5. Energy Transfers
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
How are the thylakoid membranes adapted for photosynthesis?
- Folded membranes contain photosynthetic proteins (chlorophyll) and electron carrier proteins are embedded within membranes, and both are involved in LDR
What is the stroma, and what is its function in photosynthesis?
Fluid centre which contains enzymes involved in the LIR.
What type of membrane does a chlorophyll have?
Inner and outer membranes
Where does the LDR and LIR take place?
- LDR - on thylakoid membrane in chloroplast
- LIR - stroma in chloroplast
What is the most abundant chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll A
What is the advantage of having many photosynthetic pigments?
- A wider range of wavelengths of light is absorbed
- Therefore, more light ENERGY is absorbed for the LDR (more photoionisation of chlorophyll)
What are the 2 stages of photosynthesis?
- light dependant reaction (LDR)
- light independent reaction (LIR)
What is the first stage of photosynthesis?
The light dependent reaction (LDR)
What are the 3 products of the LDR?
- ATP - goes to light independent reaction
- Reduced NADP - goes to light independent reaction
- Oxygen leaves cell as a by-product or used in respiration
What are the 4 key stages of the LDR?
1. Photoionisation of chlorophyll
2. Production of ATP (chemiosmosis)
3. Production of reduced NADP
4. Photolysis
What happens in the photoionisation of chlorophyll?
- Chlorophyll (in photosystem II) absorbs light energy (photon)
- This excites electrons to a higher energy level, releasing them from chlorophyll = photoionisation
- Some energy from electrons released during photoionisation is conserved in the production of ATP and reduced NADP
What happens in the production of ATP?
1. Electrons pass down electron transfer chain (via electron carriers) from PSII to PSI via redox reactions, losing energy at each step
2. This energy is used to actively transport protons (via proton pumps) from stroma into thylakoid
3. Creating a proton electrochemical gradient across the thylakoid membrane (higher in thylakoid than stroma)
4. Protons move by facilitated diffusion down the electrochemical gradient into the stroma via the enzyme ATP synthase EMBEDDED in the thylakoid membrane
5. Energy from this allows ADP + Pi ATP (photophosphorylation) This is the chemiosmotic theory
What happens in the production of reduced NADP?
In PSI electrons are excited and transferred to NADP (with a proton from photolysis) to reduce NADP to form reduced NADP
What is photolysis?
The splitting of water using light energy
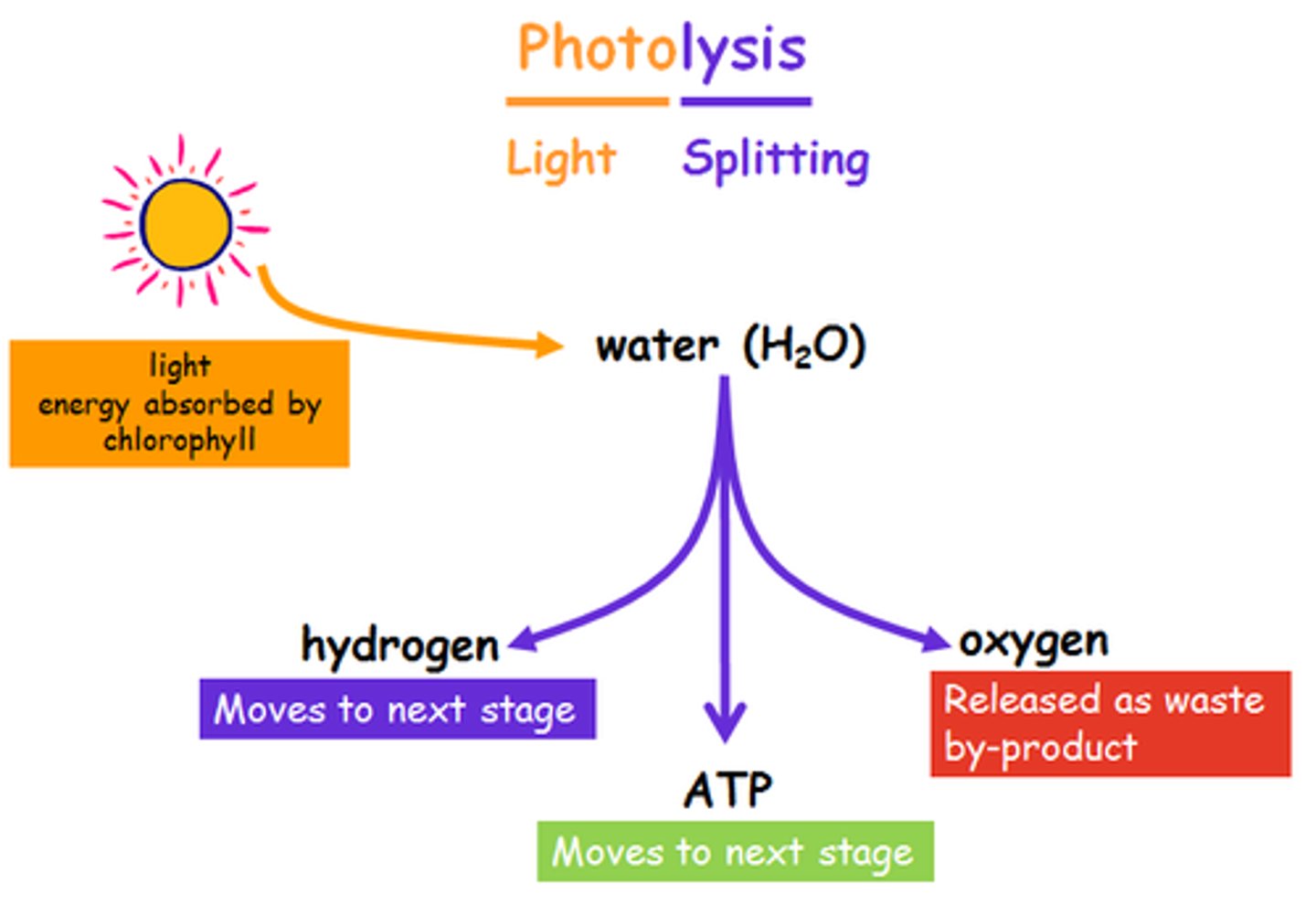
What happens in photolysis?
- Produces protons, electrons and oxygen (2H2O -> O2 + 4e- + 4H+ )
- Electrons replace those lost from chlorophyll
What is the another name for the light-independent reaction (LIR)?
The Calvin Cycle
Where does the light independent reaction take place?
- In the stroma
- Contains an enzyme called RuBisCo, which catalyses this reaction (therefore temperature sensitive)
What reactants are used in the LIR?
- Carbon dioxide
- Reduced NADP (oxidised to reduce GP)
- ATP (hydrolysed to provide energy)
Describe the 5 main stages of the LIR.
1. CO2 reacts with RuBP (5C), catalysed by the enzyme rubisco.
2. Produces 2 molecules of (GP) (3C).
3. GP reduced to triose phosphate (TP) using products from light dependent reaction: energy from the hydrolysis of ATP and H+ from reduced NADP.
4. Some TP converted into useful organic substances eg. glucose.
5. (5/6) TP used to regenerate RuBP (using energy from ATP).
What is a limiting factor of photosynthesis? (2)
1. A factor is limiting if when it's made a more favourable value, the rate of photosynthesis increases
2. until photosynthesis is limited by a different factor
What are the 3 limiting factors of photosynthesis?
- Carbon dioxide CONCENTRATION
- Light intensity
- Temperature
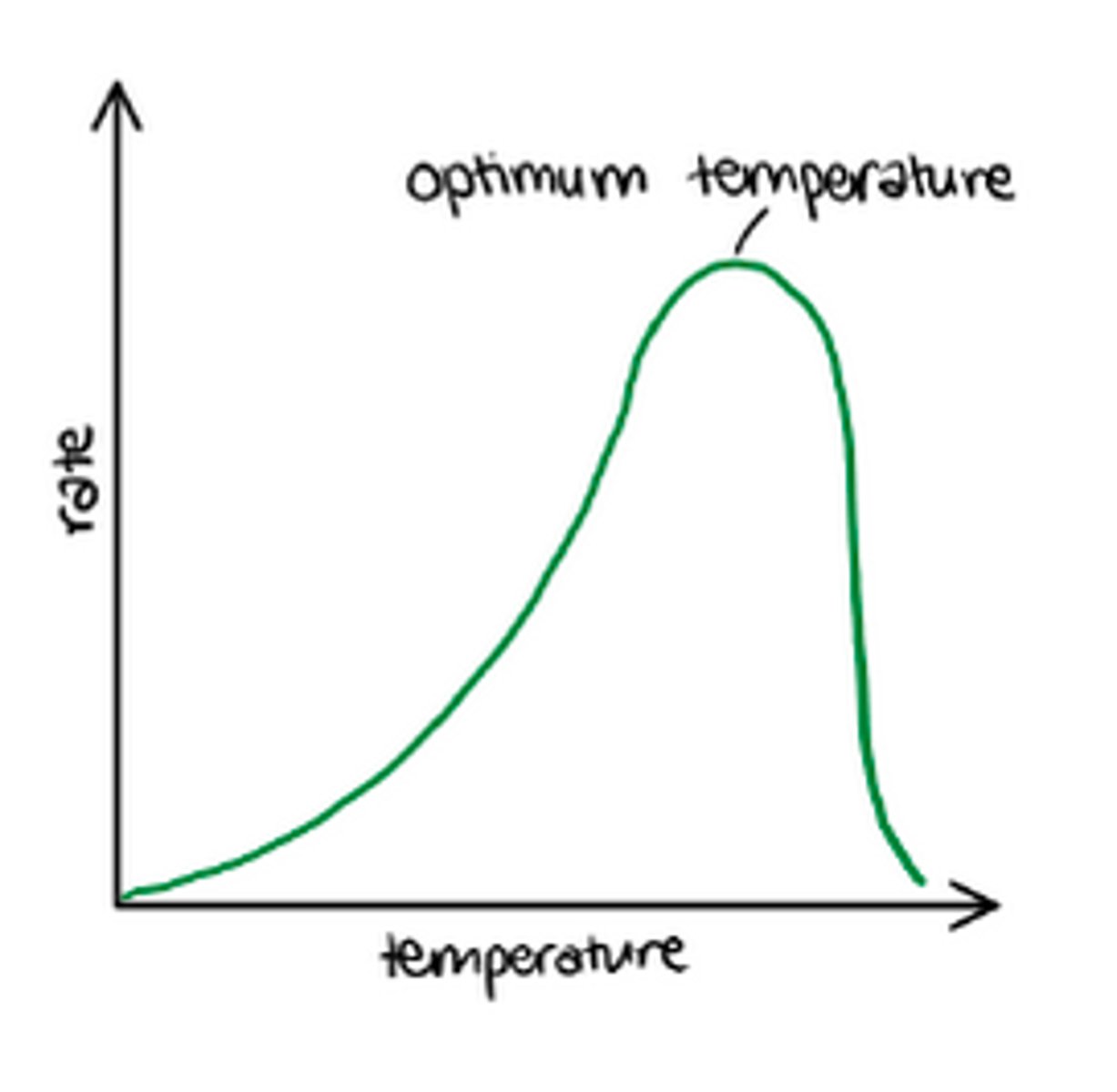
Why is temperature a limiting factor of photosynthesis?
Rate of photosynthesis increases as temp increases up to an optimum, decreases after
- Limits light independent reaction as it's enzyme controlled (rubisco)
- Increasing temp up to optimum - more Ek, so more E-S complexes (rubisco).
- Above optimum - H bonds in tertiary structure break active site changes shape / enzyme denatured (rubisco), so fewer E-S complexes
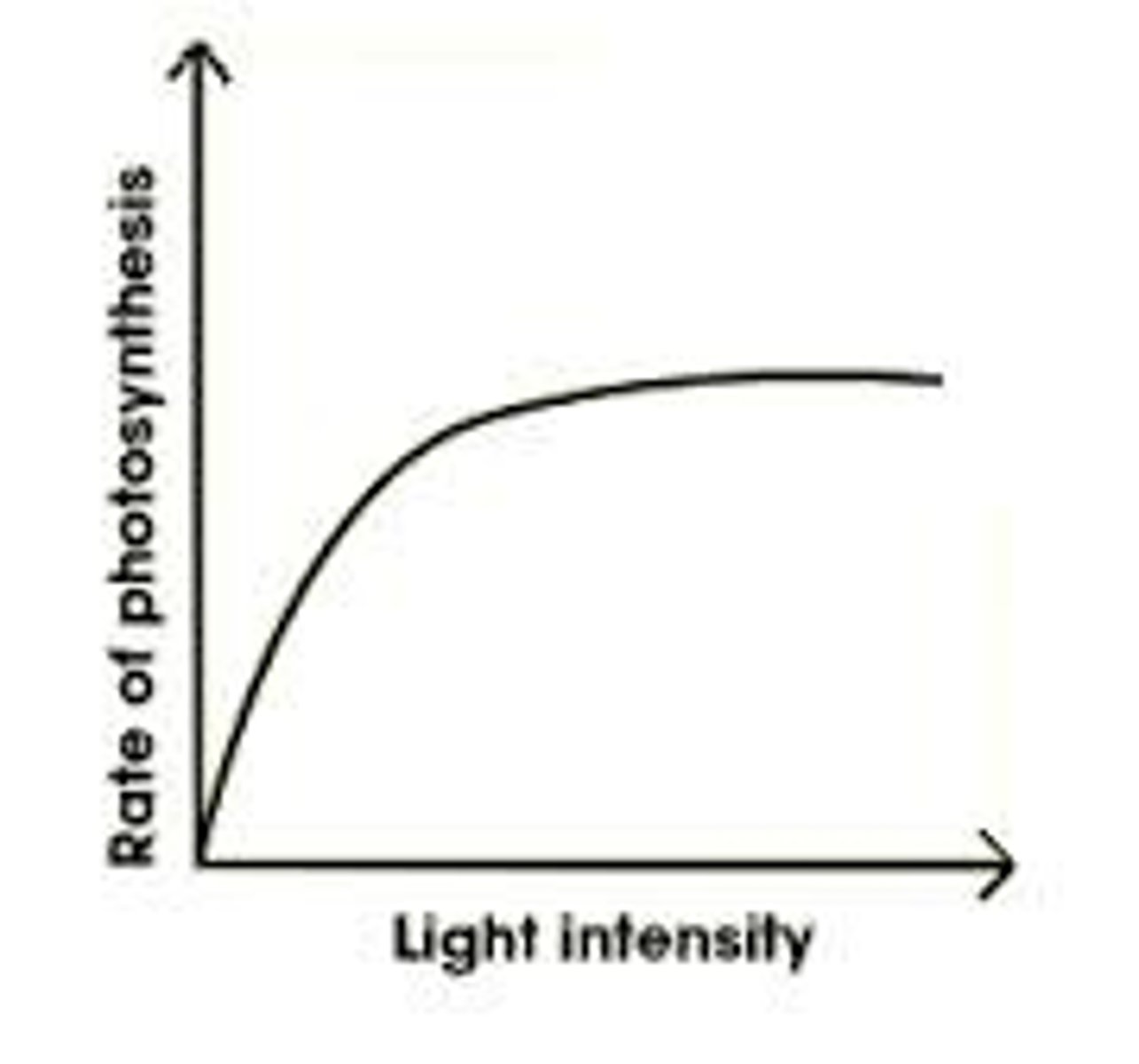
Why is light intensity a limiting factor of photosynthesis?
Rate of photosynthesis increases as light intensity increases (then plateaus)
If light intensity was dramatically reduced:
- Levels of ATP and reduced NADP would fall, because light dependent reaction limited as less photoionisation of chlorophyll (and less photolysis) •
- So, the light independent reaction would also slow/stop because GP can't be reduced to TP (requires ATP and reduced NADP) and TP can't regenerate RuBP (requires ATP)
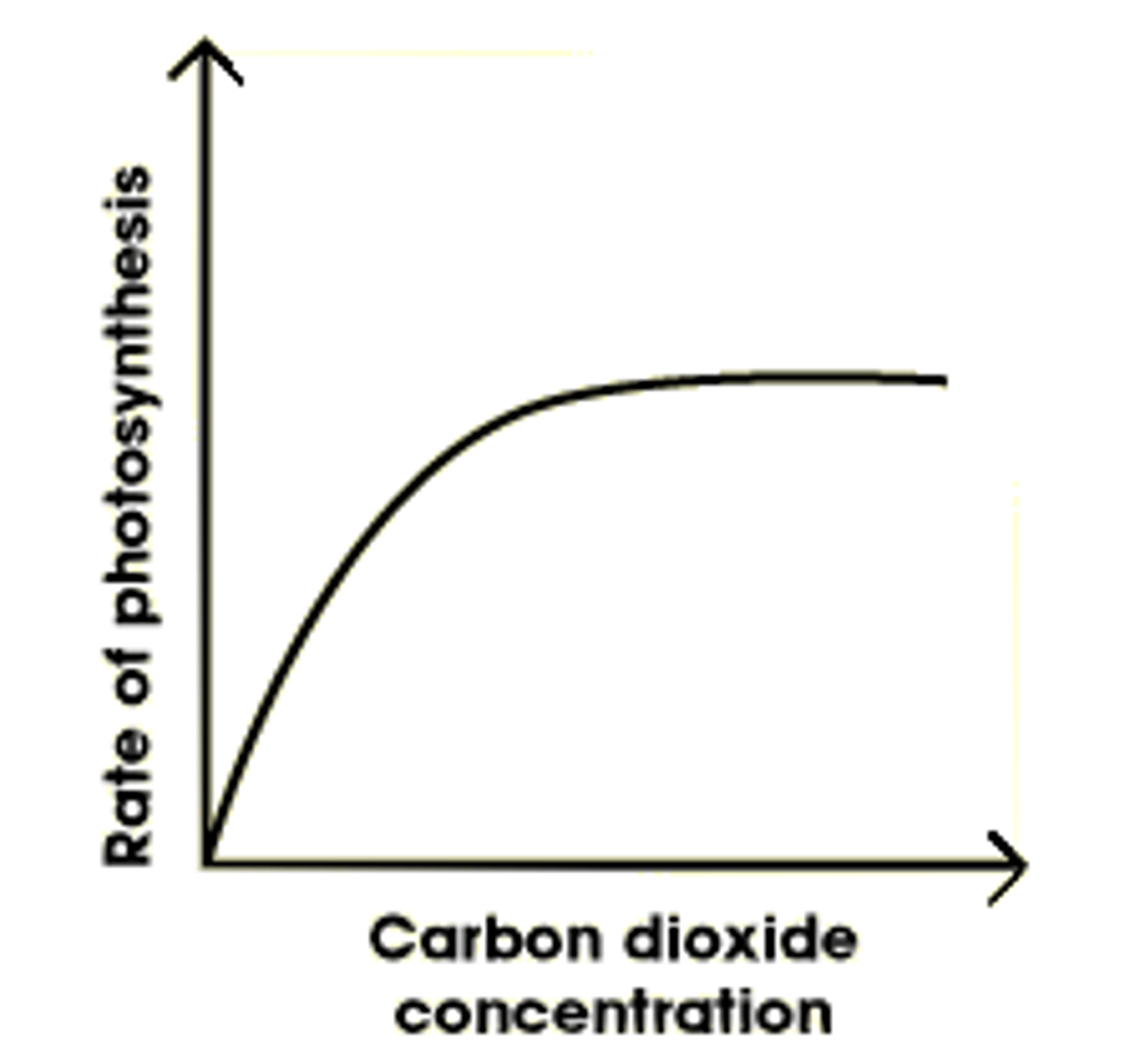
Why is carbon dioxide concentration a limiting factor of photosynthesis?
Rate of photosynthesis increases as CO2 conc increases (then plateaus)
If carbon dioxide concentration dramatically decreased
- Limits light independent reaction
- Less CO2 to combine with RuBP to form GP
- Less GP reduced to TP
- Less TP (and GP) converted to organic substances e.g. hexose and to regenerate RuBP
What are common agricultural practices used to overcome the effect of these limiting factors?
- Growing plants under artificial lighting to maximise light intensity,
- Heating a greenhouse to increase the temperature
- Burning fuel, such as paraffin burners, to release more carbon dioxide
What do you always have to consider when faced with limiting factors?
- Profit - if the extra growth for photosynthesis is minimal, it will not be cost effective
- Faster production of glucose allowing faster respiration - more ATP to provide energy for growth e.g. cell division, protein synthesis - higher yield so more profit.
What are the 4 key stages of aerobic respiration? Where do they occur?
1. Glycolysis (cytoplasm)
2. Link reaction (mitochondrial matrix)
3. Krebs Cycle (mitochondrial matrix)
4. Oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondrial inner membrane-cristae)
What is the purpose of respiration?
To produce ATP
What is important about glycolysis?
- Occurs in cytoplasm
- Anaerobic process (doesn't require oxygen); the first stage of aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Describe the 3 key stages of glycolysis.
1. Phosphorylation of glucose to glucose phosphate - using inorganic phosphates from 2 ATP
2. Hydrolysed to 2 Triose phosphates (TP)
3. 2 Triose phosphate oxidised to 2 pyruvate
- 2 NAD reduced (collects hydrogen ions)
- 4 ATP regenerated
What is the net production of ATP in glycolysis?
4 gained - 2 used = net production of 2 ATP
What does the loss of H (hydrogen) mean?
The species has been oxidised
What does the gain of H (hydrogen) mean?
The species has been reduced
Why does glycolysis occur in the cytoplasm and not the mitochondria?
Mitochondria does not have membrane transport proteins to take glucose inside.
What happens after glycolysis in aerobic respiration?
Pyruvate actively transported into the mitochondrial matrix
Describe the link reaction. (3)
- Occurs in mitochondrial matrix
1. Pyruvate oxidised and decarboxylated = acetate
2. CO2 and reduced NAD produced
3. Acetate combines with coenzyme A = Acetyl Coenzyme A
Describe the Krebs Cycle (5)
- Occurs in mitochondrial matrix
1. Acetyl coenzyme A reacts with a 4-carbon molecule (oxaloacetate), producing a 6-carbon molecule (citrate) that enters the Krebs cycle - coenzyme A released (back to link reaction)
2. 6C -> 5C -> 4C molecule (4C molecule regenerated) through a series of redox reactions - decarboxylation and dehydrogenation
3. CO2 removed
4. Coenzymes NAD & FAD reduced (key point - important for oxidative phosphorylation)
5. ATP produced by substrate level phosphorylation (direct transfer of Pi from intermediate compound to ADP)
What are the products of the Link reaction per glucose molecule?
- 2 Acetyl CoA
- 2 CO2
- 2 reduced NAD produced
Describe Oxidative Phosphorylation. (6)
- On the cristae of mitochondria
1. Reduced NAD/FAD oxidised to release H atoms split into protons (H+) and electrons (e-)
2. Electrons transferred down the electron transport chain (a chain of carriers at decreasing energy levels) by redox reactions
3. Energy released by electrons used in the production of ATP from ADP + Pi (chemiosmotic theory) - energy used by electron carriers to actively transport protons from the matrix to the intermembrane space
4. Protons diffuse down an electrochemical gradient, via ATP synthase (embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane) back into the matrix
5. Releasing energy to combine ADP + Pi to ATP
6. In the matrix at the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen is the final electron acceptor - protons, electrons and oxygen combine to form water
Why is oxygen needed for the production of ATP on the cristae of the mitochondrion?
- Oxygen = terminal electron acceptor for electrons passing along the ETC
- The ETC releases the energy for the formation of (most) ATP (from ADP + Pi)
- No oxygen to accept them = electrons can't be passed along the electron transport chain
- The Krebs cycle and link reaction also stop in the absence of oxygen because NAD and FAD (converted from reduced NAD/FAD as they release their H atoms for the ETC,) cannot be produced
What are the other respiratory substrates?
Other respiratory substrates include the breakdown products of lipids and amino acids, which enter the Krebs cycle.
For example:
- Fatty acids from the hydrolysis of lipids are converted to Acetyl Coenzyme A
- Amino acids from the hydrolysis of proteins are converted to intermediates in Krebs cycle
What happens in anaerobic respiration?
1. Pyruvate converted to lactate (animal cells, some bacteria) or ethanol (plants, yeast)
2. Oxidising reduced NAD - NAD regenerated
3. So glycolysis can continue which needs / uses NAD
What are the 2 reasons as to why anaerobic respiration releases less energy than in aerobic respiration?
- Some energy still in lactate (incomplete breakdown of glucose)
- Anaerobic respiration is much less efficient than aerobic respiration; the ATP yield is lower. The majority of ATP is formed in oxidative phosphorylation
What are autotrophs?
The producers in an ecosystem
What is the difference between photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs?
- Photoautotrophs use light energy to synthesise their own food
- Chemoautotrophs use inorganic molecules
What are the two possible sources that plants can get carbon dioxide from?
- Atmospheric carbon dioxide
- Aquatic carbon dioxide
- What are most of the sugars synthesised by plants used for? What are the rest used for?
- Used as respiratory substrates
- Rest used to make other groups of biological molecules e.g. cellulose form plant biomass
What are heterotrophs?
- Consumers in food webs
- Cannot synthesise their own energy, but must obtain it from autotrophs or other heterotrophs
What happens between trophic levels in a food web?
- Energy is lost due to respiratory heat loss and excretion. The remaining energy is used to form biomass.
- Biomass and its stored energy are transferred through trophic levels in a food web (inefficiently)
How can biomass me measured?
- Mass of carbon
- DRY mass of tissue per given area
How do you work out the dry mass of tissue per given area?
1. Sample of organism dried in an oven set to a low temperature - low temperature to avoid combustion (loss of biomass / CO2)
2. Sample reweighed at regular intervals e.g. every day 3. All water removed when mass remains constant
4. Mass of carbon taken to be 50% of dry mass
Why is working out the dry mass of tissue per given area more representative than measuring the mass of carbon?
Water content of samples varies
How can the chemical energy stored in dry biomass be measured?
- Using calorimetry
- Sample of dry biomass burnt
- Energy released is used to heat a known volume of water
- Change in temperature of water used to calculate the chemical energy
What is GPP?
- Gross Primary Production
- Chemical energy store in plant biomass, in a given area / volume, in a given time i.e. the total energy resulting from photosynthesis
What is NPP?
- Net Primary Production
- Chemical energy store in plant biomass after respiratory losses (R) to the environment have been taken into account
- NPP = GPP - R
- The NPP is available for plant growth and reproduction
- The NPP is also available to other trophic levels in the ecosystem, such as herbivores and decomposers
How do you work out the net production of consumers?
N = I - (F+R)
I = chemical energy stored in ingested food
F = chemical energy lost to environment in faeces and urine
R = respiratory losses to environment
What are the three components when calculating rates of productivity?
kJ ha^-1 year^-1
- kJ: a unit for energy
- Per unit area (e.g. ha): different environments vary in size; standardizes results so environments can be compared
- Per year: more representative as takes into account the effect of seasonal variation (temperature etc.) on biomass so environments can be compared
Why is the energy transfer between sun and producer inefficient?
- Wrong wavelength of light
- Light strikes non-photosynthetic region e.g. bark
- Light reflected
- Lost as heat
Why is the energy transfer between producers and consumers inefficient?
- Respiratory loss - energy used for metabolism e.g. active transport
- Lost as heat
- Not all plant/animal eaten e.g. bones
- Some food not digested ( faeces)
How can farming practices for crops increase energy transfer efficiency?
- Simplifying food webs to reduceenergy/biomass losses to non-human food chains:
- Herbicides kill weeds, less competition, more energy to create biomass
- Fungicides reduce fungal infections, more energy to create biomass
- Pesticides, reduce loss of biomass from crops
- Fertilisers e.g. nitrates to prevent poor growth due to lack of nutrients
How can farming practices for livestock increase energy transfer efficiency?
- Reducing respiratory losses within a human food chain (so more energy to create biomass):
- Restrict movement
- Keep warm (especially in winter)
- Slaughter animal while still growing / young, when most of their energy is used for growth
- Selective breeding to produce breeds with higher growth rates
- Treated with antibiotics to prevent loss of energy due to pathogens
What is the general sequence of a nutrient cycle?
1. Nutrients taken up by producer as an inorganic ion (simple inorganic molecule).
2. Producer incorporates nutrients into complex organic molecules.
3. Producer eaten and nutrients passed to consumer and along food chain.
4. When producers / consumers die, complex molecules are broken down by saprobiontic microorganisms (decomposition).
5. Inorganic ion released.
Why is the nitrogen cycle important?
- Nitrogen gas (N2) is unreactive and not easily converted into other compounds
- Most plants can only take up nitrogen (by active transport in roots) in the form of nitrate
- Used by plants / animals to make proteins / nucleic acids (assimilated) - growth
What are the 4 main stages of the nitrogen cycle?
1. Nitrogen fixation
2. Ammonification
3. Nitrification
4. Denitrification
What is nitrogen fixation?
- Nitrogen gas (N2) converted (reduction) to nitrogen containing compounds e.g. ammonia
- By nitrogen-fixing bacteria:
- Can be 'free living' in the soil
- Or 'mutualistic' (live in nodules on roots of plants e.g. legumes; acquire carbohydrates from plant while the plant acquires amino acids from bacteria)
What is ammonification?
- Nitrogen-containing compounds e.g. proteins from dead organisms / animal waste broken down.
- Converted to ammonia
- Which goes on to form ammonium ions (NH4+) in the soil.
- By saprobionts secreting enzymes for extracellular digestion.
What is nitrification?
- Ammonium ions in the soil - nitrites - nitrates
- A two-stage oxidation reaction
- By nitrifying bacteria
- Bacteria need oxygen to carry out conversions
- Nutrients taken up by producer as an inorganic ion (simple inorganic molecule).
What happens in denitrification?
- Nitrates in the soil nitrogen gas
- By denitrifying bacteria (anaerobically respire)
- When low oxygen conc. in soil i.e. waterlogged
- Because more anaerobic denitrifying bacteria (and less aerobic nitrifying and nitrogen fixing bacteria)
- (Reduces availability of nitrogen compounds for plants)
How do saprobionts work?
- Feed on remains of dead plants / animals and their waste products e.g. faeces, urea, and break down the organic molecules (NAME AT LEAST ONE)
- By secreting enzymes for extracellular digestion
- Saprobionts absorb soluble needed nutrients
How do farmers prevent denitrification from happening?
- Farmers plow and aerate their soil
- Increase O2
- Allowing number of nitrifying bacteria to increase and denitrifying bacteria to decrease
- Maximise nitrogen availability
What are the stages of the phosphorous cycle?
1. Phosphate ions in rocks released (to soil) by erosion / weathering
2. Phosphate ions taken into plants by roots and incorporated into their biomass (assimilated)
- DNA, RNA, phospholipids (and NADP and RuBP in plants).
- Rate of absorption increased by Mycorrhizae
3. Phosphate ions transferred through food chain e.g. as herbivores eat plants
4. Some phosphate ions lost from animals in waste products (excretion), and plants and animals die
- Decomposed by saprobionts - release enzymes for extracellular digestion
- Release phosphate ions to the soil
How does the weathering of rocks releasing phosphate into seas, lakes and rivers contribute to the phosphorus cycle?
- Taken up by aquatic producers e.g. algae
- Passed along food chain to birds
- Guano, a waste product of birds, returns a many phosphate ions to soils in coastal areas
What is the function of fertilisers?
- Replaces nutrients (nitrates and phosphates) lost from an ecosystem's nutrient cycle when... crops are harvested and livestock (animals) removed
- Nutrients removed from soil and incorporated into their biomass can't be released back into the soil through decomposition by saprobionts
- Hence, fertilisers improve the efficiency of energy transfer (more energy can be used for growth)
- Nutrient could no longer be a limiting factor
- Increase productivity of agricultural land
What are the differences between artificial fertilisers and natural fertilisers?
Artificial
- Inorganic
- Contain pure chemicals e.g. ammonium nitrate as powders / pellets
- Inorganic substances more water soluble so larger quantities washed away, impacting the environment
Natural
- Organic
- E.g. manure, compost, sewage
- Cheaper / free but exact nutrients cannot be controlled
What is the environmental impact of fertilisers?
- Leaching of nutrients
- Rain / irrigation systems wash water-soluble compounds out of soil into waterways e.g. rivers
- Worse when more fertiliser added to field than used (excess)
How does leaching lead to eutrophication?
1. Rapid growth of algae in ponds and rivers (algal bloom)
2. Algae blocks light, preventing it from reaching plants below
3. Death of the plants below as they cannot photosynthesise
4. Aerobically respiring saprobionts decompose the dead plant matter, reducing oxygen concentration of water
5. Leading to death of aquatic organisms due to lack of dissolved oxygen for aerobic respiration
Why is leaching less likely with natural fertilisers?
- Nitrogen / phosphorous contained in organic molecules
- Organic molecules less soluble in water so need to be decomposed by saprobionts before nitrogen and phosphorous are released (as soluble inorganic molecules)
How can leeching reduce species diversity?
Favour fast growing plants e.g. grass / nettles slower-growing plants lose out less organisms who feed off them