CNS DEPRESSION
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Females
_________ are more at risk of developing depression than males.
Monoamine hypothesis
a hypothesis of depression that is connected to catecholamines and says that there is depletion of monoamines like NE, 5HT and Dopamine that can cause depression.
○ SSRI
○ SNRI
○ TCA
○ MAOi’s
Drugs That Increases Levels of Monoamines
NEUROTROPHIC HYPOTHESIS
This theory hypothesizes that depression is due to deficiency of BDNF (Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor).
decreased BDNF
Increased cortisol leads to_________, and then leading to decreased PCA (Prefrontal cortex Activity) which promotes higher order cognitive processing.
NEUROENDOCRINE FACTORS
● hypothesizes that stress is associated with hypothalamic pituitary axis (HPA)
CRF (cortisol releasing factors)
When you feel stress hypothalamus will release_________________.
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone)
Pituitary gland will then be activated upon the release of CRF.
○ Pituitary gland will send____________to activate adrenal cortex
glucocorticoids,
Upon activation, the adrenal cortex then releases____________ in which one of them is cortisol
decrease PCA
In neuroendocrine factors, production of cortisol will send a negative feedback to our brain to___________, which leads to decreased higher cognitive learning.
DEPRESSION
is a common and serious medical illness that negatively affects how you feel, the way you think and how you act
hypothyroidism
Patients with__________ presents with depression as initial symptom
Hyperadrenalism
_____________or Enlarged adrenal cortex, causing increased release of cortisol may also cause depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD)
Most commonly diagnosed type of depression
○ Clonazepam is given
Persistent depressive disorder
○ Always depressed even if you communicate with others
Premenstrual depressive disorder
○ Menstruation is nearing, hormonal imbalance
post-partum depression
Depressive disorder due to another medical condition
○ Depressants induce depression
Substance/medication-induced depressive disorder
Psychotherapy Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
● is an example of one type of psychotherapy that can help people with anxiety and depressive disorders.
● It teaches people different ways of thinking, behaving, and reacting to anxiety-producing and fearful objects and situations.
ELECTROCONVULSIVE THERAPY (ECT)
● It is a medical treatment most used for patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder who have not responded to other treatments.
● It involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia to stimulate presynapse to have release of catecholamines
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI)
inhibits the reuptake of serotonin (regulation of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft).
Serotonin-norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRI)
inhibits the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine
Tricyclic Antidepressants
has 3 benzene rings in the structure, thus tricyclic.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI)
MAO metabolizes the catecholamines (most especially serotonin and norepinephrine in the synapse). Hence, MAO needs to be inhibited by___________in order for to not metabolize the neurotransmitters in the synapse and bind to the post-synapse.
Lithium
for bipolar disorder
serotonin transporter (SERT) , norepinephrine transporter (NET)
MOA OF SSRI:
● Highly-selective blockade of__________.
● Little effect on____________.
1. CItalopram
2. Escitalopram
3. Fluoxetine
4. Fluvoxamine
5. Paroxetine
6. Sertraline
EXAMPLES OF SSRI?
Citalopram
CELEXA
ESCILATALOPRAM
LEXAPRO
FLUOXETINE
PROZAC
FLUVOXAMINE
LUVOX
PAROXETINE
PAXIL
SERTRALINE
ZOLOFT
ADE OF SSRI
1. Sedation
2. Insomnia
3. Headache, drowsiness, diarrhea
4. Sexual dysfunction
5. Anxiety and suicidal thinking
6. Discontinuation syndrome
1. NSAIDS
2. Anticoagulants, antiplatelets
3. Serotonergic agents
SSRI can have interactions with?
Duloxetine
Venlafaxine
Sibutramine
Desvenlafaxine
Levomilnacipran
DRUG EXAMPLES OF SNRI?
MOA OF SNRI
Moderately selective blockade of NET and SERT - causes increased level of serotonin and norepinephrine in the synapse; hence, higher chance of binding in post-synapse and cause response
DULOXETINE
CYMBALTA
VENLAFAXINE
EFFEXOR
SIBUTRAMINE
MERIDIA
DESVENLAFAZINE
PRISTIQ
THERAPEUTIC USE OF SNRI
1. Major Depression
2. Chronic Pain Disorders
3. Fibromyalgia
4. Perimenopausal Symptoms
ADE OF SNRI
1. Anticholinergic
2. Sedation
3. Hypertension
4. Sexual dysfunction
Uncontrolled Angle-Closure Glaucoma
SNRI can have a contraindication for patients with_________ since norepinephrine increases intraocular pressure; hence, it increases the risk for UACG.
TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS (TCAs)
- They are not commonly used today because of their
side effects.
- They cause significant cardiac arrhythmia.
Imipramine
Desipramine
Clomipramine
Trimipramine
Amitriptyline
Nortriptyline
Doxepin
Protriptyline
DRUG EXAMPLES OF TCA’S
Amitriptyline
Elavil
Clomipramine
Anafranil
Trimipramine
Tofranil
MOA OF TCA’s
1. Inhibits neurotransmitter reuptake - SERT and NET
2. Blockade of serotonergic, alpha-adrenergic,
histamine, and muscarinic receptors - also blocks the
receptors where the serotonin and norepinephrine will
bind.
ADE OF TCA’s

Manic depressive patients
TCA should be used with caution in _____________patients.
MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS (MAOIs)
Does not block the reuptake transporters but blocks the enzymes in order to increase the levels of catecholamines in the synapse.
Phenelzine
Isocarboxazid
Tranylcypromine
Moclobemide
Selegiline
DRUG EXAMPLES OF MAOI’s
Phenelzine
act on MAO-A and MAO-B
Selegiline
act on MAO-B only; Used for Parkinson’s Disease; Used to increase dopamine levels
MOA OF MAOI’s
1. Blockade of MAO-A and MAO-B
2. MAO-B irreversible selective; MAO-B inhibition
MAO-A
shows greater affinity for hydroxylated amines, such as noradrenaline or norepinephrine and serotonin.
MAO-B
higher affinity for non-hydroxylated amines, such as dopamine and tyramine (amino acid).
ADE OF MAOI’s
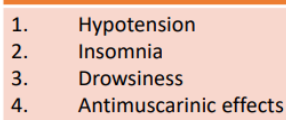
hypertensive crisis
MAOI’s can also cause _________if taken with tyrosine-rich foods (ex. nuts, cheese) (Advise patients not to eat nuts or cheese
Tyramine containing foods
MAO + SSRI
MAOI’S can interact with
Bupropion
Mirtazapine
Amoxapine
Maprotiline
VIlazodone
Buspirone
Nefazodone
Trazodone
TETRACYCLIC AND UNICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS
MOA OF BUPROPION
A dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (DNRI)
ADE OF BUPROPION
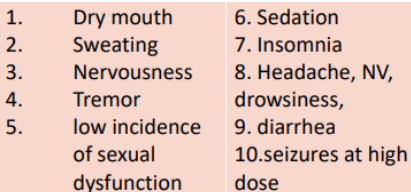
Smoking cessation
OTHER THREAPEUTIC USE OF BUPROPION?
AMOXAPINE
● Acts as a strong Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
● Weak 5HT reuptake inhibitor
● Inhibits D2 receptor
ADE OF AMOXAPINE

Parkinsonism
because of depletion of dopamine
Cardiotoxicity
- because of increase level of norepinephrine in the synapse (sympathetic responses)
MOA OF MIRTAZAPINE
Blocks ɑ2 receptor therefore enhancing NE-5HT transmission
ADE OF MIRTAZAPINE

APPETITE STIMULANT
OTHER THERAPEUTIC USE OF MIRTAZAPINE
NEFAZODONE and TRAZODONE (Desyrel)
Weak 5HT reuptake inhibitor and with chronic use may increase 5HT release
ADE OF NEFAZODONE AND TRAZODONE

LITHIUM SALTS
Most likely used for bipolar disorders
BRAND NAME: ESKALITH
MOA OF LITHIUM SALTS
Blocks recycling of phosphoinositides leading to decrease in the release of IP3 and DAG
magnesium
Lithium inhibits some enzymes that displaces the cofactor__________via transduction
MOOD STABILIZER
OLD DOC FOR BIPOLAR DISORDER AND MANIA
THERAPEUTIC USE OF LITHIUM SALTS
ADE OF LITHIUM SALTS
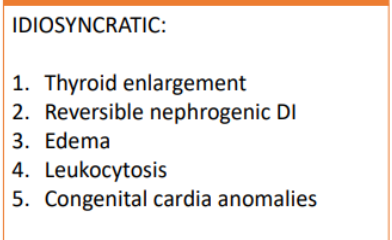
Aripiprazole (Abilify)
Olanzapine (Zyprexa)
Risperidone (Risperdal)
Quetiapine (Seroquel)
Ziprasidone
Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
Antipsychotics EXAMPLES
OTHER DRUGS FOR BIPOLAR DISORDER
1. Valproic acid (Depakote) - also used for seizure
2. Carbamazepine (Tegretol) - anticonvulsant
3. Antipsychotics