Liquid medicines
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
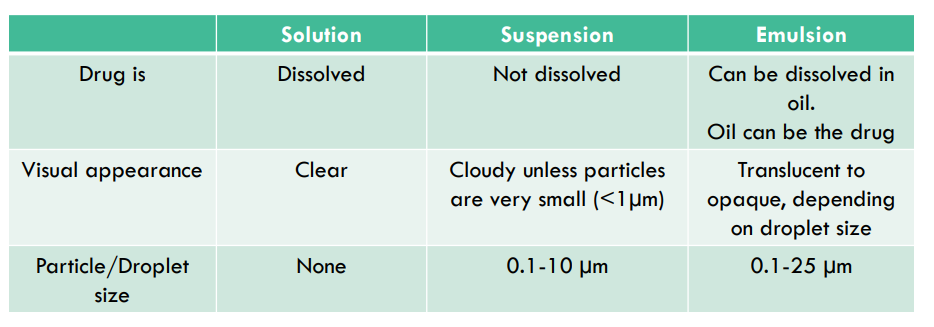
What is a solution?
The homogenous mixture of molecules or ions evenly dispersed in the solvent. Particles completely dissolved. Contains a single phase
What is a suspension?
-non-homogenous dispersion of particles that aren’t fully dissolved in the vehicle. in the mixture and there are 2 phases (dispersed phase, continuous phase)
What is an emulsion?
-1 liquid dispersed in another liquid
Give general brief differences between solutions, suspensions and emulsions
Give advantages of liquids
-don’t need water
-faster onset of action

Give disadvantages of liquids
-harder to open than blister packets
-inconvenient if needed to take with you as it is usually in a heavy or large bottle
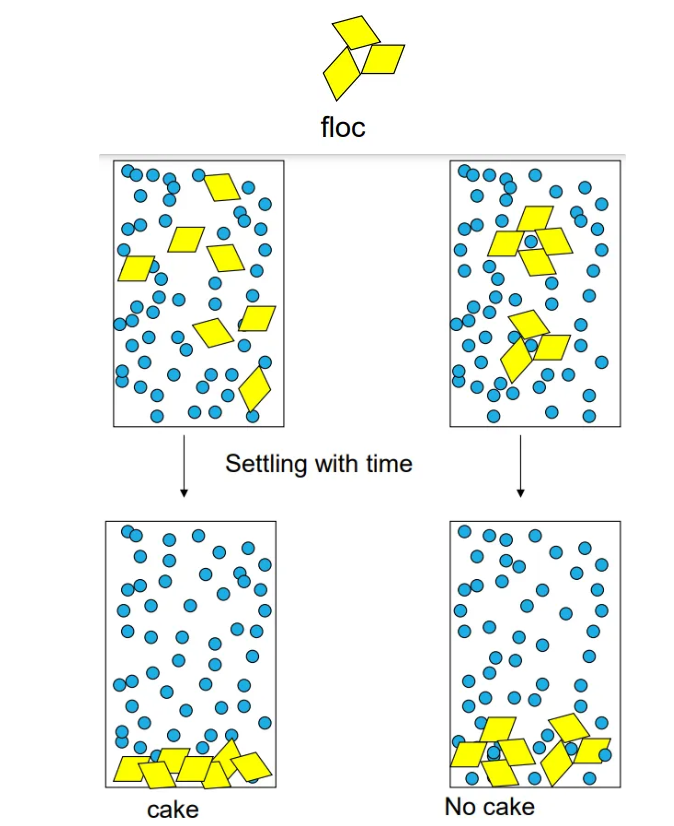
-caking can happen, causing uneven doses. Irreversible
-can expire quicker than other dosage forms

Give examples of non-aqueous solvents/solutions
oils (e.g. almond oil, arachis oil, olive oil, sesame oil, maize oil, cottonseed oil, soya oil, castor oil, ethyl oleate),
Why are non-aqueous solvents used instead of aqueous solvents sometimes?
some solutes/drugs are poorly soluble in water, so water cant be used
Why suspensions over solutions?
-good for poorly soluble drugs that can’t be dispersed into a solvent homogenously.
-taste
-drug may be more stable in a suspension than a solution because it is in non-aqueous solution, so no hydrolysis
Give examples of medicinal solutions
-eyedrops
-mouthwash
-eardrops
State different ways that solubility could be increased
co-solvents such as ethanol to increase solubility

Explain how the pH of the medium can increase solubility
A weak acid in a basic environment will become ionised, so can be solubilised much better
A weak base in an acidic environment will become ionised, so can be solubilised better
this is because the ions can form hydrogen bonds with the water
Explain how cyclodextrins can increase solubility
-due to their unique molecular structure, which features a hydrophilic exterior and a hydrophobic cavity. This cavity can accommodate hydrophobic (lipophilic) drug molecules, allowing for the formation of inclusion complexes. Encapsulate Hydrophobic Drugs: The hydrophobic cavity can trap non-polar or poorly soluble drugs, while the hydrophilic exterior allows the complex to remain soluble in aqueous environments like water
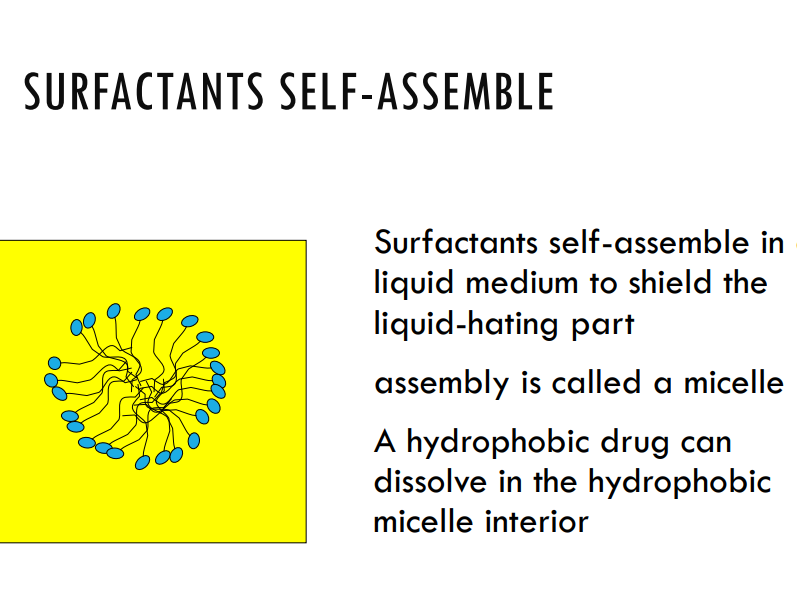
Explain how surfactants can increase solubility
A surfactant, or surface-active agent, is a compound that reduces the surface tension between two substances, such as liquids, or between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants have a unique structure with both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) parts, allowing them to interact with both polar and non-polar substances.
When the surfactant concentration reaches CMC, micelles form, which is good because micelles can trap the lipophilic drug molecules in its core whilst being in the hydrophilic solvent
What are the desired characteristics of a suspension? (3)
-Suspended material should not settle too rapidly
-be stable (explain)
-Particles that do settle to the bottom of container should not form a hard mass, but be readily dispersed when container is shaken
-Suspension must not be too viscous
What is a stable suspension?
where the particles don’t aggregate (cluster/group into). Particles remain uniformly distributed.
If particles do settle, they should be easily redispersed by moderate shaking.
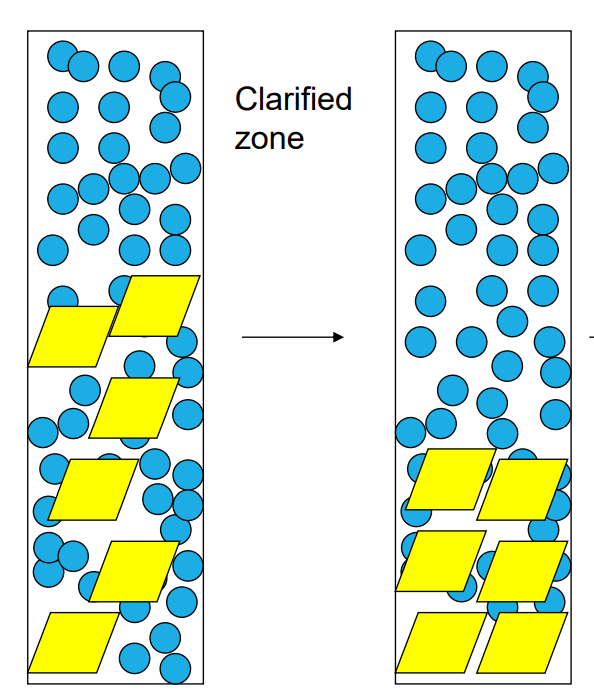
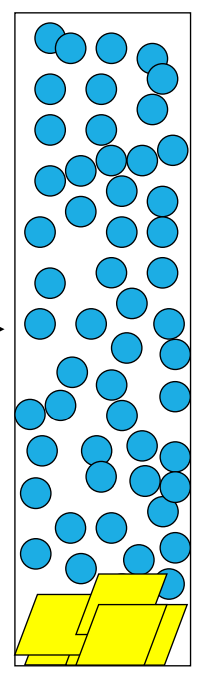
What is the clarified zone?
-the upper portion of the suspension where solid particles have settled, leaving behind a clearer or less turbid liquid. This zone forms during the process of sedimentation or settling, where denser solid particles gradually move to the bottom under the influence of gravity, while the liquid above becomes progressively clearer.
What is caking?
the layer of solid particles that accumulates at the bottom of a container or filter after the solid-liquid separation process. Can happen in suspension not solution
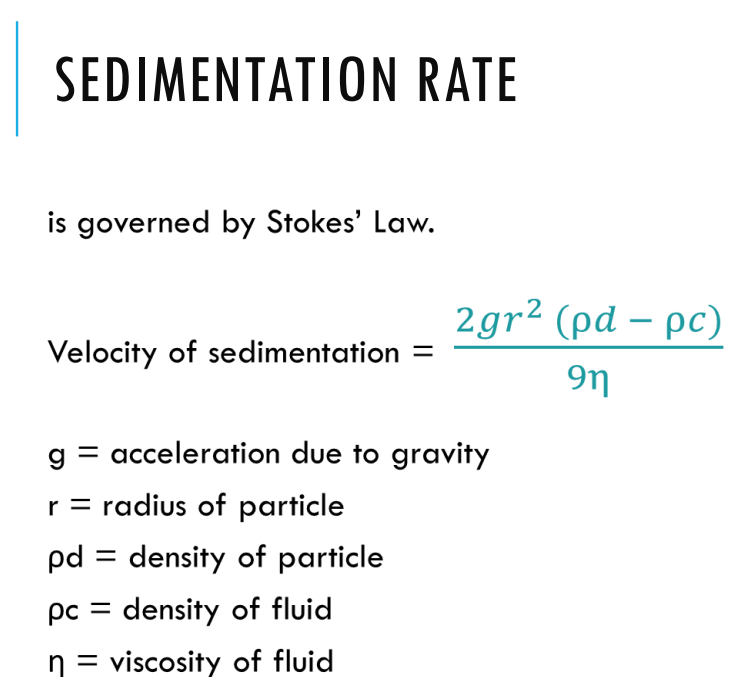
What is the equation for sedimentation rate?
sedimentation=settling down
Explain how caking can be stopped
-Form flocs of the solid particles in a controlled manner – this is called controlled flocculation. There is a faster sedimentation rate when there are flocs as floc is larger; each floc behaves like one unit so Greater sediment volume. No cake as liquid entrapped among particles, therefore Suspension is easy to redisperse