PHSC 208, L31
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
more Carbons is ______ melting point
higher
unsaturated fatty acids are _____ at room temperature
liquid
12:0
Lauric acid
14:0
Myristic acid
16:0
palmitic acid
16:1n-7
palmitoleic acid
18:0
stearic acid
18:1n-9
oleic acid
18:2n-6
linoleic acid
18:3n-3
alpha-Linolenic acid
18:3n-6
gamma-Linolenic acid
20:0
arachidic acid
20:4n-6
Arachidonic acid
20:5n-3
EPA
iClicker: Rank the following fatty acids from highest to lowest
18:1 Oleic
20:0 Arachidic
18:2 linoleic
18:0 stearic
16:0 Palmitic
2 > 4 > 5 > 1 > 3
most naturally occuring unsaturated fatty acids have ___ double bonds
cis
cause a 30 degree bend in the carbon chain
unsaturated fatty acids have ____ melting points
low
What are some essential fatty acids?
omega-3 and omega-6
must be obtained from the diet
What are triglycerols?
the primary component of fats and oils in plants and animals
Triglycerols are _____ in water
insoluble
hydrophobic
good for thermal insulation. and storing energy
What are phospholipids?
primary component of membrane bilayer
has hydrophilic polar head group and hydrophobic tail to create a barrier between cell and external environment
Cardiolipin
R groups primarily unsaturated fatty acids
negative charges
Phosphatidic acid
-H
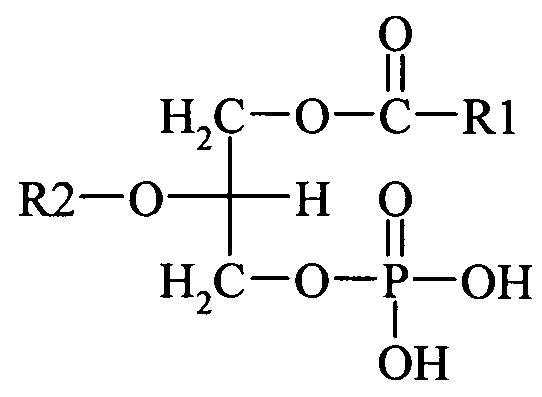
Phosphatidylethanolamine
NH3+

Phosphatidylcholine (Lecithin)
lowkey has a n*zi symbol
Phosphatidylinositol
ring shape
Phosphatidylglycerol
Phospholipases hydrolyze phospholipids
phosopholipases cleave
a1- first carbon
a2- second carbon
C+D- third carbon
Sphingolipids are made of ______
sphingosine- amino alcohol backbone
fatty acid is linked to sphingosine by an amide bond
Cerebroside
head group is a single sugar
sulfatide
sulfuric acid group on the sugar
Tay-Sachs disease
most common sphingolipid storage disease
deficiency of Beta-hexosaminidase A enzyme
accumulation of GM2
fatal for children
Cholesterol
most abundant steroid in animals
subclassified as sterol because of C3-OH group
precursor in biosythesis of steroid hormones, vitamin D, bile acids
Cortisol
stress signaling, from adrenal gland
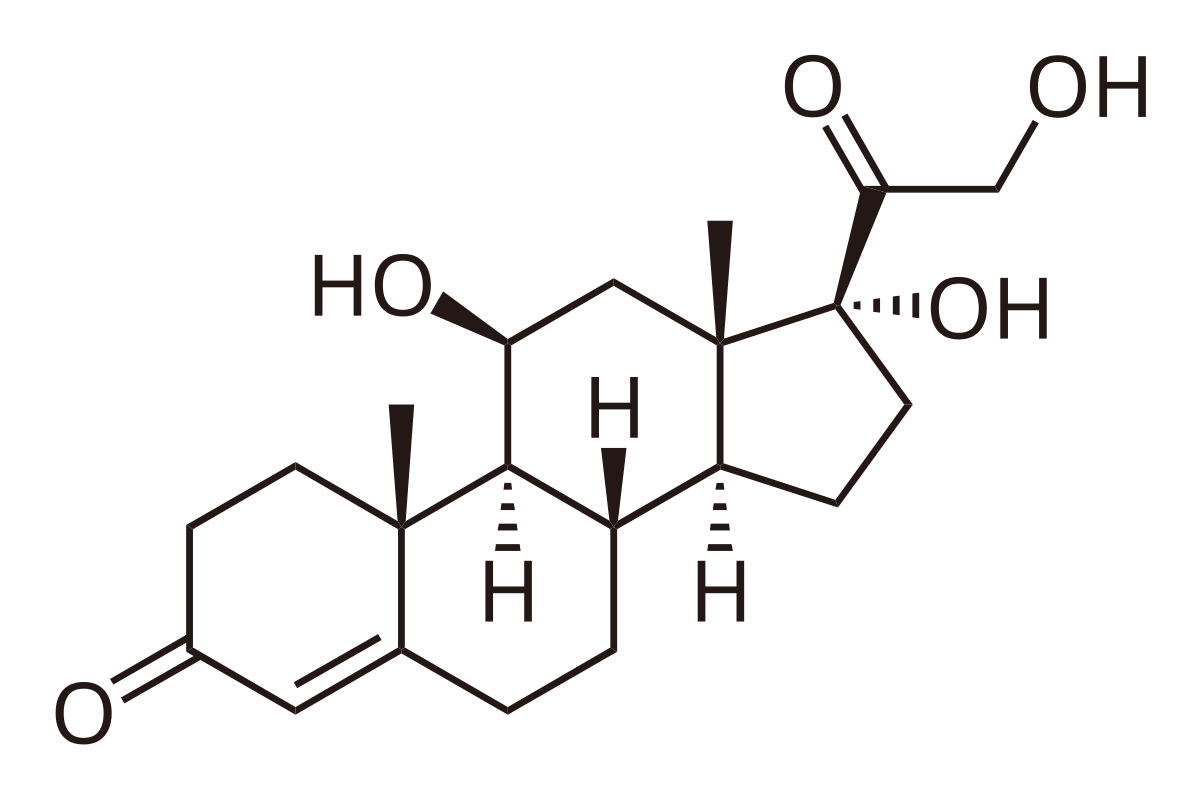
Testosterone
anabolic steroids released from sex glands
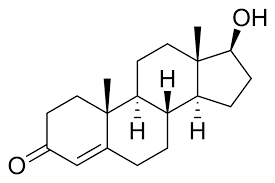
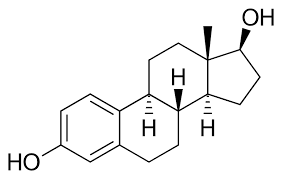
Beta- Estradiol
anabolic steroids released from sex glands
Aldosterone
sodium potassium regulation, water level regulation in blood
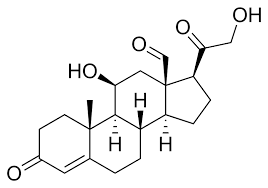
Vitamin D synthesis
UV radiation opens up 9-10 Carbon spontaneously
opened ring makes C=CH2 bond
more info needed
What is the function of hydroxylated Vitamin D?
promotes and regulations Calcium homeostasis
Naturally occurring isoprenoids have ____carbon structural units
5
Vitamin E function
prevents oxidative damage to membranes
iClicker: While fatty acids are most often formed by the condensation of ___-carbon units, isoprenoids are assembled from ___-carbon units
a. 5, 3
b. 4, 2
c. 2, 3
d. 2, 5
e. 3, 4
d. 2, 5
Eicosanoids are generated from ________
fatty acids
Eicosanoids functions
inflammation
platelet aggregation, blood coagulation
How do proteins move around in the fluid mosaic model in the plasma membrane
dynamic and float around
moves transversely easily
Fluid Mosaic Model
label 2 different cells with green or red marker
fused together by Sedai virus and forms a hybrid cell
after fusion, mouse and human proteins segregated
after 40 min at 37 C, green and red intermixed
proves the proteins in bilayer are just moving around
FRAP (fluorescent recovering after photobleaching)
protein in membrane is marked in green
hit with high energy, gets rid of fluorescent
microscope monitors how it goes from no fluorescent to fluorescent (recovery)
How do bilayers form?
lipids spontaneously be around themselves in aqueous environments (be around themselves)
Bilayer formation driven by _________
hydrophobic effect and van der waals envelope of what phospholipids look like
How does dynamic structure affect the bilayer?
lets cells and subcellular structures adjust shape and change position
proteins and lipids diffuse into membrane (fluid mosaic model)