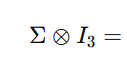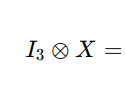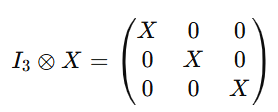L2 - Multivariate models for sales and market shares
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What do we mean with a multivariate sales model?
In a multivariate sales model we consider the sales of all brands in a product category
Why consider multivariate models?

What does our sales model look like if we include all marketing mix variables of other brands?
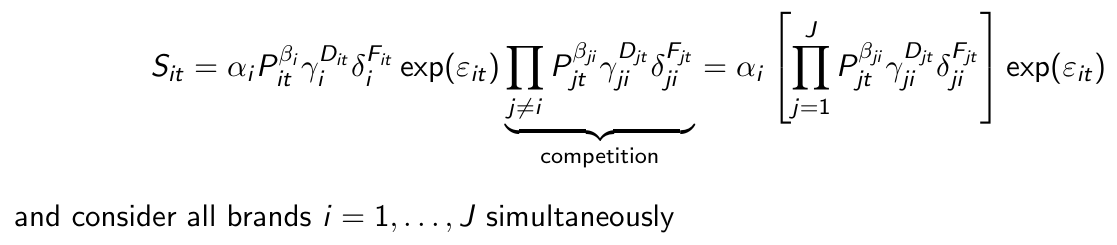
What does βji denote?
the cross-effect of the price of brand j on the sales of brand i
What does βii denote?
the own price effect
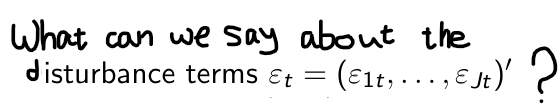
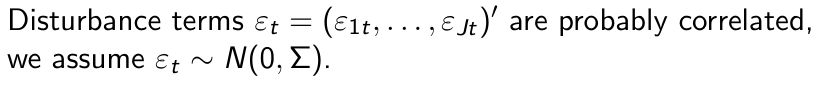
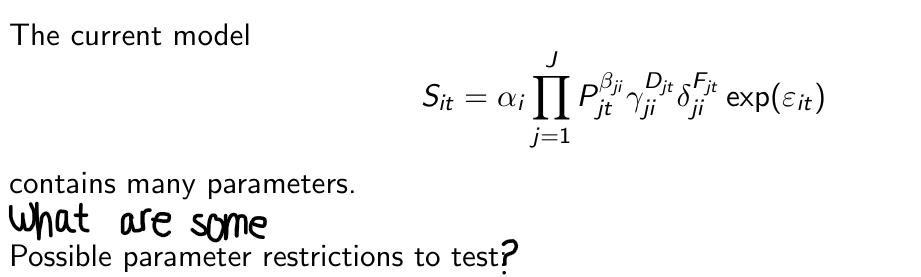

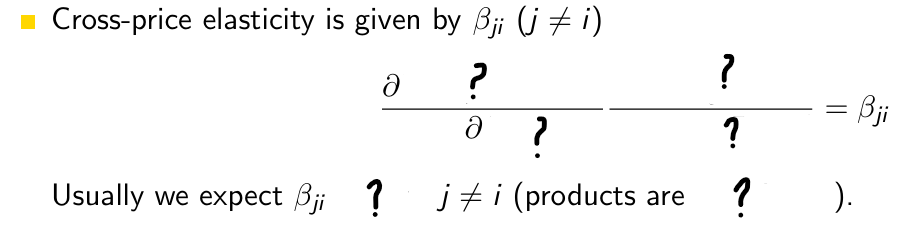
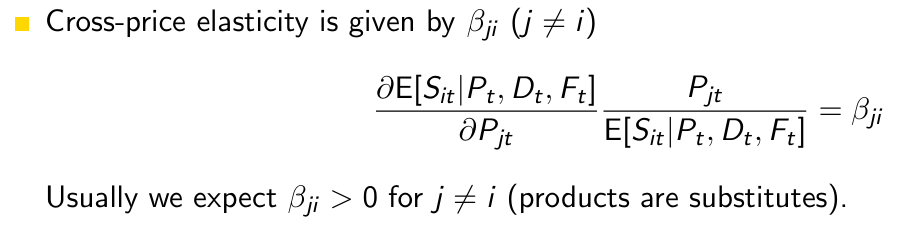

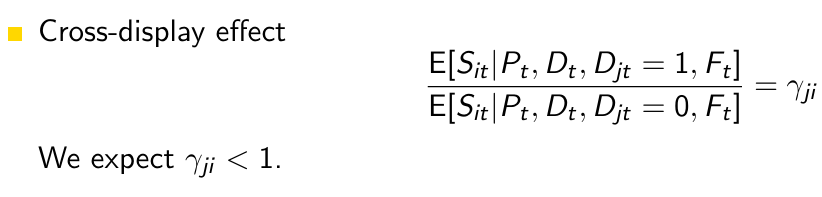
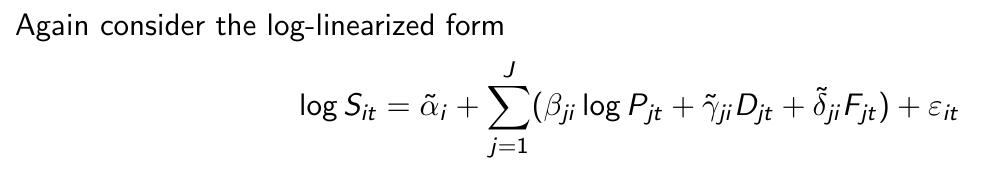
How can we summarize this model for all brands and all time periods?
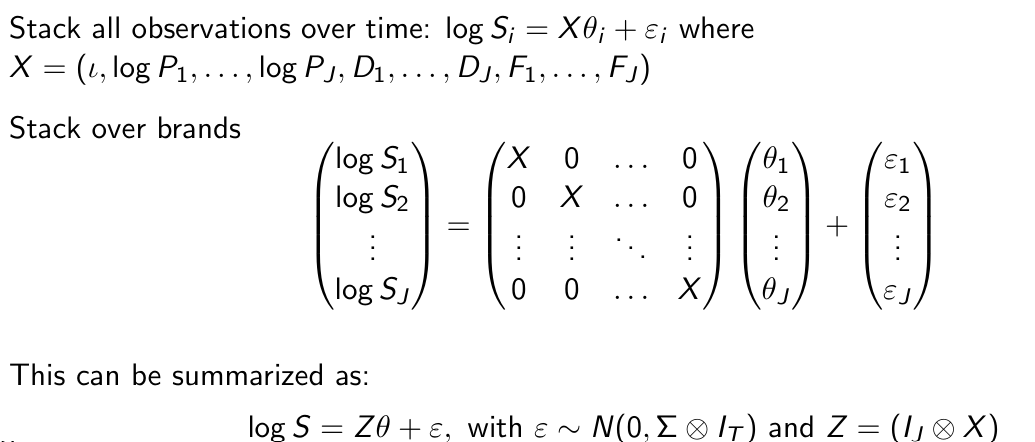
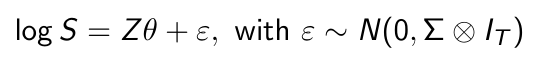
How can we estimate θ and Σ?
Feasible Generalized Least Squares [FGLS] (=Seemingly Unrelated Regressions [SUR])
Give the FGLS Algorithm we use here.
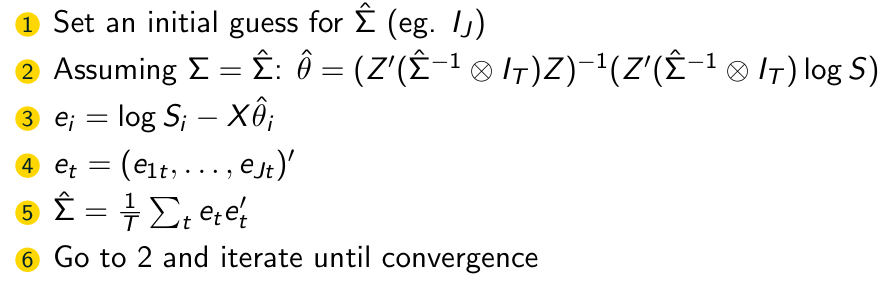
What is the first step of the FGLS Algorithm?

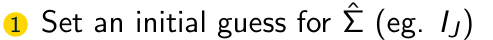
What is the second step of the FGLS Algorithm?
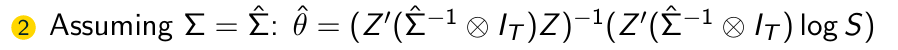
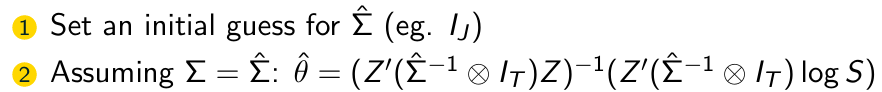
What is the third step of the FGLS Algorithm?
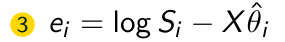
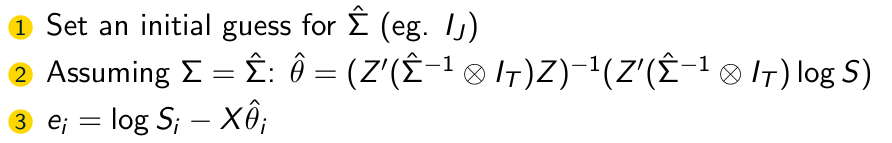
What is the fourth step of the FGLS Algorithm?
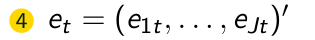

What is the fifth step of the FGLS Algorithm?
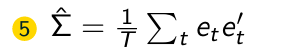
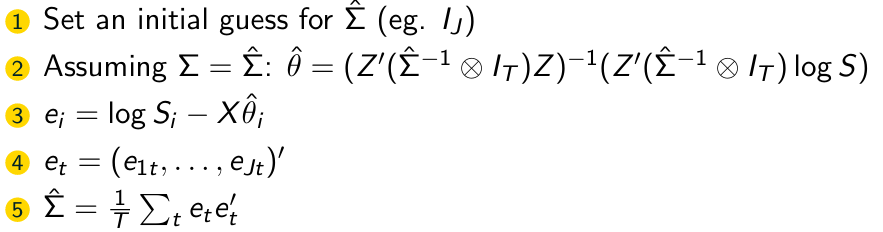
What is the sixth step of the FGLS Algorithm?

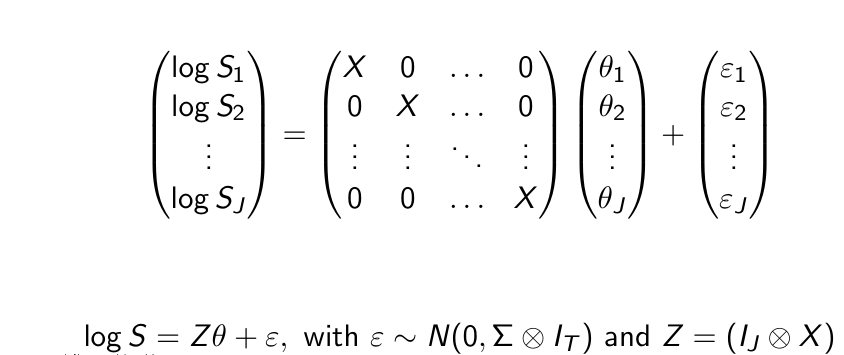
Why is this a special case?
In the previous example the same X matrix is used for each equation
→In this special case (F)GLS is the same as OLS per equation In general this is not the case
Give some examples why in reality X is not the same for every brand.

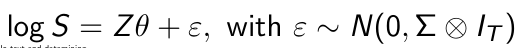
How can we obtain standard errors for our parameter estimates here?
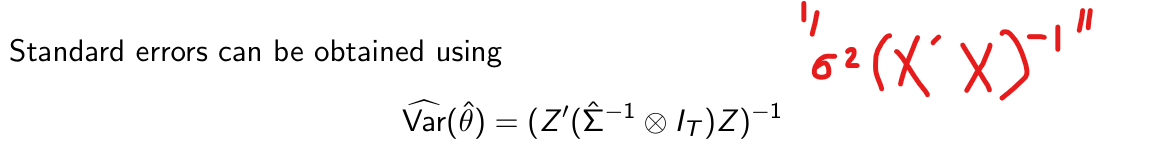
Give three reasons why we would consider market shares instead of sales.

Popular market share models are designed to be 5 things (CDPPL). What are those?

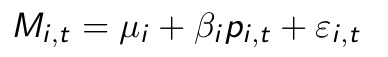
What do you think of this model for market shares?
For the linear model, predictions of market shares can become larger than 1 or smaller than 0. —> This violates logical consistency.
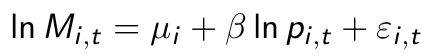
What do you think of this model for market shares?

In 1975 Bell et al. introduced a certain specification to model market shares. What specification? What were the determinants for the market share according to this model?

What are the 4 axioms for the attraction specification?


Which axiom is missing?

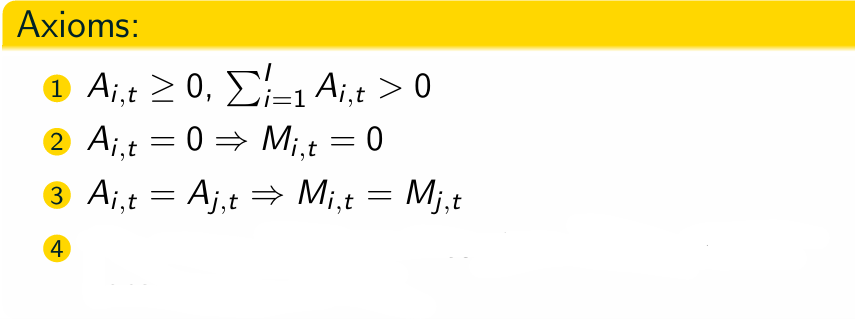
Which axiom is missing?


Which axiom is missing?


Which axiom is missing?


What do the axioms imply?
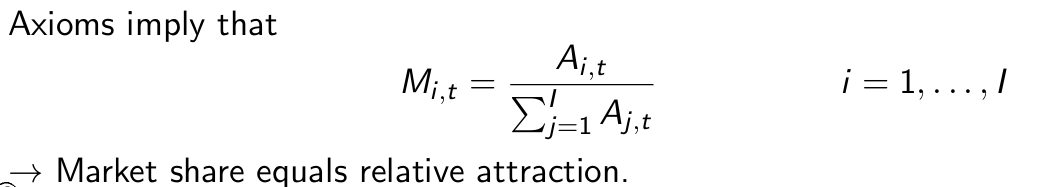
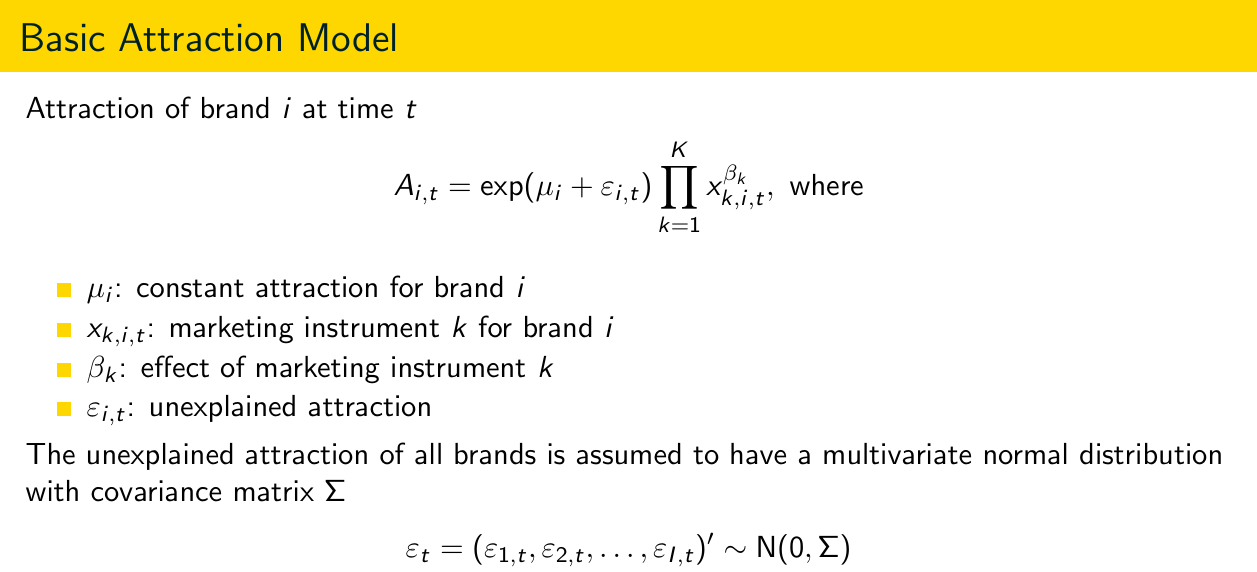
Give the formula for the basic attraction model. Explain what all variables are and give the distribution of epsilon_t.

What are the two important assumptions in this specification?
Effect of marketing instrument on attraction equal for all brands
No cross effects of instruments on attractions!
What is the MCI (multiplicative competitive interaction) model?
Same as the attraction model
What are the advantages of the Basic Attraction model/MCI model?

What do we mean with ‘Partial effects of changes in marketing instruments make sense’ for the MCI model?
What do we mean with the (price) elasticities make sense?
How can the MCI model be extended?

What is the identification issue in share models?
There are only I−1 independent observations even though there are I shares. If you tried to estimate I equations directly, you’d have perfect multicollinearity.
The fully extended [FE] model contains many parameters. In practice we will want to impose (and test) various restrictions. What are those?

If we assume Restricted covariance matrix [RCM] and we have four brands and we take the fourth brand as the benchmark, what does our covariance matrix Σ* look like?
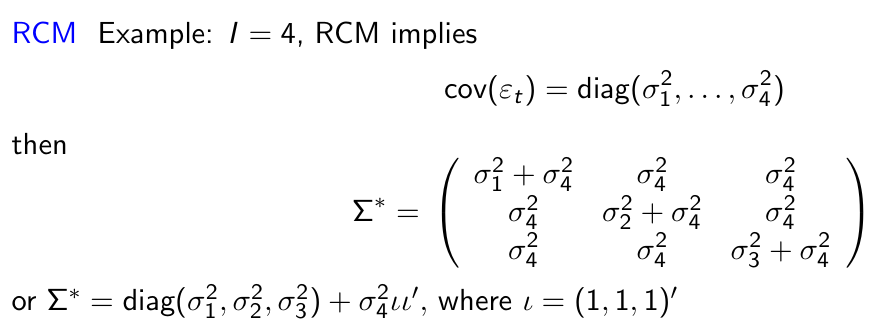
What are Ai,t and ln Mi,t − lnMI,t for RC (Restricted Competition)?
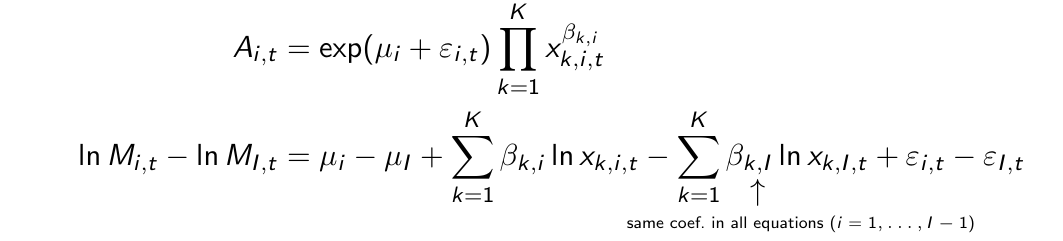
What are Ai,t and ln Mi,t − lnMI,t for RE (Restricted Effects)?

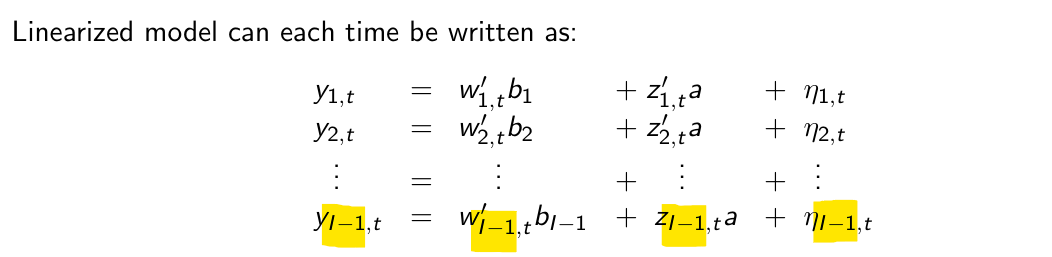
Explain what all the terms are.
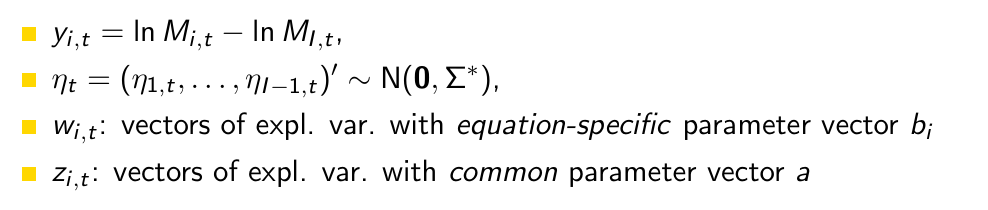

This is only for one time point t. How can we write this down for all time periods in one model? Be specific, really write it down.
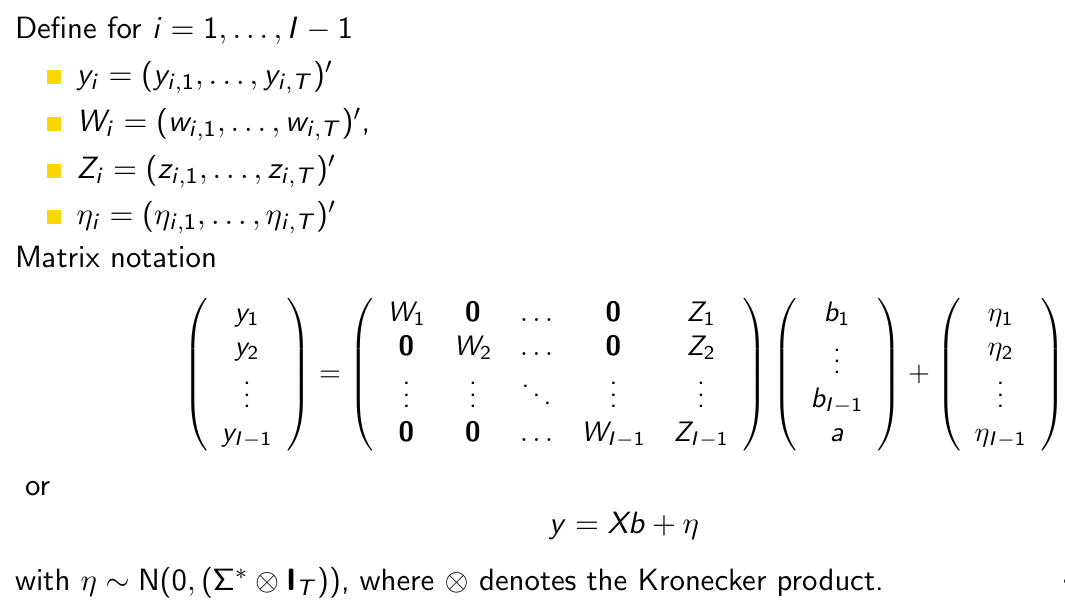

How do we estimate this model?

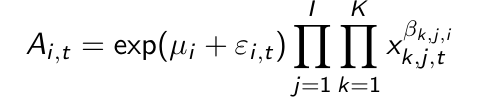
What is missing from the fully extended MCI model in this form?

Give the most general expectation of the fully extended MCI model.
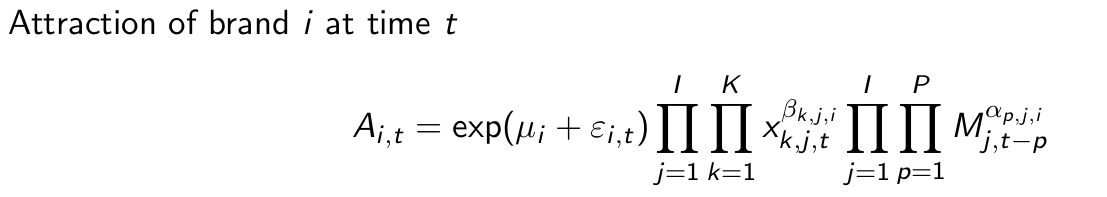
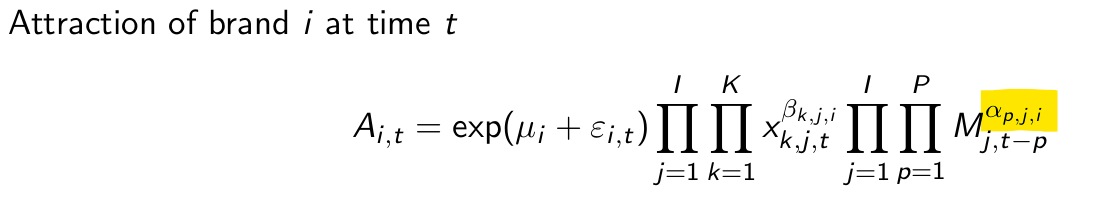
Explain what this term means.

What are the possible restrictions for the dynamic model? Also mention the number of (additional) restrictions.
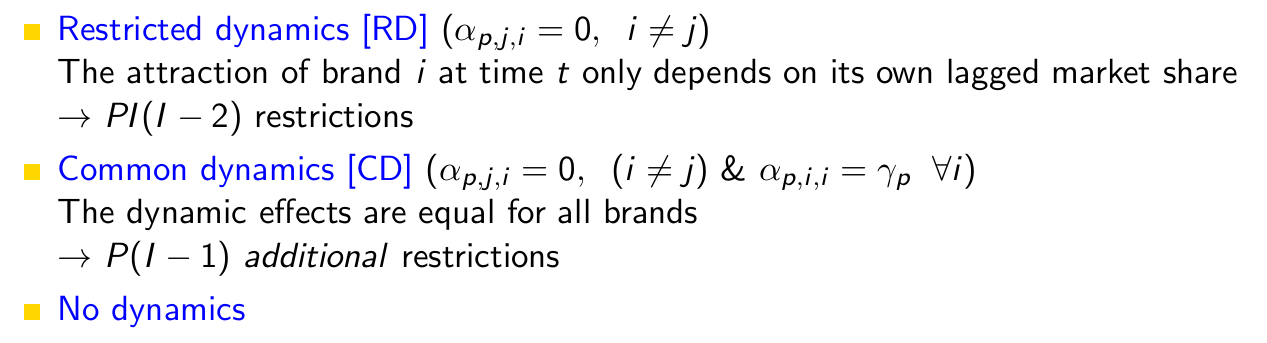
Give the attraction specification and the reduced form in the case of an RD dynamic model.
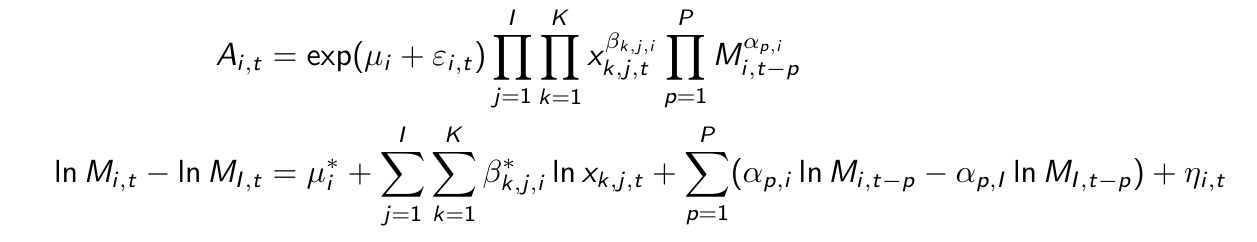
Give the attraction specification and the reduced form in the case of an CD dynamic model.
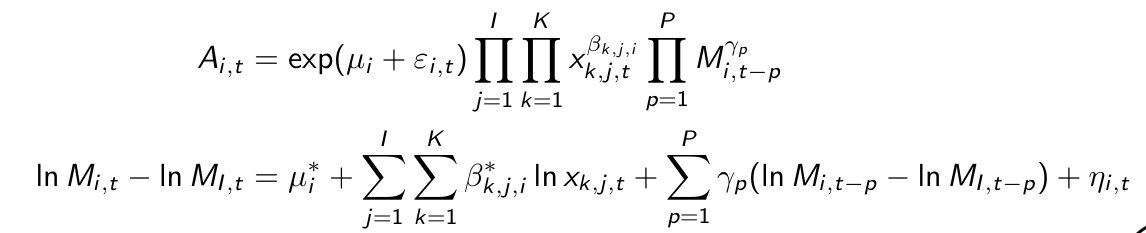
What is our model specification strategy? (Different tests etc.)

How exactly do we test whether or not to impose a restriction?

What is the big problem we have after estimating a fully extended MCI model?

How can we simplify the attraction model again after making it so complicated?
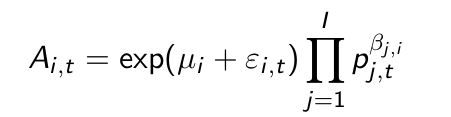
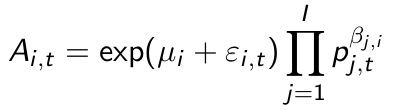
What is the price elasticity according to this model?
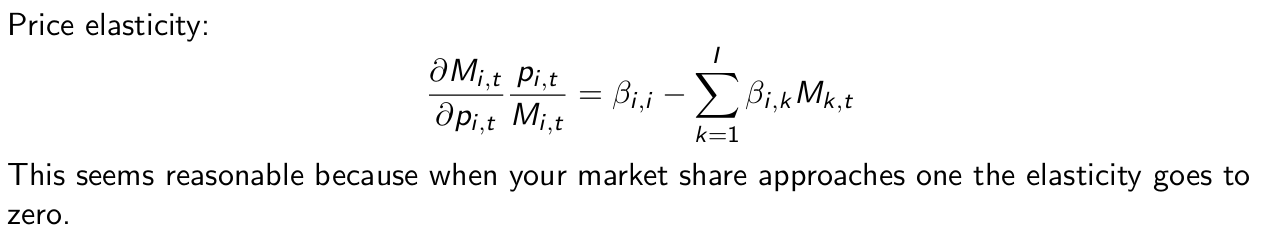
What does the price elasticity become under restricted competition?

What does the price elasticity become under restricted effect?



Why is it not easy to make forecasts for the market share?
The estimated coefficients in a MCI model refer to ln(mi,t), so the RELATIVE market share of brand i at time t (relative to the benchmark brand l).
To be able to forecast market shares we need an expression relating Mi,t to mi,t. Give that expression and explain how you found it.
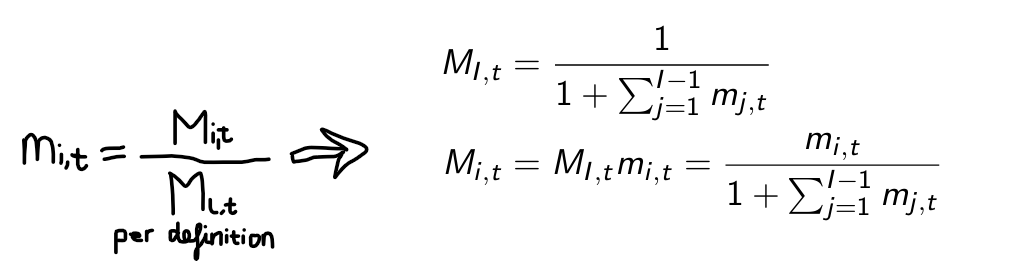
Give expressions for the (unbiased) forecasts of Mi,t+1 for all brands
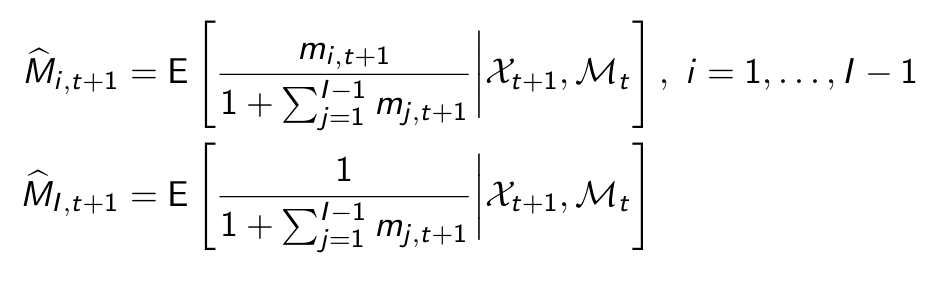
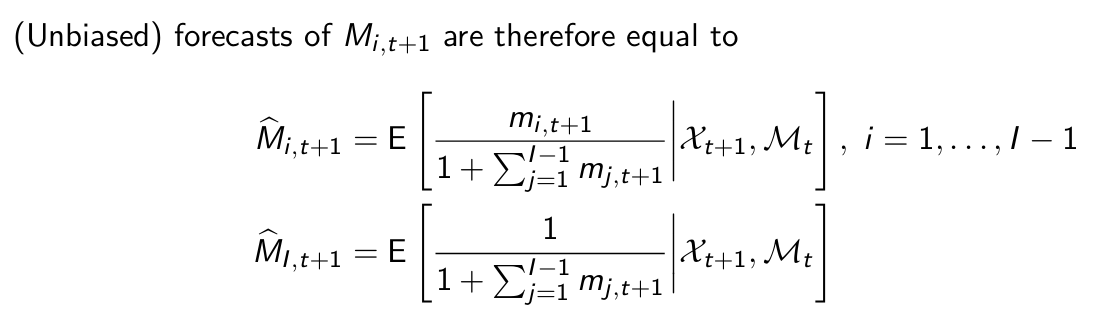
What NOT to do to obtain these? And what to do instead?

What is the simulation scheme for market shares?

What is step one of the simulation scheme for market shares?
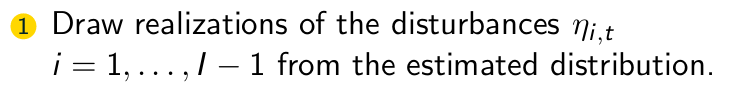
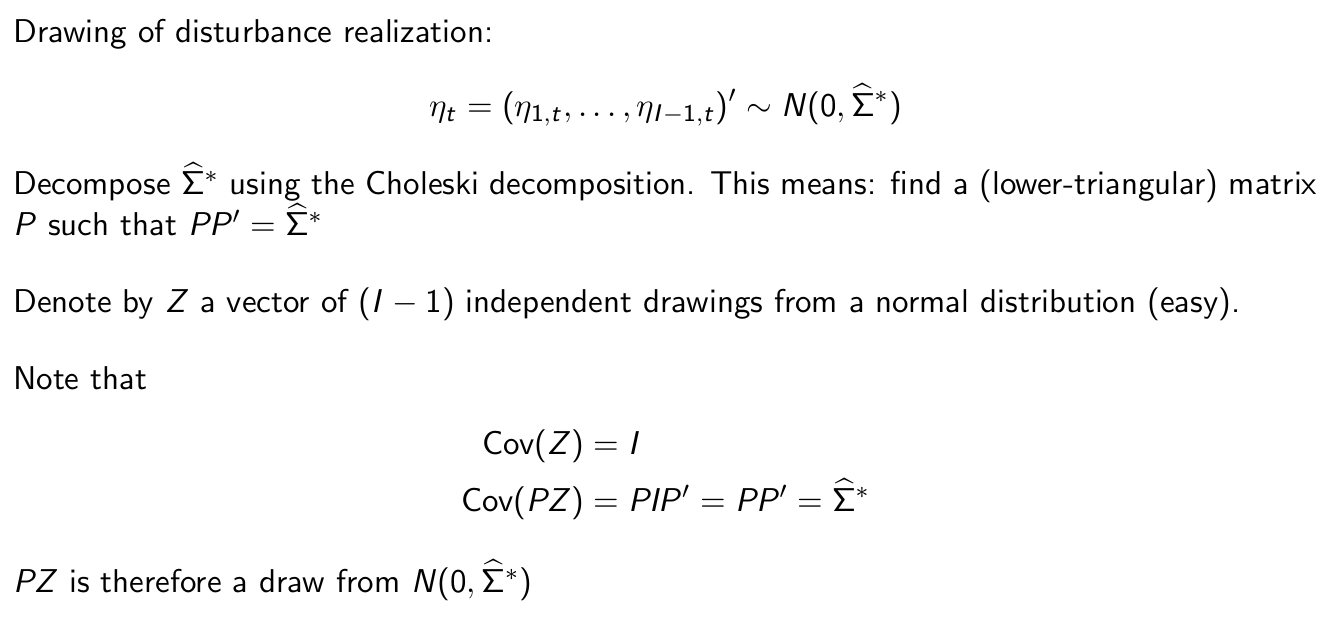
What is step two of the simulation scheme for market shares?


What is step three of the simulation scheme for market shares?


What is step four of the simulation scheme for market shares?


What is step five of the simulation scheme for market shares?



False