Chemistry Unit 1 Study guide
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Matter
Anything that has mass and occupies space
Atoms
The smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical properties.
Element
A substance that consists of only one type of atom.
Chemical Symbol
Letter representation of an element
Molecule
A group of two or more atoms bonded together.
Compound
A substance formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together.
Water Vapor (Gas)
Held together by attractive forces.
They are far apart and move freely
Water (Liquid)
Held close together by attractive forces.
but the molecules can still move around
Ice (Solid)
In solid water or ice, the molecules are located in fixed patterns by attractive forces.
Still vibrates back and forth.
Energy
The capacity to move, do work, change matter, or produce that.
Kinetic Energy
the energy of an object’s motion
ex) the ball when someone kicked
Thermal Energy
The total kinetic energy of the atoms of a substance.
Potential Energy
the energy stored in a system
Chemical Potential
energy stored in the chemical bonds of a structure.
Subatomic
Smaller than an atom that include protons, neutrons, and electrons.
System
a part of the universe on which you focus your attention.
Surroundings
everything in the universe outside of the system
Macroscopic property
a characteristic of matter that is large enough to see, handle, or measure without magnification
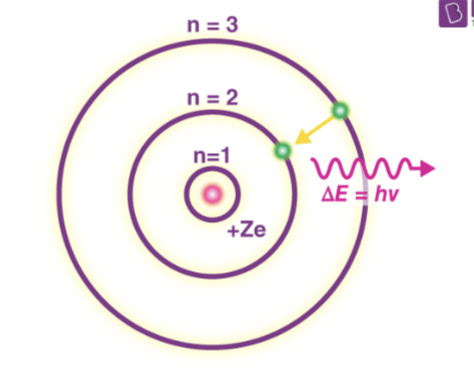
Emission Spectra
the pattern is formed when light passes through a prism or distraction.
Energy levels
the specific energies of electron in an atom or other system can have.
Quantum
the amount of energy needed to move an electron from one energy level to another
The Bohr Model
Developed to explain the hydrogen emission spectrum (but couldn’t)
Proton
Positive charge, in the nucleus
Neutron
Neutral charge, in the nucleus
Electron
Negative Charge, orbits the nucleus
Nucleus
Center of an atom (Proton+Neutron)
Automic mass
number of protons plus neutrons
Isotopes
Same number of protons, but different number of neutrons.

Dalton Model
John Dalton, Billiard ball model: Proposed that atoms are solid, indivisible particles.

Thomson’s Model
J.J. Thomson: Discovered electrons, and proposed a plum pudding model, in which atoms were thought to be positive spheres with electrons scattered inside, like raisins in a pudding.

Rutherford’s Model
Ernest Rutherford: Gold foil experiment, and discovered the nucleus. He proposed that atoms have a small, dense nucleus at the center with electrons orbiting around it, leading to the “nuclear model.”

Bohr’s Model
Niels Bohr: Planetary model, Quantized energy levels or “shells”.
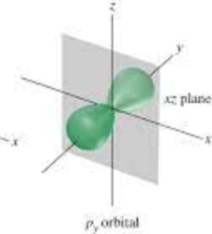
Quantum Mechanical Model
Erwin Schrodinger and others: Describes electrons as existing in probabilistic “clouds” or orbitals around the nucleus, rather than fixed orbits. It is the most accurate model used today.
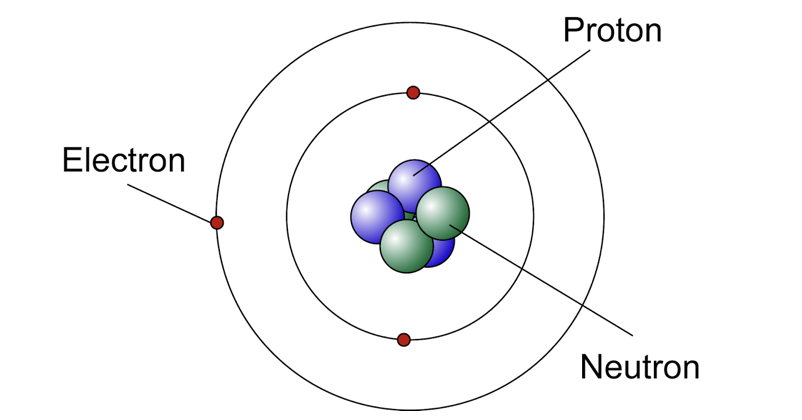
Modern Atomic Model
Central nucleus consists of protons and neutrons, the electrons are orbiting outside the nucleus in the electron shells.
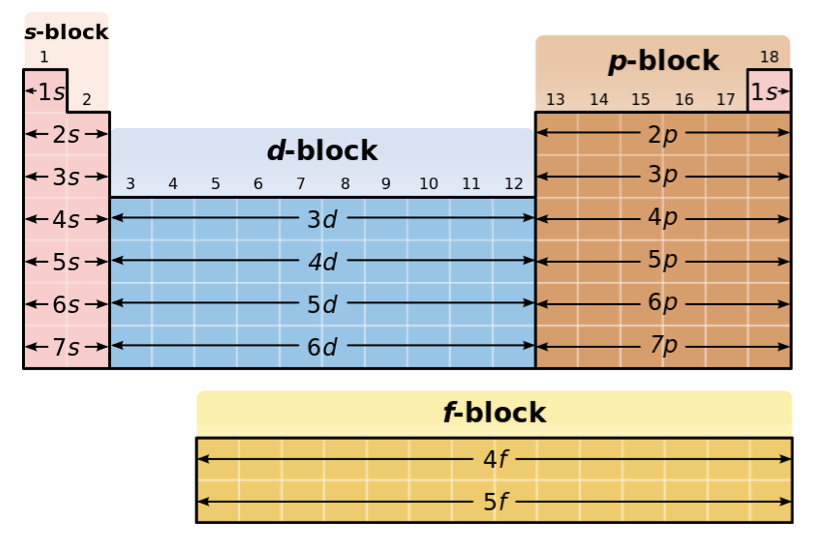
Electron Configuration
the arrangement of electrons in orbits around the atomic nucleus.
Ex) 12Mg → 1s² 2s² 2p^6 3s²
Condensed Electron Configuration
shorten ver of electron configuration
Ex) 12Mg → 1s² 2s² 2p^6 3s² → [Ne] 3s²
Valance Electron
Outmost S and P orbitals
Same group → Same number of Valance Electrons (similar chemical properties)
Ground State
the lowest allowed energy state of an atom, molecule, or ion.
Ex) 9F→ 1s² 2s² 2p^5
Excited State
energy state greater than its ground state (when a valence electron absorbs energy)
Ex) 9F^+ → 1s² 2s^1 2p^5 3s^1