Metallic bonding
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is the free electron model of metallic bonding
Free electron model of bonding in a metal considers a lattice of metal ions surrounded by a sea of electrons.
The ions are fixed in a crystal lattice, but the electrons can move. If a potential difference is applies the electrons move from high to low potential giving rise to an electrical current
What are the ionization energies of metals, and what does this lead to
Metals often have low ionization enthalpies, meaning they lose electrons relatively.
Where does the free electron model fail
Cannot explain Semiconductors
What is band theory
Band theory is based on overlap of atomic orbitals to describe metallic bonding.
Describe the banding in an insulator
There is a large energy gap between the filled valence band and empty conduction band.
Describe banding in a semiconductor
The energy gap between bands is quite small but the conduction band is still empty and the valence band is still full
Describe banding in a metal
No energy gap between the bands meaning that the electrons mix making two partially filled bands.
Use lithium as an example to describe band theory
When two lithium atoms bond to form Li2, the two 2s orbitals combine to give a filled bonding molecular orbital and an unfilled antibonding molecular orbital
Li conducts electricity because it has a partially filled band
Compounds that have filled bands may be insulators of semiconductors
Valence bond is the highest energy band that is fully occupied at ok.
Valence bonds differ between electrons
Smaller orbitals overlap less and have narrower valence bonds
Describe what the fermi level is
The energy level to and above which electrons must be promoted to for a material to conduct
What’s the fermi energy equation
Planck constant,
𝑚 is the mass of the fermion, and
𝑛 is the number density of fermions per unit volume.
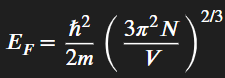
Describe the graphite band structures
Conjugated planar pi system
Bands instead of discrete energy levels
Half-full band with low density of states near fermi level
What is doping
Doping is used to tune the electrical properties of semiconductors by deliberately introducing small amounts of impurities
If this impurity contains more valence electrons then the host lattice then the doped solid has more electrons to conduct current than the pure host has