CH 18 Nitrogen Metabolism Study Gui
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1. Nitrogen metabolism primarily focuses on which element’s fate in the body?
Nitrogen metabolism focuses on the fate of NITROGEN in the body
1. Nitrogen is essential for all of the following EXCEPT:
Nitrogen is essential for AMINO ACIDS, NUCLEOTIDES, and COENZYMES
What is the major reason nitrogen metabolism must be tightly regulated?
Nitrogen metabolism must be regulated due to AMMONIA TOXICITY
1. Approximately what percentage of the Earth’s atmosphere is N₂?
Approximately 78% of the atm
1. Humans cannot directly use atmospheric N₂ because:
Humans cannot directly use atmosphere N2 because they lack the nitrogen-fixing bacteria needed to make it usable
1. Nitrogen fixation is carried out primarily by:
Nitrogen fixation is carried out primarily by nitrogen-fixing bacteria in soil and plant roots
1. In plants, nitrogen-fixing bacteria are commonly found:
Nitrogen fixing bacteria are commonly found in the roots of plants.
1. “Fixing” nitrogen refers to:
Fixing nitrogen refers to taking nitrogen and converting it to be usable
1. The enzyme responsible for reducing atmospheric N₂ to NH₃ is:
NITROGENASE reduces N2 to PRODUCE NH3
1. Nitrogenase-catalyzed nitrogen fixation:
NITROGENASE CATALYZED nitrogen fixation is:
ANAEROBIC
Requires 16 ATP
1. Nitrogenase requires which of the following conditions?
Nitrogenase requires ANAEROBIC CONDITIONS
1. The nitrogenase reaction is energetically:
Nitrogenase is energetically DEMANDING REQUIREING 16 ATP.
1. Which enzyme converts glutamate to glutamine by adding an extra amino group?
GLUTAMINE SYNTHETASE adds an extra amino group to convert glutamate to GLUTAMINE
1. Glutamine can be described as an “ammonia sponge” because it:
Glutamine is an AMMONIA SPONGE because it stores TWO amino groups
1. Nitrogen enters most biological molecules primarily in the form of:
Nitrogen is going to enter biological molecules as AMINO GROUPS (NH2)
1. The enzyme that converts glutamine + α-ketoglutarate into 2 glutamate is:
GLUTAMATE SYNTHASE converts glutamine + a-ketoglutarate INTO 2 GLUTAMATE AMINO ACIDS
1. In the glutamate synthase reaction, which TCA intermediate is used as a carbon skeleton?
a-ketoglutarate is the TCA intermediate that functions as a carbon skeleton
Together, glutamine synthetase and glutamate synthase accomplish:
Together, both processes accomplish ASSIMILATION OF NH4+ INTO ORGANIC FORM
1. Transaminases (aminotransferases) catalyze reactions that:
Transaminases (AMINOTRANSFERases) catalyze reactions that TRANSFER AMINO GROUPS between molecules.
1. Transamination reactions are important because they:
Transamination reactions are important because they move amino groups between molecules, FORMING AMINO ACIDS FROM INTERMEDIATES
THEY LINK AMINO ACID AND KETO ACID POOLS
1. A typical transamination reaction involves:
A typical transamination reaction involves an amino acid + alpha-keto acid transferring amino groups and generating a new amino acid + a new alpha-keto acid
1. Transaminations are highly regulated because:
Transamination is highly regulated due to AMMONIA TOXICITY
1. The main “amino group donor” in many transamination routes is:
The MAIN amino group donor in transamination is GLUTAMATE, which forms a new amino acid, and the glutamate turns into a new a-keto acid.
1. Which statement best describes glutamine’s role in nitrogen metabolism?
Glutamine is best described as an AMMONIA SPONGE
1. The major reason the body uses organic carriers like glutamate and glutamine instead of free NH₃ is to:
The body uses organic carriers like glutamate and glutamine instead of FREE NH3 to mitigate the chances of ammonia toxicity
The body does not leave things in their free forms
1. Which pair represents the interconversion that underlies many nitrogen assimilation pathways?
The pair that represents nitrogen assimilation is Glutamate → α-
ketoglutarate
1. Which molecule is both a key TCA intermediate and central in nitrogen assimilation?
α-Ketoglutarate
1. The main metabolic danger of elevated glutamine in the brain is:
The main metabolic danger of elevated glutamine levels in the brain is EXCESS WATER IN BRAIN
Cerebral Edema
Brain swelling
Brain shutdown
1. Which statement about nitrogen acquisition and disposal is TRUE?
Nitrogen is acquired as NH3 and incorporated into amino acids via glutamate and glutamine synthesis
Nitrogen disposal involves converting ammonia into urea and excreted through urine
1. The urea cycle is most directly linked to nitrogen:
The UREA CYCLE is for NITROGEN DISPOSAL
disposes harmful ammonia as urea in urine
1. Amino acids are derived mainly from intermediates of:
Other metabolic pathways, such as nucleotide synthesis and CAC
1. The primary nitrogen sources for amino acid biosynthesis are:
The primary NITROGEN SOURCES for amino acid biosynthesis are GLUTAMATE and GLUTAMINE
1. Essential amino acids are those that:
ESSENTIAL amino acids must be obtained THROUGH THE DIET
1. Nonessential amino acids:
NONESSENTIAL amino acids are synthesized BY THE BODY
1. The “glutamate family” of amino acids is grouped because they:
The glutamate family, including PROLINE, GLUTAMATE, and ARGININE, are grouped because of their 5-CARBON STRUCTURE
1. Serine can serve as a precursor for:
Serine can serve as a PRECURSOR for GLYCINE
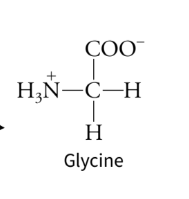
1. Folate is especially important in amino acid metabolism because it:
Folate is important in amino acid metabolism because it facilitates ONE-CARBON TRANSFERS
1. Folate has a critical role in:
Folate has a critical role in NEURAL DEVELOPMENT
1. Essential amino acid synthesis pathways are often:
The synthesis of ESSENTIAL amino acids is LONG and ENERGY-COSTING
Which is why they are obtained from the diet
1. Humans do not synthesize sulfur-containing amino acids efficiently because:
Humans cannot synthesize sulfur-containing amino acids, so we must obtain them through our diet.
1. The branched-chain amino acids include:
VALINE, LEUCINE, ISOLEUCINE
1. The aromatic amino acids include:
PHENYLALANINE, TYROSINE, TRYPTOPHAN
1. Histidine is synthesized from:
Histidine is synthesized from ATP + PRPP
1. Glutamate, GABA, and glycine are all:
GLUTAMATE, GABA, and GLYCINE are all NEUROTRANSMITTERS
1. GABA is produced from which amino acid?
GABA is synthesized from GLUTAMATE-by-glutamate decarboxylase
1. The enzyme that converts glutamate to GABA is:
The enzyme that converts glutamate to GABA is GLUTAMATE DECARBOXYLASE
1. GABA’s principal effect in the nervous system is to:
GABA functions to promote calmness and sleep
1. Drugs like benzodiazepines act by:
Benzodiazepines act to ENHANCE GABA
1. The catecholamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine are derived from:
Dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine are DERIVED FROM TYROSINE
1. Parkinson’s disease is primarily associated with deficiency of:
Parkinson’s disease = DEFICIENCY OF DOPAMINE
1. A common treatment strategy for Parkinson’s disease involves:
Common treatment for Parkinson’s involves DOPAMINE AGONISTS
1. Serotonin and melatonin are synthesized from which amino acid?
Serotonin and melatonin both come from TRYPTOPHAN
1. Prozac (fluoxetine) is best described as a:
Prozac can be described as SEROTONIN REUPTAKE INHIBITOR
1. Amino acids can be used as metabolic fuel primarily in:
Amino acids can be used as METABOLIC FUEL in the SMALL INTESTINE and LIVER
1. Amino acid catabolism usually begins with:
Amino acid catabolism BEGINS with the REMOVAL of the AMINO GROUP
TRANSAMINATION
1. After transamination, the carbon skeleton of amino acids:
After the removal of the amino group via transamination,
the CARBON SKELETON of amino acids ENTERS TCA, GLUCONEOGENESIS, or KETOGENESIS
1. A glucogenic amino acid is one whose catabolism yields:
Glucogenic amino acids YIELD TCA INTERMEDIATES → GLUCOSE
1. A ketogenic amino acid is one whose catabolism yields:
Ketogenic amino acids YIELD ACETYL-CoA or ACETOACETATE → KETONES or FATS
1. Ketosis occurs when:
Ketosis occurs when SUGAR IS LOW, making ketones the primary source of fuel
1. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is characterized by:
Phenylketonuria (PKU) = Accumulation of PHENYLALANINE
NEUROLOGICAL IMPAIRMENT
1. A key clinical feature of untreated PKU is:
PKU leads to BLACK URINE and Neurological impairment
1. PKU is typically managed by:
PKU (accumulation of phenylalanine) is managed by a DIET OF LOW PHENYLALANINE
The main physiological purpose of the urea cycle is to:
The main purpose of the urea cycle is to DISPOSE OF NITROGEN
The urea cycle occurs primarily in which organ?
The Urea Cycle occurs in the LIVER
The key enzyme that produces the committed intermediate for the urea cycle is:
Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase I (a mitochondrial enzyme) is the KEY ENZYME
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 is located in the:
Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase 1 is LOCATED IN THE MITOCHONDRIA
The first step of the urea cycle incorporates ammonia into:
Carbamoyl Phosphate
In the liver, where is toxic ammonia first handled to keep it away from the cytosol?
Toxic ammonia is first handled in the MITOCHONDRIA to be kept away from the cytosol
The ornithine-citrulline antiporter:
The ornithine-citrulline antiporter moves ORTHINE into the MITOCHONDRIA and CITRULLINE out into the CYTOSOL
N-acetylgutamate (NAG) regulates the urea cycle by:
NAG regulates the urea cycle by regulating Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase 1 (CPS 1) only when amino acid breakdown is high
A nucleotide is composed of:
A nucleotide is composed of:
Phosphate group
Sugar Group
Nitrogenous base
A nitrogenous base attached only to a sugar (no phosphate) is called a:
A NUCLEOSIDE is a nitrogenous base attached only to a sugar
Purine bases include:
PURINE (PURE AS GOLD) = ADENINE and GUANINE
Pyrimidine bases include:
PYRIMIDINE (CUT the PY) = CYTOSINE, URACIL, and THYMINE
Purines are structurally characterized by:
PURINES structurally have TWO FUSED RINGS
One six carbon the other five carbon
Pyrimidines are structurally characterized by:
PYRIMIDINES structurally have a SINGLE six carbon ring
The mnemonic “Pure As Gold” refers to:
Pure As Gold = Purines : Adenine : Guanine
The mnemonic “CUT the PY” refers to:
CUT the PY = Cytosine : Uracil : Thymine : Pyrimidines
In RNA, the sugar is:
In RNA, the sugar is RIBOSE
In DNA, the sugar is:
In DNA, the sugar is DEOXYRIBOSE
The phosphate group of a nucleotide is attached to which carbon of the sugar?
The phosphate group attaches to the 5’ CARBON of the sugar
Thymine is found mainly in:
Thymine is found in DNA
Uracil is found mainly in:
Uracil is found in RNA
One reason DNA uses thymine instead of uracil is that thymine:
THYMINE makes the DNA structure more STABLE. DNA is for long-term genetic info storage.
Which base pair forms TWO hydrogen bonds?
A-T forms TWO hydrogen bonds
Which base pair forms THREE hydrogen bonds?
C-G forms THREE hydrogen bonds
Nucleotides function as all of the following EXCEPT:
Nucleotides:
Carry genetic information
Energy Currency - energy transfer
Coenzymes - electron/carbon carriers
Signaling molecules - regulate enzyme activity
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) and cyclic GMP (cGMP) function primarily as:
cAMP and cGMP are both SIGNALING MOLECULES that REGULATE enzyme activity
In de novo purine synthesis, the purine ring is:
In PURINE synthesis, the purine ring is built on ribose (PRPP)
The amino acid precursors required for purine synthesis include:
Purine synthesis requires the following amino acids as precursors:
Glutamine
Aspartate
Glycine
1. The common purine precursor that gives rise to both AMP and GMP is:
INOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE (IMP) is the common precursor.
1. Conversion of IMP to AMP uses which energy source?
IMP → AMP requires GTP
1. Conversion of IMP to GMP uses which energy source?
IMP → GMP requires ATP
1. In pyrimidine synthesis, the ring is:
In PYRIMIDINE synthesis, the ring is BUILT FIRST THEN attached to PRPP
1. The primary precursors needed for pyrimidine ring synthesis include:
Pyrimidine ring synthesis requires:
Glutamine
Aspartate
Bicarbonate
1. Ribonucleotide reductase converts:
Ribonucleotide reductase converts NDPs to dNDPs then dNTPs
1. Ribonucleotide reductase in humans is allosterically:
Ribonucleotide reductase in humans is ATP allosterically REGULATED
1. Thymidylate synthase converts:
Thymidylate synthase CONVERTS dUTP → dUMP → dTMP
1. The methyl donor used by thymidylate synthase is:
The methyl donor used by thymidylate synthase is METHYLENE-THF → oxidized to DHF
1. In nucleotide degradation, purines are ultimately catabolized to ____, whereas pyrimidines are broken down into ____ that can feed other pathways.
Purines are catabolized to URATE
Pyrimidines are catabolized to METABOLIC INTERMEDIATES