Business Management Quiz II (FALL2025)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Organizational Design Consists of:
Organizational Structure, Organizational Chart, and Organizational Design
Organizational Structure
the formal arrangement of jobs within an organization
Organizational Chart
the visual representation of an organization's structure
Organizational Design
creating or changing anorganization's structure
Elements of organizational design
1. Work specialization
2. Departmentalization
3. Chain of command
4. Span of control
5. Centralization/decentralization
6. Formalization
Purposes of Structuring Organizations
- Divides work to be done into specific jobs and departments
- Assigns tasks and responsibilities associated with individual jobs
- Establishes formal lines of authority.
Simple structure
an organizational design with little departmentalization, wide spans of control, centralized authority, and little formalization
Functional structure
an organizational design that groups together similar or related occupational specialties
Divisional structure
an organizational structure made up of separate, semiautonomous units or divisions
Stages of Group Development
1. Forming
2. Storming
3. Norming
4. Performing
5. Adjourning
Forming
people join the group and then define the group's purpose, structure, and leadership
Storming
characterized by intragroup conflict
Norming
characterized by close relationships and cohesiveness
Performing
the group is fully functional and works ongroup task
Adjourning
group members are concerned withwrapping up activities rather than task performance
Group Processes: Conflict Management
- Conflict: perceived incompatible differences that result in interference or opposition
- Traditional view of conflict: the view that all conflict is bad and must be avoideD
- Human Relations view of conflict: the view that conflict is a natural and inevitable outcome in any group
Interactionist View of Conflict
- Interactionist view of conflict: the view that some conflict is necessary for a group to perform effectively
- Functional conflicts: conflicts that support a group's goals and improve its performance
- Dysfunctional conflicts: conflicts that prevent a groupfrom achieving its goals
Psychological Safety
A shared belief held by team members as to whether it is safe to trust each other enough to take risks
DISC Assessment
a behavioral tool that categorizes individuals into four primary styles:
Dominance
Influence
Steadiness
Conscientiousness
Why Human Resource Management is Important
- Significant source of competitive advantage
- Important part of organizational strategies
- The way organizations treat their people can significantly impact performance
Human Resource Management Process
Consists of these interrelated activities: recruitment, selection, training, compensation, and supervision. The goals are to obtain, develop, and retain employees.
quiet quitting
Those who will show up to work and do the minimum required but not much else. Taking a step back from extra work, committees and socialization with coworkers.
The Great Resignation
an ongoing economic trend in which employees have voluntarily resigned from their jobs en masse
MBTI vs DISC
DISC is behavior-focused and often used for team dynamics and communication
MBTI is preference-focused and often used for self-insight and personal development
Value of knowing your MBTI
Personal:
- Guide career decisions
- Introverts may prefer research,
- Extraverts may prefer interacting with other people
- Discover strengths and understand preferences
Professional:
- Improve communication
- Increase team effectiveness
- Increase employee/customer satisfaction
RTO
Recovery Time Objective (RTO): is the maximum acceptable downtime for an business process after a failure
Types of Workplace Connection (CLEAR)
Colleague Connection
- Trust and support between coworkers; collaboration and social support
Leader Connection
- Engagement with leaders; clarity in communication and feedback
Employer Connection
- Alignment work company values; meaningful work contributing to company goals.
Role Connection
- Job clarity and motivation; a sense of purpose/personal advancement.
Colleague Connection
- Encourages collaboration and social support through open and transparent dialogue.
Leader Connection
- Builds trust and engagement when managers provide clear expectations, feedback, and autonomy.
Communications strategies to improve CLEAR
Persuasion skills: skills that enable a person to influence others to change their minds or behavior
Speaking skills: skills that refer to the ability to communicate information and ideas in talking so others will understand
Writing skills: skills that entail communicating effectivelyin text as appropriate for the needs of the audience
Organizational Communications
the process of exchanging information within an organization, and between an organization and its external stakeholders
Communications Model
a framework that breaks down the process of information transfer, including key elements like the sender, message, and receiver
Organizational behavior
the study of the actions of people at work
Goals of from management perspective
Individual behavior:
attitudes, personality, perception, learning, and motivation of individual employees.
Group behavior:
norms, roles, team building, leadership, and conflict among groups of employees at work.
Organizational aspects: structure, culture, and human resource policies and practices at work.
Organizations as an iceberg' metaphor
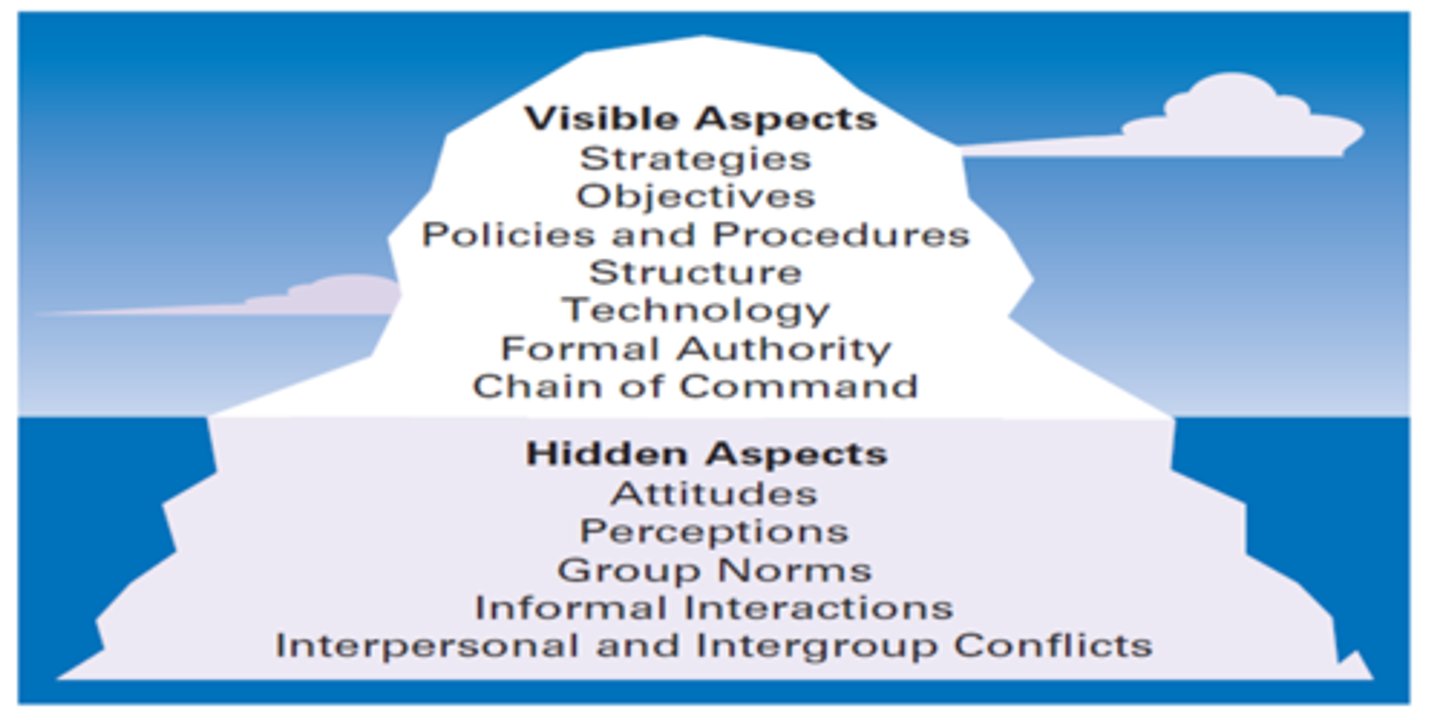
Employee Behaviors Important to OB
1. Employee productivity: a performance measure of both efficiency and effectiveness
2. Absenteeism: the failure to show up for work
3. Turnover: the voluntary and involuntary permanent withdrawal from an organization
What is EQ?
The ability to identify, use, and understand, and manage emotions in positive ways to relieve stress, communicate effectively, empathize with others, overcome challenges, and defuse conflict.
Elements of EQ
Self-awareness: The ability to recognize and understand your own emotions, moods, and how they impact others.
Self-regulation: The ability to control or redirect disruptive impulses and moods and to think before acting.
Motivation: Being driven by internal, personal goals rather than external rewards.
Empathy: The ability to understand the emotional makeup of other people and to treat them according to their emotional reactions.
Social skills: The ability to manage relationships and build networks effectively.
How EQ affects professional performance
- Ability to navigate social complexities in the workplace
- Ability to lead and motivate others
- Ability to accurately read situations and people andr espond appropriately
Strategies for improving EQ
Five key skills are integral to emotional intelligence
Quickly reduce stress
Recognize and manage emotions
Connect with non-verbal communication
Use humor to deal with change
Resolve conflicts positively and confidently