u9 evolution noncorrupted (fml)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what ev supports evolution
comparative anatomy, bio/molecule ev, embryology, vestigials, fossils
what are homologus structures and what creates them
same structures, different functions bc divergent evolution
what are analoguous strugeus and what creates them
same purpose, different structures due to convergent evolution
what biochem/molecular ev supports evolution
Amino acid graph with aa differences on the y and time on the x: closer to origin = closely related.
What is embryology and how does it support evolution
study of eraly dev and embryos of all vertebrates (all similar)
what are vestigials
organs that dont serve a purpose
what is comparative anatomy
adding and substracting from the same original structures
when does evolution occur
natural selection, nonrandom mating, small population, new individuals, mutations
What is fitness
who survives with the most offspring
What is allopatric evolution
stop mating and specitiation thru geographic isolation
What is sympatric isolation
nongeographic and prezygtotic or postzygotic evolution
what are examples of prezygotic sympatric evolution
habitat differences, temporal (seasons mating), behavioral (bird song), mechanical (parts), gamete (dont fuse)
what are examples of postzygotic sympatric evolution
zygote mortality, hybrid sterility, f2 fitness
what is adaoptive radiation
mayn species form from one common ancestor dueto newly formed habitats or mass extinction (ex. galapogos finches)
what are the components and reasons for sexual selection
male competition and female choice based off visual and behavioral male characteristics
sexy sons: females want sexy sns
good genes: good males have good genes, females want sons w good genes
What is directional phenotype evolution
selection favors extreme phenotype = bell curve moves to that phenotype over time
What is stabilizing phenotype evolution
sleeciton favors the middle = phenotype range narrows ion the bell curve
What is disruptive phenotype evolution
selection favors both extremes = gap in teh middle of the phenotype bell curve
What is phylogeny
the study of evolutionary releationshipss
what is a phylogenetic tree
shows ancestry of people.
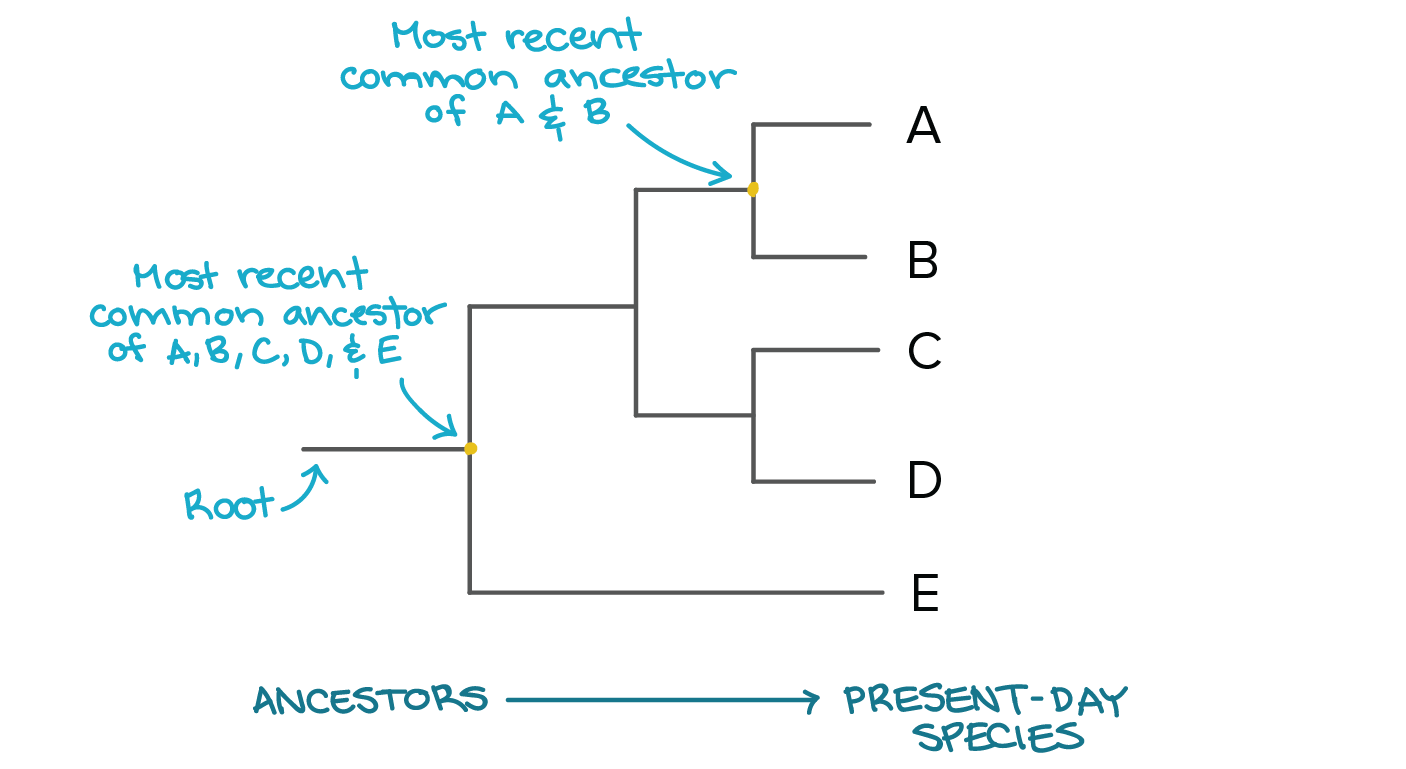
what is a cladogram
relationships by having or not having traits (derived characters):
to the left doesnt have the trai, to the right does. the nodes are the last common ancestor.
what is the result of sexual selection
sexual dimorphism: male and female differences because of natural selection
what is genetic drift generally: what does it cause
genetic luck: organisms get killed off or separated from the general population for reasons uother than fitness
causes bottleneck and founder effect.
what is genetic bottlenecking
variation of a gene pool goes down due to external factors (luck - genetic drift)
ex: tigers FIV resistance: genes of survivors become more common and thus the genes of the entire population become narrower
what is the founder effect
variation of a gene pool changes due to external factors (luck - genetic drift)
small group separates from the larger population and founds their own population resulting in their own genetic differences becoming exaggerated over time (ex: PA amish)
what is gene pool
when a new population comes and mates with the old poplation which adds variation to the gene pool
what is a mutation and its effects
a new allele comes due to a copy error adding to genetic variation
can have positive, negative or neutral effect
what is artificial selection
breeding and domestication narrows the gene pool of a popuation over time
What are preadaptations
evolution only works with what’s there and some organisms are preadapted to change over time eg dinos having feathers before flying
what is macroevolution
big changes over time result in a new species (what we think of when we think of evolution)
what is microevolution
small changes happening: 1 population and no speciation immediately following the changes.
What is classification
putting organisms into cagtegories
What do we use to classify organisms (not the acronym, just generally)
morphology (internal anatomy and fossil ev), cellular structure (uni with more diversity vs multi cellular), biochem/molecular (amino acids, DNA, protein info)
what is the acronym and classification sequence of organisms
deranged k people can often find good s
domain kingdom phylum class order family genus species
what are the weird italix species names actually saying
(genus) (species)
(homo) (sapien)
what are the 3 different domains (details in diff cards)
domain 1 = archae and extremophiles
domain 2 - prokaryotes/eubacteria (regular)
domain 3 - eukaryotes
what are archae and extremophiles
domain 1: prokaryotes that live in really weird places (eg. low ph, salt, hot springs) = have special ribosmal and cell wall sequences to survive
what are prokaryotes / eubacteria
regular prokaryotes and domain 2
requirements for nat selection (!!!!)
variation in a trait, genetic in nature (heritable), competition for survival (more produced than can survive), survival of the fittest.
very h cats frolic
what are the 4 different kingdoms (details in separate slide)
protist, fungi, plants, animals
what are protists, are the uni/multicellular, are they auto or hetero, do they have cell walls
junk drawer
they are uni and multi, auto and hetero, sometimes have cell walls (they are for everything misc)
what are fungi, are the uni/multicellular, are they auto or hetero, do they have cell walls
uni and multi cellular (it depends), heterotrophs (eat others for energy), cell wall (made out of chitin)
what are plants are the uni/multicellular, are they auto or hetero, do they have cell walls
multicellular, autotrophs (photoysnthesis), cell wall (cellulose)
what are animals, are the uni/multicellular, are they auto or hetero, do they have cell walls
multicellular, heterotrophs (eat others), no cell wall