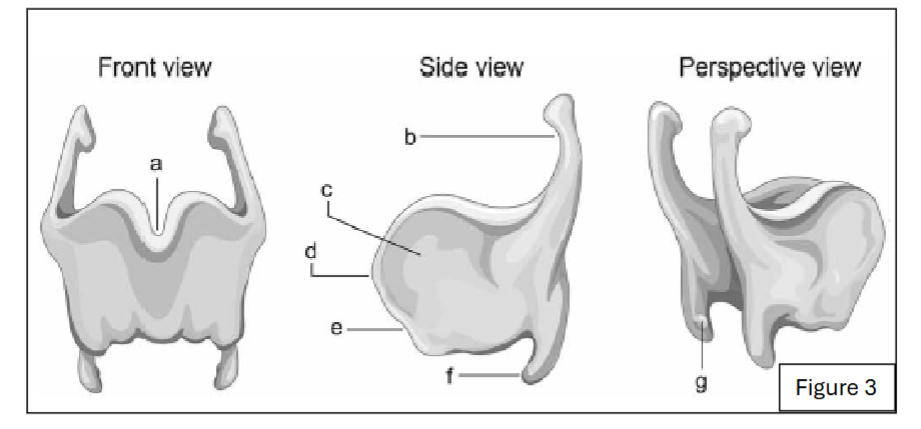
label g
thyroid facet
label a
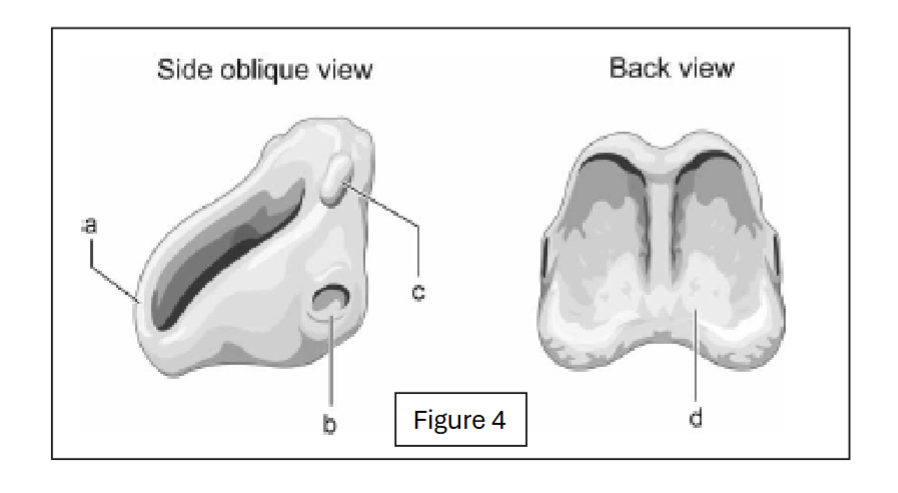
anterior arch of cricoid
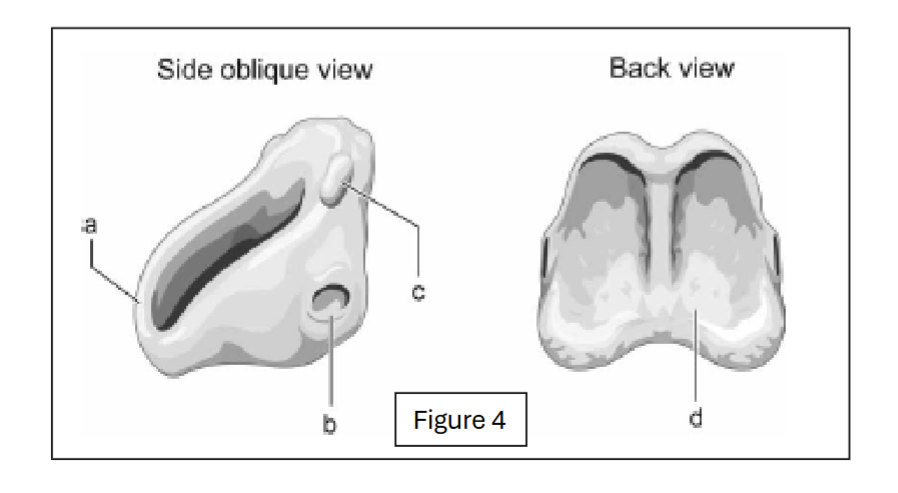
label b - where does it connect to?
inferior facet of cricoid; connects to thyroid cartilage
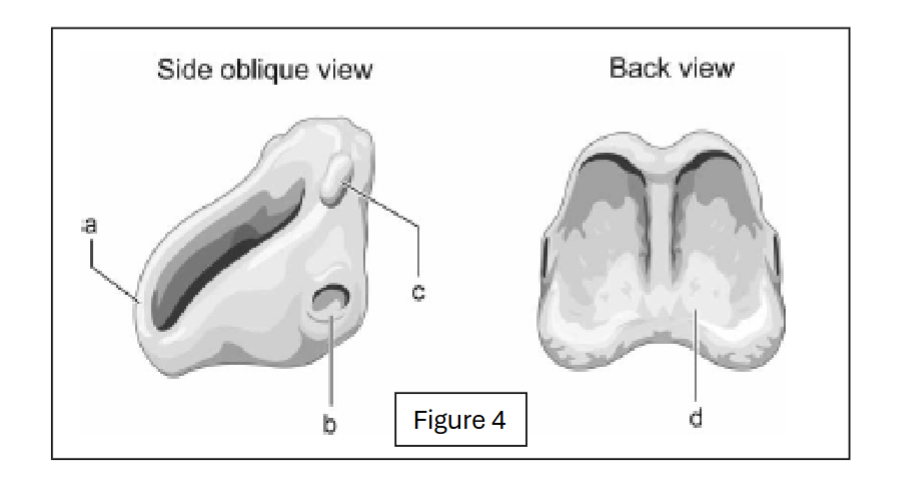
label c - where does it connect to?
superior facet of cricoid; connects to arytenoid cartilage
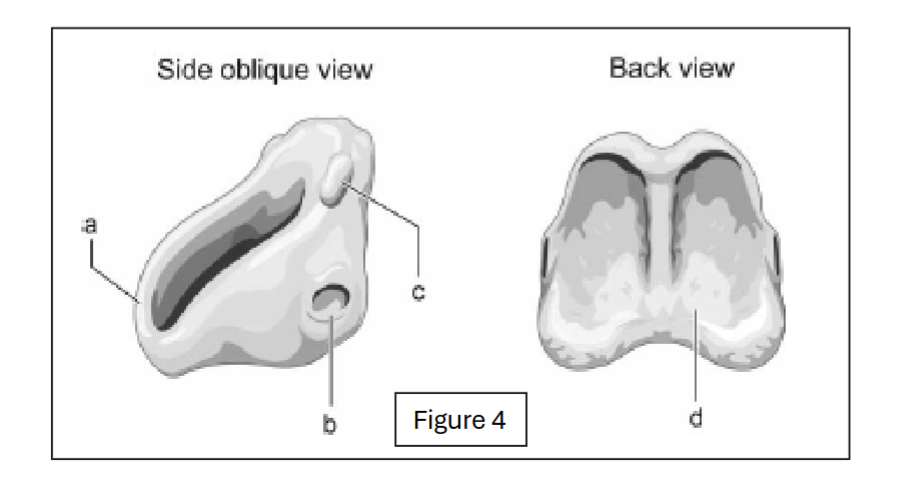
label d
cricoid lamina
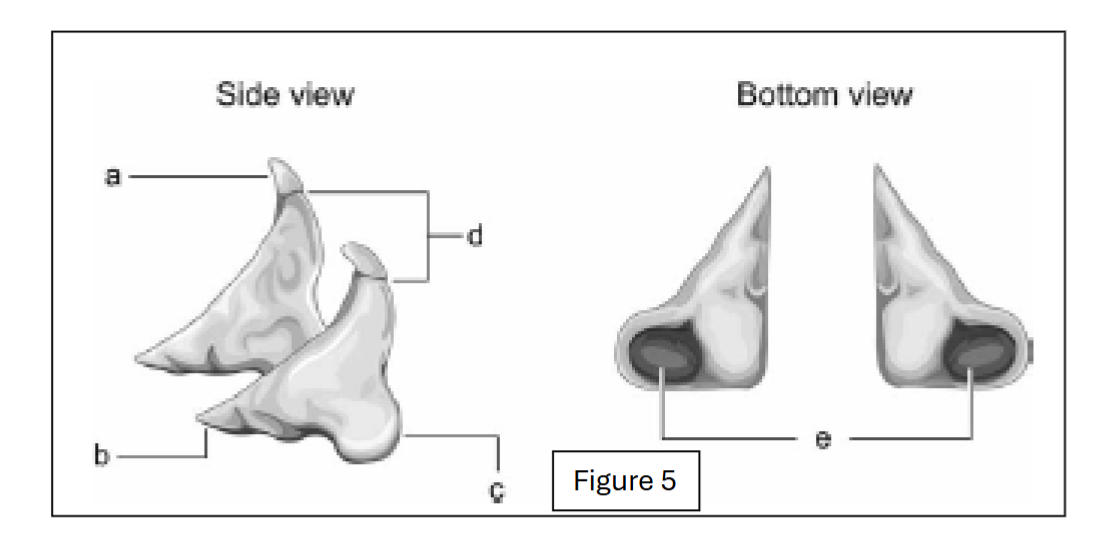
label a
corniculate cartilage
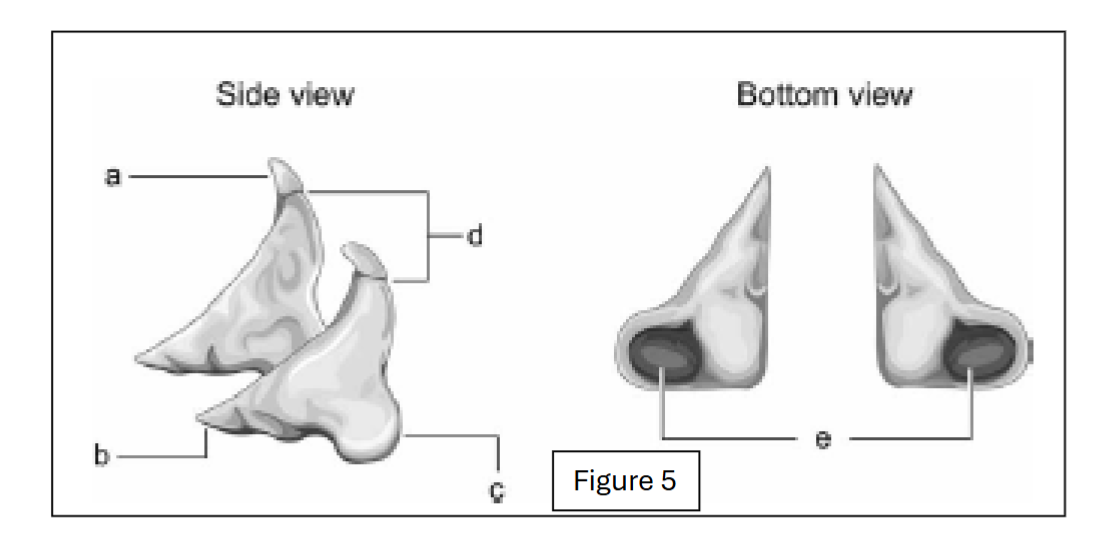
label b
vocal process (towards the internal larynx cavity)
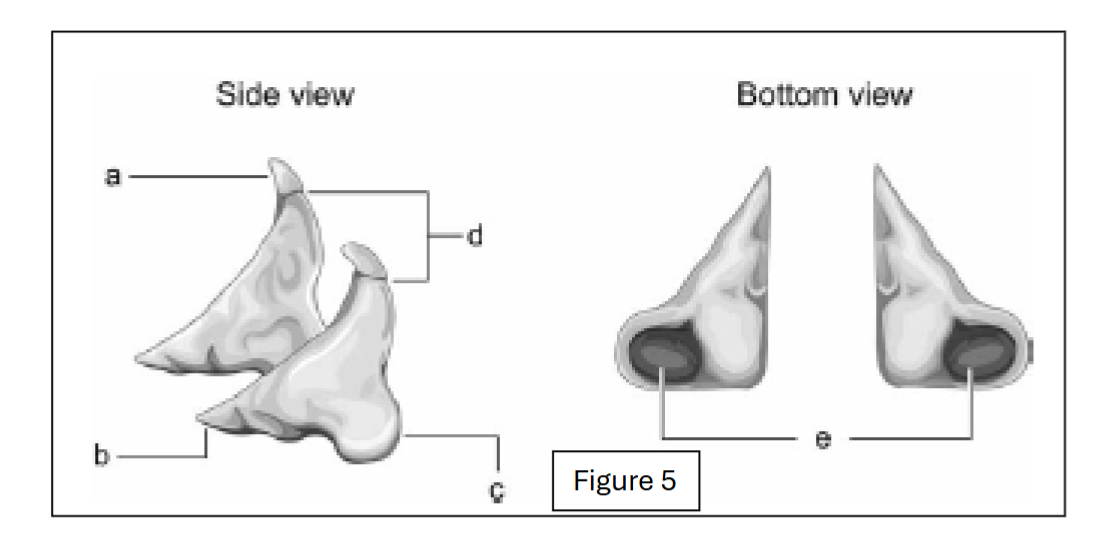
label c
muscular process (away from the internal larynx cavity)
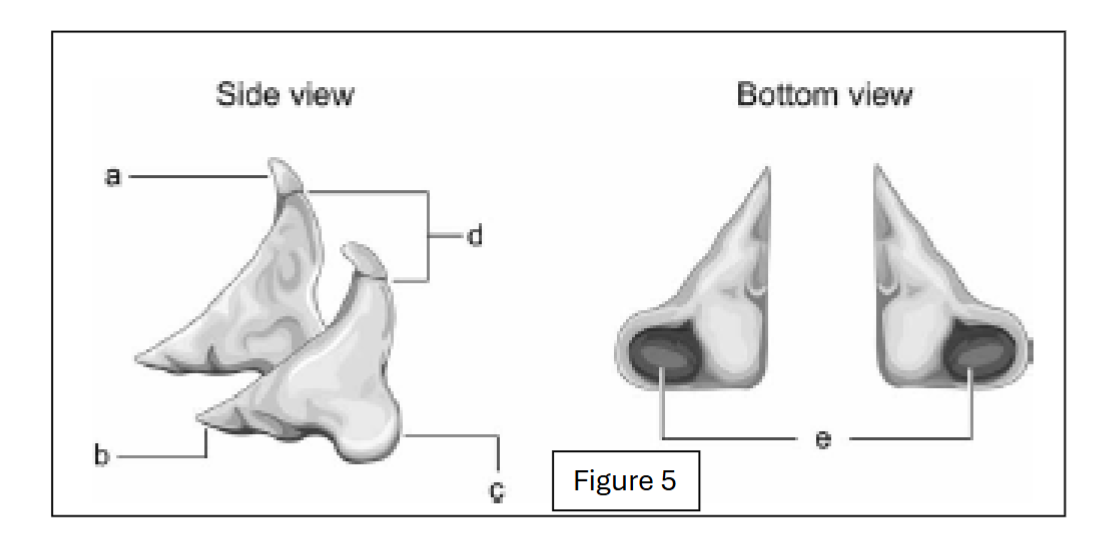
label d
apex (top point; excludes corniculate cartilage)
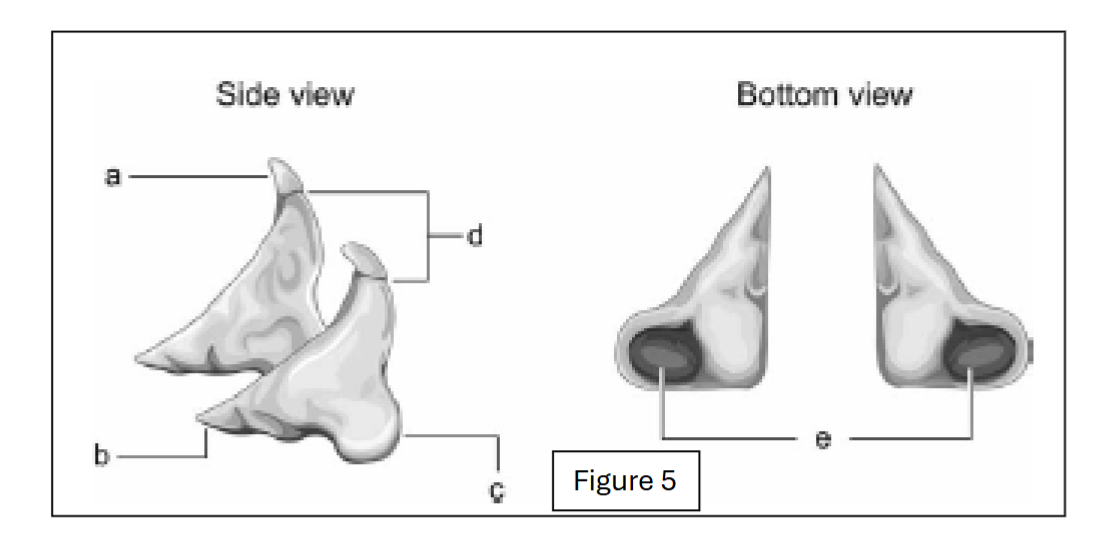
label e - where does it connect to?
facets; connect to cricoid cartilage
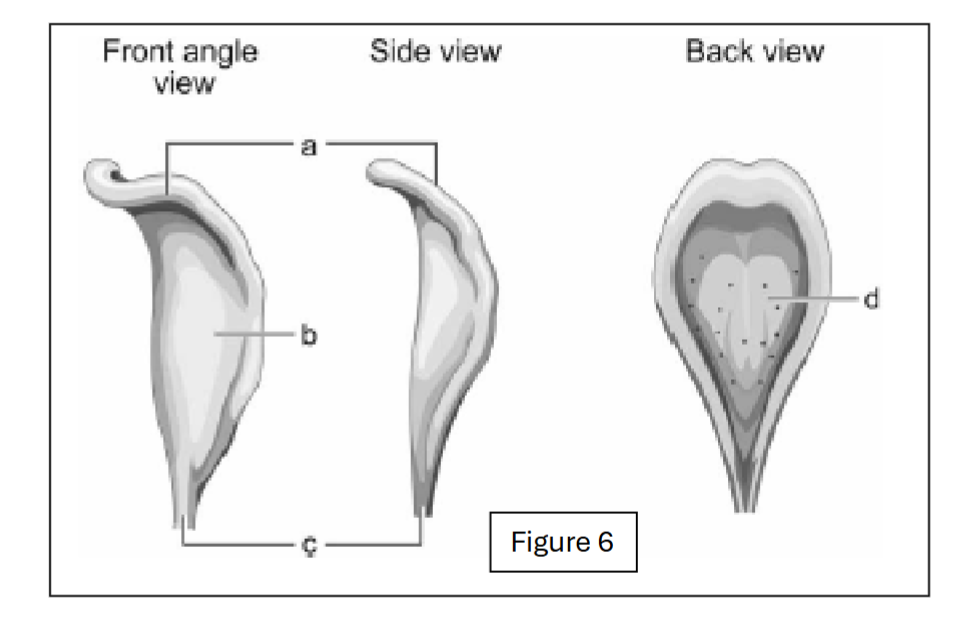
label a
body of epiglottis
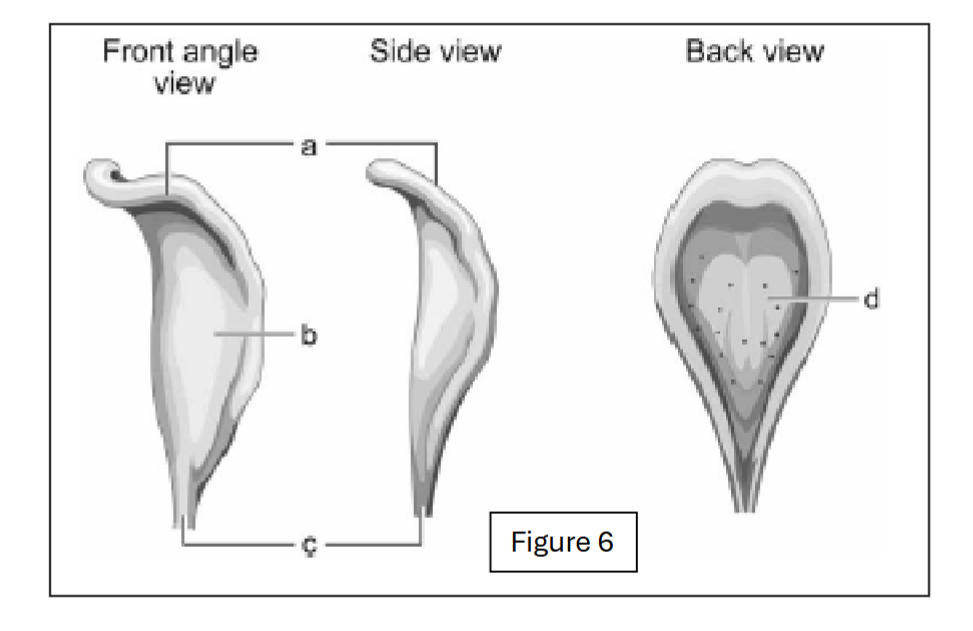
label b
lingual surface of epiglottis
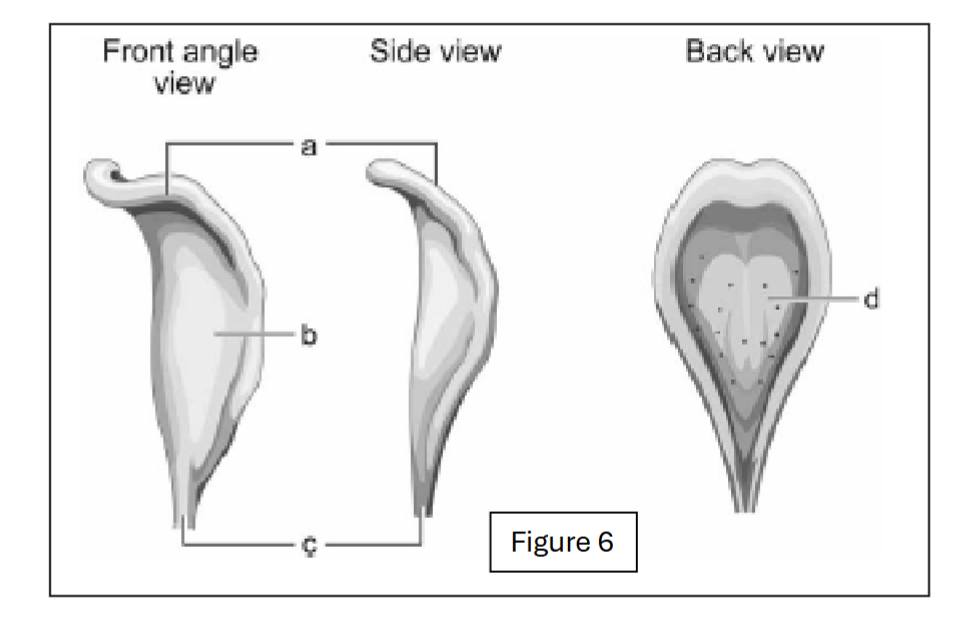
label c
petiole (base of epiglottis)
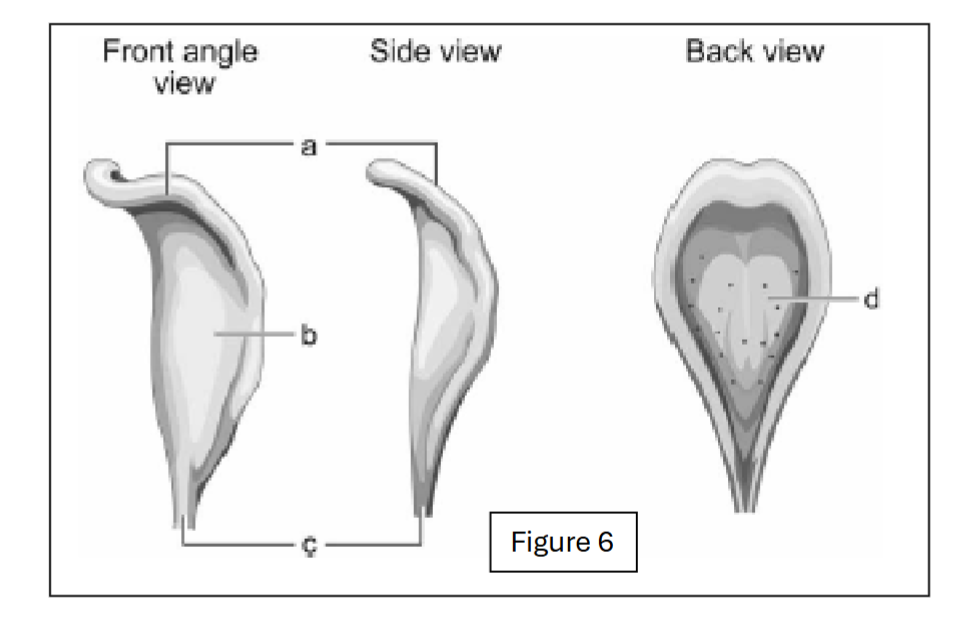
label d
laryngeal surface of epiglottis
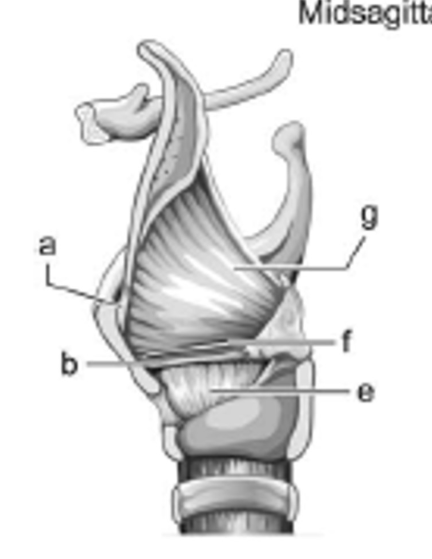
label b - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
vocal ligament; intrinsic
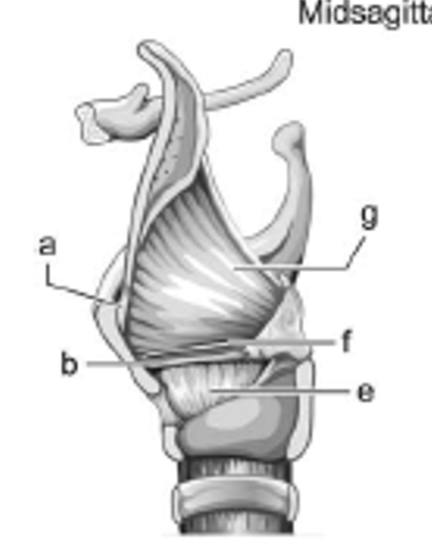
label g - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
quadrangular membrane; intrinsic
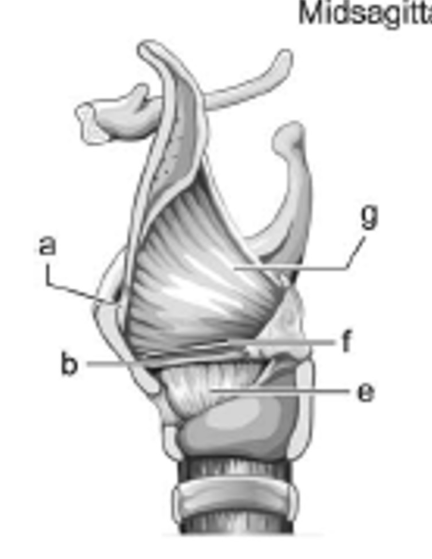
label f - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
ventricular ligament (false VFs); intrinsic
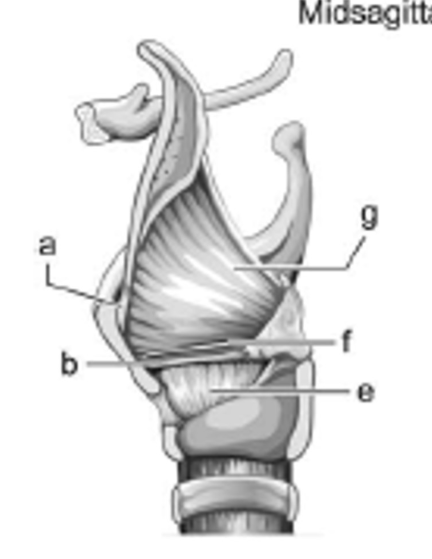
label e - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
conus elasticus; intrinsic
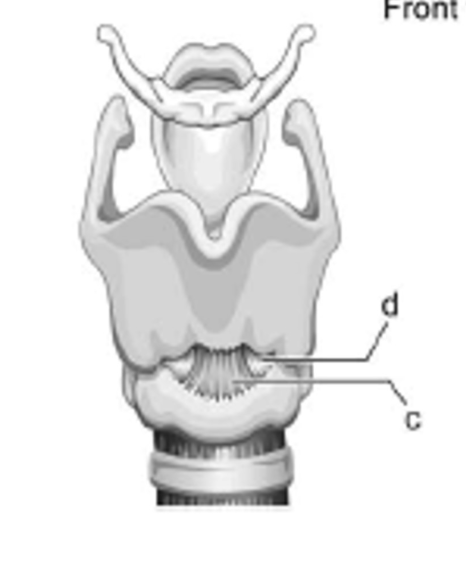
label d - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
lateral cricothyroid ligament; intrinsic
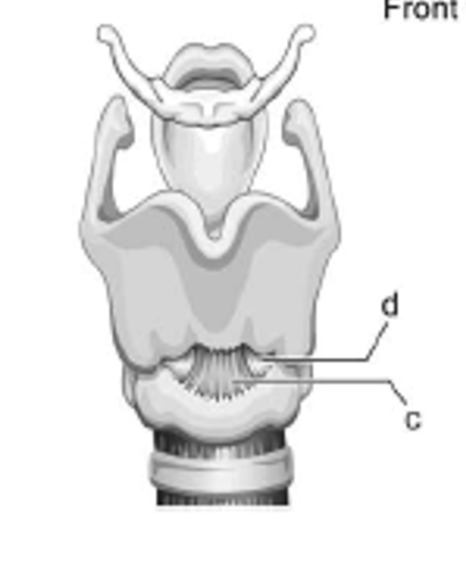
label c - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
medial cricothyroid ligament; intrinsic
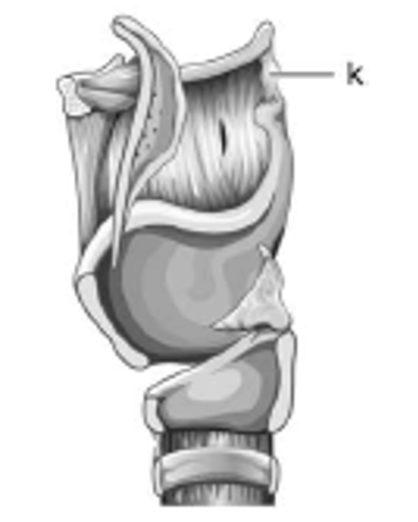
label k - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
lateral thyrohyoid ligament; extrinsic
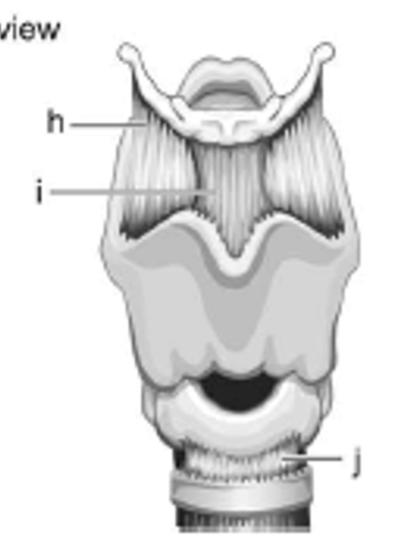
label h - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
thyrohyoid membrane; extrinsic
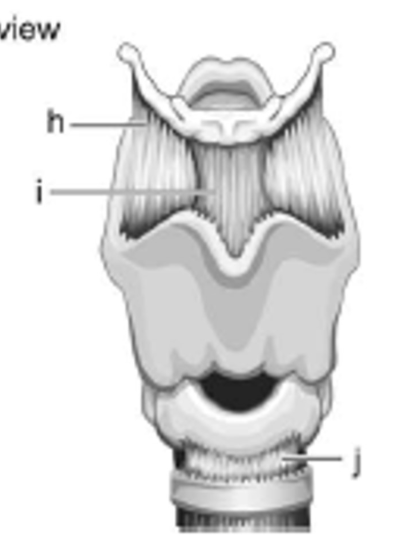
label i - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
medial thyrohyoid ligament; extrinsic
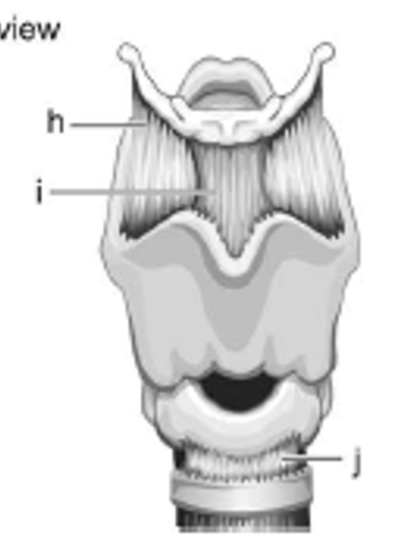
label j - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
cricotracheal ligament; extrinsic
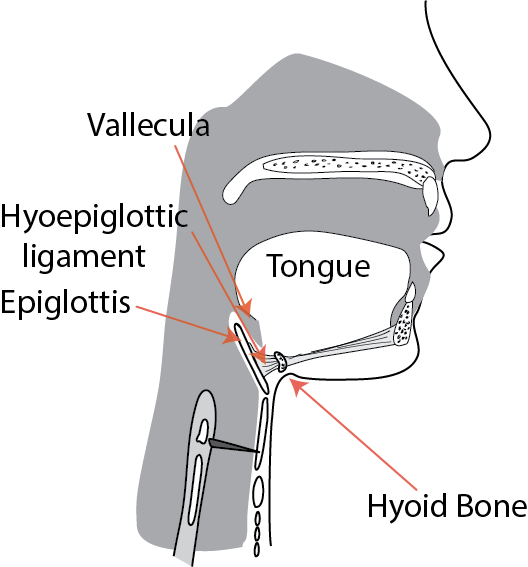
label connection between epiglottis and hyoid bone - is it extrinsic or intrinsic?
hyoepiglottic ligament; extrinsic
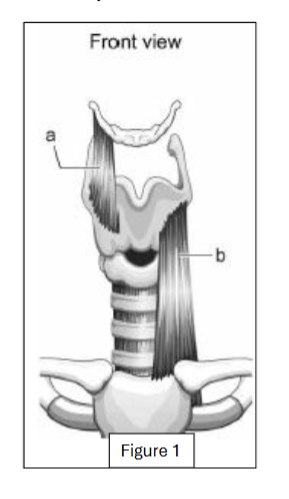
label a
thyrohyoid
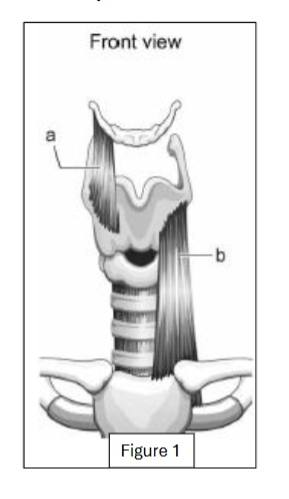
label b
sternothyroid
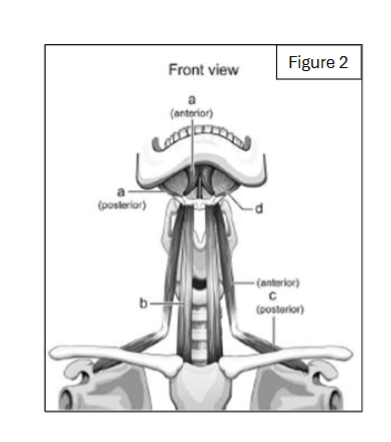
label a
digastric (anterior and posterior bellies)
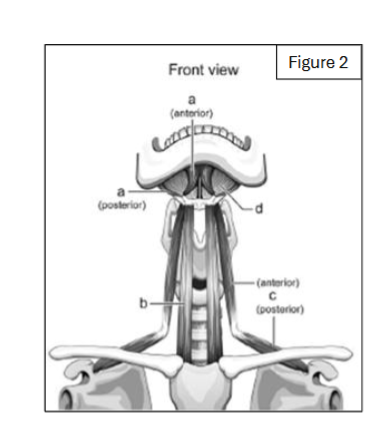
label b
sternohyoid
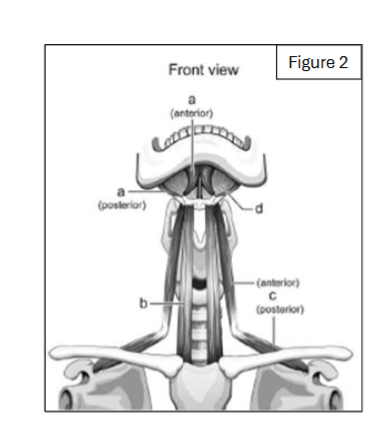
label c
omohyoid
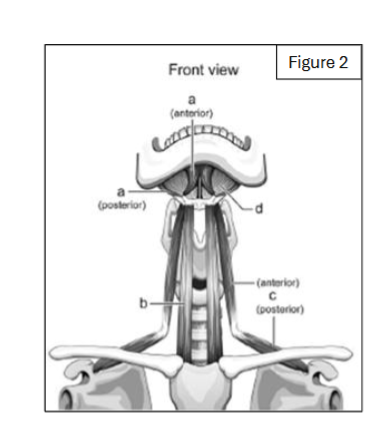
label d
mylohyoid
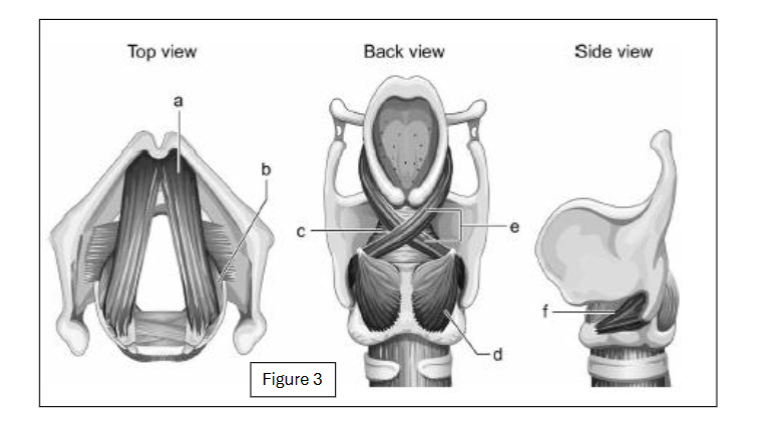
label a
thyroarytenoid
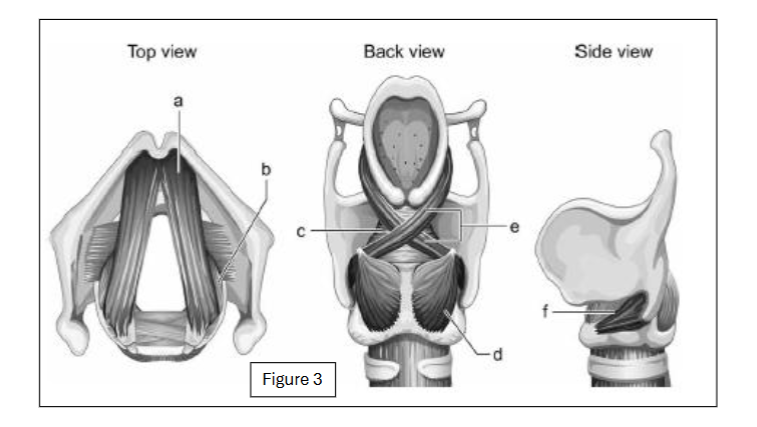
label b
lateral cricoarytenoid
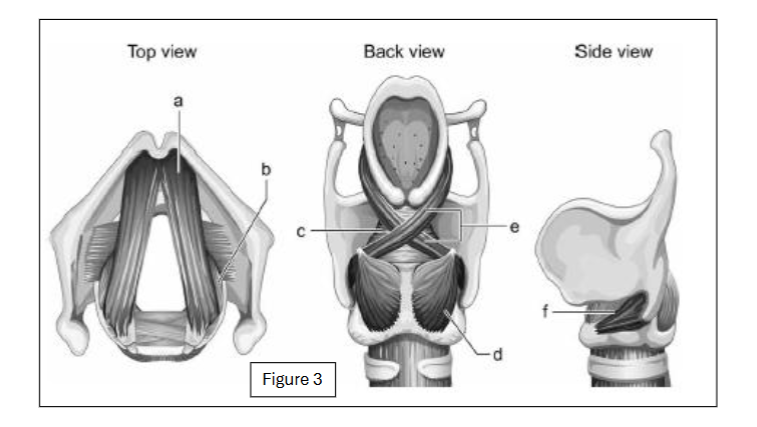
label c
transverse arytenoid
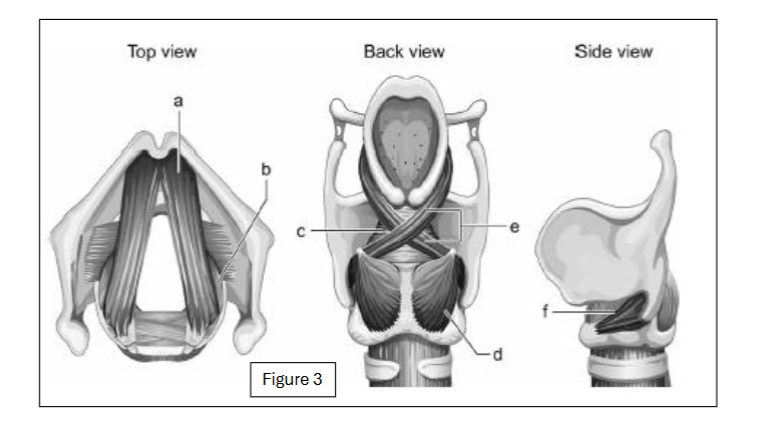
label d
posterior cricoarytenoid
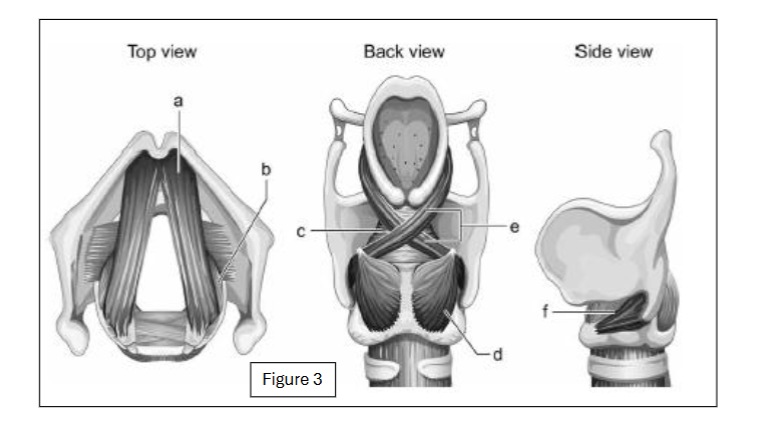
label e
oblique arytenoid
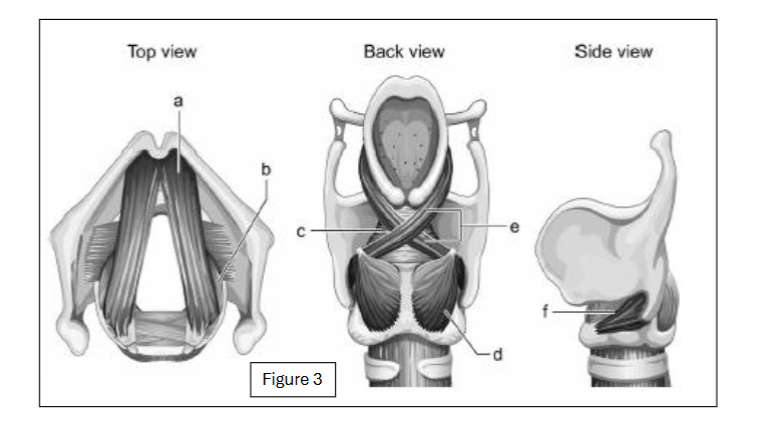
label f
cricothyroid
intrinsic vs extrinsic laryngeal muscles
extrinsic - one attachment to structures outside the larynx
intrinsic - both attachments are within the larynx
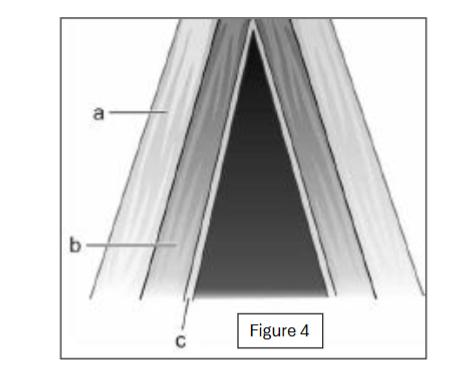
label a
thyromuscularis
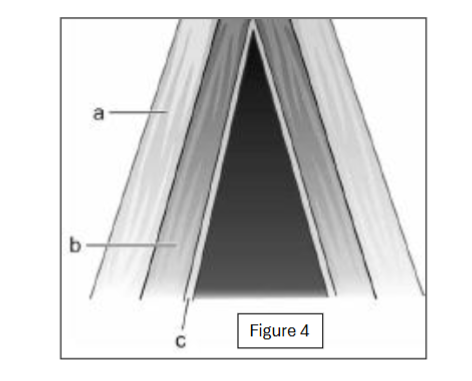
label b
thyrovocalis
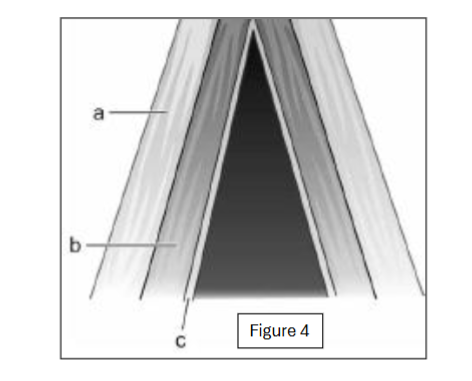
label c
vocal ligament
part that makes up the anterior 2/3rds of the vocal folds
membranous portion
part that makes up the posterior 1/3rd of the vocal folds
cartilaginous portion
muscle that rocks the arytenoid cartilages away from the midline (abduction)
posterior cricoarytenoid (function)
muscle that rocks the arytenoid cartilages toward the midline (adduction)
lateral cricoarytenoid (function)
muscles that pull the arytenoid cartilages toward each other to close the posterior glottis
interarytenoids (function)
thyroarytenoid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: decrease the distance between the thyroid and arytenoid cartilages, which will shorten the VFs and decrease the pitch of the voice (***secondary: adduction***)
motor innervation: CNX (vagus), recurrent laryngeal nerve
intrinsic or extrinsic: intrinsic
posterior cricoarytenoid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: rock the arytenoid cartilages upward and outward (abduction)
motor innervation: CNX (vagus), recurrent laryngeal nerve
intrinsic or extrinsic: intrinsic
lateral cricoarytenoid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: rock the arytenoid cartilages downward and inward (adduction of the membranous portion of the VFs)
motor innervation: CNX (vagus), recurrent laryngeal nerve
intrinsic or extrinsic: intrinsic
interarytenoids - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: adduction of the cartilaginous portion of the VFs and approximation of the arytenoid cartilages
motor innervation: CNX (vagus), recurrent laryngeal nerve
intrinsic or extrinsic: intrinsic
cricothyroid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: increase the distance between the thyroid cartilage and the vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage, which will increase the pitch of the voice
motor innervation: CNX (vagus), superior laryngeal nerve
intrinsic or extrinsic: intrinsic
sternothyroid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: depress the larynx
motor innervation: CNXII (hypoglossal) via C1-C3
intrinsic or extrinsic: extrinsic
point of attachment: sternum
thyrohyoid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: elevate the larynx
motor innervation: CNXII (hypoglossal) via C1
intrinsic or extrinsic: extrinsic
sternohyoid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: depress the larynx (by depressing the hyoid bone)
motor innervation: CNXII (hypoglossal) via C1-C3
intrinsic or extrinsic: extrinsic
point of attachment: hyoid bone + sternum
omohyoid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: depress the larynx (by depressing the hyoid bone)
motor innervation: CNXII (hypoglossal) via C1-C3
intrinsic or extrinsic: extrinsic
point of attachment: shoulder
anterior belly of digastric - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: moves the hyoid bone upward and forward
motor innervation: CNV (trigeminal)
intrinsic or extrinsic: extrinsic
point of attachment: mandible + intermediate tendon
posterior belly of digastric - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: moves the hyoid bone upward and backward
motor innervation: CNVII (facial)
intrinsic or extrinsic: extrinsic
point of attachment: mastoid process
stylohyoid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: move the hyoid bone upward and backward
motor innervation: CNVII (facial)
intrinsic or extrinsic: extrinsic
point of attachment: styloid process
mylohyoid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: move the hyoid bone upward and forward
motor innervation: CNV (trigeminal)
intrinsic or extrinsic: extrinsic
point of attachment: mandible
geniohyoid - function and motor innervation; intrinsic or extrinsic?
function: move the hyoid bone upward and forward
motor innervation: CNXII (hypoglossal) via C1
intrinsic or extrinsic: extrinsic
cranial nerve that transmits sensory information from the laryngeal mucosa
CNX (vagus)
steps involved in the opening phase of the vibratory cycle
contraction of the lateral cricoarytenoid muscle = adduction of the VFs
build-up of subglottal pressure
opening force develops; when the force exceeds the resistance provided by the adducted VFs, the VFs will be forced apart in the vertical direction in a bottom-up fashion***
lateral excursion of VFs (VFs separate in the lateral direction in a bottom-up fashion)***
complete abduction of VFs; flow of air dissipates
***occurs simultaneously
steps involved in the closing phase of the vibratory cycle
elastic recoil of VFs will return them to the position of equilibrium, but not full adduction
inertia will keep the VFs moving closer together
aerodynamic forces + biomechanical properties
Bernoulli effect
constriction due to VF configuration will cause the air molecules to speed up
as the air molecules speed up, the pressure will drop to keep the total energy constant
a drop in pressure creates a suction force, which will bring the VFs together
pressure differential due to VF configuration (divergent shape - bring VFs together)
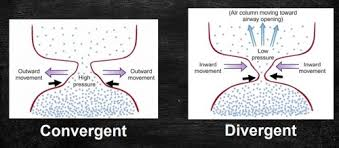
convergent glottal configuration
separation at the bottom of the VFs
glottal pressure is high
push VFs AWAY from the midline
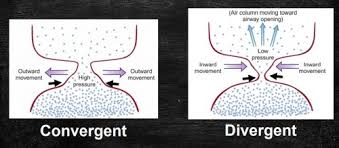
divergent glottal configuration
NO separation at the bottom of the VFs
glottal pressure is low
push VFs TOWARD the midline (“suction” force)
vertical phase - abduction and adduction
abduction - bottom-up
adduction - bottom-up
longitudinal phase - abduction and adduction
abduction - bottom-up
adduction - up-bottom (like a zipper)
glottic space/glottis
space between the true vocal folds
supraglottic space
above the vocal folds
laryngeal vestibule
cavity from the entrance of the larynx to the ventricular ligaments (false VFs)
laryngeal additus
opening to the larynx
subglottic space
below the vocal folds
laryngeal ventricle (and function)
space between the false and true VFs
contains mucous glands that secrete mucus to lubricate the true VF (smooths the contact between one VF and the other to prevent damage/lesions)
mucosa of VF - layers that make up it and function
squamous epithelium
superficial layer of lamina propria
function: the part that primarily vibrates
vocal ligament of VF - layers that make up it and function
intermediate layer of lamina propria
deep layer of lamina propria
function: provides structure
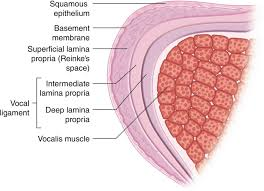
5 layers of VF
squamous epithelium - outer shape; most external
superficial layer of lamina propria
intermediate layer of lamina propria
deep layer of lamina propria
vocalis muscle - main body of VFs
***increase in pliability from internal to external layers (example: deep layer is less pliable than the superficial layer)
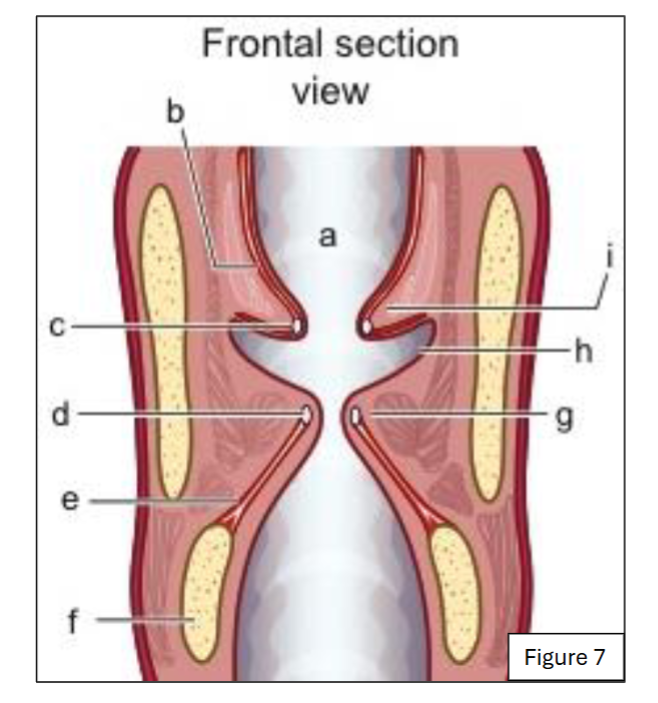
label a
supraglottic space (and laryngeal vestibule)
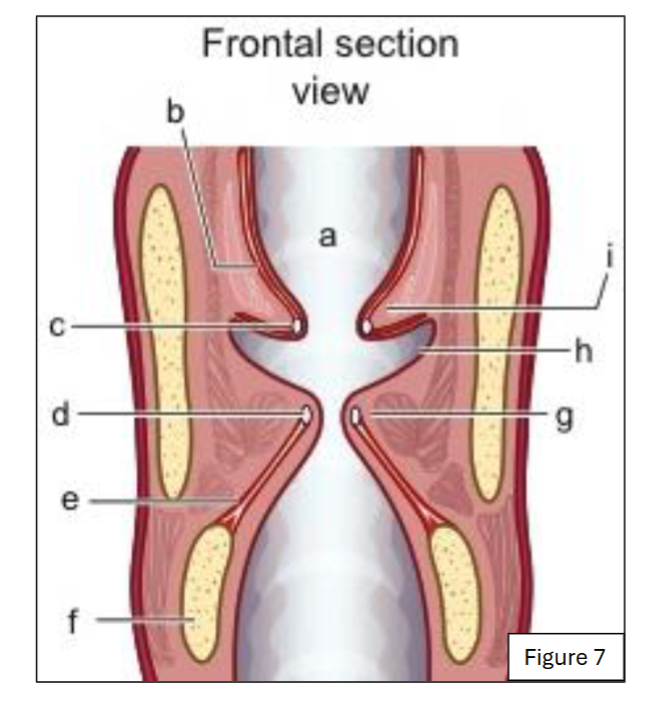
label b
quadrangular membrane (internal laryngeal view)
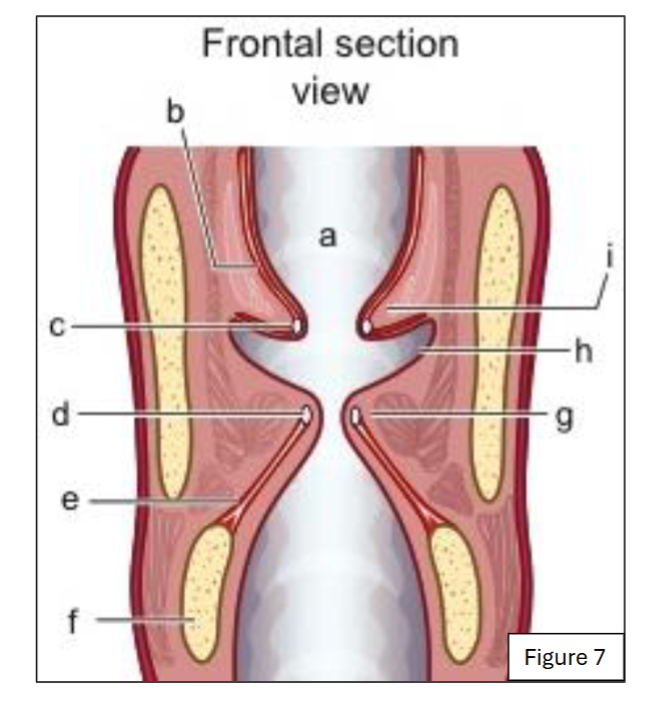
label c
ventricular ligament (internal laryngeal view)
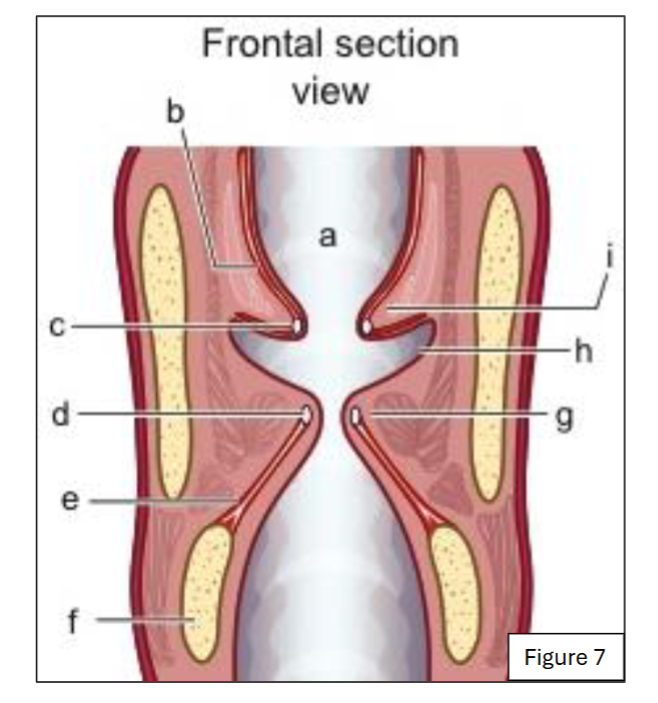
label d
vocal ligament (internal laryngeal view)