AFCP Middle Mediastinum + Heart
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Mediastinal shift
Deviation of the mediastinum, causing structures to get displaced
Mediastinal widening is caused by which conditions?
Tumors, aneurysms (widening of BVs), pericardial effusions (excess fluid around heart)
Tip: TAP
Mediastinal narrowing is caused by which conditions?
Lung masses, pleural effusion
The heart lies in which mediastinum?
Middle
What are the 3 layers of the pericardium (outermost → innermost)?
Fibrous pericardium
Parietal serous pericardium
Visceral serous pericardium
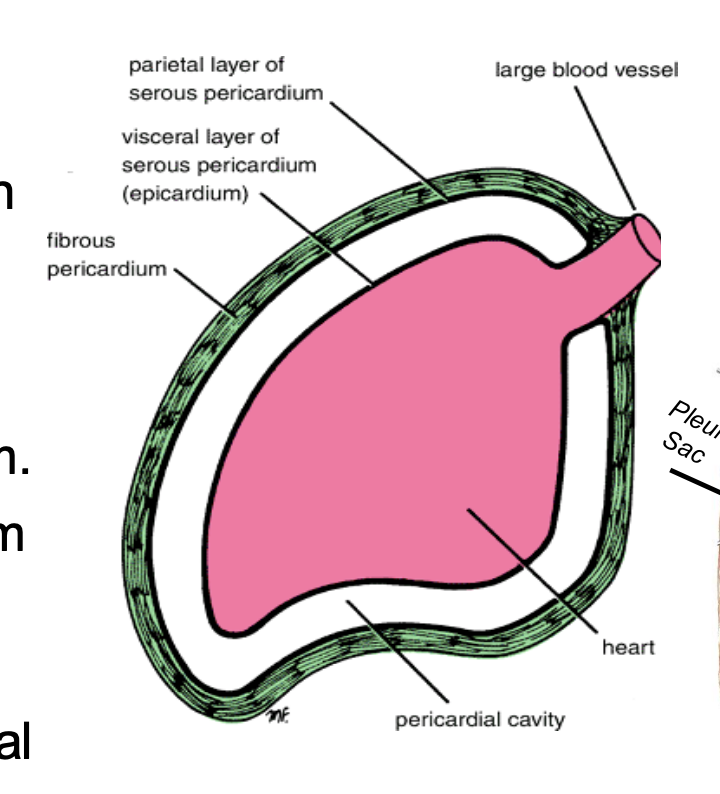
The pericardial cavity is the space between the _______ and contains _______
space between the parietal and visceral serous pericardium
contains pericardial fluid
What makes the pericardial fluid and what’s the purpose of it?
Serous pericardium
To reduce friction during heartbeats
What is the significance of the 2 sinuses of the pericardium?
They are 2 places where the visceral and parietal layers fuse (separated everywhere else) to keep the pericardial cavity closed
The transverse sinus is enclosed anteriorly by the _______ and posteriorly by the _______
Anteriorly: pulmonary trunk, aorta
Posteriorly: vena cava, pulmonary veins
The oblique sinus is a _____-shaped sinus located ______
J
behind the left atrium
During cardiac surgery, a ligature is passed through the ______ to clamp the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk
transverse sinus
What are the 3 arterial supplies of the pericardium and which one specifically supplies the visceral serous pericardium?
Pericardiacophrenic artery
Branches from the thoracic aorta
Coronary arteries - supplies the visceral serous pericardium
The pericardiacophrenic a. is a branch off of the _______
internal thoracic a.
The pericardium has which 2 venous supplies?
Pericardiacophrenic vv.
Azygos venous system
The vagus nerve is also called the _____
cranial nerve X (CN X)
The phrenic nerves stem from which spinal nerves?
C3-C5
The cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves stem from which spinal nerves?
T1-T4
What is the sensory, sympathetic, and parasympathetic innervations of the pericardium?
Sensory: phrenic nerves (C3-C5)
Sympathetic: cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves (T1-T4)
Parasympathetic: vagus nerve (CN X)
Pericarditis is _________ and causes ____ pain. It may make the _____ rough, causing the pericardial friction rub sound.
inflammation of the pericardium
causes chest pain
serous pericardium
Cardiac tamponade is caused by hemopericardium, which is _________
blood in the pericardial cavity
What is the effect of cardiac tamponade?
Heart is compressed → cardiac output is reduced
Hypotension
Jugular - venous distention
Muffled heart sounds
Beck’s triad - indicative of cardiac tamponade
Pericardiocentesis is the treatment for _______, where ____ is withdrawn from the pericardial sac at the ______ intercostal space near the ____ angle.
Pericardiocentesis is the treatment for cardiac tamponade, where fluid is withdrawn from the pericardial sac at the 5th-6th intercostal space near the infrasternal angle.
The heart is located at which intercostal spaces? Which space is the apex found?
2nd - 5th intercostal space
Apex: left 5th ICS
The anterior (sternocostal) surface of the heart is formed by ______
2/3 right ventricle, 1/3 left ventricle
The posterior surface of the heart is formed by ______
2/3 left atrium, 1/3 right atrium
The inferior (diaphragmatic) surface of the heart is formed by ______
2/3 left ventricle, 1/3 right ventricle
The right surface of the heart is formed by _______
the right atrium
Dysphagia is the compression of the _____ that can result from _____-
Dysphagia is the compression of the esophagus that can result from a dilated left atrium.
What are the 4 venous supplies of the right atrium?
Superior and inferior vena cava
Coronary sinus
Anterior cardiac veins
A landmark for the AV node
Triangle of koch
The following make up what structure and where is this structure located?
Tendon of todaro
Ostrium (os) of the coronary sinus
Septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve
Boundaries of the triangle of koch
Located in the right atrium
The chordae tendineae connects which 2 structures?
The tricuspid/bicuspid valve to the papillary muscles
The moderator band contains ______
the right branch of the AV bundle
The pulmonary trunk/arteries carry _____ blood from the _____ to the ______.
The pulmonary trunk/arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
The bicuspid and tricuspid valves are _____ valves that prevent ______.
AV (atrioventricular) valves
backflow of blood from the ventricles back to the aorta
The aortic and pulmonic valves are _____ valves.
semilunar valves
Explain which structures the following valves are located between:
aortic valve
mitral (bicuspid) valve
tricuspid valve
pulmonic valve
aortic valve: left ventricle and aorta
mitral (bicuspid valve): left atrium and left ventricle
tricuspid valve: right atrium and right ventricle
pulmonic valve: right ventricle and pulmonary trunk/artery
The 1st heart sound, or the ____, is caused by closure of the _____ valves
lub
atrioventricular valves (AV valves)
The second heart sound, or the _____, is caused by closure of the ______
dub
semilunar valves
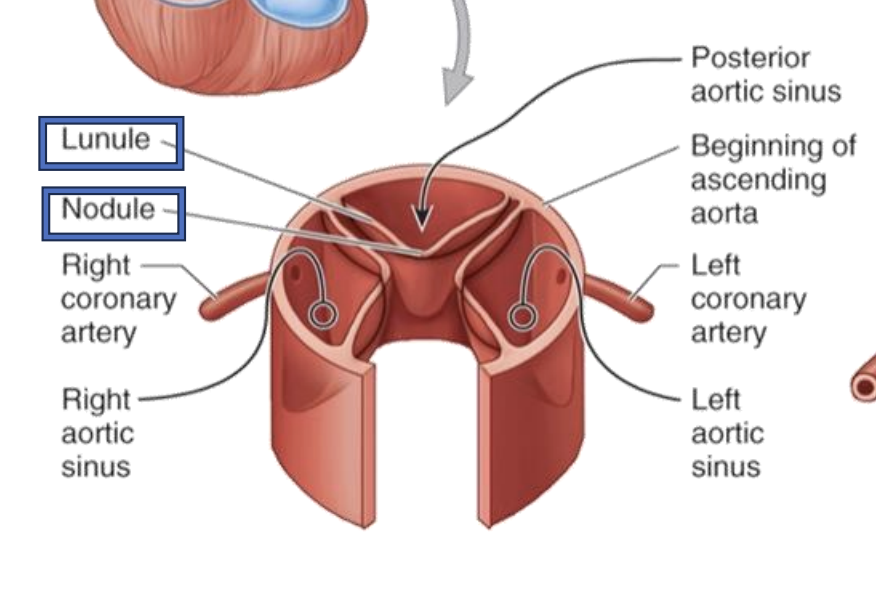
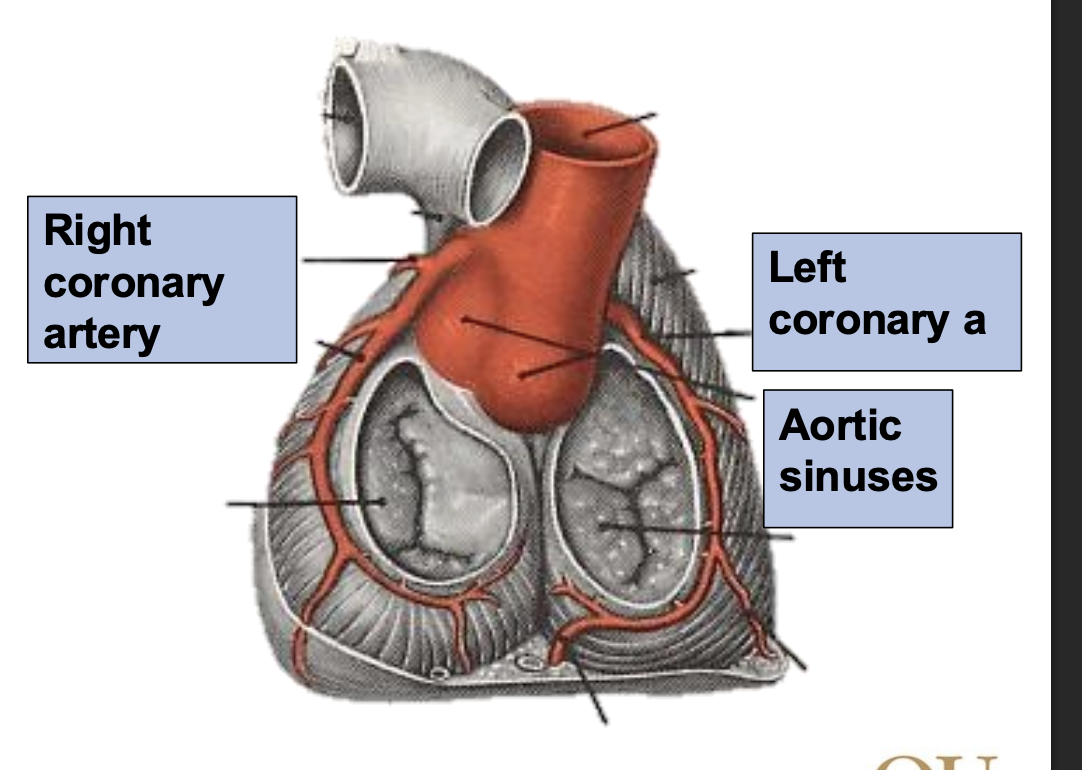
The aortic valve contains which 3 sinuses? Which 2 arteries come out of these sinuses?
Posterior aortic sinus
Right aortic sinus → right coronary artery
Left aortic sinus → left coronary artery
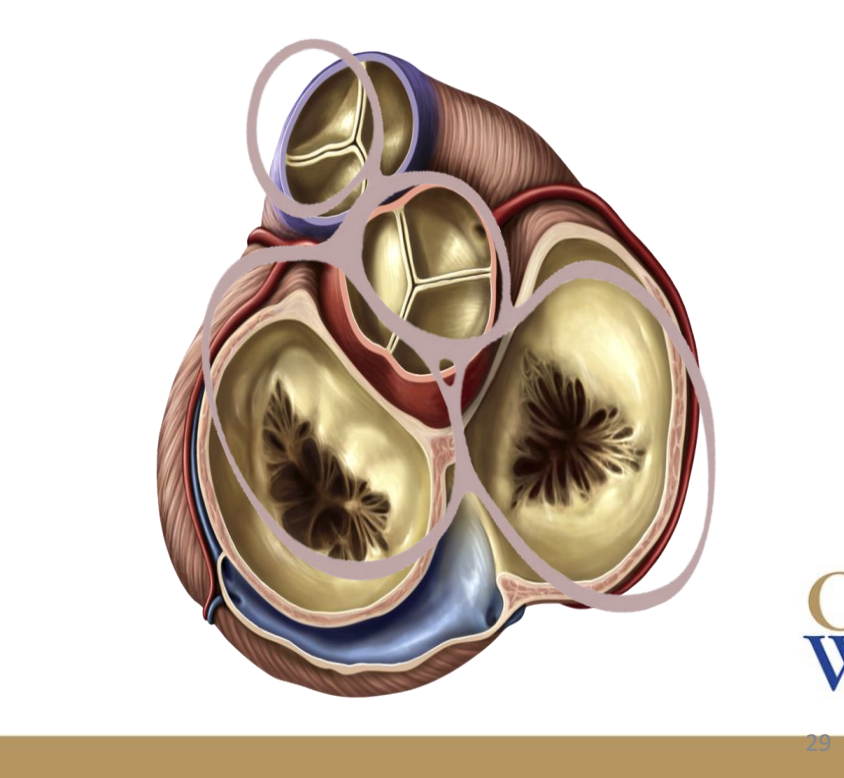
The _____ skeleton of the heart anchors and provides an attachment point for the _______ of the heart’s valves
The fibrous skeleton of the heart anchors and provides an attachment point for the cusps of the heart’s valves
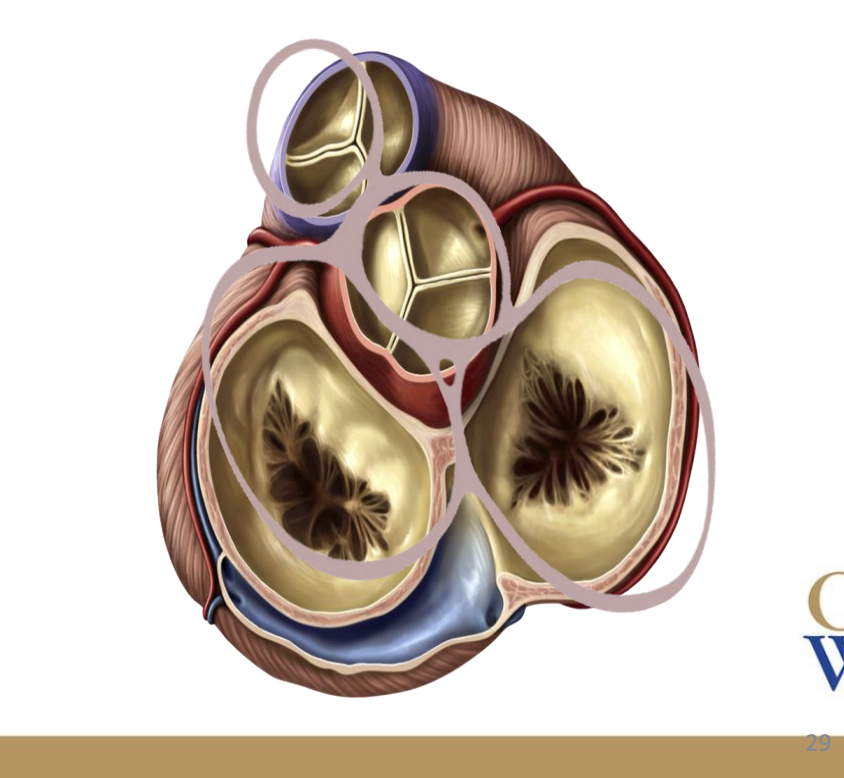
The fibrous skeleton of the heart is made from __ ______ rings
4 dense collagen rings
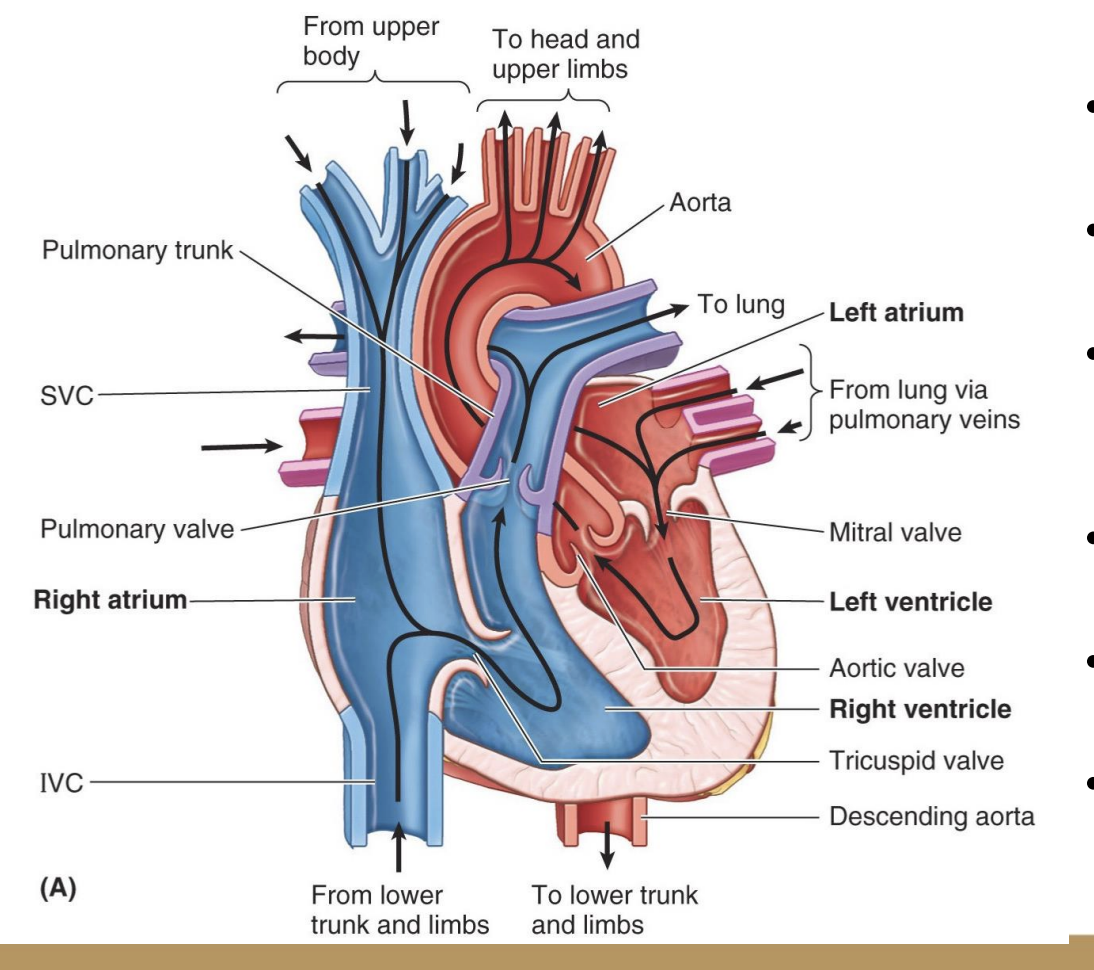
Circulation of the blood through the heart:
O2 (rich/poor) blood flows into the _______.
______ → _______.
_____ → lung.
At the lung, O2 (rich/poor) → O2 (rich/poor) blood.
O2 (rich/poor) blood flows into the ____.
_____ → ______.
_____ → body.
Circulation of the blood through the heart:
O2 poor blood flows into the superior and inferior vena cava.
right atrium → right ventricle.
pulmonary artery → lung.
At the lung, O2 poor → O2 rich blood.
O2 rich blood flows into the pulmonary veins.
left atrium → left ventricle.
aorta → body.
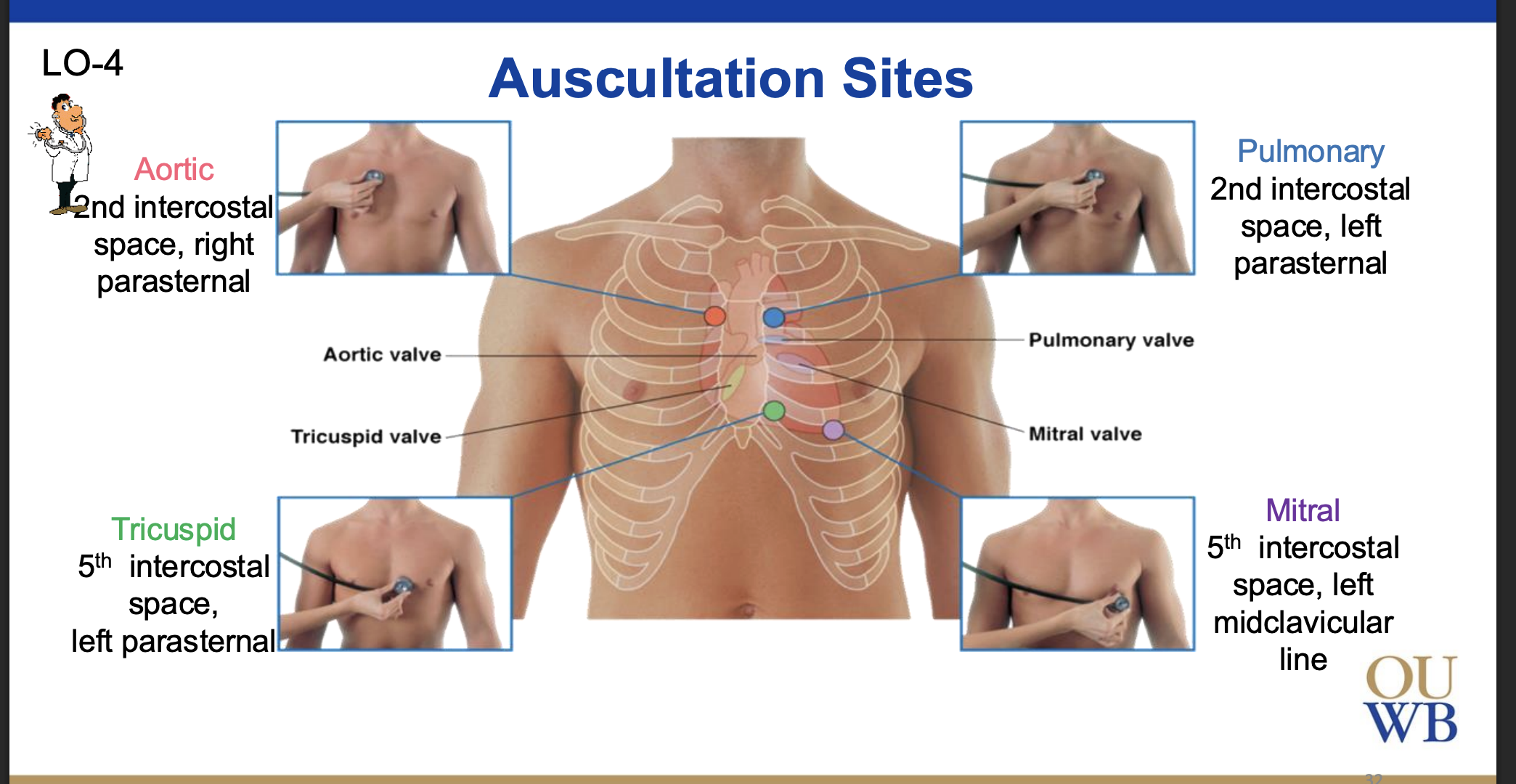
Auscultations of the heart are performed _______, NOT _______.
where the waves reverberate
NOT at the location of the valves
There are 4 heart auscultation sites, describe each:
Aortic
Tricuspid
Pulmonary
Mitral/bicsupid
Aortic: 2nd intercostal space, right parasternal
Tricuspid: 5th intercostal space, left parasternal
Pulmonary: 2nd intercostal space, left parasternal
5th intercostal space, left midclavicular line
Tip: All The Pretty Men
The aortic sinuses give rise to the _______ and _______ arteries, which are the main arterial supplies of the heart.
left and right coronary arteries
What are the 3 branches of the right coronary artery?
Posterior interventricular artery
Right marginal artery
Sinoatrial nodal branch
Tip: P(Q)RS
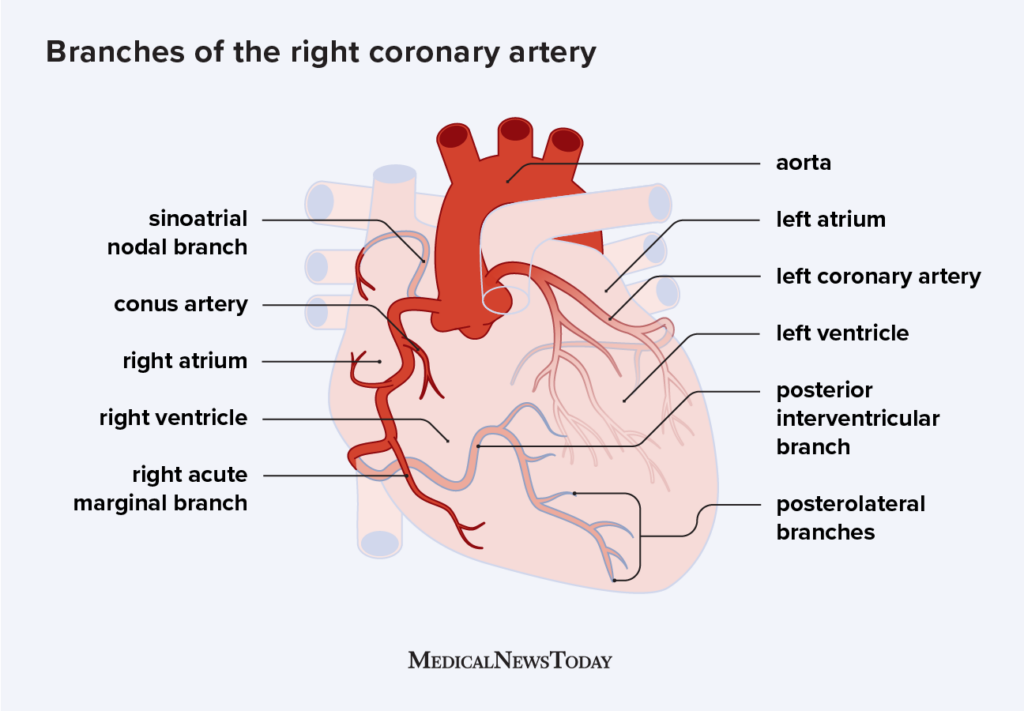
In right coronary dominance, the _______ artery supplies what?
posterior intraventricular artery supplies the back of the ventricles, the right atrium, most of the right ventricle, and the SA and AV nodes
In left coronary dominance, the ____ artery supplies what?
anterior intraventricular artery supplies both ventricles, the left atrium, most of the left ventricle, and the SA and AV nodes
Which is more common, right or left coronary dominance?
Right - 80%
Left: 10%
What are the 3 branches of the left coronary artery?
Anterior interventricular artery (LAD)
Circumflex artery → left marginal artery
Great cardiac vein accompanies which artery?
The anterior interventricular branch of the left coronary artery
What are the 2 anastomoses of the coronary arteries?
Anterior interventricular (LAD) and posterior interventricular arteries
Left and right coronary arteries
The main venous drainage of the heart comes from the _______, which contains branches from the ______, ______, and ______
coronary sinus
branches from the great, middle, and small cardiac veins
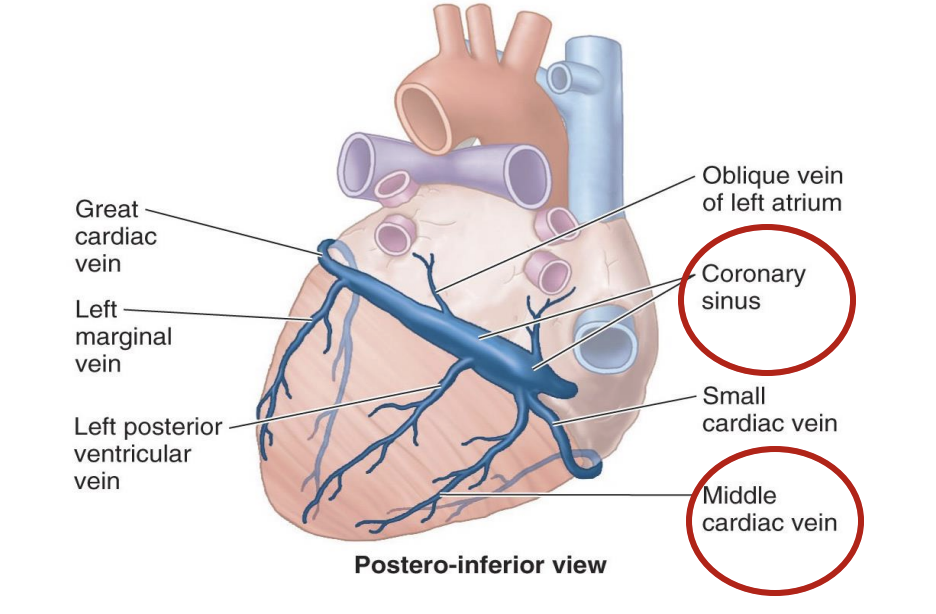
The coronary sinus drains into _____
the right atrium
Coronary atherosclerosis
Narrowing of the coronary arteries due to plaque accumulation
Angina pectoris
When does it occur/relieve?
Cardiac pain that occurs during exertion and relieved by rest due to narrowing of coronary arteries
Narrowing of coronary arteries can lead to ________
myocardial infarction (heart attack)
What are the following treatments used for: bypass graft, coronary angioplasty, intravascular stenting
Treating coronary artery disease
Coronary artery bypass graft
Taking an artery/vein from a different part of your body and inserting it to bypass the damaged coronary artery and create a new blood flow
Coronary angioplasty
A catheter with a balloon tip flattens the plaque and allows blood to flow through the coronary arteries
Intravascular stenting
Stent is placed to maintain dilation of the coronary artery
“Pacemaker” that generates cardiac electrical impulses
Sinuatrial (SA) node
Slows down electrical impulses and transmits it to the ventricles
Atrioventricular (AV) node
Divides the electrical impulses to the R and L ventricles
Bundle of his
Causes ventricles to contract
Purkinje fibers
Located in the right atrium between the crista terminalis and opening of the SVC
Sinuatrial (SA) node
Located in the right atrium at the interatrial septum
Atrioventricular (AV) node
Located at the membranous part of the interventricular septum
Bundle of his/AV bundle
What artery mostly supplies the SA and AV nodes?
Right coronary artery
What mostly supplies the AV bundle/bundle of his?
Anterior interventricular artery (LAD)
_____ of the conducting system causes asynchronous contraction of the heart.
Ischemia (lack of blood flow)
What do artificial cardiac pacemakers replace?
Replaces the SA node to initiate contraction
The _____ nerve is the parasympathetic innervation of the heart and _____ heart rate.
vagus nerve (CN X)
slows heart rate
The ______ nerves are the sympathetic innervations of the heart and _____ heart rate.
cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves (T1-T4)
increases