431 Lec 34
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:43 PM on 4/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
Understand the area/ signaling pathway of the brain impacted most significantly that leads to PD and why
•Associated with deficit of dopamine
•Characterized by destruction of DA containing neurons in the substantia nigra leading to DA deficiency in nerve terminals in corpus striatum
•Characterized by destruction of DA containing neurons in the substantia nigra leading to DA deficiency in nerve terminals in corpus striatum
2
New cards
Be able to recognize the three main contributors to the cause of PD.
Genetic component
Oxidative Metabolism component
Environmental Neurotoxins component
Oxidative Metabolism component
Environmental Neurotoxins component
3
New cards
Know how alpha-synuclein may be involved in PD.
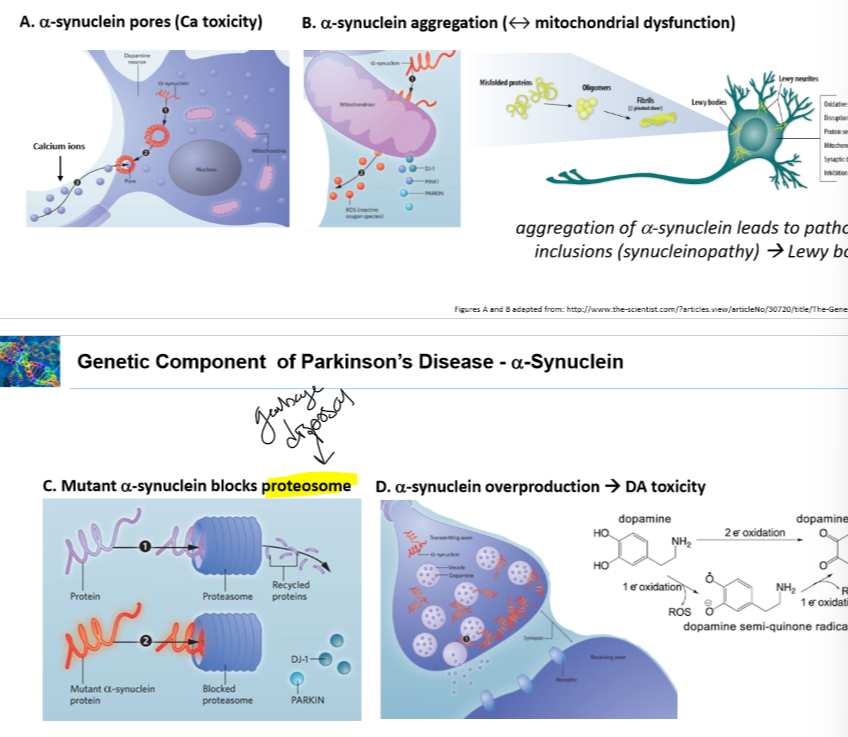
•Can aggregate and form donuts then attach to neuron membrane and make a whole leading to calcium flux leading to toxicity
•can aggregate and attach to mitochondria
•block proteosomes
•overprodced leading to block release of dopamine, causing dopamine toxicity
•can aggregate and attach to mitochondria
•block proteosomes
•overprodced leading to block release of dopamine, causing dopamine toxicity
4
New cards
Know what other genes are involved and how their dysfunction can lead to PD.
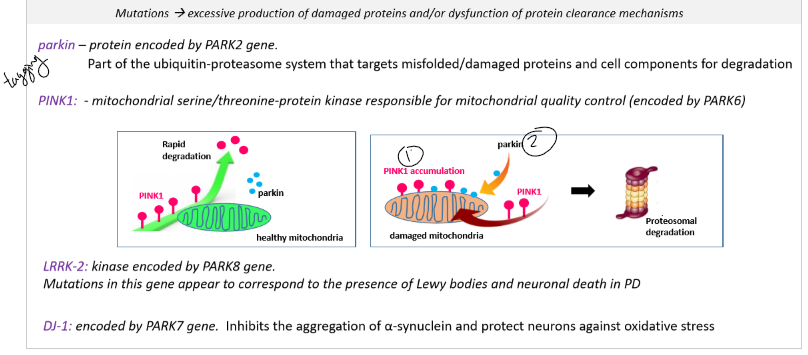
DJ1- inhibits aggregation of alpha syn nuclein
PINK1- protein kinase thats responsible for mitochondrial health
Parkin- responsible for tagging misfolded proteins to be broken down
LRRK- kinase, mutations in this gene lead to lewy bodies and neuronal death in PD
PINK1- protein kinase thats responsible for mitochondrial health
Parkin- responsible for tagging misfolded proteins to be broken down
LRRK- kinase, mutations in this gene lead to lewy bodies and neuronal death in PD
5
New cards
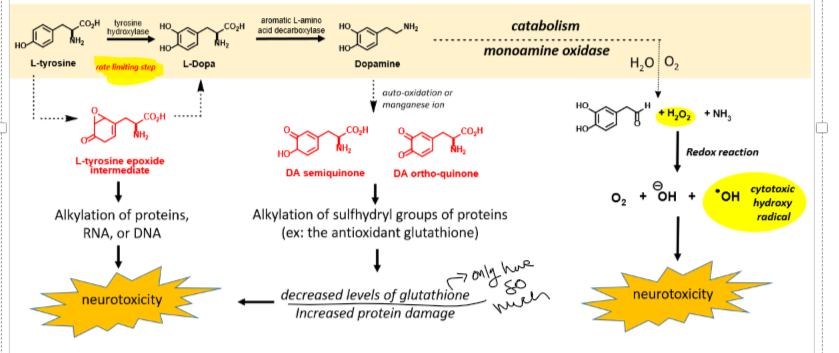
Be able to recall at which points in the dopamine biosynthesis or catabolism pathways reactive intermediates may be generated and how this relates to PD
6
New cards
Recognize what environmental neurotoxins we discussed are likely to cause PD and which one is not
\
Rotenone, Cyperquat, Paraquat
\
Rotenone, Cyperquat, Paraquat
Rotenone (most likely), Cyperquat, Paraquat (least likely- does not bind mitochondrial complex 1)
\
MPTPS causes severe parkinsons syndrome
\
MPTPS causes severe parkinsons syndrome
7
New cards
Understand the correlation between mitochondrial complex 1 inhibition and PD
Important in the electron shuffling of mitochondria- inhibiting it is bad for the mitochondria which is essential to cells
8
New cards
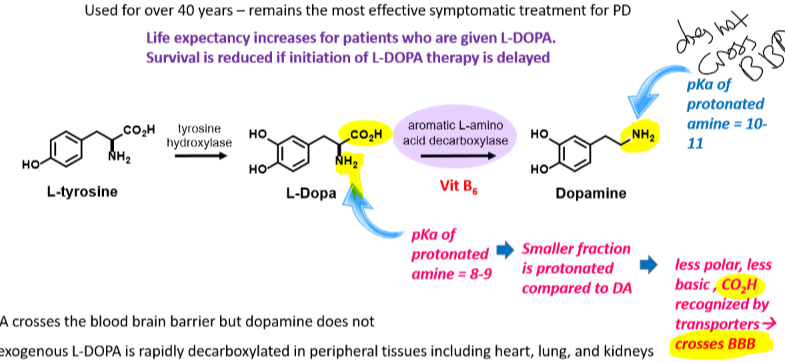
Know how dopamine is biosynthesized from L-tyrosine, and what enzymes and co-factors are involved.
9
New cards
Does dopamine cross the BBB?
No
10
New cards
Does L-DOPA cross the BBB?
Yes
11
New cards
Know how carbidopa works mechanistically and how it is used to treat symptoms of PD. You do not need to know the arrow pushing mechanism but the general concepts are important.
Inhibits the conversion of LDOPA to dopamine in the periphery because we want LDOPA to cross the BBB BEFORE it gets converted to dopamine
\
Carbidopa does not cross BBB
\
Carbidopa does not cross BBB
12
New cards
Understand at what stage of PD using L-DOPA is most appropriate and why.
Early on use of LDOPA increases life expectancy
Needs vitamin B6
Needs vitamin B6
13
New cards
Know how dopamine receptor agonists are used in PD (what do they do and what stage of disease are they most useful)?
Enzymes to convert LDOPA don’t work→ bring in molecules that mimic dopamine action at the receptor
\
Usually used at nigrostriatal degeneration (fewer nerve terminals lef tot convert LDOPA to DA)
\
Usually used at nigrostriatal degeneration (fewer nerve terminals lef tot convert LDOPA to DA)
14
New cards
How do DA agonists differ from L-DOPA in duration of action and side effect profile?
Longer duration of action than L Dopa and may be less likely to produce on off effects and dyskinesias but can produce other adverse effects:
→ nausea
→vomiting
→Sedation
→Hallucination
→psychiatric disturbances
→ nausea
→vomiting
→Sedation
→Hallucination
→psychiatric disturbances
15
New cards
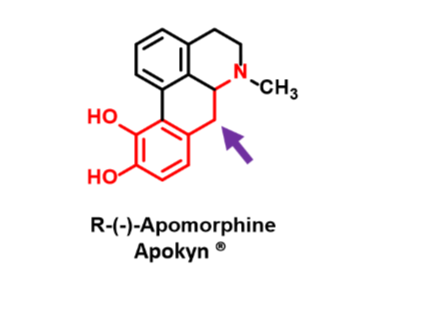
Apomorphine
Dopamine receptor agonist
Nonselective
No oral bioavailability
Controls motor dysfunction in PD
\
Agonizes D1 & D2
Crosses BBB
Nonselective
No oral bioavailability
Controls motor dysfunction in PD
\
Agonizes D1 & D2
Crosses BBB
16
New cards
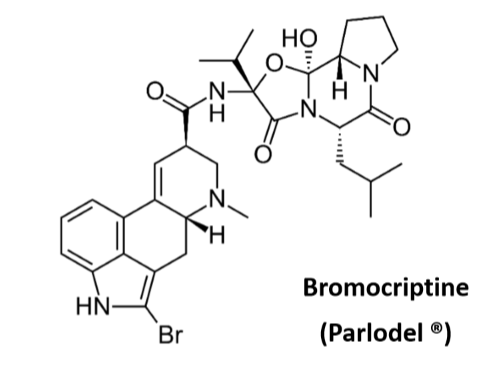
Bromocriptine
Selective D2 agonist
Orally active
Extensive liver metabolism
Inhibits prolactin release from pituitary cells which exclusively expressed D2 receptors
Orally active
Extensive liver metabolism
Inhibits prolactin release from pituitary cells which exclusively expressed D2 receptors
17
New cards
Mirapex/(S)- pramipexole & ropinirole/Requip
Both commonly prescribed for PD
First line treatment sometimes before LDOPA
D2 receptor agonists
\
Side effects: initial nausea, vomiting, postural hypotension, fatigue
Hallucinations, delusions, confusion- esp in elderly dementia patients with PD
First line treatment sometimes before LDOPA
D2 receptor agonists
\
Side effects: initial nausea, vomiting, postural hypotension, fatigue
Hallucinations, delusions, confusion- esp in elderly dementia patients with PD

18
New cards
How are monoamine oxidase inhibitors used in PD (what is their mechanism of action)?
Inhibition of MAO could increase DA concentrations because MAO turns dopamine into DOPAL
19
New cards
What MAOIs are NOT used in PD and why?
Long acting nonselective are contraindicated in combination with LDOPA due to risk of inducing hypertensive crisis and delirium
20
New cards
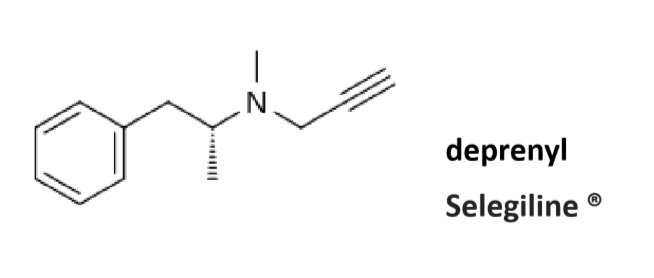
Know the structure/name and mode of action of Selegiline/deprenyl in PD.
Irreversible, MAO B selective
Reduces dosages needs of LDOPA
N-dealkylated by CYPs to L methamphetamine
\
L methamphetamine metabolized to L amphetamine→ vasoactive activity → associated with cardiovascular and psychiatric side effects
Reduces dosages needs of LDOPA
N-dealkylated by CYPs to L methamphetamine
\
L methamphetamine metabolized to L amphetamine→ vasoactive activity → associated with cardiovascular and psychiatric side effects
21
New cards
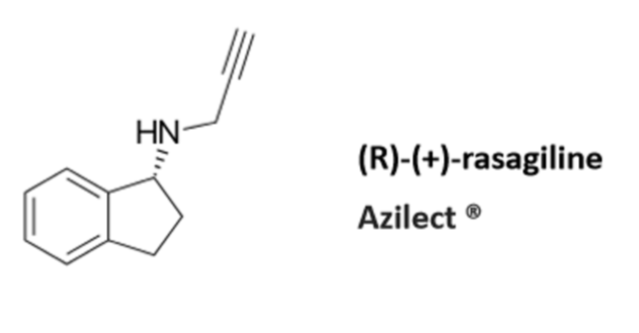
Azilect/rasagiline in PD
•Irreversible, MAOB selective
•Reduces dosage needs of LDOPA
•Ndealkylated by CYPS
•Not vasoactive
•1mg.day dose is neuroprotective
•Reduces dosage needs of LDOPA
•Ndealkylated by CYPS
•Not vasoactive
•1mg.day dose is neuroprotective
22
New cards
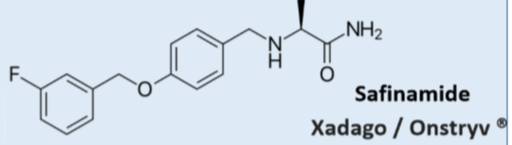
Safinamide/Xadago
MAOI
Multiple MOA:
→ reversible MAOB selective inhibitor
→Blocks sodium and calcium ion channels
→Inhibits glutamate release
\
Add on therapy: Reduces dosage needs of LDOPA
Oral
\
Contraindications:
Patients with severe liver impairment
Patients with retinal disorders
Preggo and breast feeding
In combination with other MAOIs/SSRIs/tyramine containing foods
Multiple MOA:
→ reversible MAOB selective inhibitor
→Blocks sodium and calcium ion channels
→Inhibits glutamate release
\
Add on therapy: Reduces dosage needs of LDOPA
Oral
\
Contraindications:
Patients with severe liver impairment
Patients with retinal disorders
Preggo and breast feeding
In combination with other MAOIs/SSRIs/tyramine containing foods
23
New cards
Know the Catechol O-Methyltransferase (COMT) pathways relevant to PD.
COMT can degrade LDOPA to different intermediates before it turns into dopamine
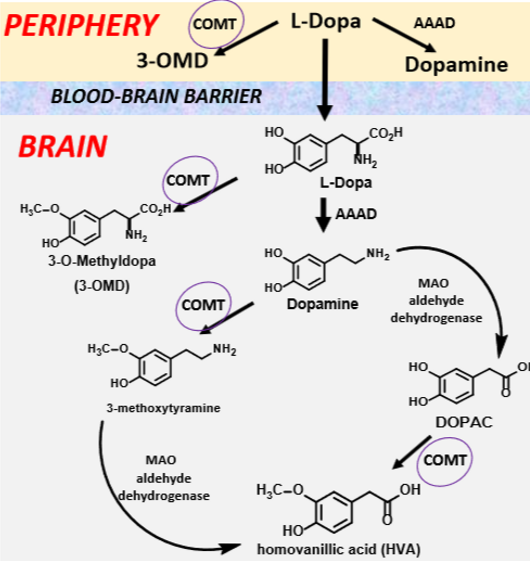
24
New cards
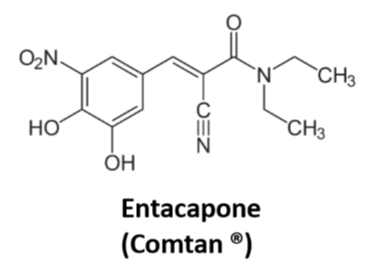
Entacapone/Comtun
Reversible COMT inhibitor
Short duration of action
**Works only in periphery**
Severe diarrhea
Short duration of action
**Works only in periphery**
Severe diarrhea
25
New cards
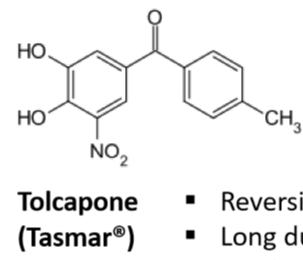
Tolcapone/Tasmar
Reversible COMT inhibitor
Long duration of action
**Works in brain and periphery**
Hepatic toxicity
Severe diarrhea
Long duration of action
**Works in brain and periphery**
Hepatic toxicity
Severe diarrhea
26
New cards
What is a common side effect of Entacapone/Comtun and Tolcapone/Tasmar?
Severe diarrhea
27
New cards
Know the components and utility of Stalevo.
Entacapone- Peripheral reversible COMT inhibitor
Carbidopa- Aromatic L amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor
L-Dopa- Precursor to DA synthesis
\
Helpful to:
→Replace equivalent dosage of individual components
→Help with wearing off effects of L-Dopa/carbidopa alone
Carbidopa- Aromatic L amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor
L-Dopa- Precursor to DA synthesis
\
Helpful to:
→Replace equivalent dosage of individual components
→Help with wearing off effects of L-Dopa/carbidopa alone
28
New cards
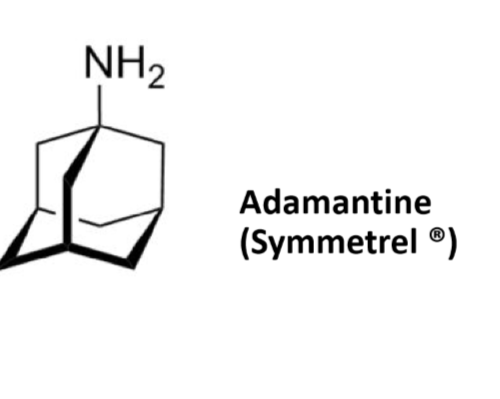
Adamantine/symmetrel
Adjunct therapy
Antidyskinetic (helps with sudden uncontrolled movements)
Causes release of DA and NE from storage vesicles
Blocks reuptake of DA
NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist
Antidyskinetic (helps with sudden uncontrolled movements)
Causes release of DA and NE from storage vesicles
Blocks reuptake of DA
NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist
29
New cards
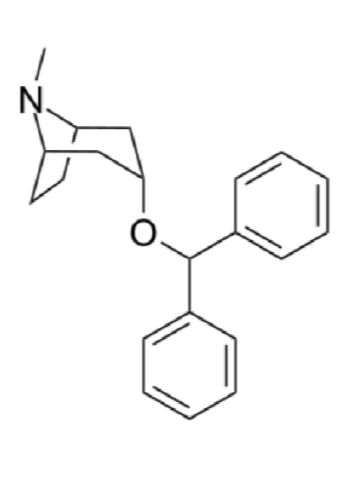
Benzatropine/Cogentin
Adjunct therapy
Muscarinic antagonist (relaxes muscle to avoid spasm)
Control extrapyrimidal effects well so still used despite adverse events
Muscarinic antagonist (relaxes muscle to avoid spasm)
Control extrapyrimidal effects well so still used despite adverse events
30
New cards
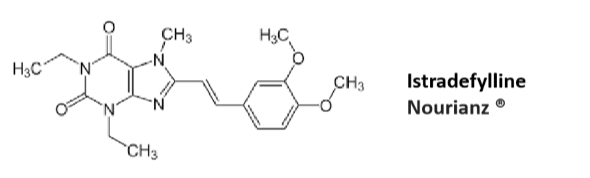
Nourianz
Adjunct therapy with LDOPA/Carbidopa
For treating “off time” in PD
Adenosine A2A receptor antagonist
Metabolized by CYP3A4
Patients with renal failure may need to adjust dose down
For treating “off time” in PD
Adenosine A2A receptor antagonist
Metabolized by CYP3A4
Patients with renal failure may need to adjust dose down
31
New cards
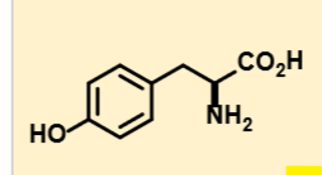
what molecule is this
tyrosine
32
New cards
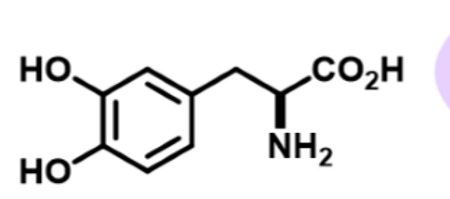
what is this
LDOPA
33
New cards
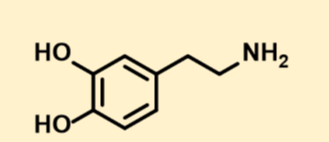
what is this
Dopamine
34
New cards
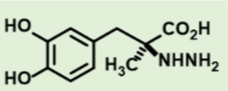
what is this
Carbidopa