lower leg and ankle- applied kinesiology
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
what is a complex arrangement of 26 bones and 34 joints?
the lower leg and ankle
what is the function of the lower leg?
functions as both as a mobile adaptor and as a rigid lever
within 1 second
what is the most common orthopedic injuries sustained?
ankle injuries
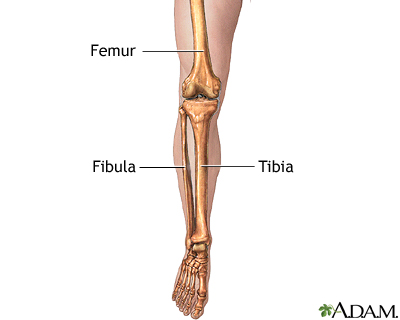
what are the bones of the lower leg?
tibia
fibula
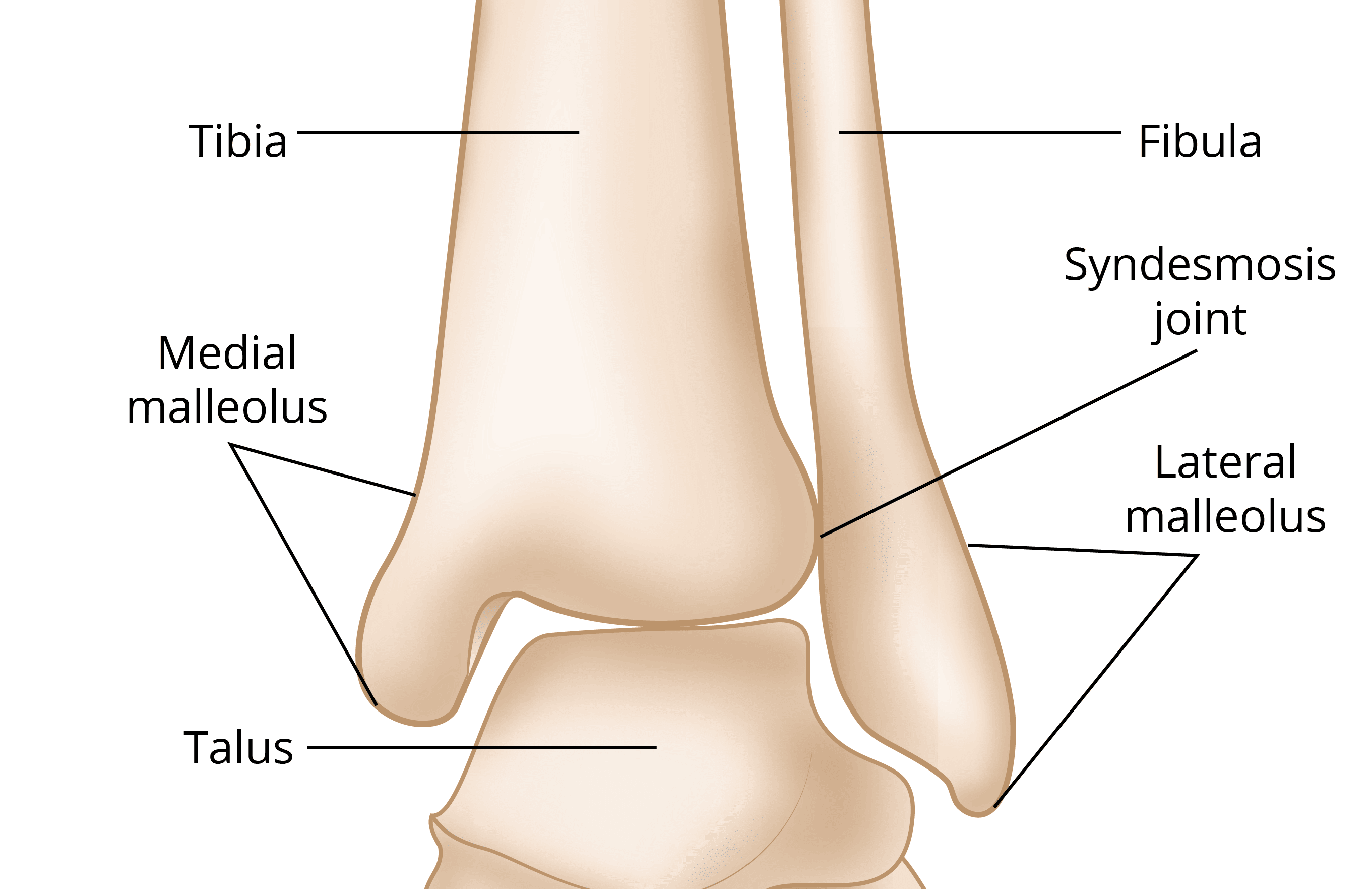
which contains the medial malleoli?
tibia
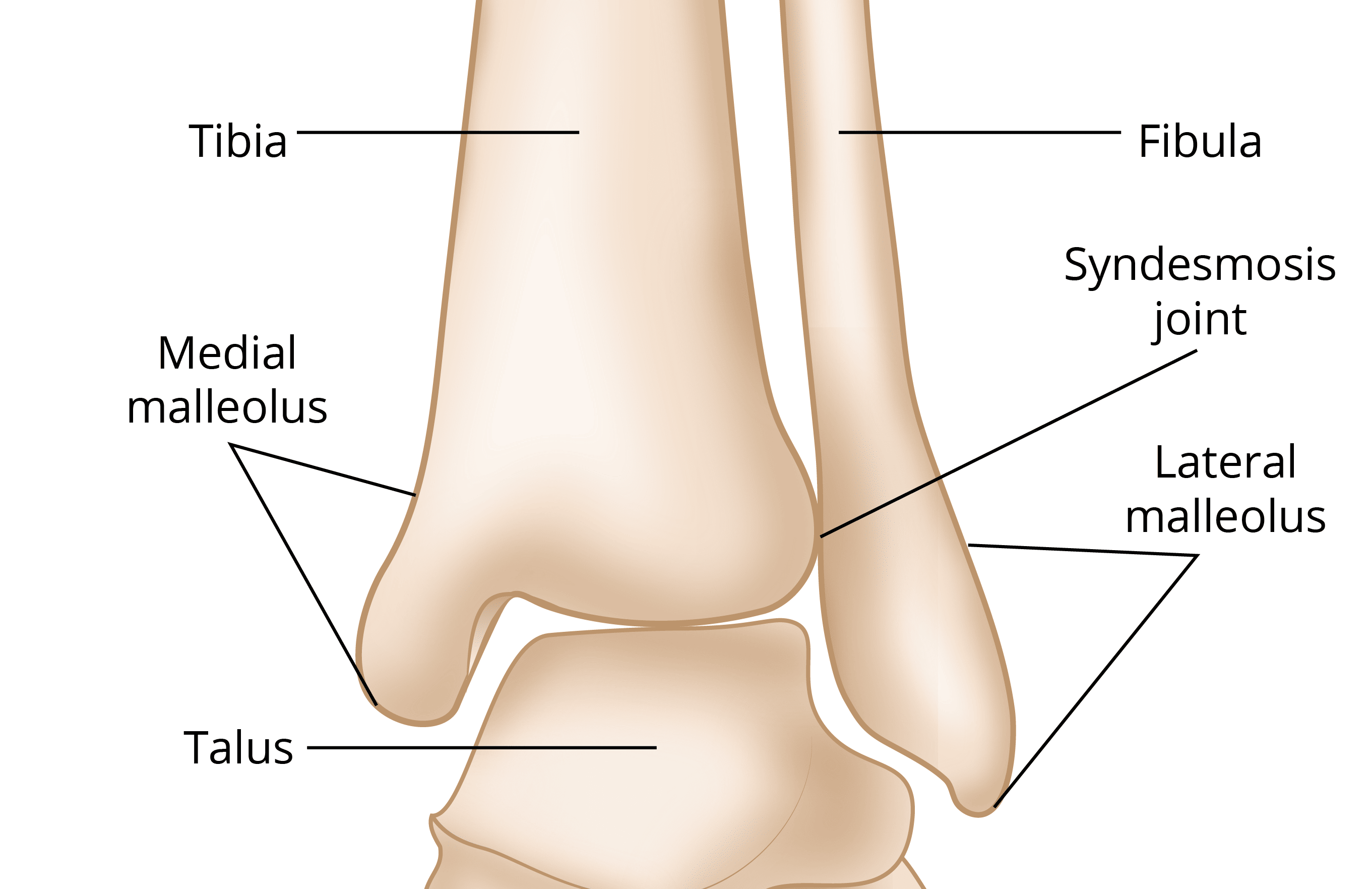
which contains the lateral malleoli?
fibula, it is longer and projects further than medial
which of the lower leg is the major weight bearing bone?
tibia
how much weight does the fibula bear?
about 10% of body weight
what are the tarsal bones?
cuneiforms
cuboid
navicular
calcaneus
talus
*go in shape of a C and start with C
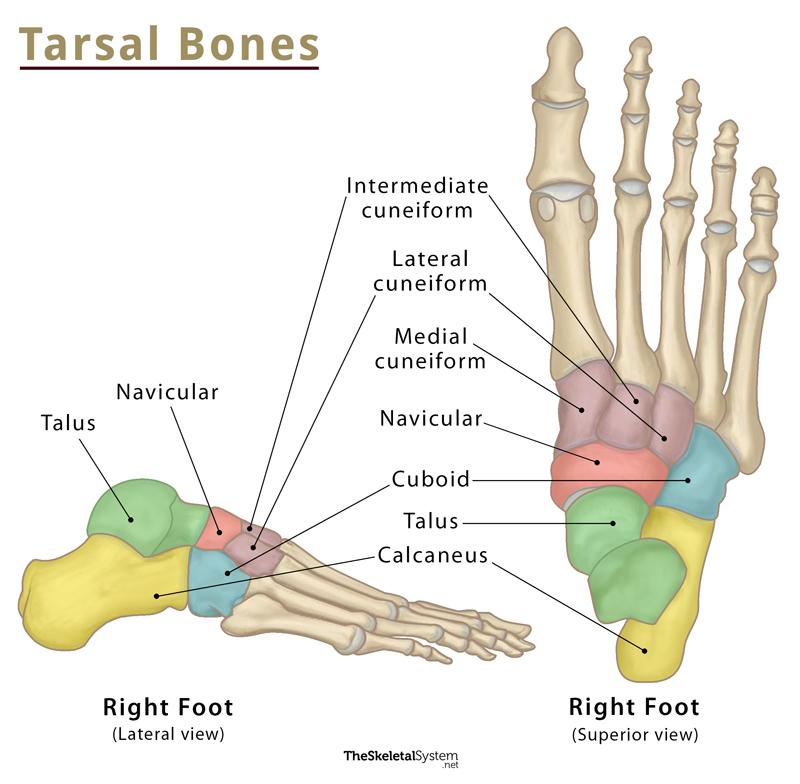
how many cuneiforms are there?
medial (1st)
intermediate (2nd)
lateral (3rd)
what are the landmarks of the tarsal bones?
talus
calcaneus
navicular tuberosity
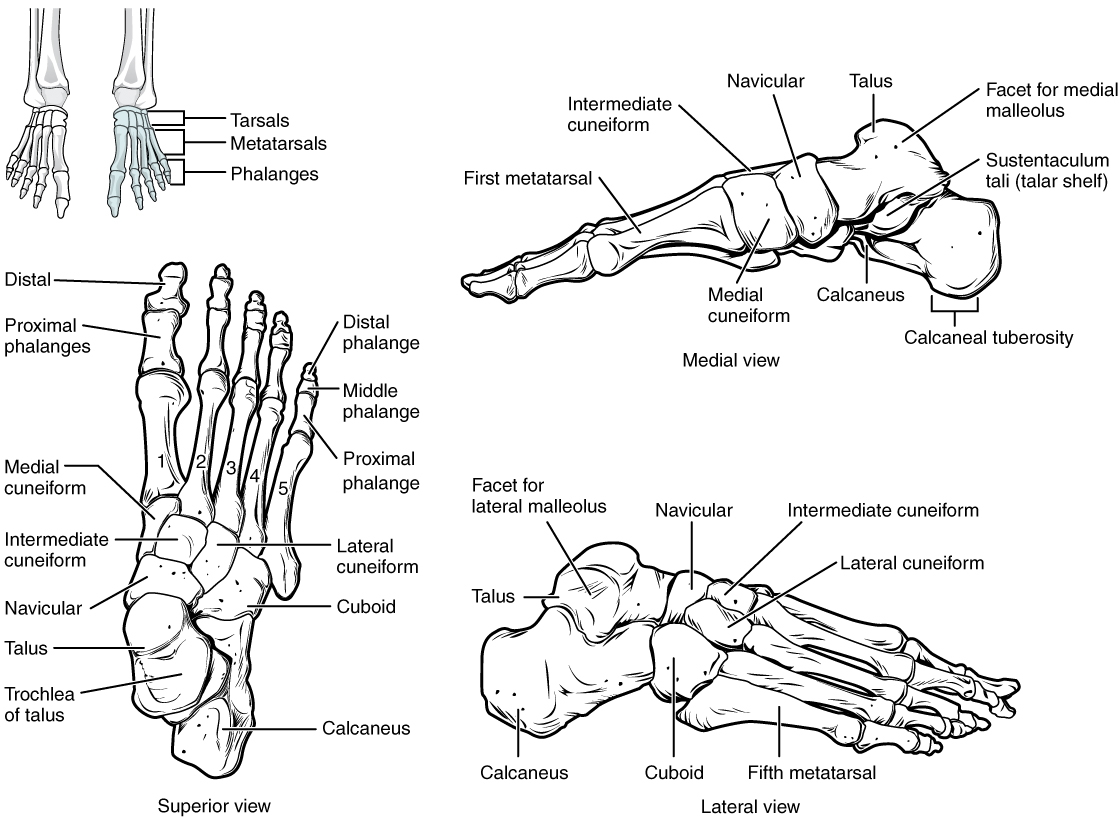
does the talus have any muscular attachments?
no muscular attachments, but has ligaments
what is the talus composed of?
head
neck
body
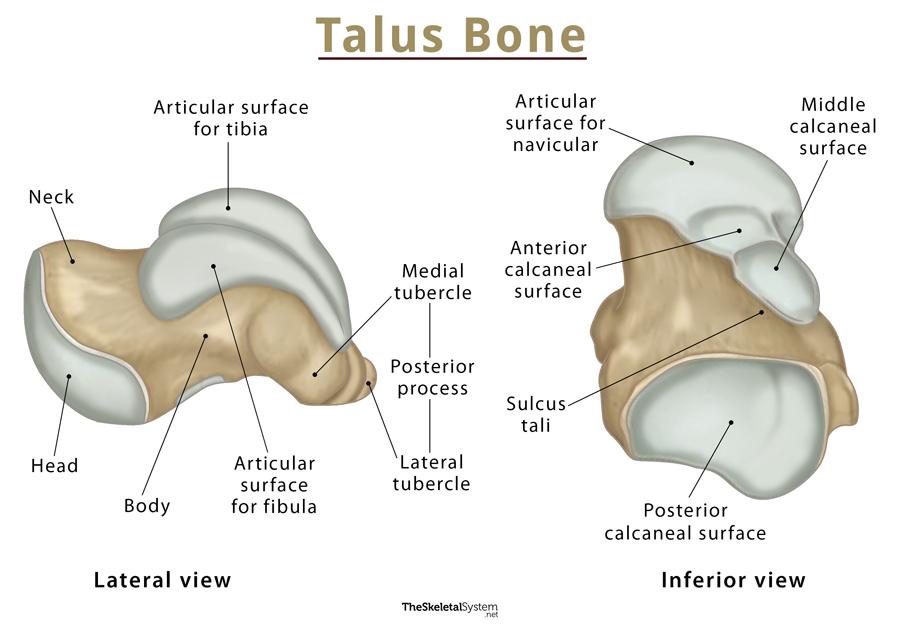
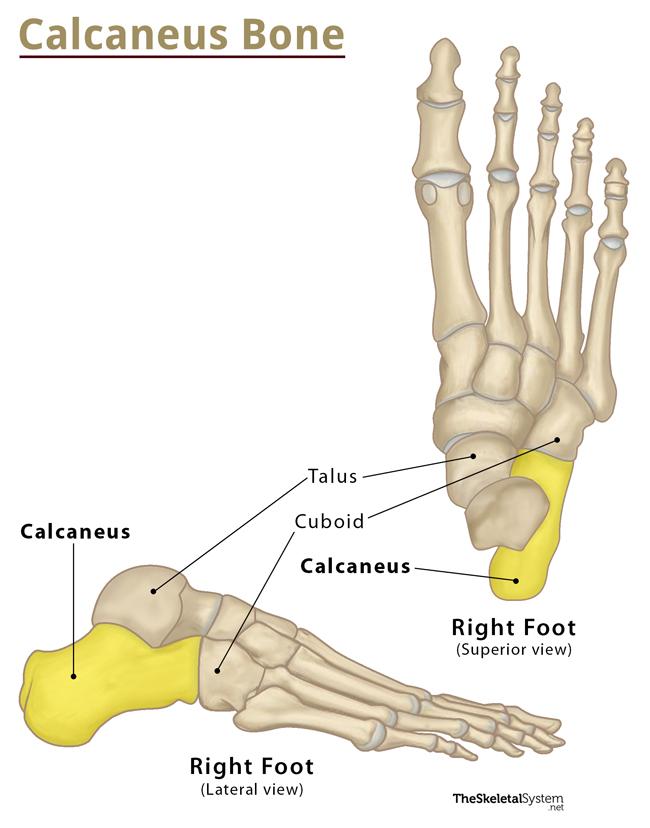
what is the calcaneus?
longest and strongest tarsal bone
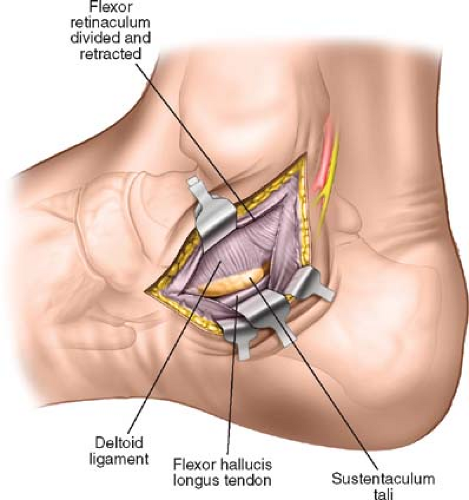
what is an important landmark of the calcaneus?
sustentaculum tali
what is the sustentaculum tali?
shelf of calcaneus where tali sits on
what is the navicular tuberosity?
attachment sites for tibialis posterior
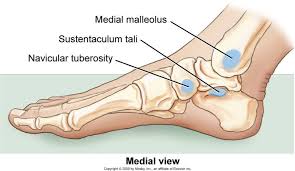
what happens if you're flat footed?
basically walking on navicular tuberosity
what are the bones of the foot?
metatarsals
phalanges
what do the metatarsals look like?
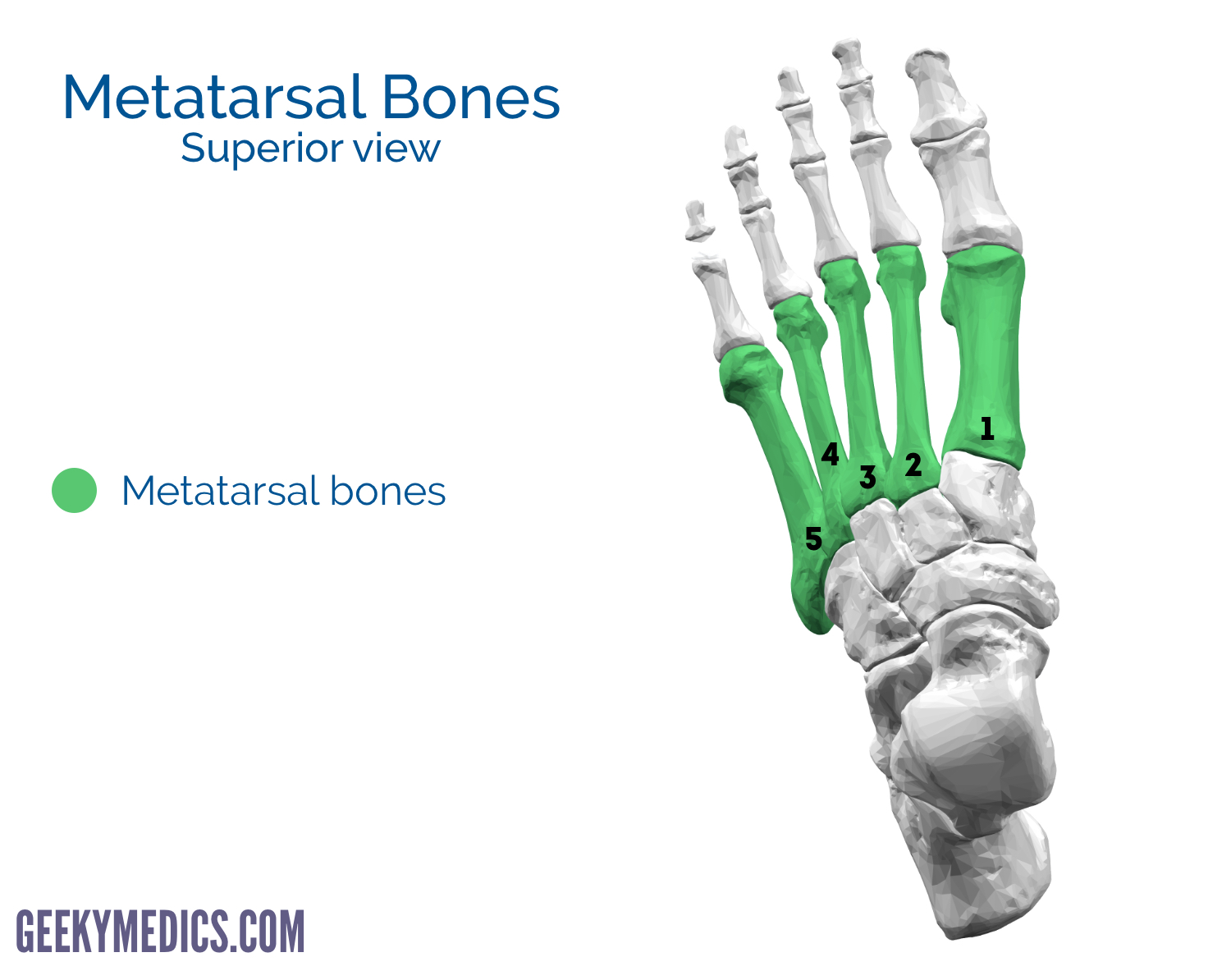
what are the landmarks of the metatarsals?
base
shaft
head
what is the styloid process of the 5th metatarsal?
insertion site for peroneus brevis
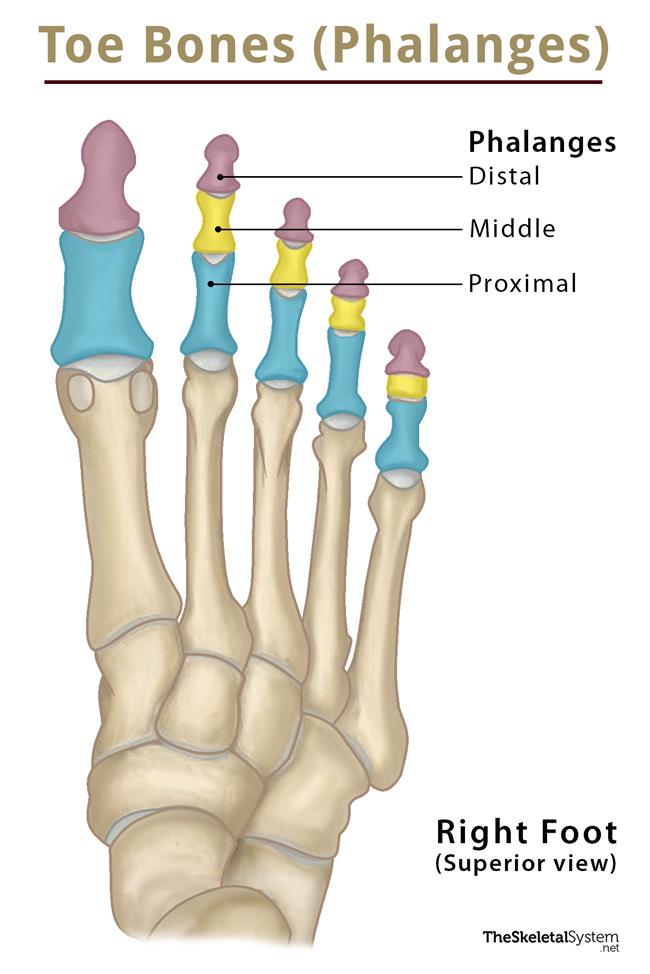
how are the phalanges of the foot based on?
distal
middle
proximal
what are the landmarks of the phalanges of the foot?
base
shaft
head
what do the phalanges of the foot look like?
are there sesamoid bones at the foot?
yes, there are sesamoid bones at the foot
where can the sesamoid bone at the foot be found?
head of first metatarsal and lie in the tendons of the flexor hallucus brevis
can we fracture our sesamoid bones at the foot?
yes they can be fractured
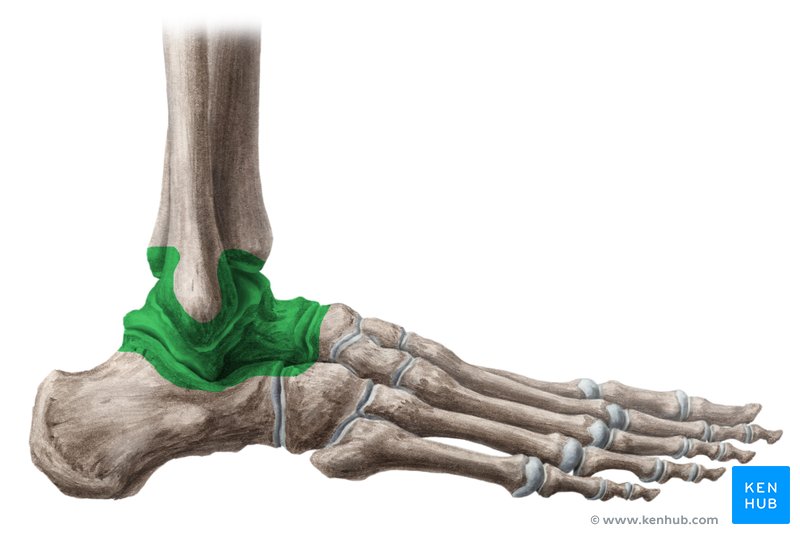
what are the joints of the ankle complex?
distal tibiofibular joint
talocrural joint
subtalar joint
what type of joint is the tibiofibular joint?
syndesmosis joint
what are the ligaments of the tibiofibular joint?
anterior inferior tibiofibular (AITF)
posterior inferior tibiofibular (PITF)
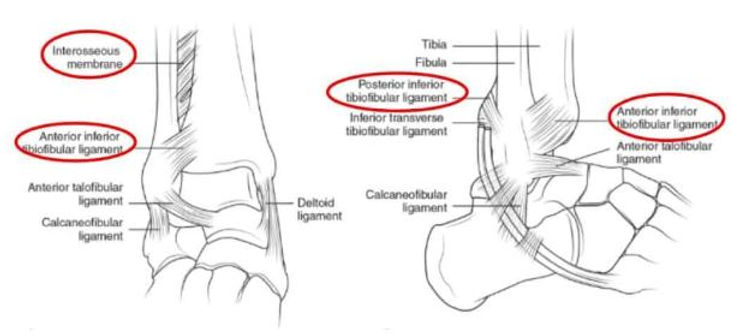
what is the talocrural joint?
known as the ankle joint
what can the talocrural joint also be classified as?
mortise joint
tibiotalar joint
fibulotalar joint
what are the motions of the talocrural joint?
plantar flexion
dorsiflexion
how many DOF does the talocrural joint have?
1 DOF
what are the lateral ligaments of the talocrural joint?
anterior talofibular (ATF)
posterior talofibular (PTF)
calcaneofibular (CF)

which ligament of the talocrural joint will be the 1st to be injured in an ankle sprain?
anterior talofibular (ATF)
which ligament of the talocrural joint will be 2nd to be injured in an ankle sprain?
calcaneofibular (CF)
what does a grade 3 ankle sprain mean?
DOESNT mean you have tore all 3
what are the medial ligaments of the deltoid ligament?
anterior tibiotalar
tibionavicular
tibiocalcaneal
posterior tibiotalar
what is the deltoid ligament?
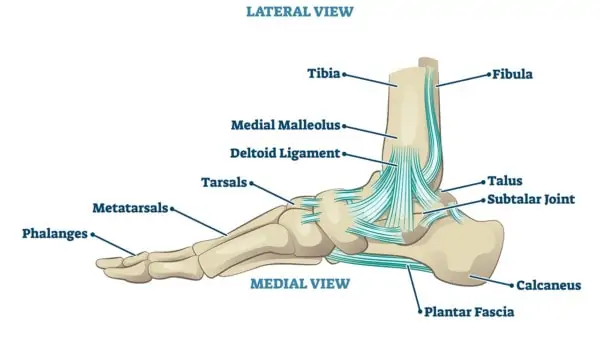
what does the deltoid ligament do?
restrict eversion
where do we have more ankle injuries?
more ankle injuries laterally than medial
what is the subtalar joint?
below talis
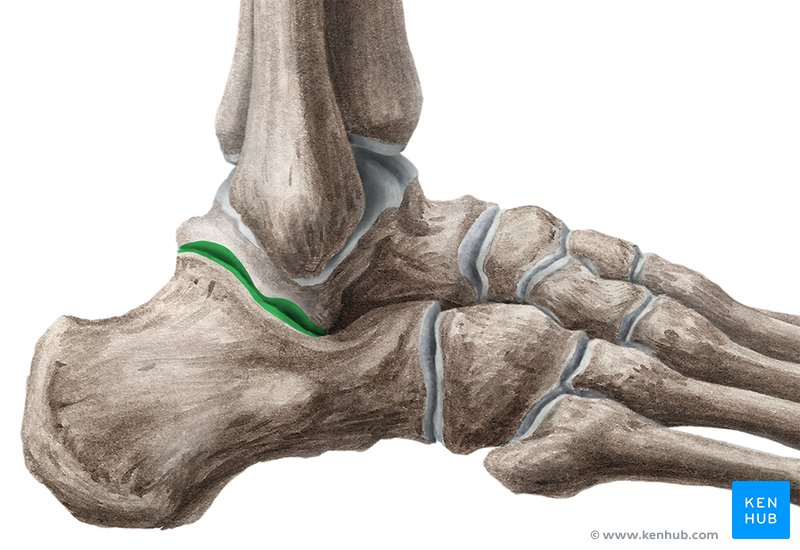
what are the 3 articulations of the subtalar joint?
anterior
middle
posterior
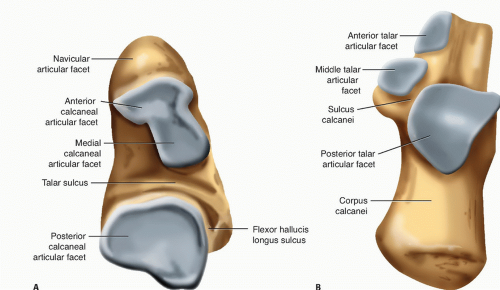
what are the motions of the subtalar joint?
inversion
eversion
rotation
what is the sinus tarsi?
small bony cancel that separates anterior to posterior articulations
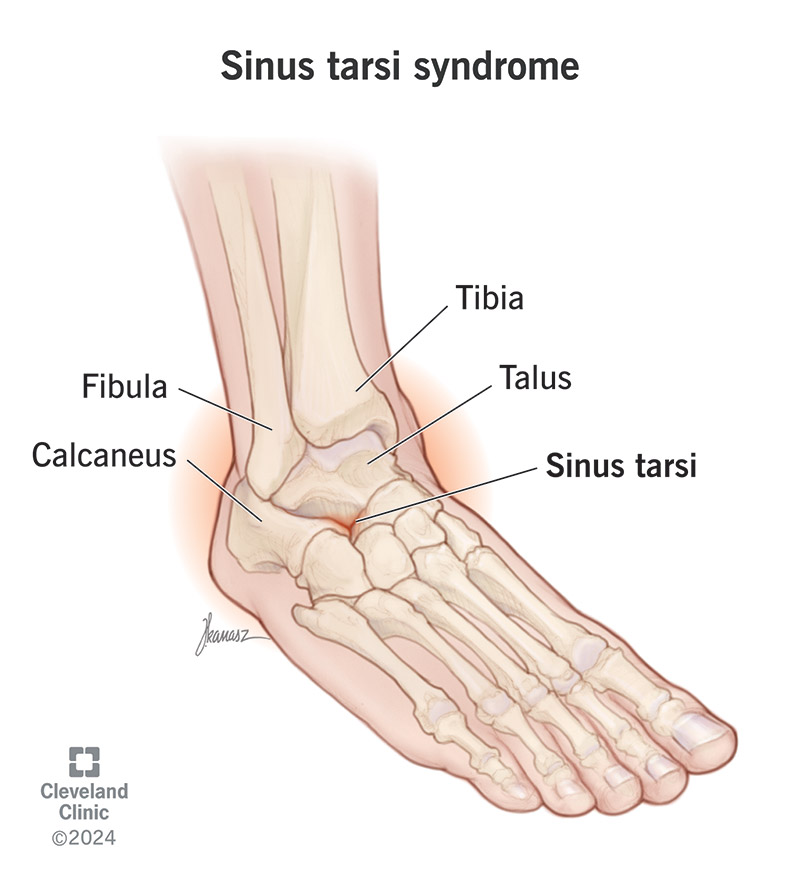
when we sprain our ankle, where does the swelling go?
sinus tarsi
what are the ligaments of the subtalar joint?
interosseous ligament
cervical ligament
what does the interosseous ligament of the subtalar joint do?
end range inversion
what does the cervical ligament of the subtalar joint do?
end range eversion
what are the joints of the foot?
interphalangeal joints
(DIP, PIP)
metatarsophalangeal joints
intermetatarsal joints
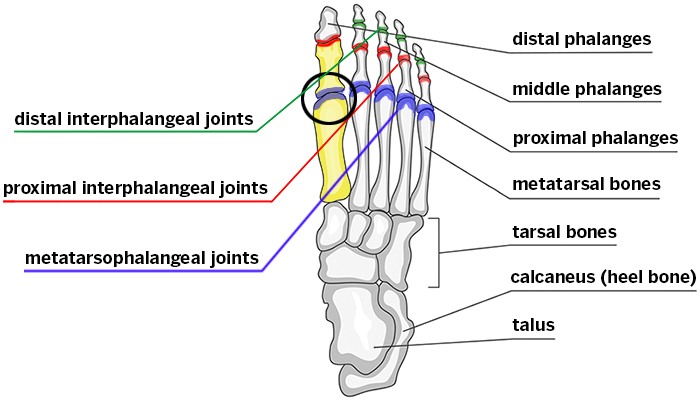
what are the other joints of the foot?
intermetatarsal joints
tarsometatarsal joints
(lisfranc joint)
intertarsal joints
where is the tarsometatarsal joints of the foot?
they form transverse metatarsal arch
what does the intertarsal joints look like?
“s” shaped, start from talonavicular joint to the calcaneocuboid joint
what do the 1,3,4,5th metatarsals do?
they all rotate around the stable 2nd metatarsal
which metatarsal joint is the most stable?
2nd is the most stable joint
what is the lisfranc joint?
medial cuneiform to base of 2nd metatarsal
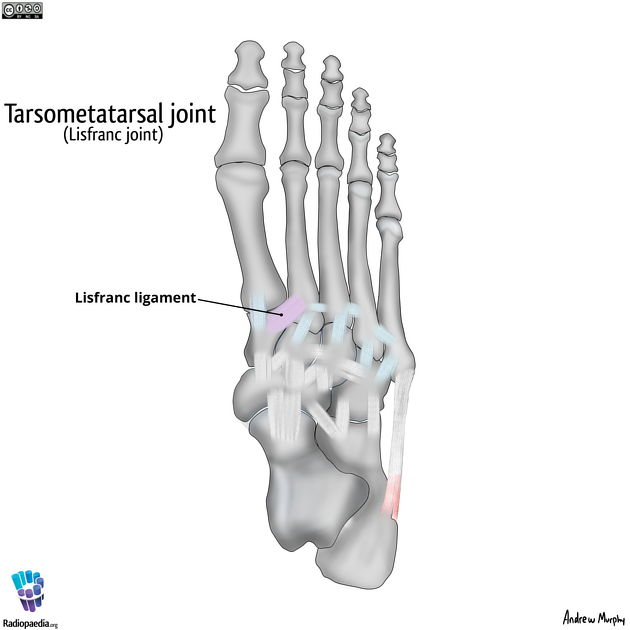
what are the intertarsal ligaments?
spring ligament
short plantar ligament
long plantar ligament
bifurcate ligament
what is the bifurcate ligament?
supports transverse tarsal metatarsal joint
what are the movements of the bifurcate ligament?
eversion
inversion
what is plantar fascia?
plantar aponeurosis
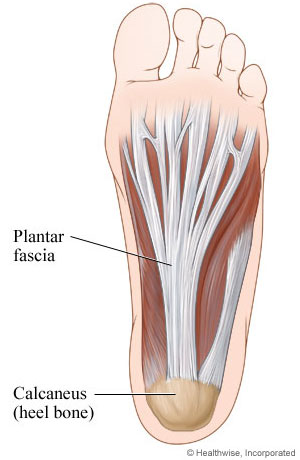
plantar fascia
O: medial tubercle of calcaneus
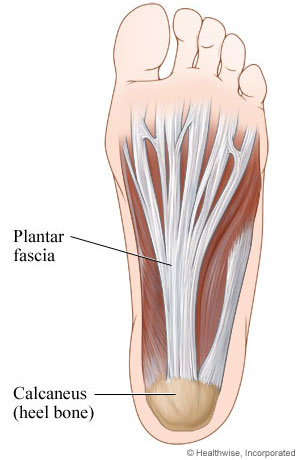
what does the plantar fascia look like?
will band out and bands out to base of toes
what are the arches of the foot?
medial longitudinal arch
lateral longitudinal arch
transverse tarsal arch
transverse metatarsal arch
which arch of the foot is the longest and highest?
medial longitudinal arch
in what plane does dorsiflexion and plantar flexion occur?
sagittal plane
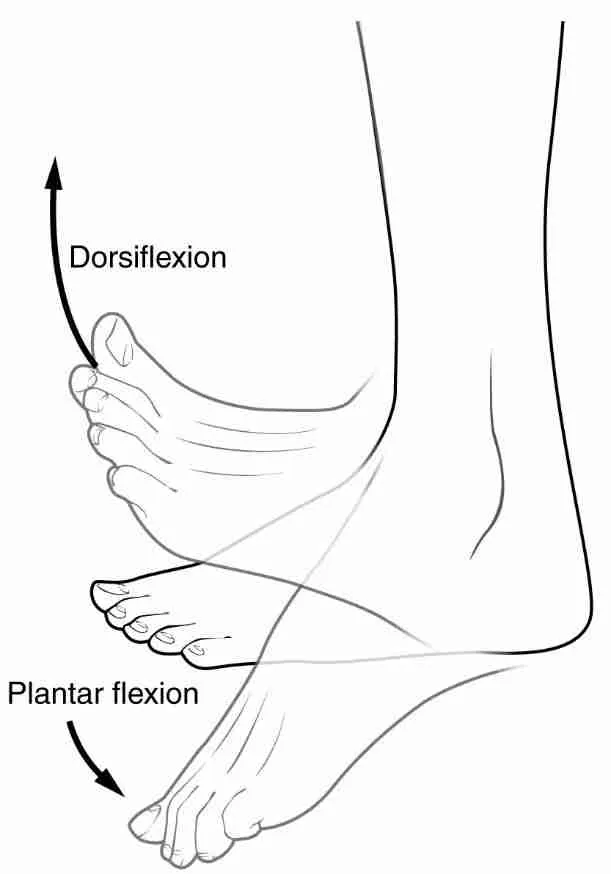
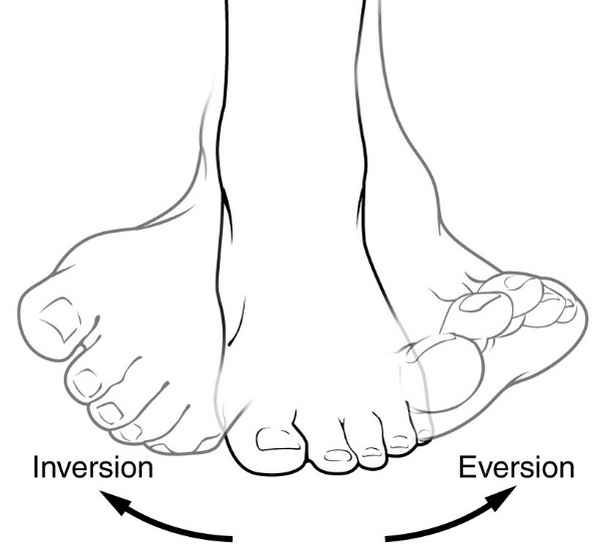
in what plane does inversion and eversion of the foot occur?
frontal plane
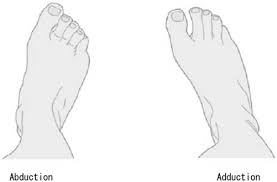
in what plane does abduction and adduction of the foot occur?
transverse plane
how many DOF does the foot have of pronation and supination?
1 DOF
what are the motions of pronation of the foot?
everesion
abduction
dorsiflexion
what are the motions of supination of the foot?
inversion
adduction
plantaflexion
motion of pronation and supination occurs in how many planes?
occurs in 3 planes
how many extrinsic muscles are there of the foot?
12
how many compartments of the extrinsic muscles are there?
4 well defined compartments
what are the 4 muscular compartments?
anterior
lateral
deep posterior
superficial posterior
what are the muscular compartments separated by?
intramuscular septa
what muscles are on the anterior compartment?
anterior tibialis
extensor hallucis long
extensor digitorum long
peroneus tertius
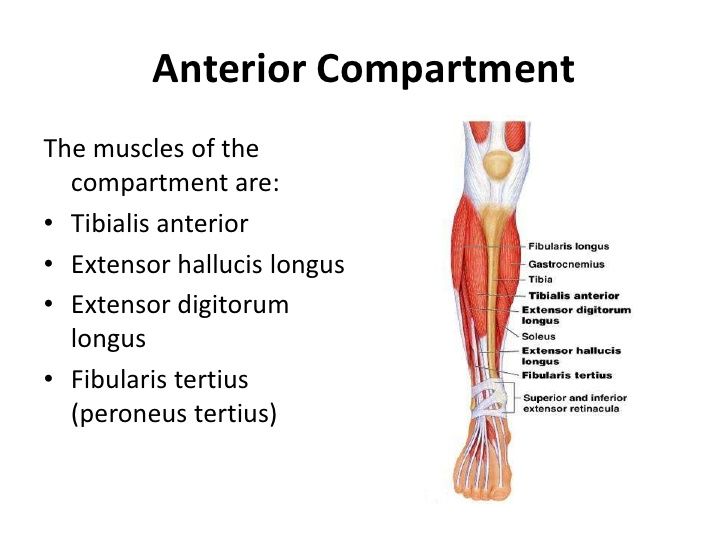
what nerves are on the anterior compartment?
deep peroneal nerve
anterior tibial artery
what does the tibialis anterior look like?
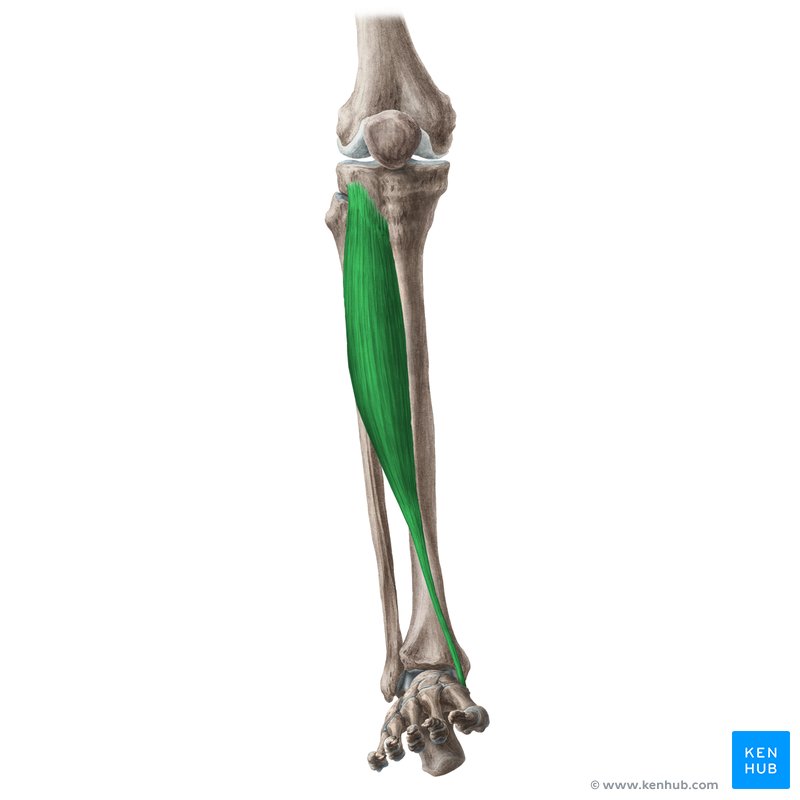
tibialis anterior
O: lateral condyle of tibia and prox ½ of lateral tibia
I: 1st cuneiform and base of 1st metatarsal
A: ankle dorsiflexion and inversion
N: deep peroneal
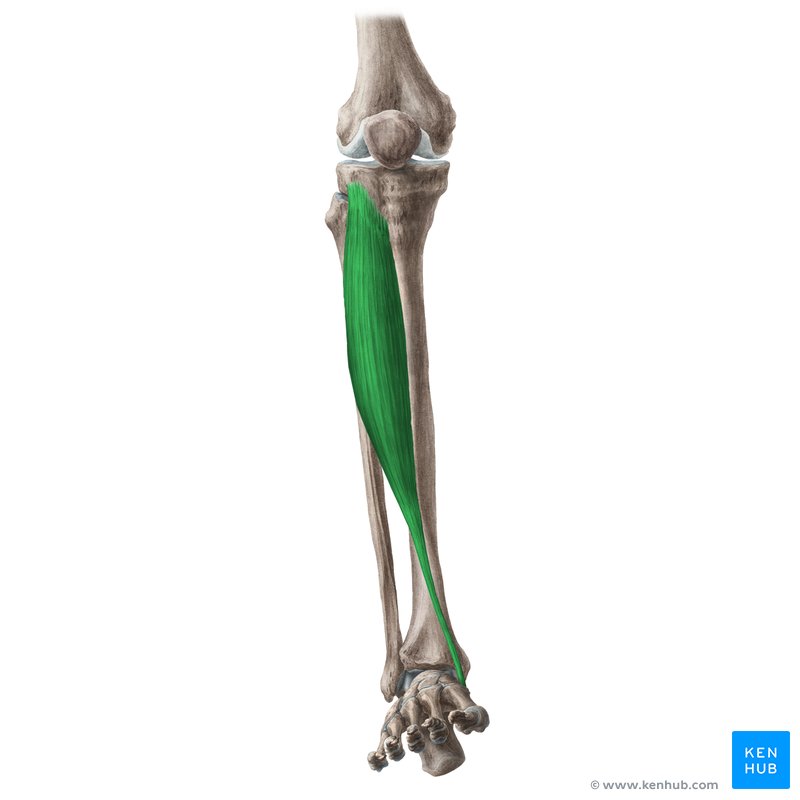
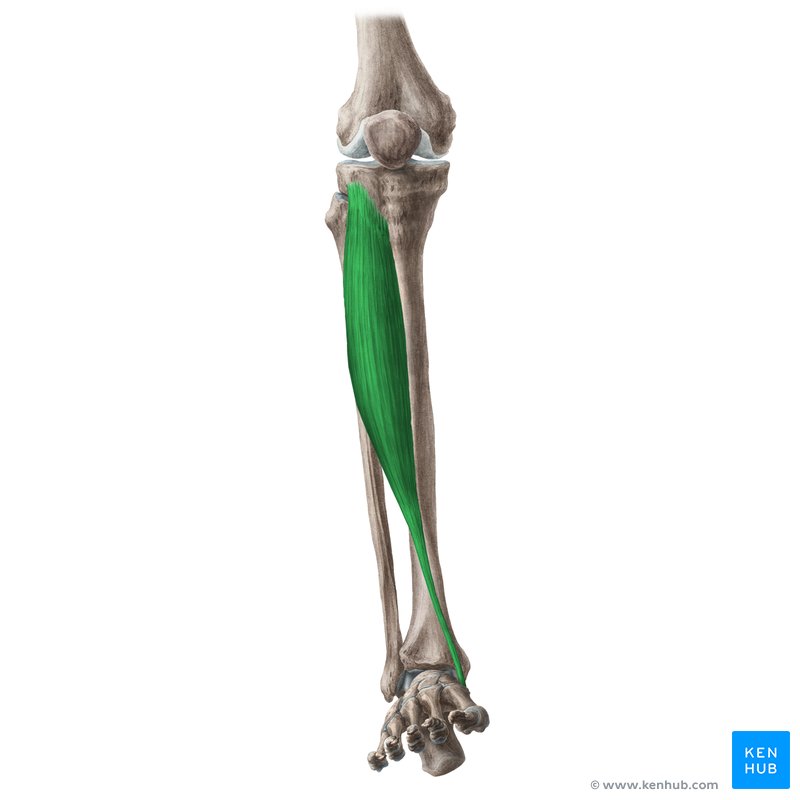
tibialis anterior origin?
lateral condyle of tibia and prox ½ of lateral tibia
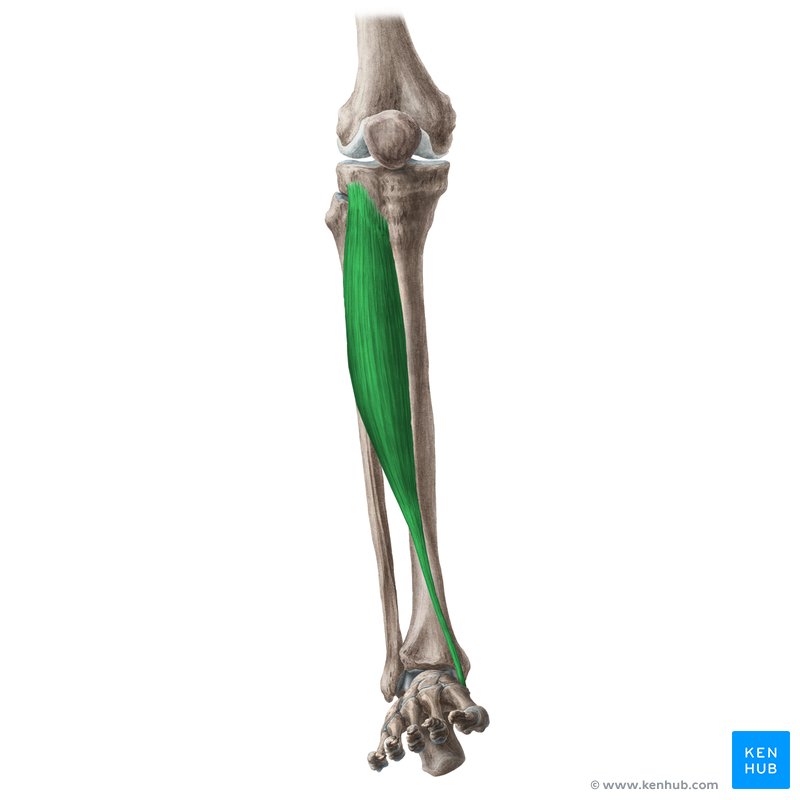
tibialis anterior insertion?
1st cuneiform and base of 1st metatarsal
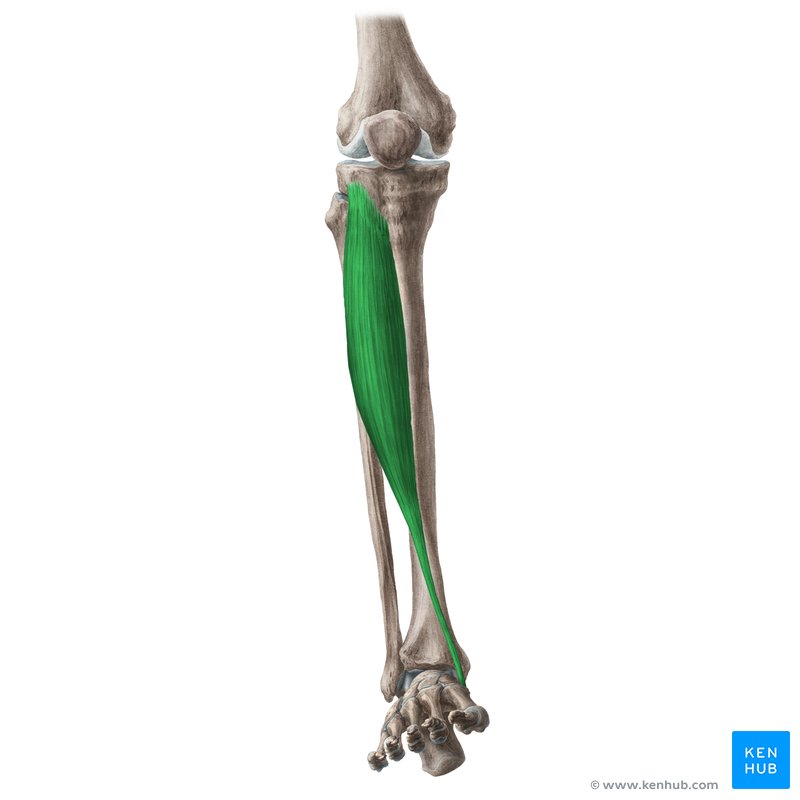
tibialis anterior action?
ankle dorsiflexion and inversion
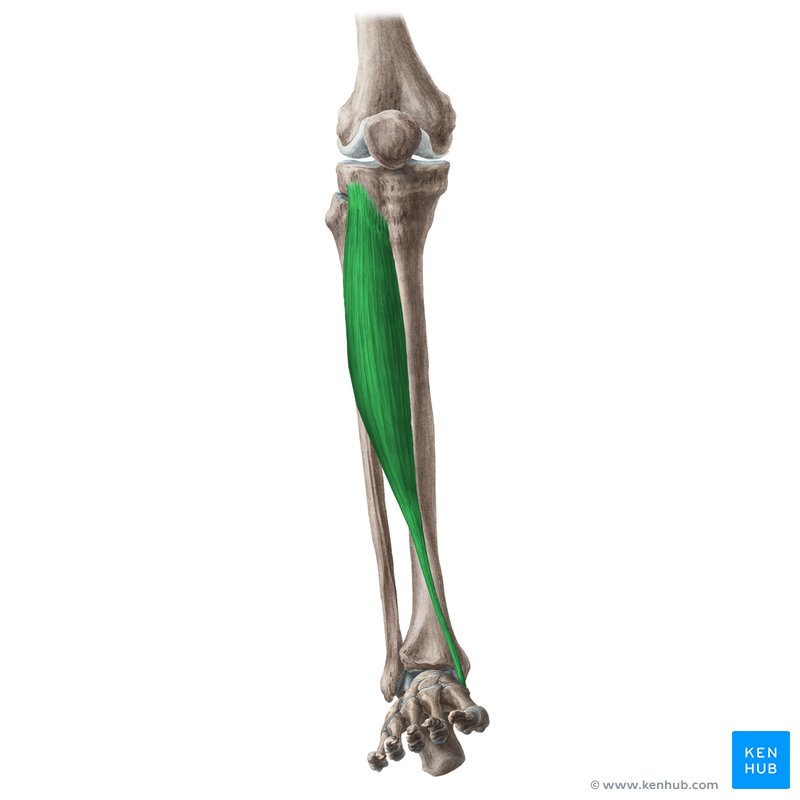
tibialis anterior nerve?
deep peroneal nerve
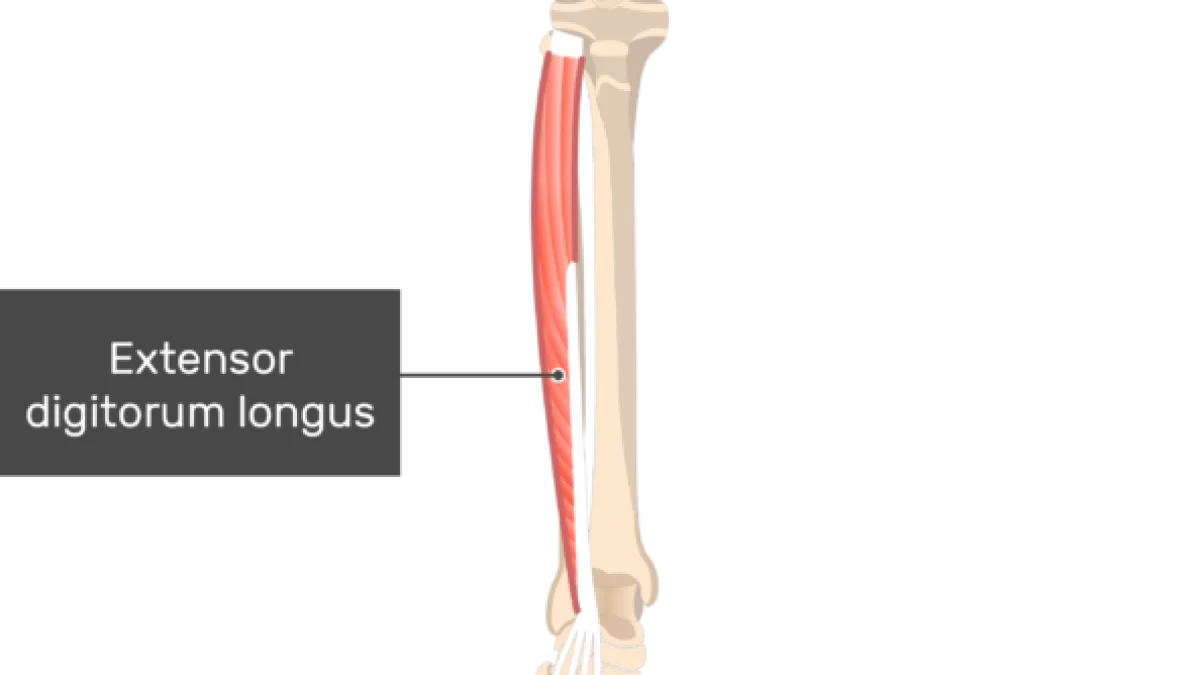
what does the extensor digitorum longus look like?
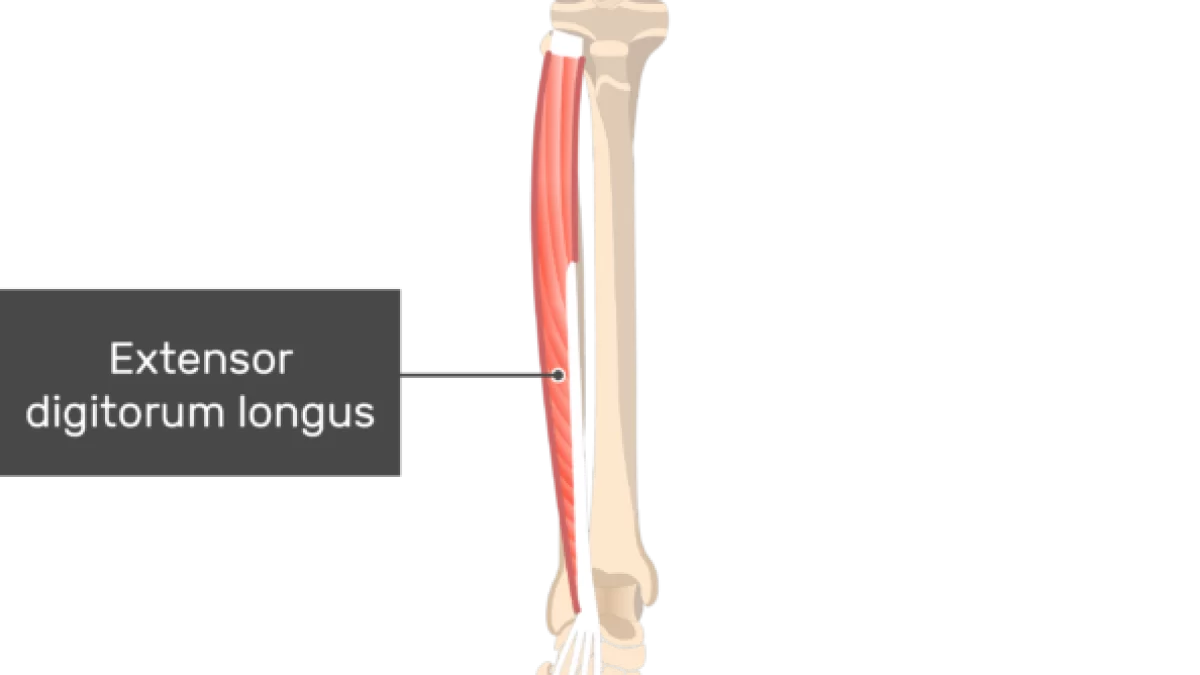
extensor digitorum longus
O: lateral condyle of tibia, proximal fibula
I: bases of the middle and distal phalanges of 4 lesser toes
A: dorsiflexion, eversion, extension of toes
N: deep peroneal
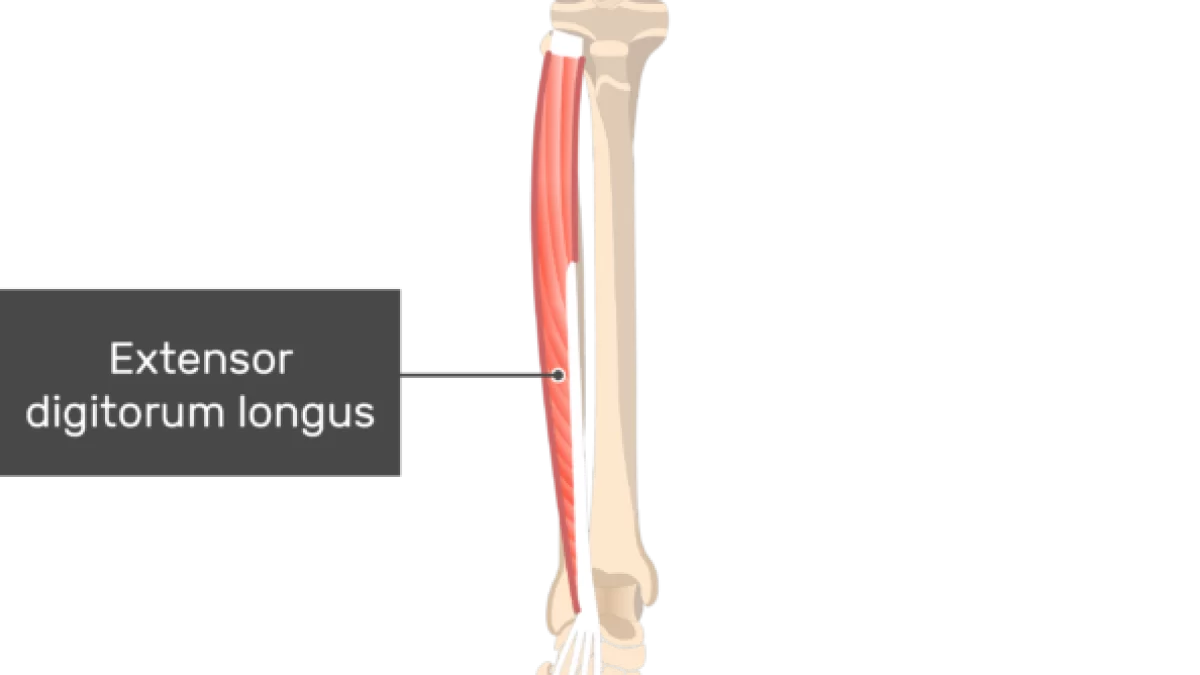
extensor digitorum longus origin?
lateral condyle of tibia, proximal fibula
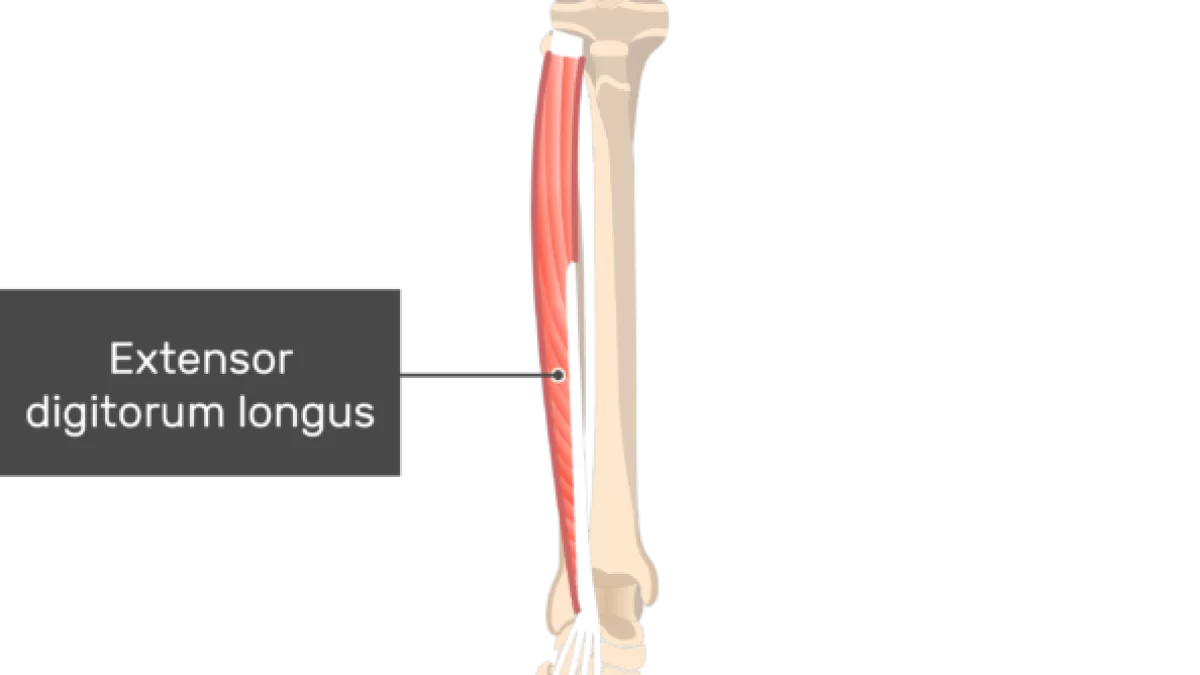
extensor digitorum longus insertion?
bases of middle and distal phalanges of 4 lesser toes
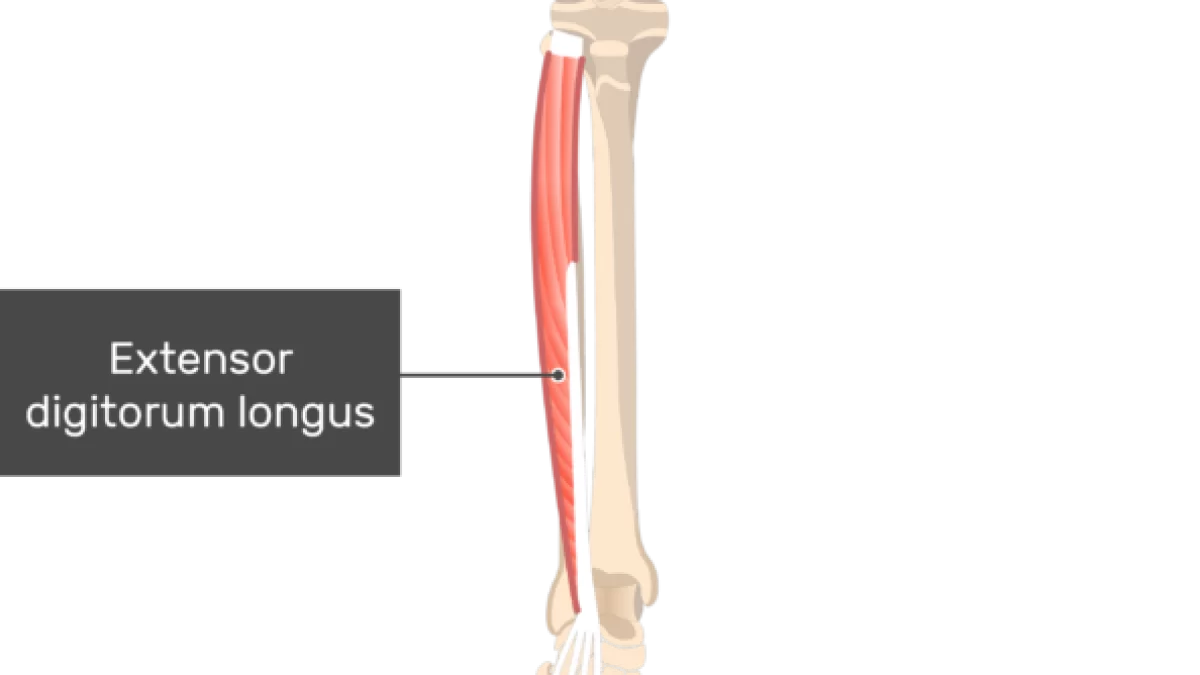
extensor digitorum longus action?
dorsiflexion, eversion, extension of toes
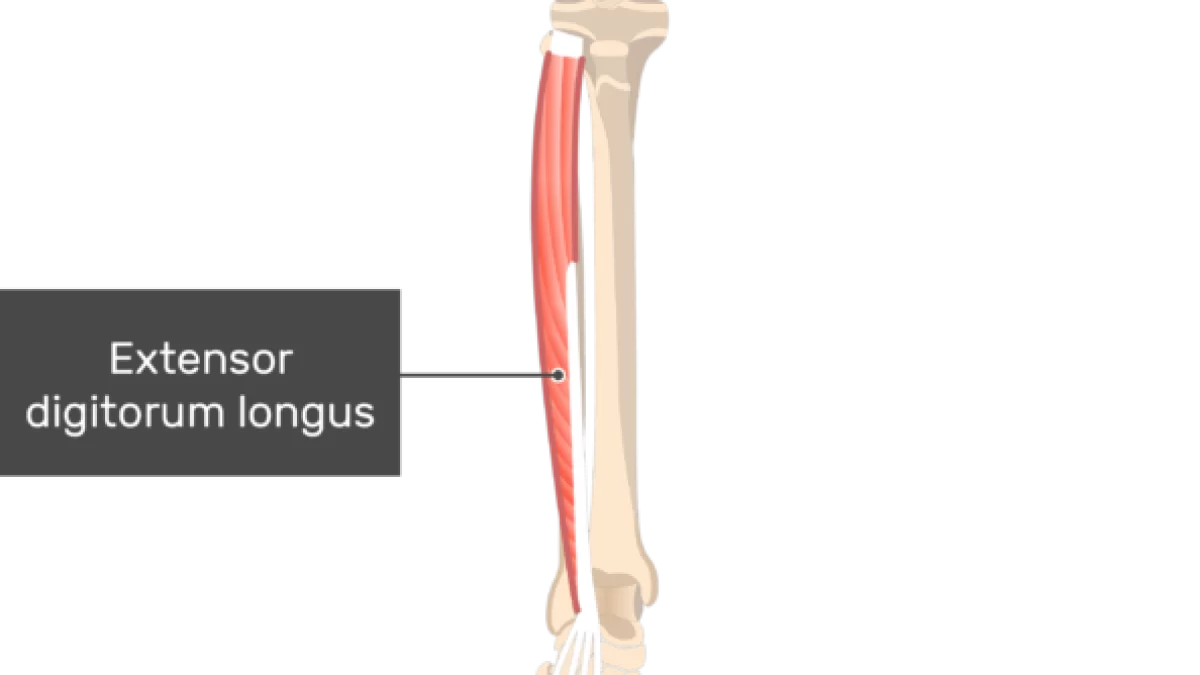
extensor digitorum longus nerve?
deep peroneal nerve
what does the extensor hallucis Longus look like?
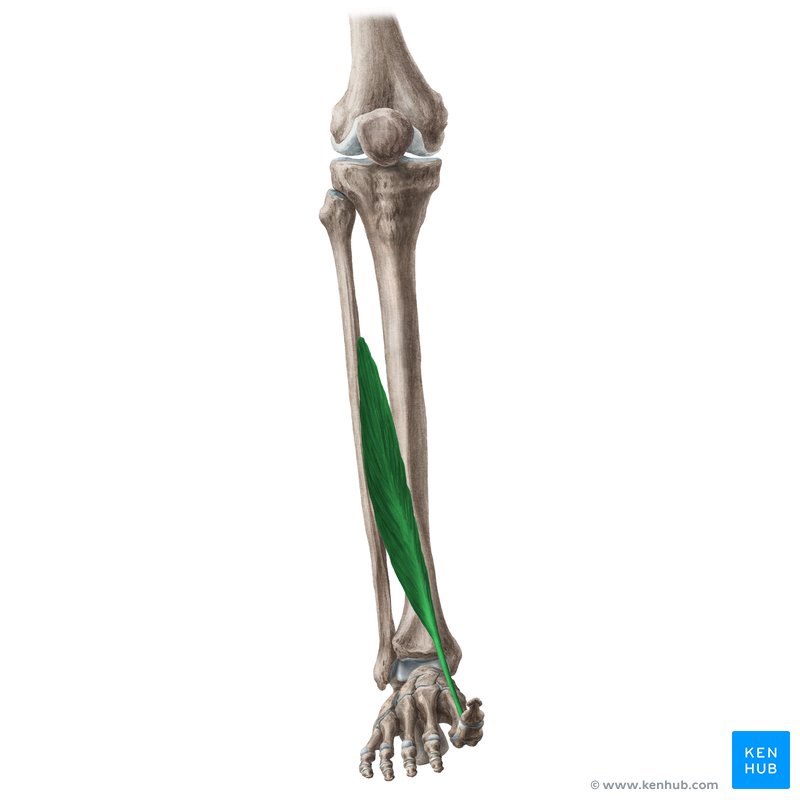
extensor hallucis longus
O: middle 1/3 of fibula
I: base of distal phalanx of great toe
A: dorsiflexion, inversion, extension of great toe
N: deep peroneal
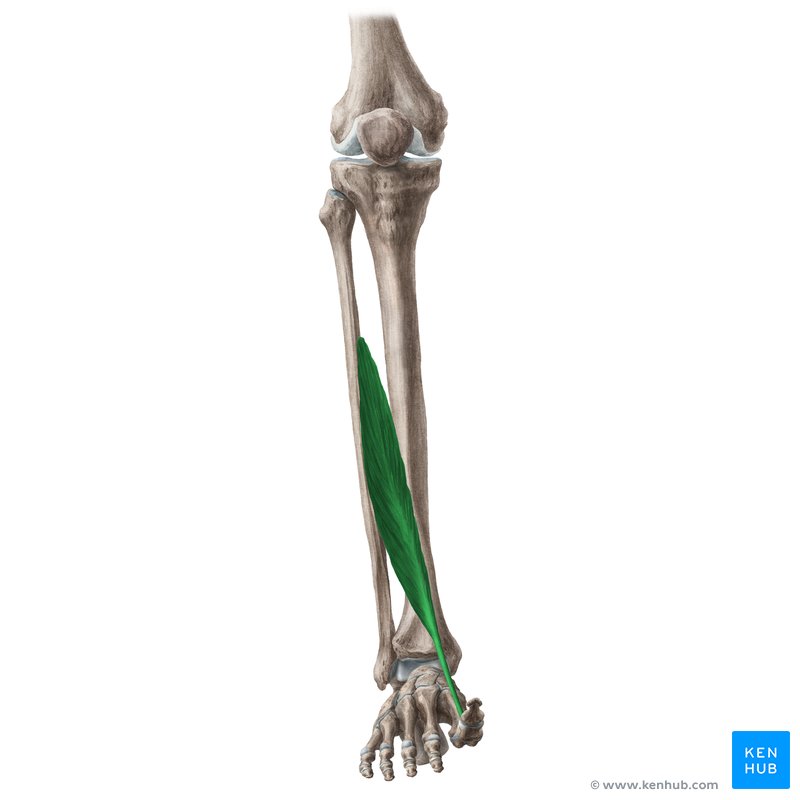
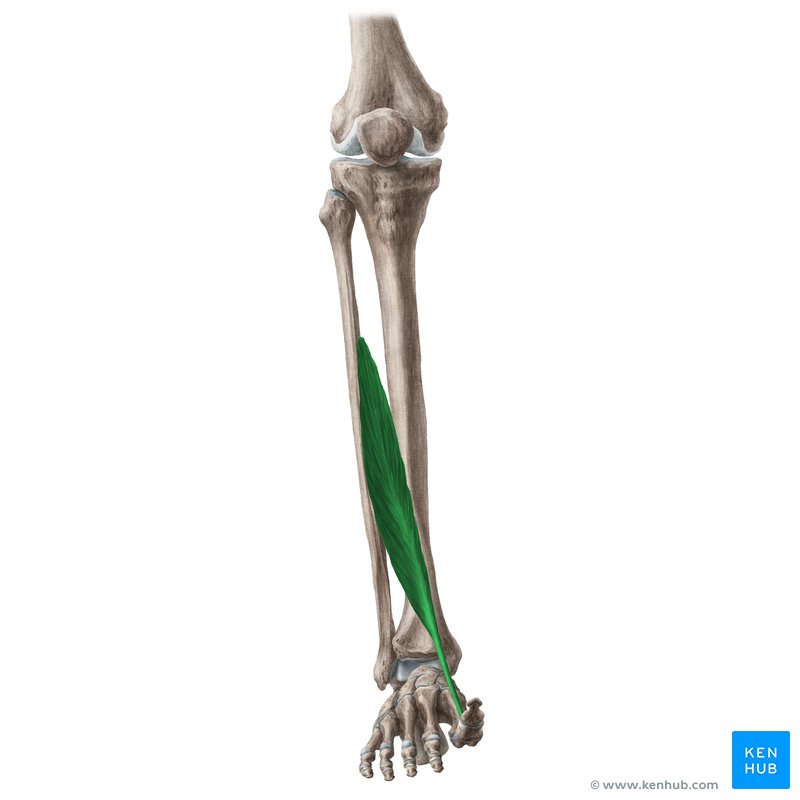
extensor hallicus Longus origin?
middle 1/3 of fibula
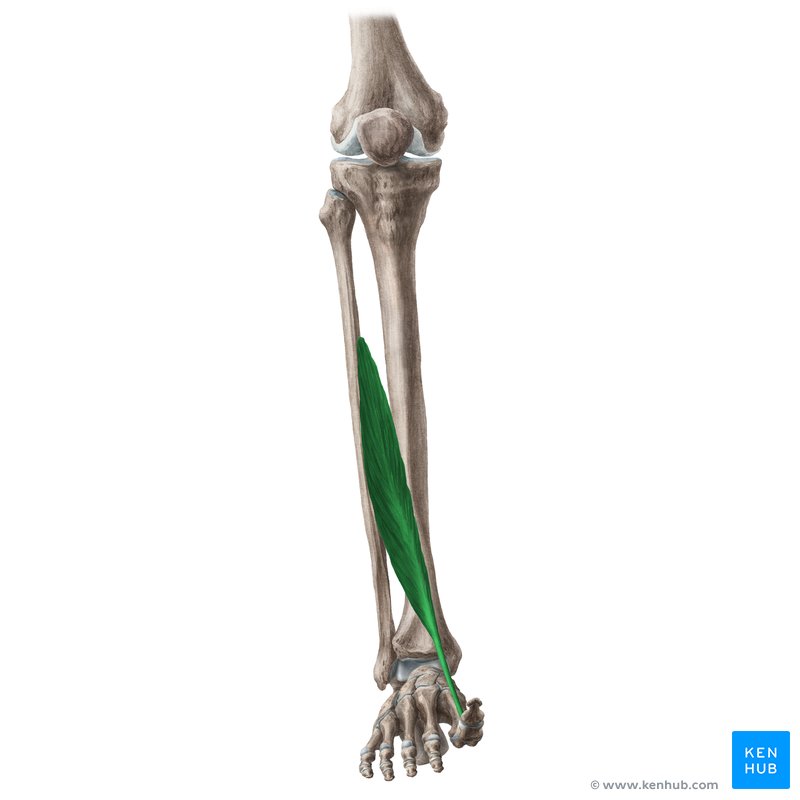
extensor hallicus Longus insertion?
base of distal phalanx of great toe
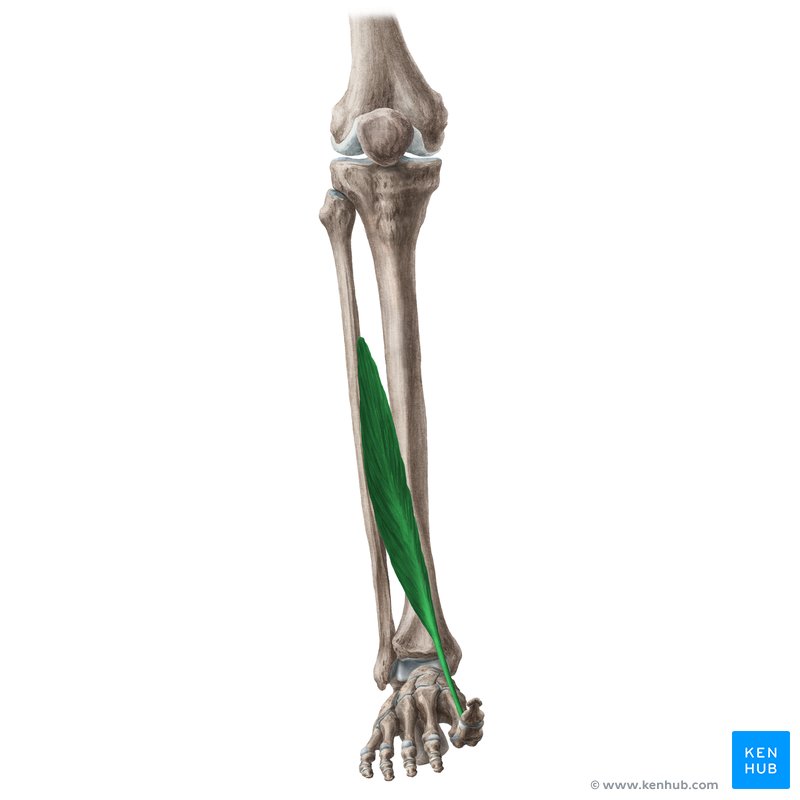
extensor hallicus longus action?
dorsiflexion, inversion, extension of great toe
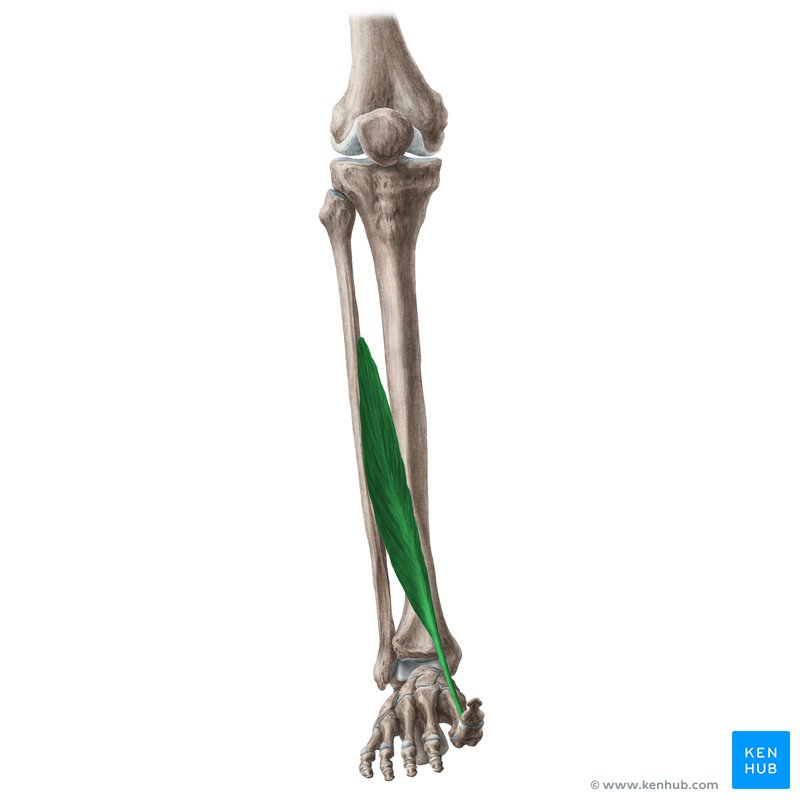
extensor hallicus Longus nerve?
deep peroneal nerve
what does the peroneus Tertius look like?
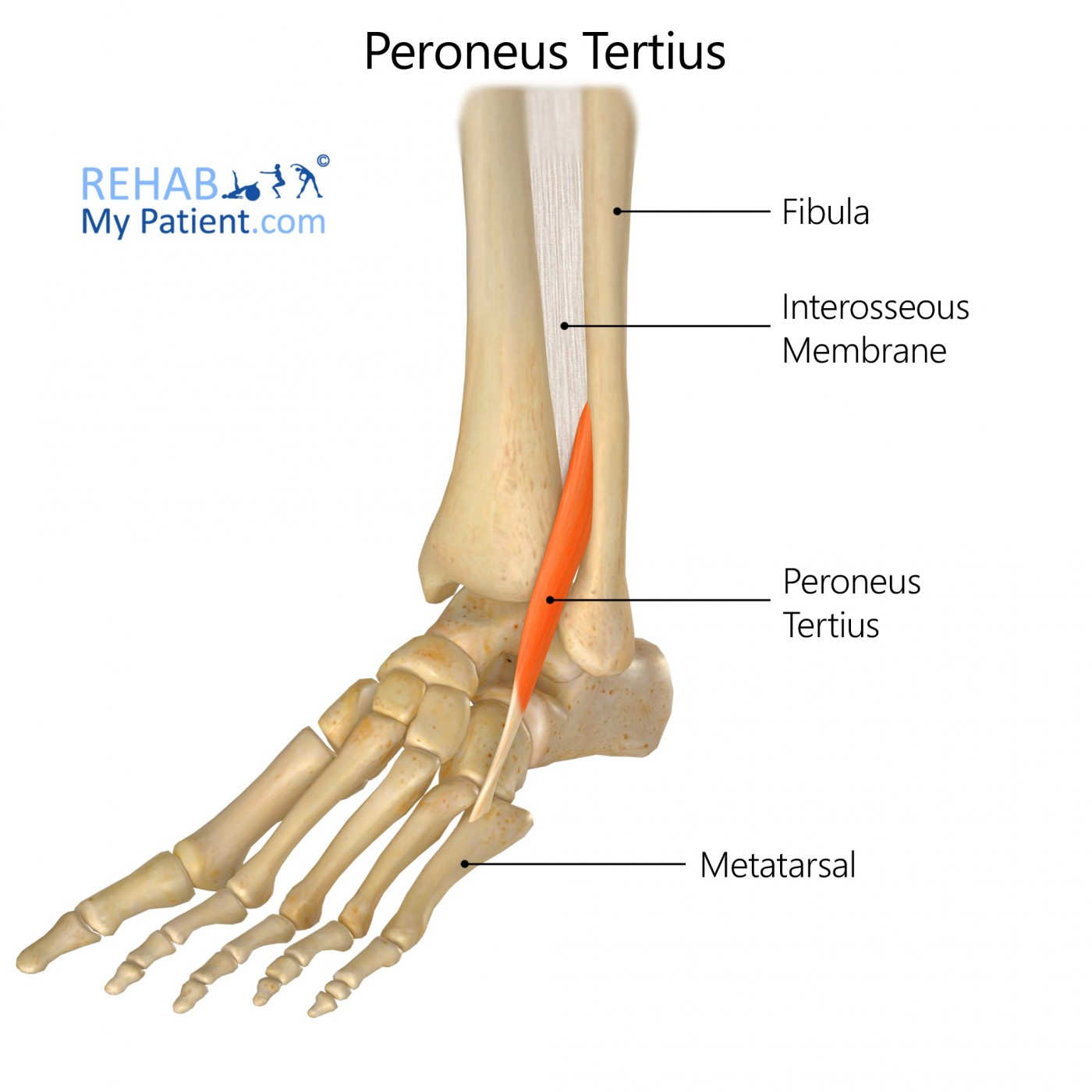
peroneus Tertius
O: distal 1/3 of fibula
I: dorsal aspect of base of 5th metatarsal
A: dorsiflexion and eversion
N: deep peroneal
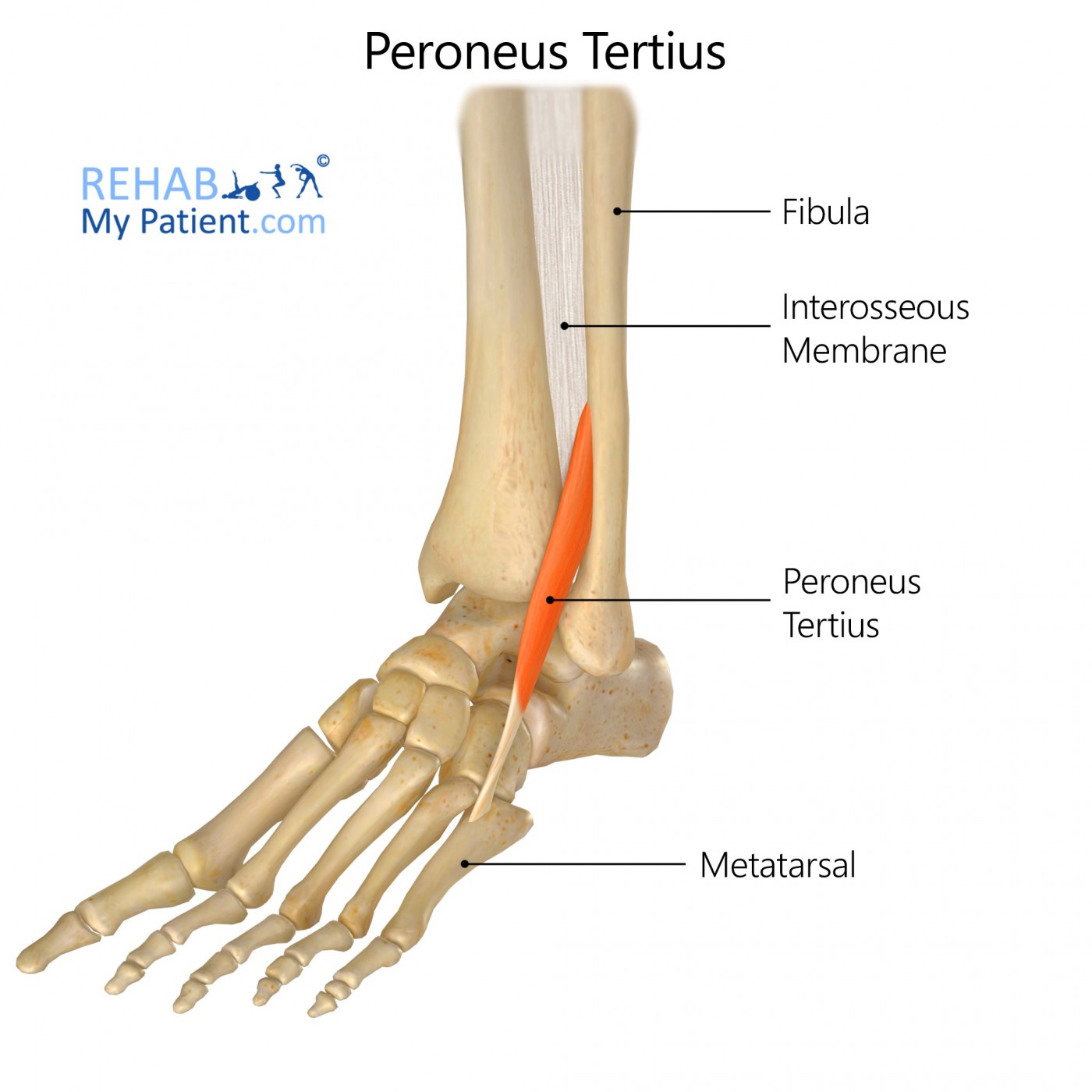
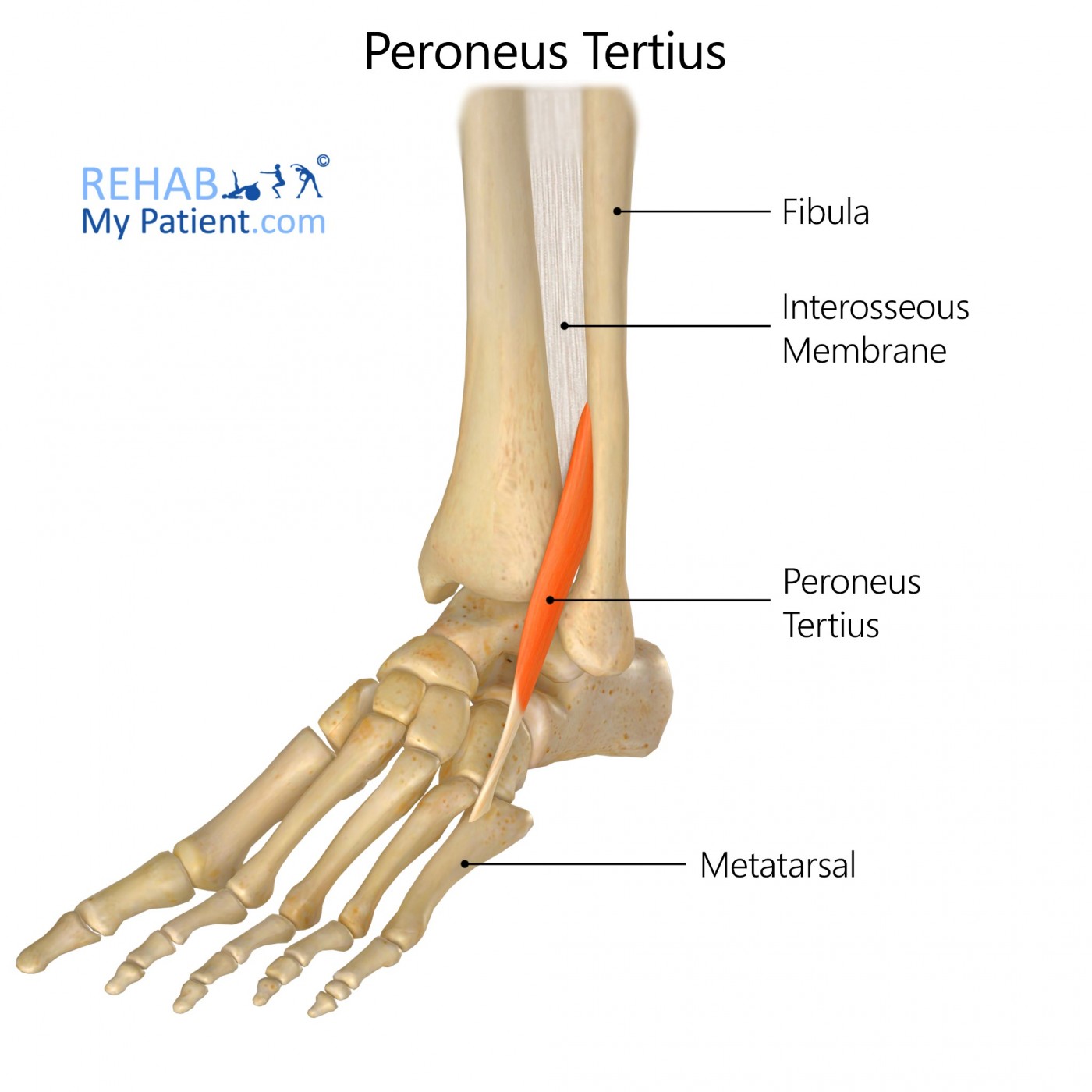
peroneus Tertius origin?
distal 1/3 of fibula