Vitamins (my copy)
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
Vitamins
are organic (carbon containing) compounds that are essential in small amounts for body processes
do not provide energy but enable the body to use the energy provided by carbohydrates, fats, and proteins
the name vitamin implies their importance “Vita” in Latin, means life.
are found in minute amounts in foods
_________ in Latin, means life
Vita
Classification of Vitamins
Fat Soluble Vitamins
Water Soluble
Fat Soluble
Vitamins A, D, E , and K
they are not lost easily in cooking, but are lost when mineral oil is ingested
fat soluble vitamins are transported through the blood by lipoproteins because they are not soluble in water
excess amounts can be stored in the liver
megadoses should be avoided to prevent toxicity
Vitamins under Fat Soluble Vitamins
A, D, E , K
fat soluble vitamins are transported through the blood by ________because they are not soluble in water
lipoproteins
Fat soluble vitamins: excess amounts can be stored in the _________
liver
__________ should be avoided to prevent toxicity
megadoses
Water Soluble Vitamins
include Vitamin B Complex and Vitamin C
these vitamins dissolve in water and are easily destroyed by air, light, and cooking
they are not stored in the body to the extent that fat soluble vitamins are stored
Vitamins under Water Soluble Vitamins
Vitamin B Complex and Vitamin C
dissolve in water, not stored in the body and easily destroyed by air, light and cooking
water soluble vitamins
Active form of Vitamin A
Retinol
Retinol can be converted to?
retinal and retinoic acid
Retinol can be found in?
fat containing animal foods such as liver, butter, cream, whole milk, whole milk cheeses, and egg yolk,
also found in low fat milk products and in cereals fortified with vitamin A
Inactive form of Vitamin A?
Carotenoids
Carotenoids can be found in?
plants
common carotenoids are?
beta carotene, lutein, lycopene, and zeaxanthin
beta carotene is most efficiently converted to _________
retinol
important role of carotenoids ?
in vision, bone growth, reproduction, and cell division, regulate the immune system
carotenoids are labeled as an _________
antioxidant
beta carotene best sources are _____________
carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, broccoli, pumpkin, squash (butternut), mango, and cantaloupe
Retinol Equivalent (RE)
1 μg retinol or 6 μg beta carotene or 3.33 IU (international units)
Hypervitaminosis
excessive intake of vitamin A
Signs of excessive intake of Vitamin A
birth defects, hair loss, dry skin, headaches, nausea, dryness of mucous membranes, liver damage, and bone and joint pain
Vitamin A Deficiency signs
night blindness; dry, rough skin; and increased susceptibility to infections.
avitaminosis
serious lack of vitamin A
avitaminosis can result in
blindness or xerophthalmia
xerophthalmia
a condition characterized by dry, lusterless, mucous membranes of the eye
lack of vitamin A is the leading cause of
blindness in the world
D2
ergocalciferol
D2 is formed in?
plants
D3
cholecalciferol
D3 is formed in
humans from cholesterol in the skin
D2 and D3 each is formed from a provitamin when irradiated with (exposed to) _________
ultraviolet light
D2 and D3 are ______
equally effective in human nutrition
Vitamin D is _____ and _______
heat stable and not easily oxidized
Vitamin D is converted to a?
hormone
promotes _________ and _________ absorption in the body for normal bone and tooth growth
calcium and phosphorus
mineralization to occur and prevents __________
tetany (involuntary muscle movement)
tetany
involuntary muscle movement
best source of Vitamin D?
Sunlight ; which changes a provitamin to vitamin D3 in humans
best food sources of vitamin D
milk, fish liver oils, egg yolk, butter, and fortified margarin
Vitamin D levels are given as ____________
Adequate Intake (AI)
Hypervitaminosis D
must be avoided because it can cause deposits of calcium and phosphorus in soft tissues, kidney and heart damage, and bone fragility
vitamin D deficiency inhibits the absorption of ___________
calcium and phosphorus in the small intestine and results in poor bone and tooth formation.
Vitamin D deficiency in children may develop?
rickets
Vitamin D deficiency in adults may develop?
osteomalacia (softening of bones)
osteoporosis
brittle, porous bones
Vitamin E
Tocopherols and Tocotrienols
Vitamin E is an __________ aided by vitamin C and the mineral selenium
antioxidant
Vitamin E is found helpful in the
prevention of hemolytic anemia among premature infants
Vitamin E enhances the __________
immune system
Vitamin E is used in commercial food products to _______
retard spoilage
Best sources of Vitamin E
Vegetable oils made from corn, soybean, safflower, and cottonseed and products made from them, such as margarine
wheat germ, nuts, and green leafy vegetables
the vitamin E requirement __________ if the amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the diet ______________
increases
Vitamin E appears to be relatively ______
nontoxic
Excess Vitamin E is stored in?
adipose tissue
____________ is detected in premature, low birthweight infants and in patients who are unable to absorb fat normally (Vit. E)
Deficiency
___________ can cause serious neurological defects in children, but in adults, it takes __________ before deficiency symptoms occur
malabsorption
5 to 10 years
Vitamin K is absorbed from the _________
small intestine and slightly from the colon
Vitamin K1
phylloquinone
Vitamin K2
menaquinone
Phylloquinone is found in?
green leafy vegetables such as spinach and in animal tissue
Menaquinone is synthesized in the?
intestine by bacteria and is also found in animal tissue
Synthetic Vitamin K
menadione
Menadione is essential for the formation of ______
prothrombin
___________________may be given to newborns immediately after birth because human milk contains little __________
Vitamin K
Vitamin K may be given to patients who
suffer from faulty fat absorption
Vitamin K may be given to patients after
extensive antibiotic therapy
Vitamin K can be also act as an
antidote for an overdose of anticoagulant (blood thinner such as or to treat cases of hemorrhage
___________ milk is much better source of Vitamin K than Human Milk
Cow’s milk
Vitamin K is provided in AIs and measured in __________
micrograms ( μg )
Vitamin K must be ingested ______
daily
what is absorbed today will be utilized immediately with very little storage in the liver
ingestion of excessive amounts of synthetic vitamin K can be toxic and can cause a form of ______________
anemia
the only major sign of a deficiency of vitamin K is _____________
defective blood coagulation
__________________ may be caused by faulty fat metabolism, antacids, antibiotic therapy, inadequate diet, or anticoagulants
human deficiency
also known as Ascorbic Acid
Vitamin C
it is absorbed in the small intestine and considered nontoxic
Vitamin C
prevents scurvy, an iron enhancer and believed to reduce the severity of colds
Vitamin C
has an important role in the formation of collagen proteins that are the primary structural component of connective tissues
Vitamin C
has antioxidant properties and protects foods from oxidation, and it is required for all cell metabolism
Vitamin C
Vitamin C may be involved with the formation or functioning of __________, some amino acids, folate, leukocytes (white blood cells), the immune system, and allergic reactions
it can reduce cancer risk in some cases by reducing nitrites in foods
norepinephrine
Best sources of Vitamin C
citrus fruits, melon, strawberries, tomatoes, potatoes, red and green peppers, cabbage, and broccoli.
Vitamin C is measured in?
milligrams (mg)
an average female adult requires _________a day (Vitamin C)
75 mg
an average male _________. (Vitamin C)
In times of stress, the need is increased.
90 mg
cigarette smokers are advised to ingest _________ a day.
125 mg or more
Excessive absorption of Vitamin C
can cause diarrhea, nausea, cramps, an excessive absorption of food iron, rebound scurvy (when megadoses are stopped abruptly), and possibly oxalate kidney stones
Vitamin C deficiency
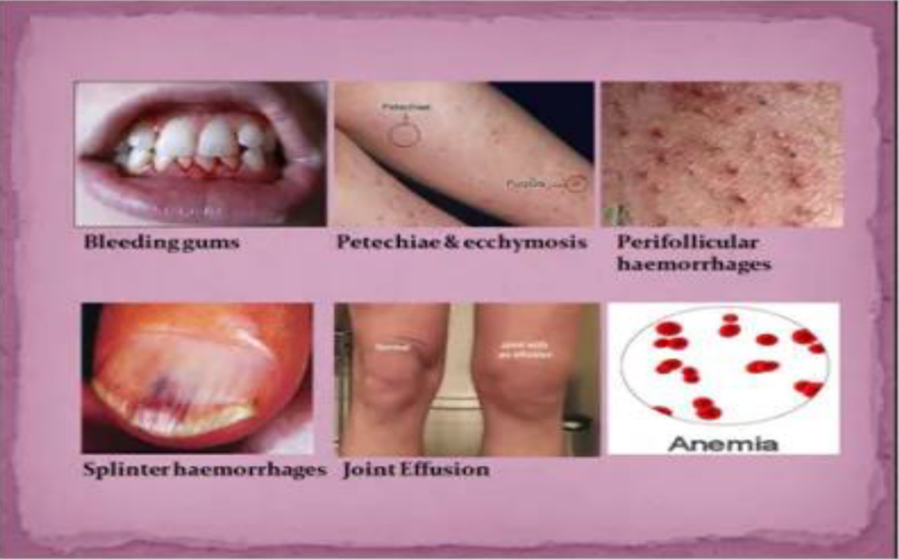
bleeding gums, loose teeth, tendency to bruise easily, poor wound healing, and, ultimately scurvy
Vitamin B Complex
thiamine
riboflavin
niacin
pantothenic acid
pyridoxine
biotin
folic acid
cobalamin
A coenzyme, absorbed in the small intestine and essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates and some amino acids
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
also essential to nerve and muscle action
is found in many foods, but generally in small quantities
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Vitamin B1
Thiamine
daily thiamine requirement for the average adult female is ________mg a day
1.1 mg
daily thiamine requirement for the average adult male it is ______mg a day
1.2
an increase in calories increases the need for _______
thiamine
Vitamin B1 deficiency symptoms
loss of appetite, fatigue, nervous irritability, and constipation
an extreme deficiency causes
beriberi
its deficiency is rare, however, occurring mainly among alcoholics
others at risk include renal clients undergoing long term dialysis , clients undergoing gastric bypass surgery for weight loss, and those who eat primarily rice
beriberi
frequent consumption of large amounts of raw fish could cause ___________
thiamine deficiency