NUR 317 - Neurological Disorders
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
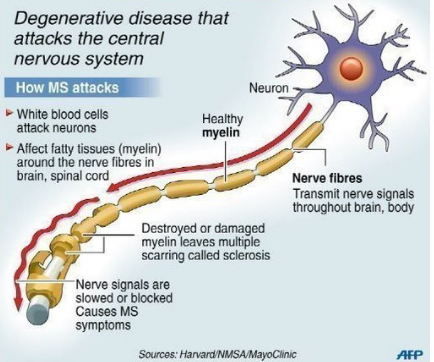
Mutiple sclerosis etiology and pathophysiology
Destroyed or damaged myelin leads to scarring (sclerosis)
Autoimmune process
Activated T cells migrate to CNS, disrupting blood-brain barrier
Likely the initial event in development of MS
Subsequent antigen-antibody reaction leads to demyelination of axons
Multiple sclerosis progression
Onset insidious, gradual
Vague symptoms
Diagnosis long after 1st symptom
Rapid progression vs exacerbations and remissions
Life expectancy after diagnosis is 25+ years
Multiple sclerosis 1st symptoms
1st symptoms may include:
Vision changes
Color distortions
Blindness in one eye
Multiple sclerosis common symptoms
Symptoms vary based on area of CNS affected
Other common symptoms include
Extremity weakness
Loss of coordination and balance
Sensory problems (numbness and tingling, Lhermitte’s sign)
Emotional problems (depression, anger, anxiety)
Speech impairment, dysarthria, dysphagia
Hearing loss
Fatigue
Multiple sclerosis bowel and bladder functions
May be impaired
Constipation
Variable urinary problems
Spastic bladder
Flaccid bladder
Multiple sclerosis sexual dysfunction
Can occur in MS
Erectile dysfunction
Decreased libido
Difficulty with orgasmic response
Painful intercourse
Decreased lubrication
Multiple sclerosis cognitive issues
Short-term memory
Concentration
Information processing (speed)
Multi-tasking
Visual perception
Word finding
Multiple sclerosis manifestations
Early warning signs
Vision problems
Numbness/tingling
Dizziness/balance issues
Common manifestations
Weakness
Cognitive impairment – 50%
Bladder dysfunction – 80%
Don’t Ignore...
Depression
Irritability
Mood swings
Sexual dysfunction
Multiple sclerosis diagnostic studies
Definitive diagnostic test for MS
Based primarily on history, clinical manifestations, and results of certain diagnostic tests
MRI of brain and spinal cord may show presence of plaques, inflammation, atrophy, and tissue breakdown and destruction
MS diagnosis based on:
Evidence of at least 2 inflammatory demyelinating lesions in at least 2 different locations within the CNS
Damage or an attack occurring at different times (usually 1 month or more apart)
All other possible diagnoses ruled out
Multiple sclerosis drug therapy
No cure for MS
Treat the disease process/provide symptomatic relief
Tailored therapy
Early intervention is most effective
Slowing progression of multiple sclerosis
Immunosuppressants
Suppress strength of immune system
Immunomodulators
Includes, amplifies, or inhibits components of the immune system
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
From the anterior pituitary gland – regulates cortisol
Mulltiple sclerosis immunomodulator drug therapy
Begin with Immunomodulator drugs
Interferon β-1a (SQ Rebif and Plegridy; IM Avonex)
Interferon β-1b (SQ Betaseron and Extavia)
SQ Glatiramer acetate (Copaxone)
Patients need:
To be able to self administer medications and rotate injection sites
Use NSAID or acetaminophen
To wear sunscreen / protective clothing
More sensitive to sun
Drug therapy for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis
Teriflunomide (Aubagio)
Immunomadulatory agent with antiinflammatory properties
May cause severe liver disease
Fingolimod (Gilenya)
Prevents lymphocytes from reaching the CNS and causing damage
Regular monitoring of BP and HR
Drug therapy for more active and aggressive forms of multiple sclerosis
Natalizumab (Tysabri)
Used when other medications ineffective
Risk of fatal brain infection
Alemtuzumab (Lemtrada)
Used when ineffective response to 2 or more medications
Ocrelizumab (Ocrevus)
Increases risk of infection and breast cancer
Multiple sclerosis disease modifying therapy considerations
Patients need to report side effects of medications
Patients need to talk to provider before taking over the counter medications
Avoid pregnancy with most medications
Assess for depression, suicidal ideation
All immunosuppressants put patient at risk for infection
Avoid large crowds, people who have infections
Multiple sclerosis drug therapy
Muscle relaxant – spasticity
CNS stimulant
Anticholinergics – bladder symptoms
Tricyclic antidepressants – chronic pain
Antiseizure drugs – chronic pain
Selective potassium channel blocker – improves nerve conduction in damaged nerve segments
Multiple sclerosis nursing interventions and care
Avoid and identify triggers
Climate change or hot/cold extremes
Infection
Stress
Build general resistance to illness
Exercise
Rest
Healthy diet
Reassurance
Tests
Procedures
Education
Support groups/resources
Medication
Treatment plans
Multiple sclerosis symptom management
Fatigue – schedule activities and rest periods
Limited mobility – walking aids, promote and maintain mobility, avoid injury
Bowel and bladder dysfunction – bladder training, intermittent cathing, external catheter, adequate fiber and fluids
End stage multiple sclerosis
Symptoms increase in severity, may see more symptoms at one time, or symptoms may be come permanent
May not be able to live independently/function independently
May see serious complications
Palliative care may be helpful
Parkinson’s disease
Chronic, progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by
Bradykinesia
Rigidity
Gait disturbance
Parkinsonism
Mimics PD but often resolves after removal of the cause
Causes of Parkinsonism:
Medications - metoclopramide (Reglan), reserpine, methyldopa, lithium, haloperidol (Haldol), and chlorpromazine
Amphetamine or methamphetamine
Hydrocephalus, stroke, trauma, infection, hypoparathyroidism
Parkinson’s lack of dopamine
Degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in substantia nigra of midbrain
Lose 80% of dopamine before symptoms are seen
Parkinson’s etiology and pathophysiology
Unusual clumps of protein deposited inside neurons
Unknown cause
Lewy bodies
Found in brains of patients with PD
Presence indicates abnormal brain functioning
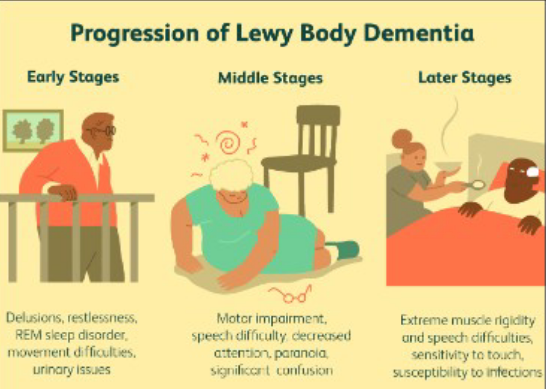
Lewy body dementia
Can be misdiagnosed as PD
Sleep
Behavior changes
Parkinson’s clinical manifestations
Onset is gradual and insidious with ongoing progression
Just one side may be affected at first
TRAP
Tremor
Rigidity
Akinesia
Postural instability
Speech impairments
Parkinson’s - tremor
Often first sign
Initially minimal
More prominent at rest
Aggravated by
Emotional stress
↑ Concentration

Parkinson’s - rigidity
↑ Resistance to passive motion when limbs are moved through their ROM
Cogwheel rigidity
Jerky quality
Like intermittent catches in passive movement of a joint
Occurs due to sustained muscle contraction
Muscle soreness
Tired/achy
Slow movements
Parkinson’s - akinesia
Absence or loss of control of voluntary muscle movements
“Freezing”
Distinct, rigid gait
Expressionless
Parkinson’s - bradykinesia
Slowness of movement
Particularly evident in the loss of automatic movements
Parkinson’s - postural instability
Propulsion or retropulsion (forward and backward movement) is common
Pull test
Parkinson’s - nonmotor symptoms
Depression and anxiety
Apathy
Fatigue
Pain
Urinary retention and constipation
Erectile dysfunction
Memory changes
Sleep disturbances
Parkinson’s complications
Swallowing difficulties increase -
Malnutrition
Aspiration
General debilitation, increasing weakness -
Pneumonia
UTIs
Skin breakdown
Orthostatic hypotension is common -
↑ Risk for falls and injuries
Parkinson’s disease progression
Complications increase
Motor symptoms
Weakness
Akinesia
Neurologic problems
Neuropsychiatric problems
Dementia often results
Associated with ↑ mortality
Parkinson’s diagnostic tests
No specific tests exist
Diagnosis based on history and clinical features
Requires presence of:
Asymmetric onset
Confirmation is a positive response to antiparkinsonian drugs
Parkinson’s drug therapy
No cure for PD, care aimed at symptom management
Drug therapy should correct imbalances of neurotransmitters within the CNS
Antiparkinsonian drugs either
Enhance the release or supply of DA (dopaminergic)
Antagonize or block the effects of overactive cholinergic neurons in the striatum (anticholinergic)
PD - Dopamine agonists drugs
Amantadine
Apomorphine (Apokyn)
Pramipexole (Mirapex)
Ropinirole (Requip)
Amantadine
PD treatment
Antiviral agent
↑ Dopamine release; blocks reuptake
May be useful early on, but used with levodopa in later stages
Apomorphine (Apokyn)
PD treatment
Injection
Take with antiemetic (but not ondansetron)
Pramipexole (Mirapex)
PD treatment
Also used for restless leg
Side effects vary based on early or late stages of PD
Filtered through kidneys - considerations with kidney impairment
Ropinirole (Requip)
PD treatment
Also used for restless leg
Side effect considerations
Nausea, fatigue, dyskinesia, dry mouth (common in many PD meds)
PD - MAO-B inhibitors drugs
Selegiline
Rasagiline
Safinamide (Xadago)
MAO-B inhibitors actions
↑ Levels of dopamine
May be used in combo with Levodopa
When used with other medications, may minimize “off” times and extend “on” times
PD - Levodopa drugs
Increases avaliable dopamine
Levodopa, Sinemet (levodopa with carbidopa)
Carbidopa, levodopa, entacapone (Stalevo)
Sinemet (levodopa with carbidopa)
PD treatment
Levodopa converts to DA in the basal ganglia
Carbidopa inhibits an enzyme that breaks down levodopa before it reaches brain
Carbidopa combining with levodopa reduces chance of side effects from levodopa
Stalevo (carbidopa, levodopa, entacapone)
PD treatment
For “off” episodes
Advanced PD
PD - Levodopa/carbidopa considerations
Sinemet is added when moderate to severe symptoms develop
Effectiveness of Sinemet could wear off after a few years of therapy
Some HCPs initiate therapy with a DA receptor agonist
Ropinirole (Requip), pramipexole (Mirapex), rotigotine (Neupro)
Add Sinemet when moderate to severe symptoms develop
When taking Sinemet:
Monitor for dyskinesia
Report uncontrolled movements (eyes, face, extremities), difficulty urinating, mental changes, palpitations
Monitor for nausea, vomiting, light-headedness (short term side effects)
Do not give with food (protein inhibits drug absorption)
PD - Anticholinergic drugs
Bentyl
Scopolamine
Benztropine (Cogentin)
Anticholinergic actions
Help blocks acetylcholine
Decrease involuntary muscle movements
Potential adverse effects include blurred vision, dry mouth, constipation and urinary retention
Parkinson’s drug therapy things to note
Use of only one drug is preferred
Fewer side effects
Dosages are easier to adjust
Combination therapy often required as disease progresses
As “off” episodes occur
Often occur within 3-5 years
PD - Antiemetic drug therapy
Ondansetron (Zofran) drug of choice
Avoid metoclopramide (Reglan) and promethazine (Phenergan)
PD - Antipsychotic drug therapy
Exacerbate symptoms
Olanzapine (Zyprexa), quetiapine (Seroquel), risperidone (Risperdal)
PD - Dopaminergic drug therapy
Excessive use can lead to paradoxic intoxication
Parkinson’s interprofessional care
Surgical therapy – for patients
Unresponsive to drug therapy
Have developed severe motor complications
DBS – Deep brain stimulation - delivers current to the targeted brain location)
Ablation – destruction of tissue that produces abnormal chemical or electrical impulses leading to tremors or other symptoms
Duopa - stoma created, gel containing carbidopa/levodopa is injected directly (through a pump) and into small bowel through PEG tube
Transplantation
Deep brain stimulation
Parkinson’s treatment
Most common surgical treatment
Reversible and programmable
↓ Increased neuronal activity produced by DA depletion
Improves motor function
Reduces dyskinesia and medications
Parkinson’s nursing management
Promote well balanced diet
Malnutrition and constipation can be serious consequences
Adequate fiber and fruit
Need to consider diet of patients with dysphagia and bradykinesia
Promote physical exercise
Exercise limits consequences from decreased mobility - contractures, constipation, muscle atrophy
Physical therapy
Occupational therapy
Educate/promote sleep hygiene
For patients who are at risk of falls or “freeze”...have patient
Consciously thinking about stepping over a line on the floor
Lifting toes when stepping
One step back and . . .two steps forward
Rock side to side before stepping forward
Parkinson’s promoting independence and self-care
Get out of a chair by using arms and placing the back legs on small blocks
Remove rugs and excess furniture
Simplify clothing (no buttons or hooks)
Use elevated toilet seats
Use an ottoman to elevate legs
Parkinson’s resources and support
As disease progresses
End stage – around the clock care, wheelchair or bedridden, hallucinations/delusions
Emotional support - depression, anxiety
Family