water balance with Na, P, Cl, and pH
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Water Distribution in the Body (functions-6)
- chemical reactions
- body temp & regulation
- lube & protect
- solvent & transport medium
- blood volume maintenance
- acid base balance (ABB)
changes to water during growth/aging (3)
- total water decreases
- extracellular decreases
- intracellular increases (within cell)
what factors play a role in the maintenance of fluid balance in the body
- beverages
- liquid in food
- <10% from metabolism
total about 2500ml
what are the components of extracellular fluid
interstitial fluid (intercellular)
plasma/intravascular
lymph
transcellular fluid
interstitial fluid =
intercellular
interstitial/intercellular fluid refers to
fluid surrounding the cell (between cells)
What is the function of interstitial fluid?
directly bathes the cells.
What is the role of interstitial fluid?
It provides a medium for the exchange of nutrients and metabolic products to and from plasma and cells.
What is plasma?
fluid portion of the blood.
intracellular fluid %**
2/3
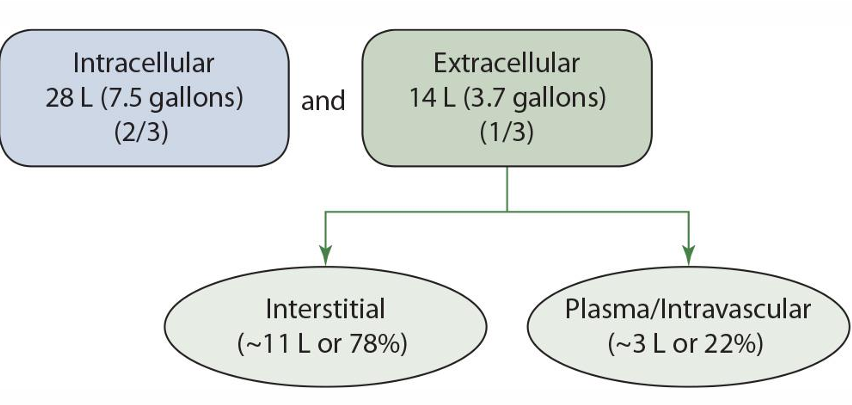
extracellular fluid %**
1/3
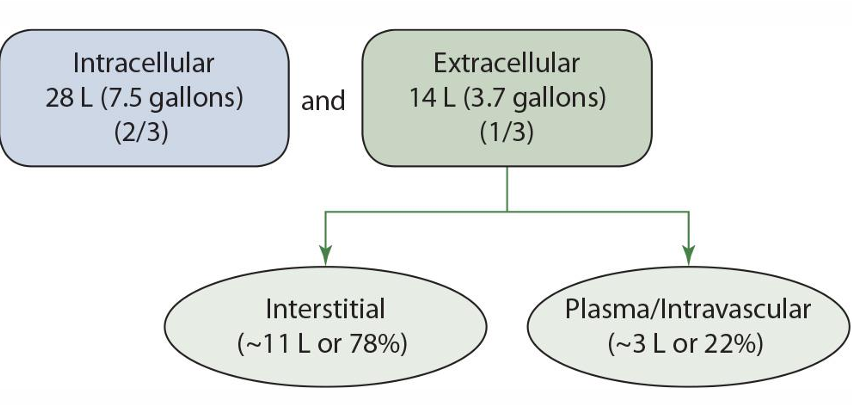
extracellular is broken up into what 2 groups
interstitial and plasma/intravascular
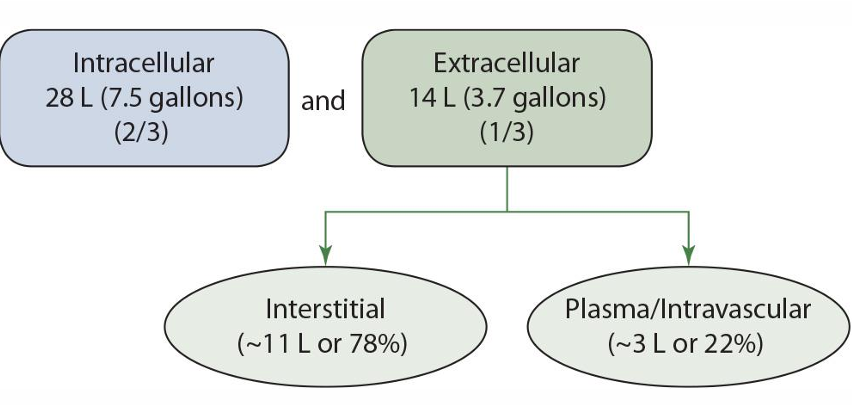
interstitial fluid % of extracellular fluid **
78%
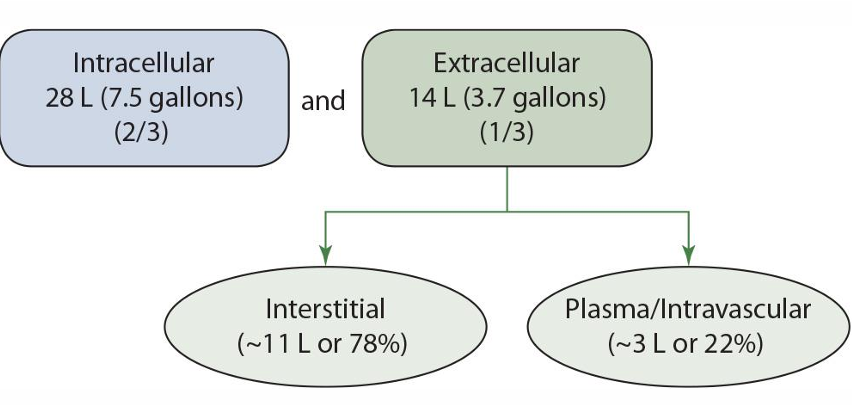
plasma/intravascular % of extracellular fluid **
22%

most of the water of the body is lost through
urine
smaller amounts of water are lost through (3)
feces, respiratory tract, and skin
AI (water)
adults women: 2.7L
adult men: 3.7L
needs based on activity & energy intake AND VARY
water movement strongly affected by ....
Na in extracellular fluid
movement between interstitial space & extracellular regulated by
osmotic pressure
formaintaintenanceoffluidbalance,movement across capillary blood vessel walls _______________, governed by _____________ & _________
separate plasma from interstitial
differences in hydrostatic pressure & colloidal osmotic pressure
maintenance in fl balance
osmosis
osmolarity
K major cation inside cells
osmosis
Movement of water across semipermeable membrane in response to differences in solute concentrations
osmolarity
solute (particle) concentration of a fl
K major cation inside cells
Na major cation in ECF
arteries maintain a
positive net filtration pressure
veins maintain a
negative net filtration preassure
where is protein found in fl balance?
within plasma & intracellular space
sustaining ECF volume is...
vital to BP & CV system functions
several hormones correct imbalances in fl & Na levels are....
vasopressin
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
natriuretic peptides
CV system
vasopressin is a
anti-diuretic hormone
Vasopressin is released by ____ in response to ______
hypothalamus ; slight increases in ECF osmolarity
vasopressin stimulates ...
resorption of water in kidneys & thirst
Vasopressin increases BP by ....
stimulating vasoconstriction of the arterioles
Bowmans capsule is
glomerulus capillary network
the kidney includes
Proximal & distal convoluted tubule
loop of Henle
collecting duct
Glomerulus filters...
water & solutes from the blood
_____ collects the filtrate
Bowman's capsule
Urine composition depends on
1. Filtration through which the glomerular filtrate is formed
2. resorption of filtrated into blood
3. secretion into tubules from capillaries
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) enhances ....
Na & Cl resorption
(1) Renin released when....
BP & plasma fl volume are low
(2) Renin then....
hydrolyzes angiotensinogen
angiotensin II increases BP
aldosterone promotes resorption of ___ & excretion of ____ in _____
Na
K
distal tubule
Natriuretic peptides
oppose RASS (ANP & BNP)
promote Na+ & water excretion (lowers BP & volume)
inhibits RAAS ( -> renin -> aldosterone)
Natriuretic peptides increases
GF pressure & GFR
table salt composition
40% Na, 60% Cl
processed foods account for ___ total Na, ~____ form natural sources, ~___ Na added at table/cooking, ~___ from water consumption
75%
10%
15%
<10%
Na AI 19-50yrs
1500mg
Na is the most ...
abundant EC cation
____ on bone surface to be released w/ ___
30% ; hyponatremia
major source is table salt, 1tsp = _____mg
2300
DV for food labels
2400mg
Na linked with ___ in some
HTN
_______ of ingested Na is absorbed, little excreted in ____
95-100% ; feces
Na Absorption initiates from the ___ (__), ___ & ___
stomach (Cl), SI & colon
Na absorption pathway utilizes
Na/glucose co-transport system through the SI
the _____ pathway works in the SI & proximal colon (sodium)
Na/Cl electroneutral
_____ Na absorption occurs in the colon
electrogenic
for blood transport, _____ are kept within a tight range similar to K & Ca
serum Na concentration
For transport in blood, what hormones/enzymes regulate
vasopressin
aldosterone-atrial-natriuretic
renin
angiotensin II
key function of Na: +ions in the ECF to maintain....
osmotic pressure
key function of Na: ___ is the main regulatory hormone associated w/ Na balance
aldosterone
key function of Na: key for retaining ___
body water
key function of Na: Na participates in ....
nutrient absorption
muscle contraction
conduction of nerve impulses
key function of Na: Na creates ...
an electrical potential charge (muscle contraction/conduction)
Na interaction w/ Ca
- high Na = high Ca requirements
- Na influences Ca excretion
Na deficiency
- V/D
- excessive perspiration (lose 2-3% body wt)
- depletion of Na
- cramps, dizziness, shock, coma
- kidneys conserve Na
___-___ of Na intake added to food by individuals
1/3 - 1/2
___-___ of Na added to food by manufacturers
1/2 - 2/3
Na needs
body needs:
minimum:
AI:
DV:
typical intake:
Body needs 100mg/d
Minimum 500mg/d
AI 1500mg/d
DV 2400mg/d
typical intake 3500mg/d
Salt sensitive adults
10-15% adults
high Na leads to high BP
Salt sensitive guidelines
1-1.5g Na/d
all individuals recommended <2.5g/d
K is a ___ in the ICF (intracellular fl) & ___% found inside the cell
+ion ; 95-98%
higher K sources are associated w/
natural & unprocessed foods
K used for
salt substitutes
higher intakes are associated w/
lowering (normalizing) BP
____ of K consumed is absorbed
90%
K absorption takes place primarily in ....
SI, some in colon
K absorption regulated by
aldosterone & kidneys
K passive or facilitated via ___ of the mucosal cell by the ____
apical membrane; K+/H+ ATPase pump
exchange IC __ for luminal ___
H+ ; K+
to enter blood, K ____ in the cell & diffuses across the cell membrane via ____ & maintained by ___
accumulates ; K channel ; Na/K ATPase pump
___ & ____ influence K transport & concentrations
Insulin & catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine)
Functions of K
Fluid & electrolyte balance
• Maintenance of pH
• nerve-impulse transmission
• Muscle contraction (smooth and cardiac)
• Decreases urinary excretion of calcium (DASH diet)
K DV
4700mg
Minimum requirement & typical intake of K
minimum; 2000mg/d
typical; 2000-3000mg/d
excess K excreted by
kidneys
K toxicity
Hyperkalemia (high serum K)
- diuretics
- Loss of appetite, cramps, confusion, constipation, irregular heart beat
K deficiency
- alcoholics, anorexia, bulimia
- Loss of appetite, cramps, confusion, constipation, irregular heart beat
Hypokalemia (low serum K)
Cl is the most abundant
-ion for ECF
Cl most important function
electrolyte balance
Cl is obtained from ___ & high intake may ___
salt ; high BP
Cl is a major electrolyte in relation to ...
shift that moves Cl in opposite to bicarbonate across membrane
Cl is absorbed in the
SI & colon
Cl absorbed through ____ (follows __)
Na+ glucose cotransport system (Na)
_______ and the ______ also have chloride accompanied to maintain electric neutrality
Electroneutral co-transport ; electrogenic sodium absorption
Cl formation via
hydrochloric acid
Cl released via _____ to destroy ____
WBC ; foreign substances
Exchange anion for HCO3 in ____, ; contribute to ___
RBC: Cl shift
Cl plays a role in
nerve function (depolarization of ion channels)
Excess Cl is excreted via
GI, kidneys, skin