Egypt Quiz
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Predynastic Period
5000-2920 BC
Early Dynastic Period
2920-2649 BC

title, date, materials, findspot
Pot with Boats and Standards
Predynastic Period (Nagada II), 3500-3200 BC
Red paint on buff-colored vessel
El-Amra
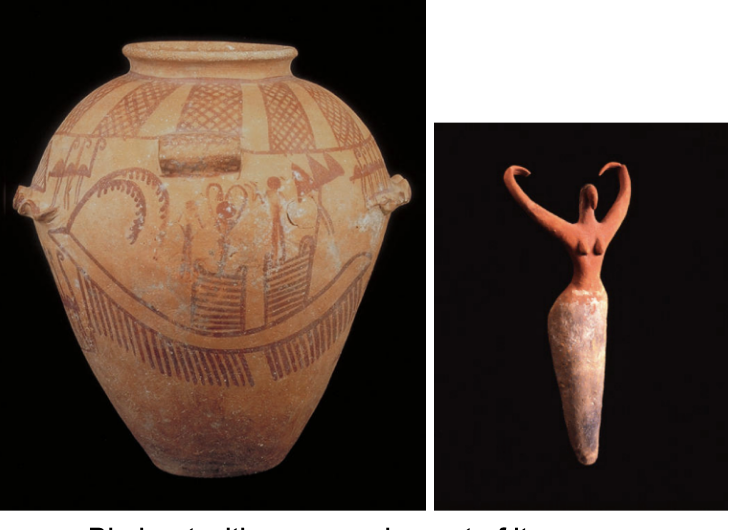

Pot with Boats and Standards
Big boat with oars coming out of it
Towers on boat
Standards and birds around boat
Pottery is a typical is Nagada II/Gerzean period
Creme-colored pot with red paint
Red = ox blood
Most common type of artifact found in predynastic Egypt
In addition to boat with towers/standards:
People (women) with upraised arms
Upraised arms occur in 3D
Painted and sculpted in 3D
On other part, there are mountains
Not entirely clear what is happening in scene, but shows the complexity in the artists
Loose compositions
Not organized

title, date, materials, findspot
Hierakonpolis Wall Painting
Predynastic Period (Nagada II), 3500-3200 BC
Paint on Plaster
Tomb 100, Hierakonpolis
Hierakonpolis Wall Painting
Found in a tomb at Hierakonpolis
Tomb might have belonged to late predynastic ruler
Filled with funerary gifts
Constructed well
Lavish
drawing^
Introduction to large scale paintings!!!
Earliest ones
Took designs from pot, and blew them up to the scale of an entire wall
Lined walls with bricks, filled bricks with plaster, then put artwork on plaster
Funeral scene
Combat scene
Figures raising arms out (wailing women)
Could be women who are mourning in some type of funerary ritual
Animals scattered throughout
Pairs of men locked in combat
Animals standing around circle → animals caught in a trap
Link between art and writing
Three figures on lower right hand → squatted men turns into a hieroglyph making the word plural
Hieroglyph → opposite side (left corner) – image of man striking three smaller people/prisoners → mace (stick with round ball at top) = symbol of pharaoh dominating his enemies (smiting king pose)
Working stone
Artist beginning to create more realistic drawings of people and animals
Progression to a very more orderly arrangement→ registers
Use of art to record historical events and people
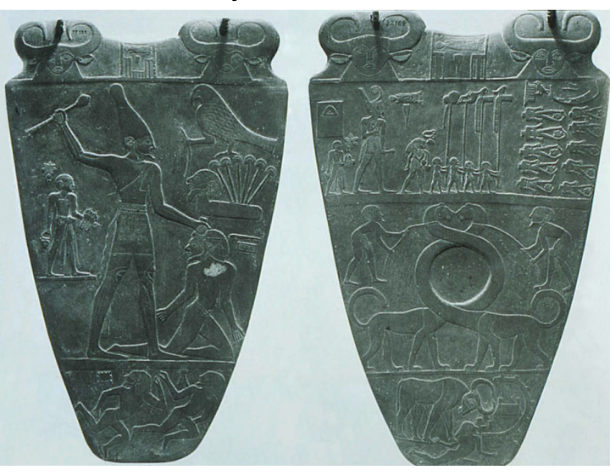

title, date, materials, findspot
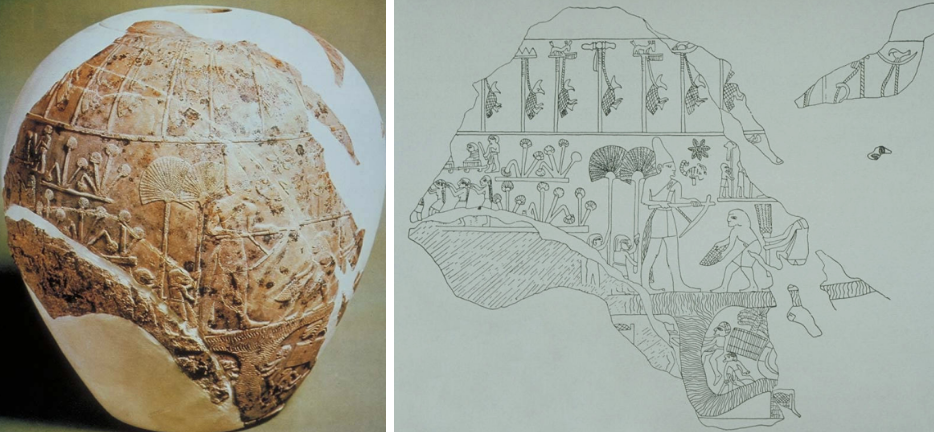
Narmar Palette
Predynastic Peroid (Nagada III), 3100-2890 BC
Slate
Horus Temple, Hierakonpolis
Narmar Palette
Serpents (serpopards) → entwined necks to grind makeup
Heads and body of leopards and necks of serpents
Crowded with iconography/historical events, they have to leave a space to grind the makeup
Ceremonial palette
Whole thing is showing the unification of lower and upper Egypt
Showing first king of Egypt unifying lower and upper Egypt
Top of palette:
Frontal facing heads of Goddess Harthor (mother of god of sky/sun)
Cow heads staring directly at viewer
Last of non-profile
Never use frontal in paintings or reliefs
Human or incarnation of Horus (god of sky/sun)
Mother at top of palette
In between frontal heads, there is a fish that is over a chisel
King Narmer’s name!
Narmer means striking catfish
Writing still associated with art
Divided into three registers
Serpopards are being controlled by attendants
Allegory of unification of upper and lower Egypt
In top register is the result of what happens in the bottom registers
Bottom register:
Giant bull
Bull trampling on enemies and crashing through city wall
In act of conquering other portion of Egypt
Bull = symbol of king (epithet – description)
Standard epithet for the king was a “strong bull of Horus”
Top register shows the result of the bottom register
King (largest figure) is facing two rows of decapitated enemies (head between legs)
Enemies are surrounded by boat
King is behind standard bearers (different regions)
Another fish and chisel
Wearing a crown → Red Crown of Lower egypt (northern egypt)
On other side → White Crown of Upper Egypt
Victory of upper egypt over lower egypt
Narmar holding mace
Giant falcon is a symbol of Horus → godly component
Falcon on top of papyrus (symbol for lower egypt)
Falcon is controlling lower egypt
Bottom register shows enemies (drowning in marsh?)
Sandal bearer behind king <3
Establishes a lot of king iconography:
Hieratic scale!!!
Crowns (white crown of upper egypt and red crown of lower egypt)
King wearing false beard (king iconography)
King has bull’s tail (bull’s tail is symbol of king)
King’s generally have nude torsos and short kilt
Standard smiting king pose!!
Torso facing one way and the legs and head in profile (frontal eyes)
Striding pose (always striding)
Have to stand somewhere
ex.) bearer is standing on something
Groundlines!
Broken into registers
Done on stone! Slate is a very hard stone
Choosing stone because they had a lot of it
Interested in stone because it was permanent
title, date, materials, findspot
Scorpion King Macehead
Predynastic Period (Nagada III), 3200-3100 BC
Stone
Horus-Temple at Hierakonpolis
Scorpion King Macehead
Horus → God Horus
Scorpion King Macehead is example of a tool → pear shaped stone
Big stone club
Stick wooden handle in the middle
Used during warfare
Pound on enemy
Way too large (at widest = 1 foot long)
Way to fancy to have been used during warfare
More ceremonial
A macehead also served as ceremonial badge for military – attribute for kings (rulers and powerful)
1. Super early use of narrative in art to send messages about kingship
2. Establishes many conventions of Egyptian art
3. One of the first formalatic (?) of kingship
Scene
King → hieratic king, white crown of upper Egypt and has bull's tail
In open ceremony → opening canal
Canal winds its way through the scene below the king
Banks and channels
Various workmen are working on new canal (doing maintenance)
See tree and huts, prowl of boat → landscape elements
In front of king are standard bearers (on shelf) an behind are fan bearers
On top register, there are seating figures being carried on chairs and below them are dancers surrounded by papyrus plants (lower egypt)
Bird looking things that are bound
A bound bird is a symbol for a captured enemy
Dangling from standard that are topped with deities of gods
Right by face = scorpion
Message
All powerful man
Sanctioned by the gods
Celebratory support (workers and regions of Egypt are supporting him)
He is not only able to defeat enemies, but master of landscape
He controls the power of water
Egypt is land of dichotomy
Water is the life of Egypt → lived in world of dichotomy (few steps away from water, they were in desert [which is harsh])
Via symbols and conventions of art
Whole narrative of controlling people, environment is occurring on an object that was a tool of war
Effect method of communicating rule
Using art to communicate rule
Each community/locals were in charge of the water source, but king showed up to see the control of the water
Conventions of Egyptian Art
Profile and striding, but frontal shoulders and eyes
Static
Boxy (rectangular/cubic)
Registers
Division of plane → grounding line, never floating in space
Use of hieroglyphics in art!!!
Standard King Iconography
Crowns
red crown and white crown → symbolize the two parts of Egypt
Hieratic scale
Symbols, like to scorpion, to represent the kings
Bull’s tail
Holding things to show power (mace and ho)
Bare torso and wear short skirts
Role of king → maintain stability (ma’at)
Human embodiment of the divine
Divine spirit was inside the king
Incarnation of the creator god

title, date, materials, findspot
Funerary Stele of King Wadj
Dynasty I, c. 2920-2770 BC
Limestone
Tomb of Wadj, Abydos
Funerary Stele of King Wadj
Serekh
Horus name
Inside palace
Combo: plan and elevation
Recessed and buttressed facade
Bird holding nose in Narmar Palette → Horus
Actually from a tomb
Format is similar → Stele (slab of stone)
Tomb stele (functioned as a funerary complex and it marked the burial of this king) → sending message
Usually in pairs and put on eastern side of tombs
Tombs were called mastaba(s)
Depicted
Ziggurat/temple and has recessed and buttressed walls
Inside is the pictograph of the name of the king
Sitting on top is the bird that is the emblem of the Egyptian god Horus
Serekh name
Seeing name of king with bird on top of it (referred to as Horus name/Serekh name of the king)
King was human embodiment of Horus on earth
Writing is the art
Egyptian artists are starting to carve out of all stones
This piece is made out of soft stone, limestone (easy to carve)
Stele of King Djet
Stele of marking an early king at a Mastaba
Shows name tag of king

title, date, materials, findspot
Label of King Den
First Dynasty (c. 3100-2800 BC)
Wood/Ebony
Tomb of King Den, Abydos
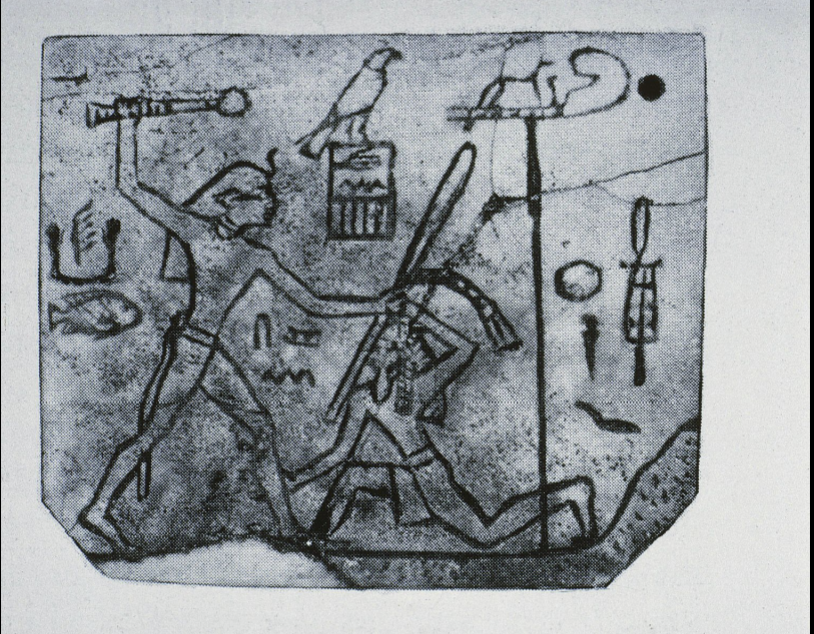
Label of King Den
Serkh
Horus name
Inside palace
Serkh is in many Egyptian art
Recessed and buttressed facade
Bird on top of facade
See on top ground line → looks like someone running
Festival → Heb Sed cloak

title, date, materials, findspot
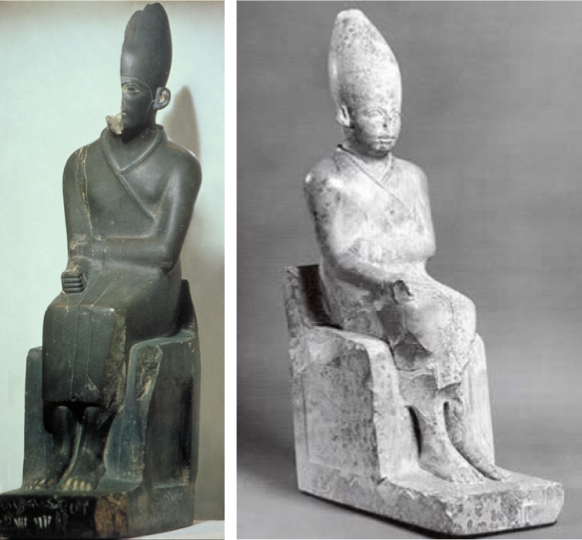
Khasekhmewy
Dynasty II, c. 2770-2649 BC
Limestone
Hierakonpolis
Khasekhnewy
Another important trend → 3D in hard stone
Right = harder stone
Two portraits of last king of Dynasty II
Shows carves in different stones
Found in temple
King Iconography
Robe → ceremonial robe = Heb Sed Cloak
Positioning of arm → one hand clenched (like holding something) and other hand folding across
White crown of Upper Egypt
Relief carved on front → defeated enemies on base
Only three positions that the king can be doing with his posture
1. Seated on throne
2. Smiting pose
3. Striding or standing
Style doesn’t really change over time
Archaic Style
Head is large in proportion of body
Awkward transition in neck to the body
Gesture with left hand across waist and left hand resting on thigh → archaic gesture
Cloak is off of neck → stiffness in archaic style
Can see how it is carved
Not far from shape of rectangular block
Quadra Frontal approach
Get block of stone and draw grid on front (frontal view), and the rest of the sides
Then carve the stone at all angles
Mathematical carving

title, date, materials, findspot
Offering Scene
Dynasty II, c. 2770-2649 BC
Limestone
Saqqara
Offering Scene
Dynasty III King Djoser
2630-2611 BC
title, date, material, findspot
Tomb (= Mastaba) of Merneith
Dynasty I, 3100-2890 BC
Mudbrick
Saqqara
Tomb (= Mastaba) of Merneith

title, date, material, findspot
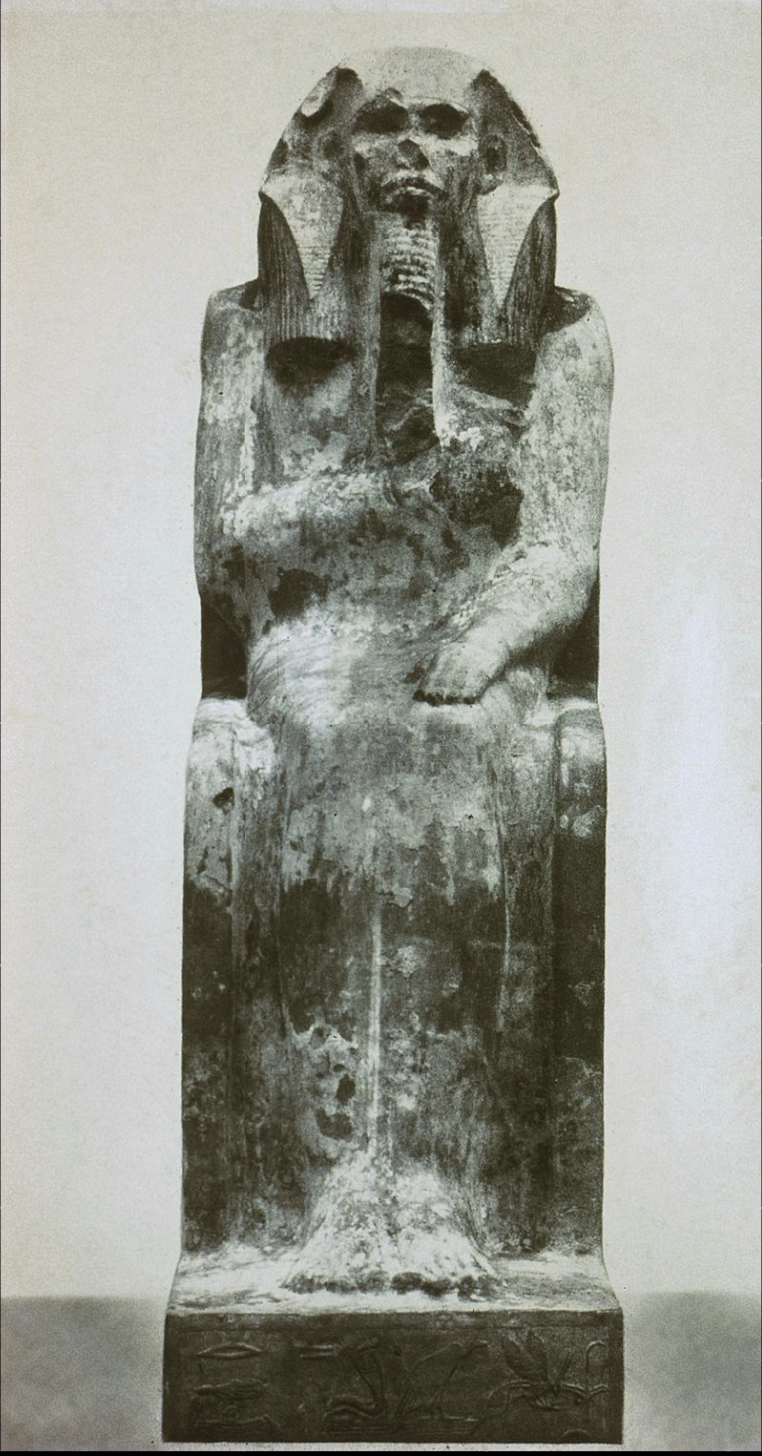
Statue of King Djoser
Dynasty III, 2630-2611 BC
Limestone
Saqqara
Statue of King Djoser

title, date, material, findspot
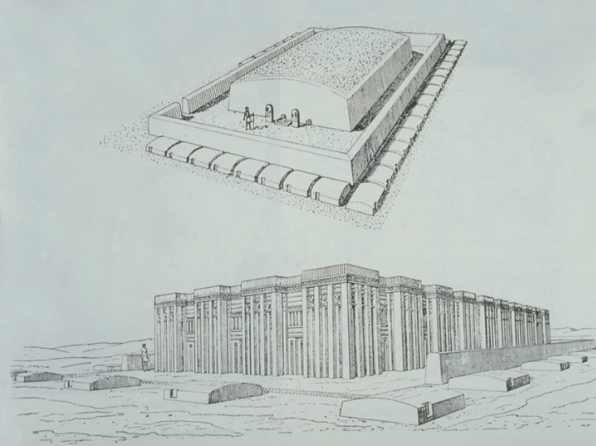
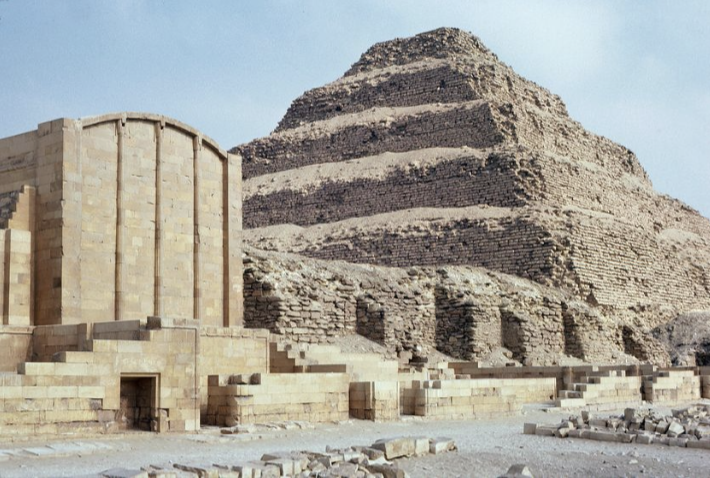
Step Pyramid of King Djoser
Dynasty III, 2630-2611 BC
Limestone
Saqqara
Step Pyramid of King Djoser
title, date, material, findspot
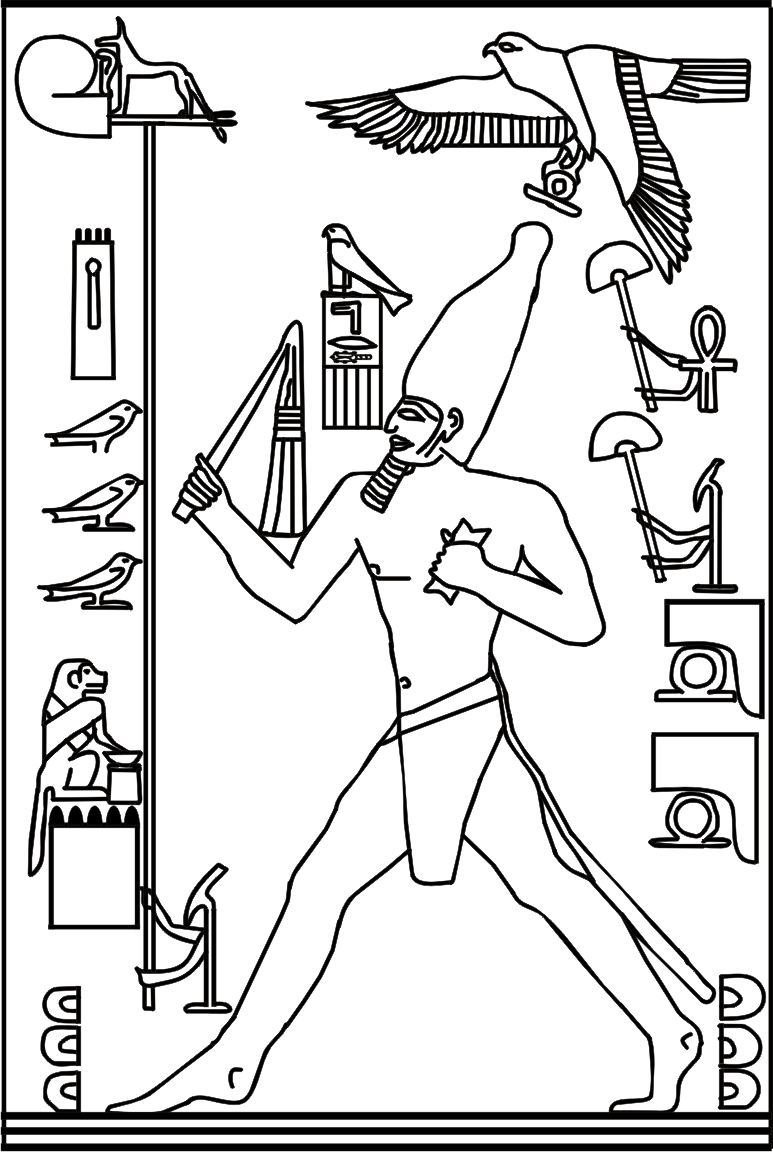
Relief, King Djoser Running between Territorial Markers
Dynasty III, 2630-2611 BC
Limestone
Beneath Step Pyramid of King Djoser, Saqqara
Relief, King Djoser Running between Territorial Markers

title, date, material, findspot
Wooden Panel of Hesira
Dynasty III, 2630-2611 BC
Wood
Tomb of Hesira, Saqqara
Wooden Panel of Hesira
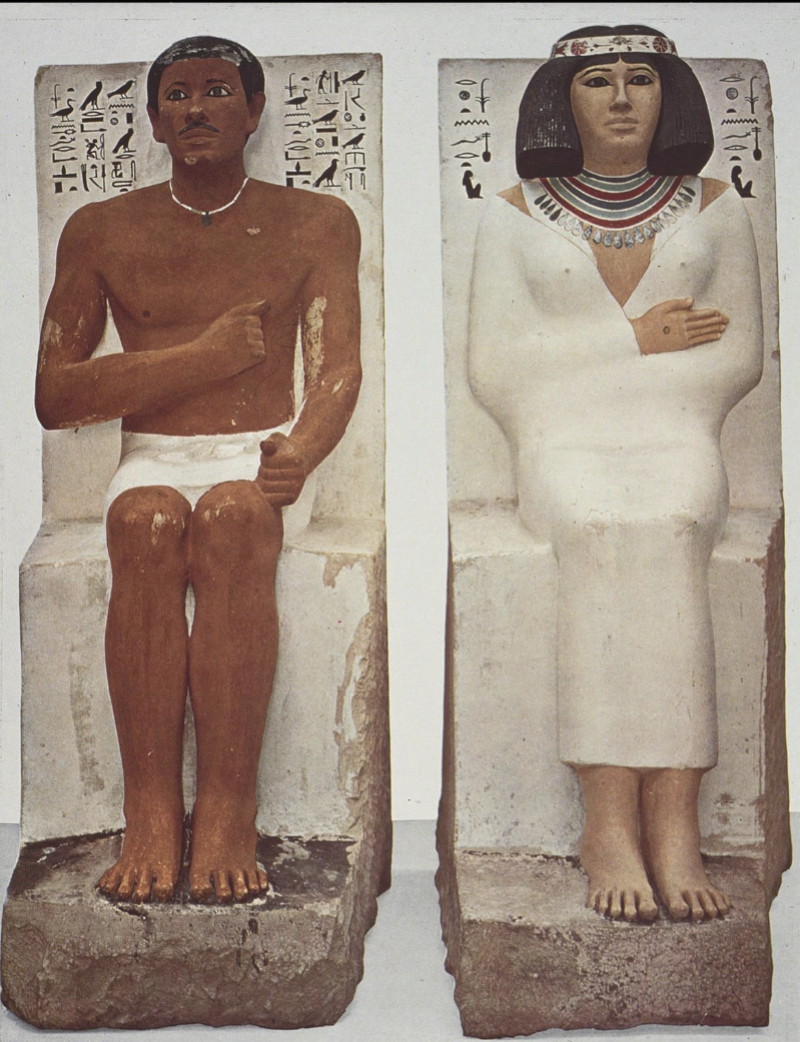

title, date, material, findspot
Ka Statues of Rahotep and Neferet
Dynasty IV, 2575-2465 BC
Limestone and paint
Meidum
Ka Statues of Rehotep and Neferet
Old Kingdom
Dynasties IV-VI —> 2575-2134 BC
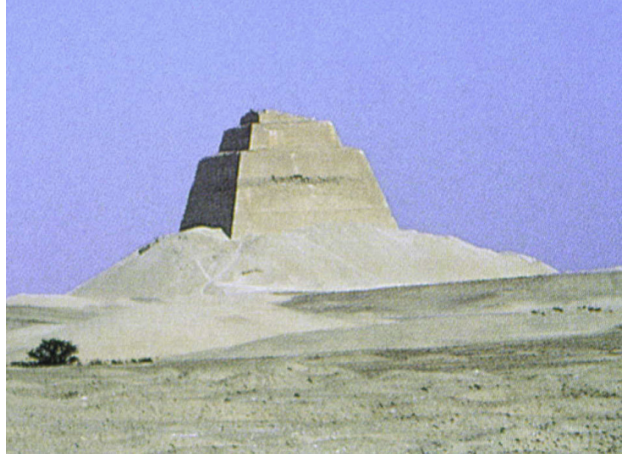

title, date, material, findspot
Pyramid of King Huni
Dynasty III-IV, 2780-2680 BC
Limestone
Meidum
Pyramid of King Huni
Begun by the last king of Dynasty III, but finished by his son-in-law [Snefru] (ruler in Dynasty IV)
1. Establishes the 4 standard components of a pyramid complex
2. Really is the first attempt to a geometrically true pyramid
Standard Elements of a Pyramid Complex
4 standards components
Built on west side of nile
When you die, you die in the west (sun sets on the west side)
Always a valley temple
A pharaoh would be transported to site via boat
Special boats were built for this that would symbolically show the birth-death that goes along with the sun rise-set
Boat would stop at valley temple
Pharaoh would be picked up by funerary procession
Carried through causeway
Processional way
Mortuary
Temple that was positioned at the eastern side of the temple
Pyramid itself
Pyramid of King Huni had all 4 standards
Cross Section
First attempt of a true geometrically true pyramid
Core of pyramid was constructed out of 7 steps → only 3 remain today
Step pyramid to a true pyramid
Took packing stones and then sheathed the packing stones in a white limestone
Steep incline and lack of bonding material between the packing stone resulted in a massive collapse
Packing stone and limestone collapsed and slid down, they grounded themselves
Limestone shattered
They got ground into rubble
That is at the base of the temple

title, date, material, findspot
Bent Pyramid of Snefru
Dynasty IV, 2680-2565 BC
Limestone
Dashur
Bent Pyramid of Snefru
First king of Dynasty IV
Dynasty IV → great age of pyramid building!!
Snefru was the most prolific pyramid builders of ancient Egypt
Bent shape and because it was the pyramid where we have the first excavated temple
Know about decoration
Snefru completed Huni’s tomb and made North (red) pyramid and lower temple
Two burial chambers
The king was known for foreign travels (lebanon)
Out and about king
Shape
Archaeologists are not clear why the incline changes and the slope becomes far less deep
Theory:
Died and someone else finished it
Perhaps it was constructed when Huni’s pyramid collapsed and wanted to rethink the plan of the pyramid
First valley temple that was excavated
Excavations gave us understandings of these temples
Entrance hall would have been lined with reliefs
Temple has open court and pillars
Meant to hold statues of the king

title, date, material, findspot
Relief of Procession of Egyptian Nomes, Valley Temple, Bent Pyramid of Snefru
Dynasty IV, 2680-2565 BC
Limestone
Dashur
Relief of Procession of Egyptian Nomes, Valley Temple, Bent Pyramid of Snefru
Relief from bent pyramid
Reliefs showed procession of female personifications of nomes/districts of Egypt (word for regions/districts of Egypt)
Bringing produce all over Egypt for the king in the afterlife
Each nome has a name above their head, holding trays, and also bringing offerings that are listed out in front of them for the king
Perpetual offerings for the kings
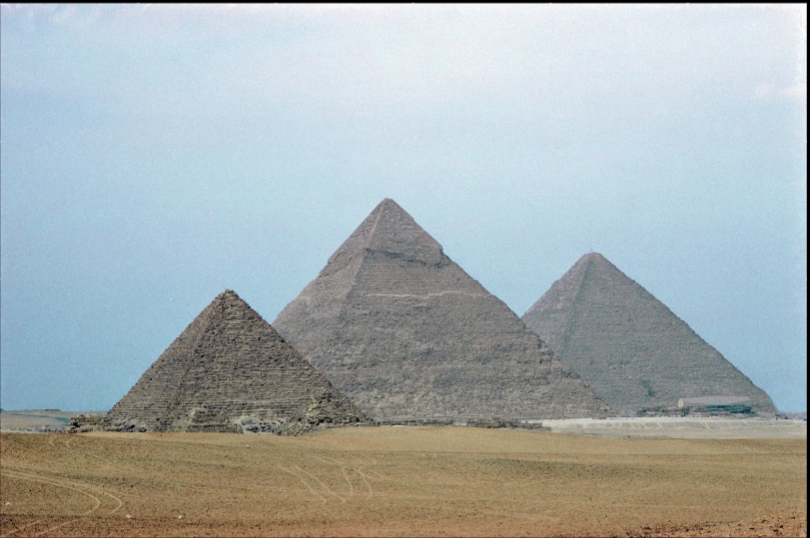

title, date, material, findspot
Pyramids of Cheops, Chefren, Mycerinus
Dynasty IV, 2680-2565 BC
Limestone
Giza
Pyramids of Cheops, Chefren, Mycerinus
One of the seven wonders of the ancient world
Only ones of the seven wonders of the ancient world that remain standing today!
Burial center of the three most famous kings of Dynasty IV
Cheops (Kufu) → The Great Pyramid
Central Pyramid (and Sphinx) of Chefren
Mycerinus → Satellite pyramids with it
This complex preserves more than a standard complex
Variety of other features (boat burials, queens, kids)
Allow us to study technology
Pyramids of Cheops —> The “Great” Pyramid
It is the largest of all the pyramids
it was in fact the tallest building until the 19th century (CE)
Incredibly, controlled mathematical proportions
Square base
Very accurate measurements
Entire building would have been encased in limestone (white limestone)
Limestone was removed when building the Cairo museum (?)
Pyramid shape… like why?
Why was there an urge for an important burial spot?
Probably related to the worship of the sun god
Heleopolis = stone was famous for its pyramid shape → became symbol for the sun
Scholars aren’t making up relationship between shape of pyramids to the sun god
Kings started to begin to give themselves a second name (nickname) was sun of Ra
Ra is sun god!
Connection between kings, pyramids, and sun gods
Huge, but no cap/casing preserved
Pyramid of Chefren
Still has casing left on top
And still has sphynx
4 standard elements with added stuffSphynx in front of pyramid
Originally carved on an outcrop bedrock that occurred at the start of the causeway
Some of it was carved, and some of it was built up (look at feet)
Mixed mythological guardian figures
Lion bodies with human heads
Human head with nemus cloth
Portrait of Chefren himself? → most likely a depiction of the guardian figure
Right at start of causeway
Pyramid of Mycerinus
Final of the group
Tiny third pyramid
Can tell this pyramid because he has three satellite pyramids on the side
Other elements:
Satellite pyramids
Khafre also has satellite pyramids
Built for the queens
Mastabas behind the Great Pyramid (for officials)
Boat pits for the burial of the boats used during the funerary procession
Huge range for satellite features that went along with the pyramids
Not only preserve the 4 standard components, but other components
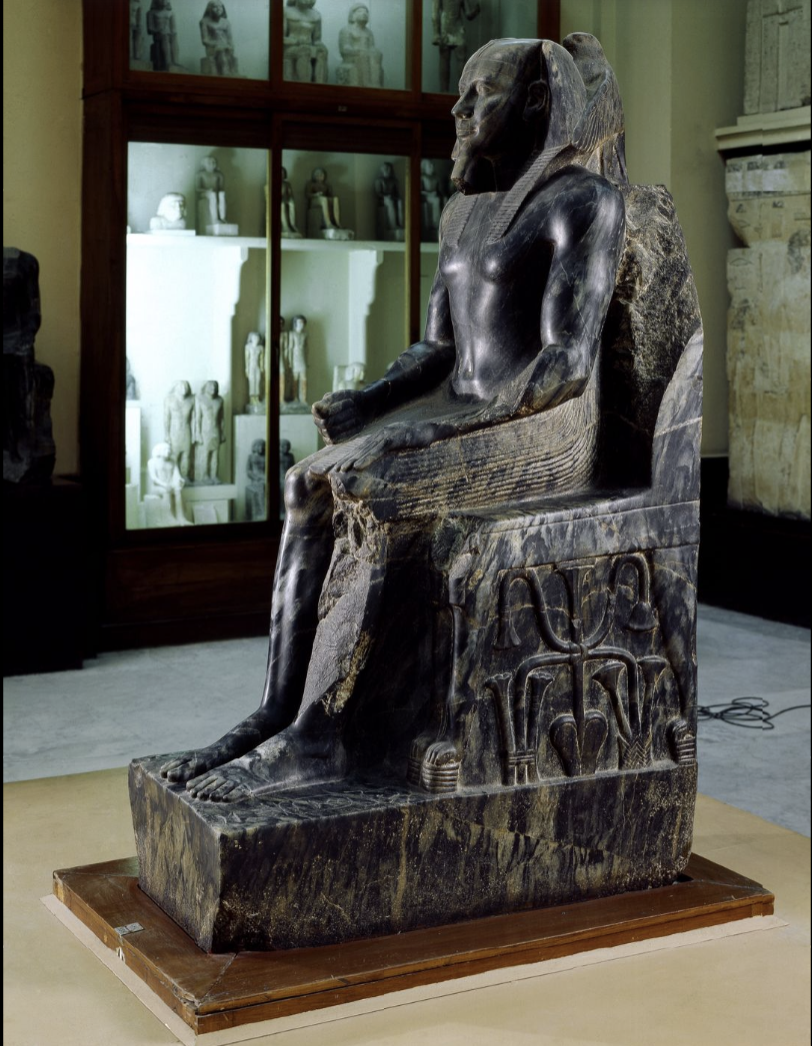

title, date, material, findspot
Khafra/Chefren
Dynasty IV, 2520-2494 BC
Diorite
Giza
Khafra/Chefren
Still has casing left on top
And still has sphynx
4 standard elements with added stuffSphynx in front of pyramid
Originally carved on an outcrop bedrock that occurred at the start of the causeway
Some of it was carved, and some of it was built up (look at feet)
Mixed mythological guardian figures
Lion bodies with human heads
Human head with nemus cloth
Portrait of Chefren himself? → most likely a depiction of the guardian figure
Right at start of causeway
Famous piece
Found in a pit in his valley temple with 6 others
Probably stored there for safekeeping
One of 23 statues from his valley temple
Don’t have all 23 statues, but it is marked in the pyramid where they were
None of these statues are exactly similar as the other
Dislike of absolute repetition
Each one is different
Vary in the types of seats
Some have high-back seat with lion arm rests, and others have low-back seat
Inscribed with different variations of the king’s name
Bird behind his head
King iconography
Period where the king iconography get fully developed
Found in valley temple (pit in valley temple) along with 6 other statues
Stored for safekeeping
Wonderful to have found multiples of this statue → no two of them are exactly the same
Dislike of absolute repetition
Inscribed with different versions of titles and names
Arranged differently on each statute
In this reign for the first time, they fully established the regalia of kingship
King iconography
False beard (fastened with a string)
Headcloth is sorta new (nemis headcloth)
Nemis headcloth also have a cobra euraius
Regalia → bare torso and kilt
But now pleated kilts
Falcon on the back of the neck
Falcon → horus
Horus is the embodiment and protector of the living king
On the sides of the high backed throne → papyrus and lotus that are knotted around each other (tied together → plants of upper and lower egypt)
Lion’s head on the throne
Throne is adorned with lion heads at the end of the arm rests
Emblem of egyptian kingship
Iconic → not only was it very crisp, clear, but also its material
Extremely hard diorite
Much harder to carve than limestone
Dense composition, dense structure
Very fine details and create a much smoother surface
Diorite comes from south of Egypt (outside of Egypt)
He could get diorite → demonstrated Khafre’s power
Diorite → Khafran’s diorite
Emblematic = style
Different than archaic style
Has a much smoother surface, delicate modeling of the body, and the pose is slightly different
Hand on lap, not on chest/torso
BIG DEAL
title, date, material, findspot
Sun Temple at Abu Gurob
Dynasty V, c. 2524-2400 BC
Limestone
Abu Gurob
Sun Temple at Abu Gurob
Sun temple
Shape = relation with the sun god
Non funerary building from Dynasty V
Pyramids built from sun god, Ra
Abu Gurob
Construction of the sun temples really emphasis the pharaoh and the sun god
Pharaohs began to considered themselves the reincarnation of the sun god
In style/in plan, it echos the standard components of pyramid complexes
Entrance on the eastern side
Western end = podium with a giant masonry obulus
Represented the “Ben ben”
Center of court = altar for offerings/sacrifices
Covered corridors
Chapel on the east side
Found on this west side of the nile (like the Pyramids)
Sun temples had connections to the pyramids
Offerings for the king would be sent from the sun temple to the pyramids
Funerary function
Would have been a causeway
“Pyramid” itself
title, date, material, findspot
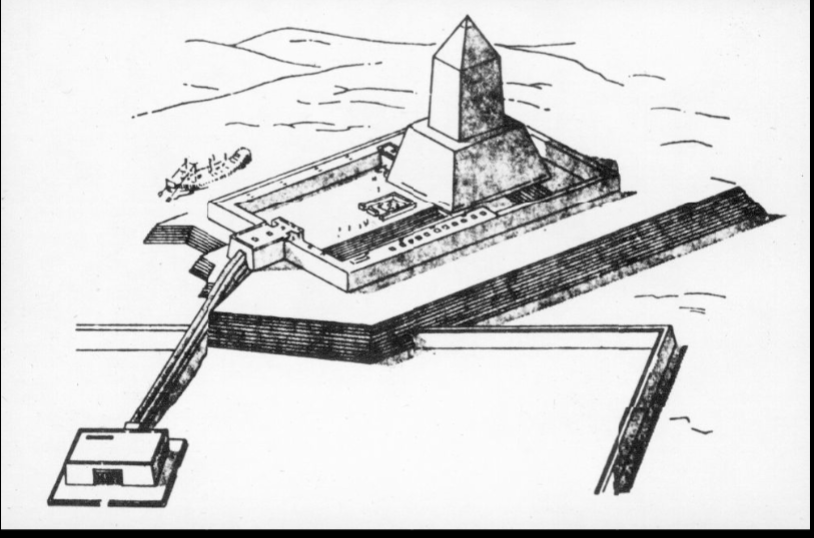
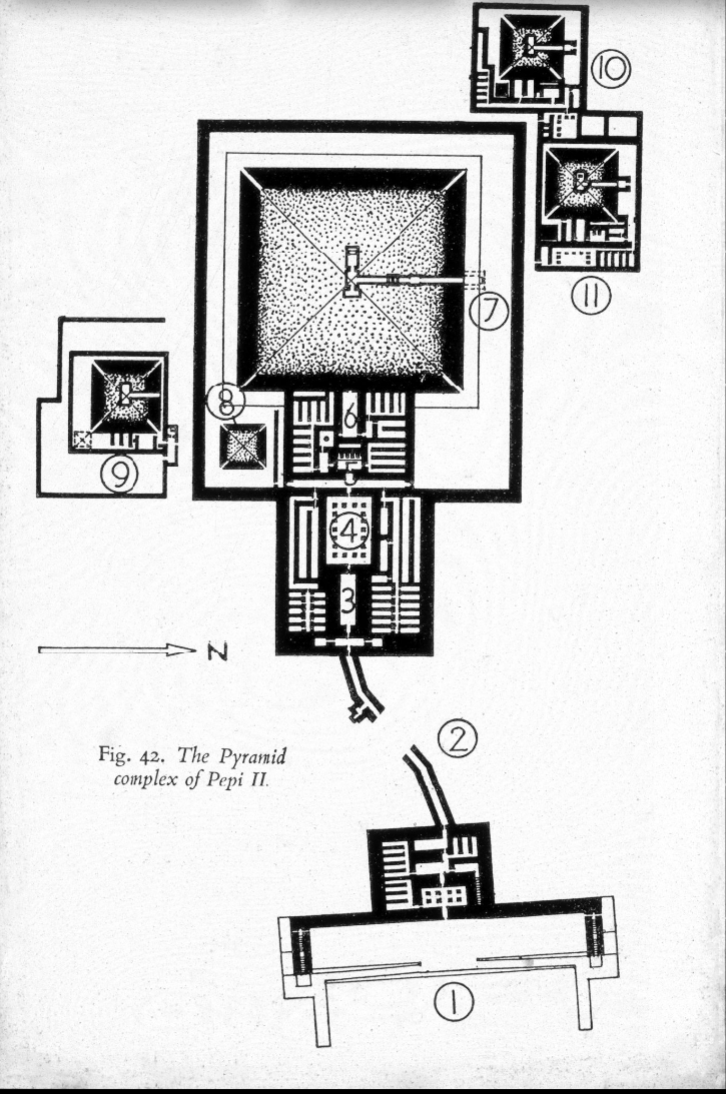
Pyramid of Pepe II with Pyramid Texts
Dynasty VI, 2400-2250 BC
Limestone
Saqqara
Pyramid of Pepe II with Pyramid Texts
Final pyramid complex of the old kingdom
Old Kingdom = Dyns. IV-VI
Late old kingdom, the pyramid complex elements remained the same, but are no longer as huge as they were in Dyns IV
Pyramids became the same height and the bases were very similar
Even the pyramid temple became standardized in this period
Open court with statue of king and altar for offerings
Has long entrance hall with open court
Satellite pyramids
Lots of decoration in the temple
Kingship
King interacting with other deities
Added transverse hall after open court
Statue chapel
Offering chambel before the actual pyramid itself
Pepe II is a very interesting pharaoh because he began his reign as a child (as early as age 6)
Because he was so young, his mother ruled as his regent until he was old enough to rule by himself

title, date, material, findspot
Statuette, Pepy II and his Mother
Dynasty VI, c. 2400-2250 BC
Alabaster
Findspot unknown
Statuette Pepy II and his Mother
Tiny little with big mother
Mother acted as regent until he was old enough to rule
Mother is portrayed as ruler
Handful of female rulers
Art historical significance:
Translucent stone (alabaster)
Incredible experiment
Two figures are intersecting at 90º angles
Two intersecting cubes
Each one has her and his own title on the front of the statue

title, date, material, findspot
Triad of Mycerinus, Hathor, and a Nome
Dynasty IV, c. 2630-2524 BC
Schist
Giza
Triad of Mycerinus, Hathor, and a Nome

title, date, material, findspot
Shepsi and Nikauhathor
Dynasty V, c. 2524-2400 BC
Limestone and paint
Tomb Chapel of Shepsi, Saqqara
Shepsi and Nikauhathor
Group statues
Ka statue
Tomb statue from the old kingdom (dynasty V)
Depicts this couple and their child
Every tomb needed at least one statute of the deceased
Generally free standing, but could have been carved into the rock wall
Often hidden → weren’t meant to be seen by visitors!
Meant for the ka
Limestone
Some would have been made of wood and plaster with paint
Conventions of Egyptian Art:
Idealized anatomy of woman
Arm around husbands shoulder
Red men, yellow women
Gesture of hands
Nice child iconography → index finger on its mouth with sidelocks
Hieratic scale
Children depicted naked
All three would have been buried in the same complex