Pharmacodynamics: Receptors
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
ligand, receptor
physiological receptors: exert action by binding to a ____________, signaling/message propagation, resulting in _____________ action
second messengers
intermediary cellular signalling molecules
effector
cellular targets mediating the response
ligand-gated ion channels
receptors that directly opens an ion channel that causes hyperpolarization or depolarization
GPCR
receptors that activate signaling cascade that opens an ion channel
kinase-linked
receptors in which phosphorylation cascade that ends up changing gene transcription
nuclear receptors
ligand binds to receptor within the nucleus and affects gene transcription
ionotripic
another name for ligand-gated ion channels
metabotropic
another name for GPCRs
lipophilic
drugs that act on nuclear receptors must be _____________ to enter the cell
milliseconds
timescale for effects of ionotropic receptors
seconds
timescale for effects of metabotropic receptors
hours
timescale for effects of kinase-linked and nuclear receptors
nicotinic ACh receptor
Example of ionotropic receptor
muscarinic ACh receptor
example of metabotropic receptor
cytokine receptor
example of kinase-linked receptors
oestrogen receptor
example of nuclear receptor
ion channels
1. Ligand binds to extracellular site of the receptor
2. Conformational change of the receptor results in pore opening
3. Ion flux down electrochemical gradient
4. Pore closes
7
GPCRs have ________ transmembrane domains
dissociate
the alpha and beta/gamma subunits of a GPCR _______________ when the alpha subunit exchanges GDP to GTP after the ligand binds
RGS (regulator of G protein signaling)
protein that returns the active alpha-GTP complex to its basal state
Gs
alpha subunit:
-activates adenylyl cyclase
-activates calcium channels
Gi
alpha subunit:
-inhibits adenylyl cyclase
-activates calcium channels
Go
alpha subunit
-inhibits calcium channels
Gq
alpha subunit
-activates phospholipase C
beta-gamma
G-protein subunit that modulates ligand gated ion channels and activates the PI3 K pathway
PKA
__________ levels are increased by Gs alpha subunit when it activates AC, and decreased by Gi alpha subunit when it inhibits AC
increase, increase, decrease
Increase PKA by Gs alpha subunit (activates AC) results in:
_______________ lipolysis in liver
_______________ glycogen breakdown in liver
_______________ glycogen synthesis in liver
decrease, decrease, increase
Decrease PKA by Gi alpha subunit (inhibits AC) results in:
_______________ lipolysis in liver
_______________ glycogen breakdown in liver
_______________ glycogen synthesis in liver
calcium
cAMP activates PKA, which increases intracellular levels of _______________ and phosphorylates metabotropic enzymes
adenylyl cyclase
enzyme that converts ATP into cAMP
PLC (Phospholipase C)
enzyme that splits PIP2 into IP3 and DAG
PKC (protein kinase C)
regulates enzyme activity when activated by DAG
calcium
IP3 triggers and increase in intracellular ____________ levels, which regulates gene expression, contraction, secretion, metabolism, and electrical activity
cardiac muscle
tissue in which calcium stimulates muscle contraction
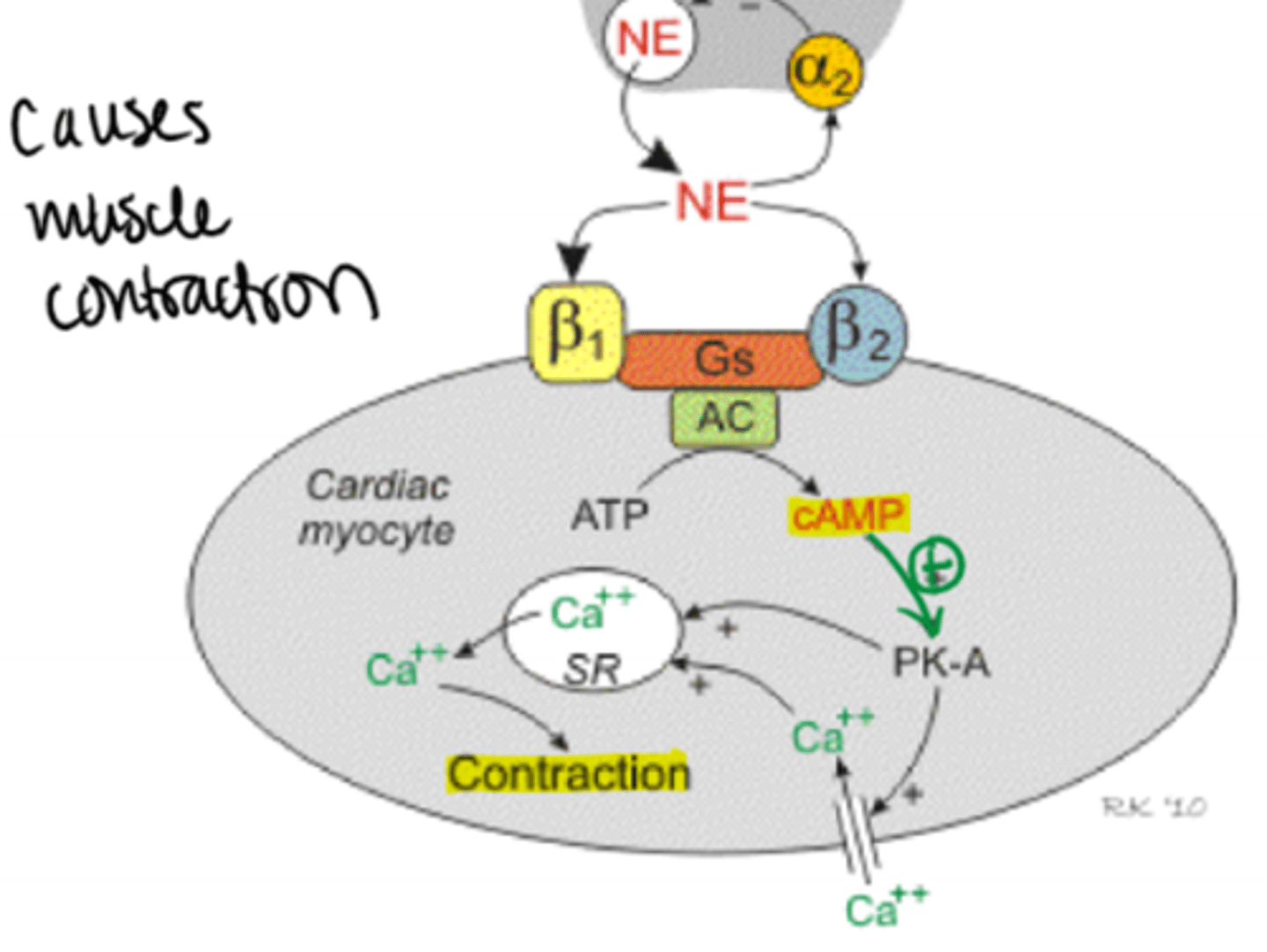
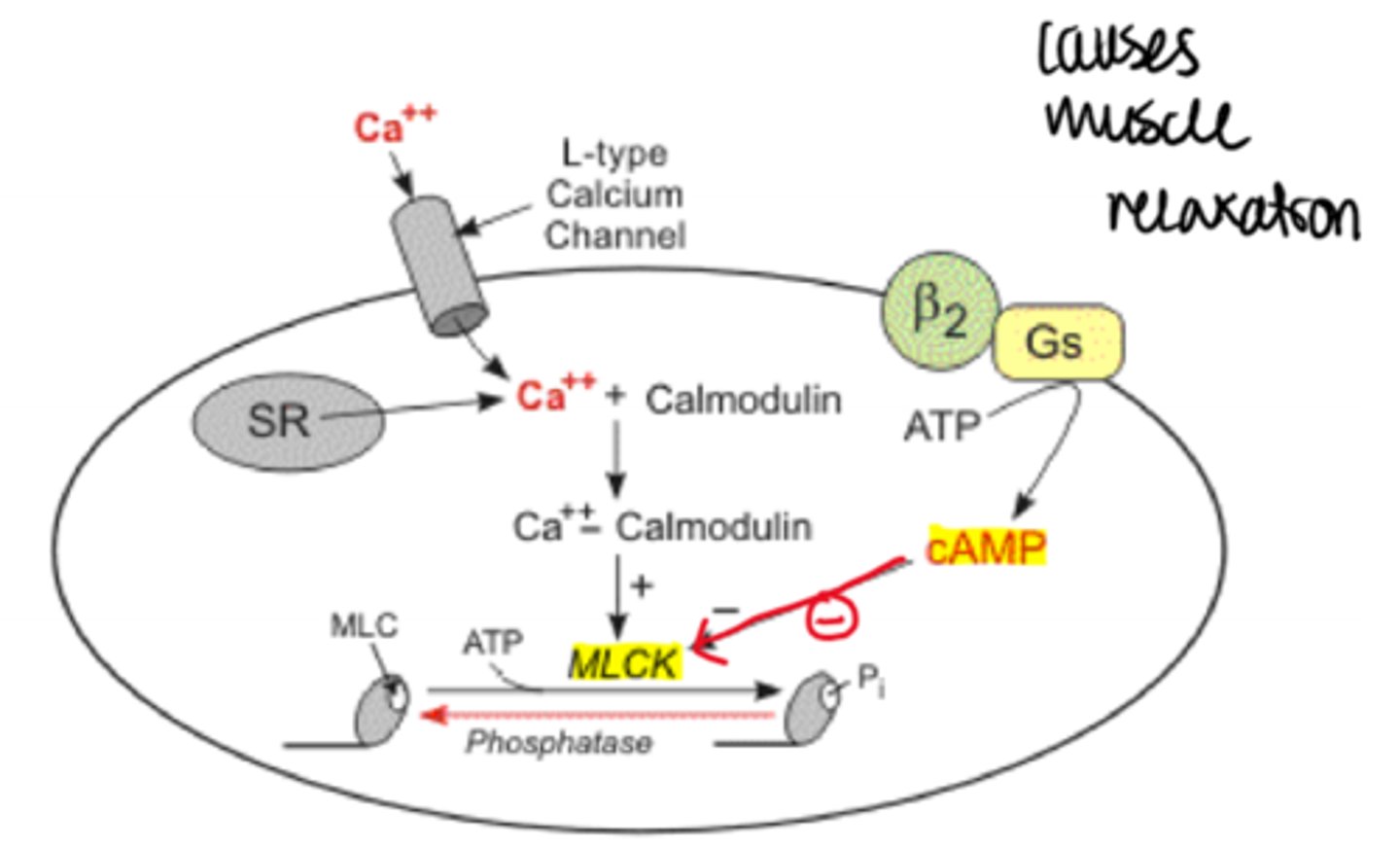
bronchial smooth muscle
tissue in which cAMP inhibits MLCK (myosin light chain kinase) which results in muscle relaxation
beta arrestin
puts phosphorylated GPCR in a coated pit ("jail") where the receptor may be resensitized or destroyed
resensitization
recovery of a receptor after agonist is removed
desensitization
destruction of receptors after continuous use of an agonist
homologous desensitization
Receptor loses ability to couple G protein and to undergo endocytosis --> desensitization initiated by activation of the receptor itself
heterologous desensitization
Phosphorylation of the activated GPCR by PKA, PKC that have been activated by another receptor --> impairing coupling of activated receptor and G protein (not specific)
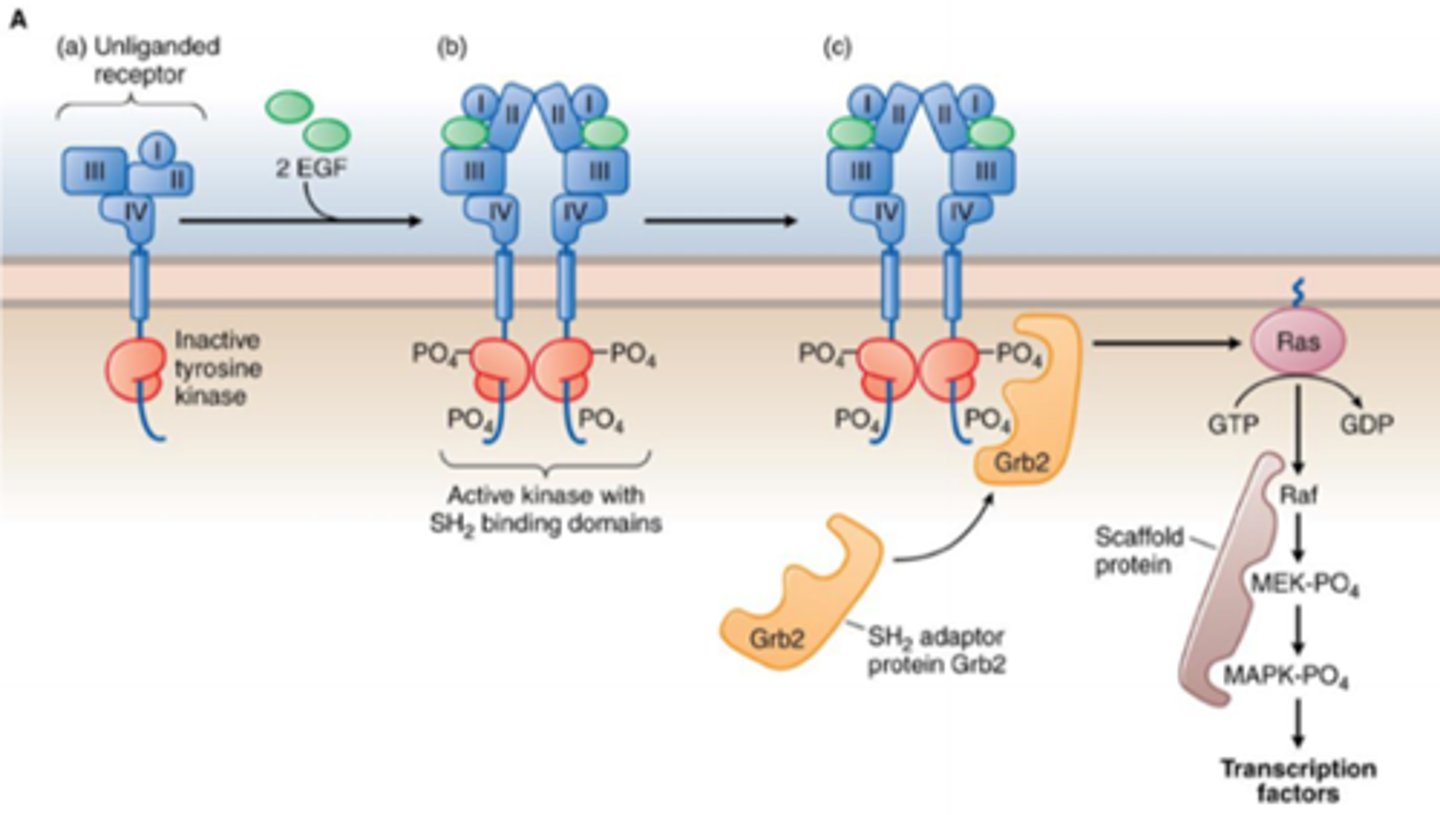
tyrosine kinase
___________________ receptor:
-Ligands bind to their receptors
-Receptors dimerize, activating the tyrosine kinase
-Grb2 binds to tyrosine kinase and activates Ras, which converts GTP to GDP
-Transcription factors adjust growth
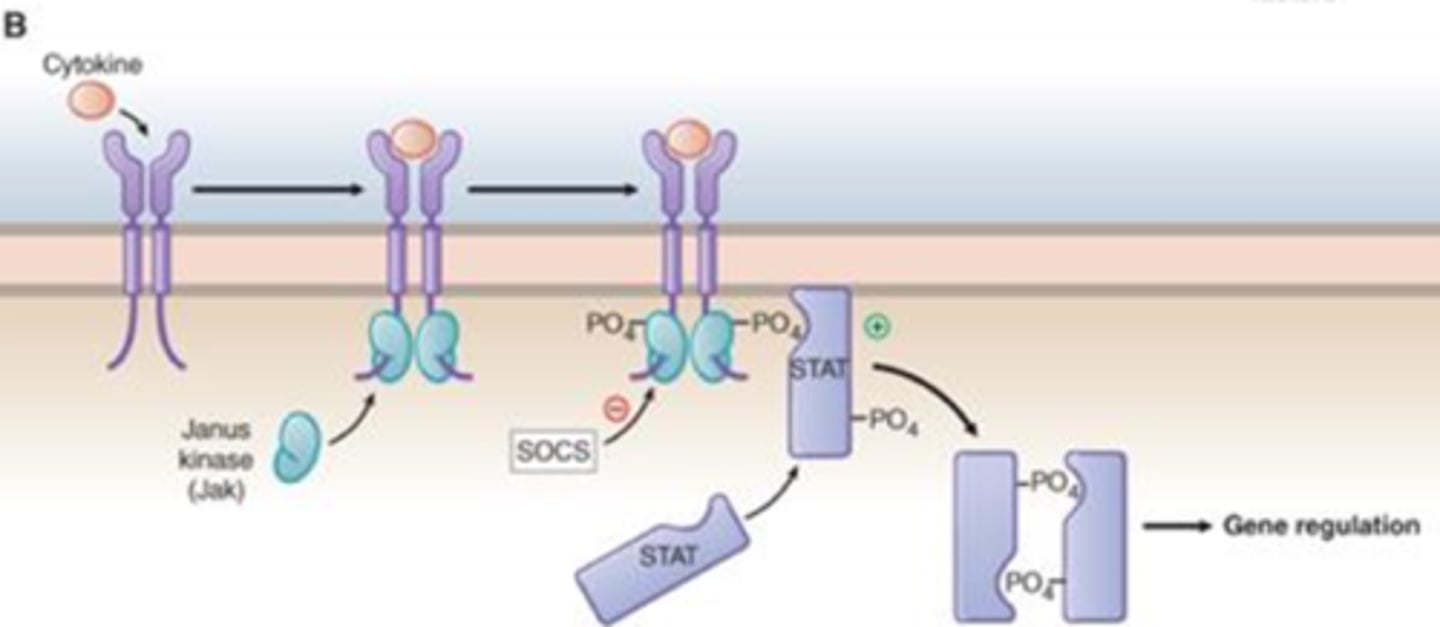
JAK-STAT
_________________ Receptor Pathway
-Cytokines bind to receptor
-Hormones (GH, prolactin)
-Promotes growth, proliferation, and cell survival (gene regulation)
GC (Guanylate Cyclase)
ANP binds to receptors coupled to _______________ enzyme and becomes active, converting GTP to cGMP
smooth muscle relaxation
cellular effect of ANP when cGMP is produced
NO
produced by endothelial cells which diffuses to adjacent cells, activating soluble GC and resulting in smooth muscle relaxation
steroid
nuclear receptors are for circulating ____________ hormones (androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormone, vitamin D)
heat shock
when steroid protein binds to its receptor, ______________ leaves and exposes the DNA binding site
downregulation
mechanism of loss of tissue receptor response in which there are reduced receptor numbers and loss of receptor binding affinity to ligands or coupling proteins
sequesterization
mechanism of loss of tissue receptor response in which receptors are internalized so they are not accessible to the ligand (failure to recycle receptor to surface)
degradation
mechanism of loss of tissue receptor response in which receptors are degraded by lysosomes