A1.1 Water
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Water
Is the medium of life
First cells arose in water
Is enclosed in a membrane where substances are dissolved and chemical reactions can occur
Is needed for
transport of nutrients and waste products
regulating body temperature
pH balance
Respiration & photosynthesis
Solvent
Water is a solvent that can dissolve a variety of substances to make solutions
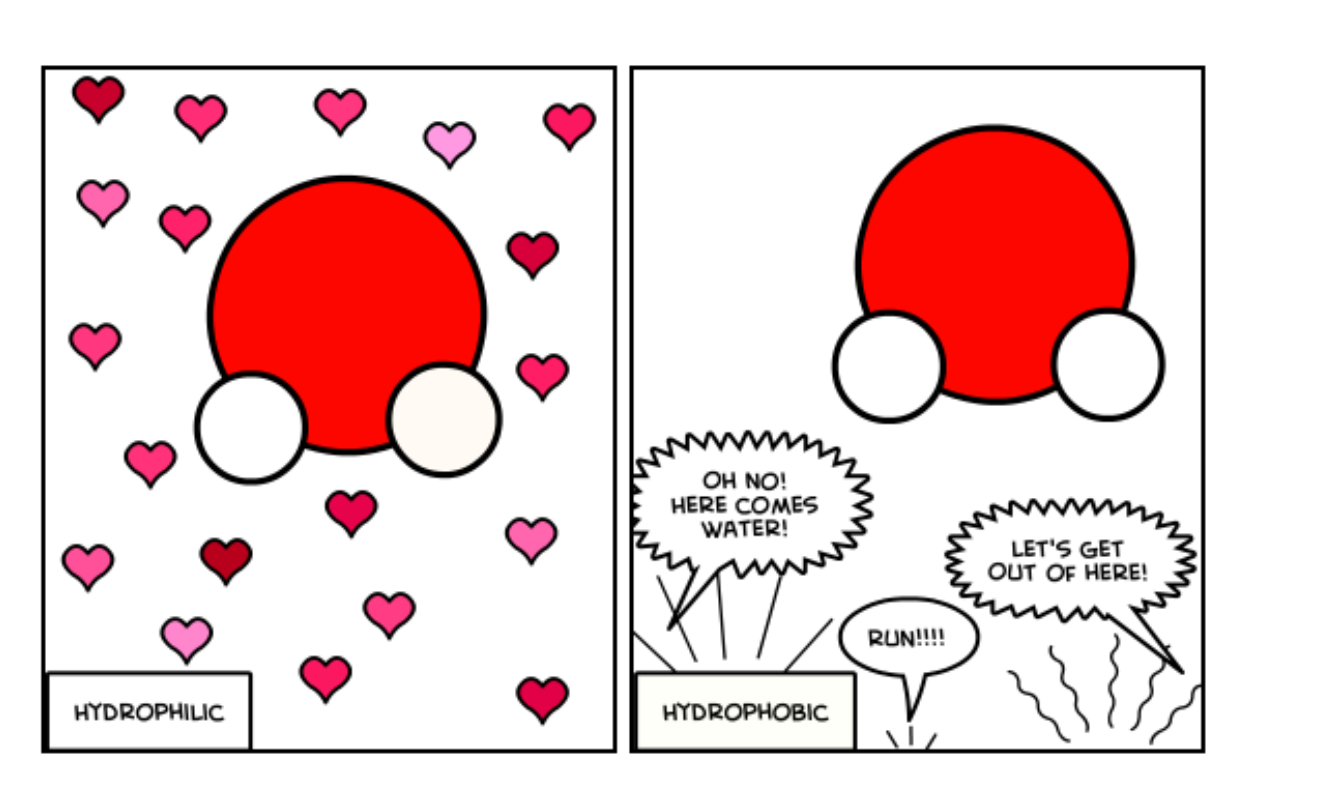
Hydrophilic
Substances that dissolve in water
Include polar molecules and charged ions
Water (is polar) forms around charged molecules to keep them dissolved; water is a charged molecule to keep them dissolved
Cytoplasm in cells is an aqueous solution with a mix of dissolved substances that substances can move in and interact
Enzymes are found inside
Catalyze chemical reaction
All reactions that occur are known as metabolism
Hydrogen bonds
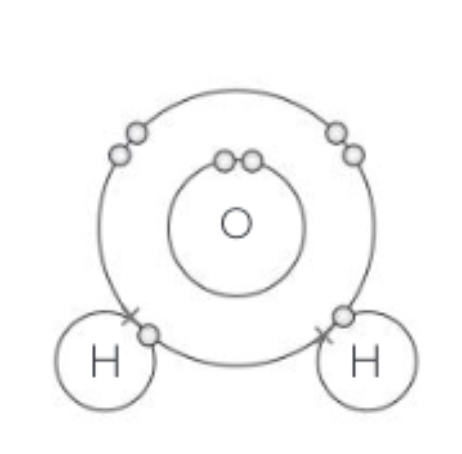
Hydrogen bond is when two or more water molecules bond together.
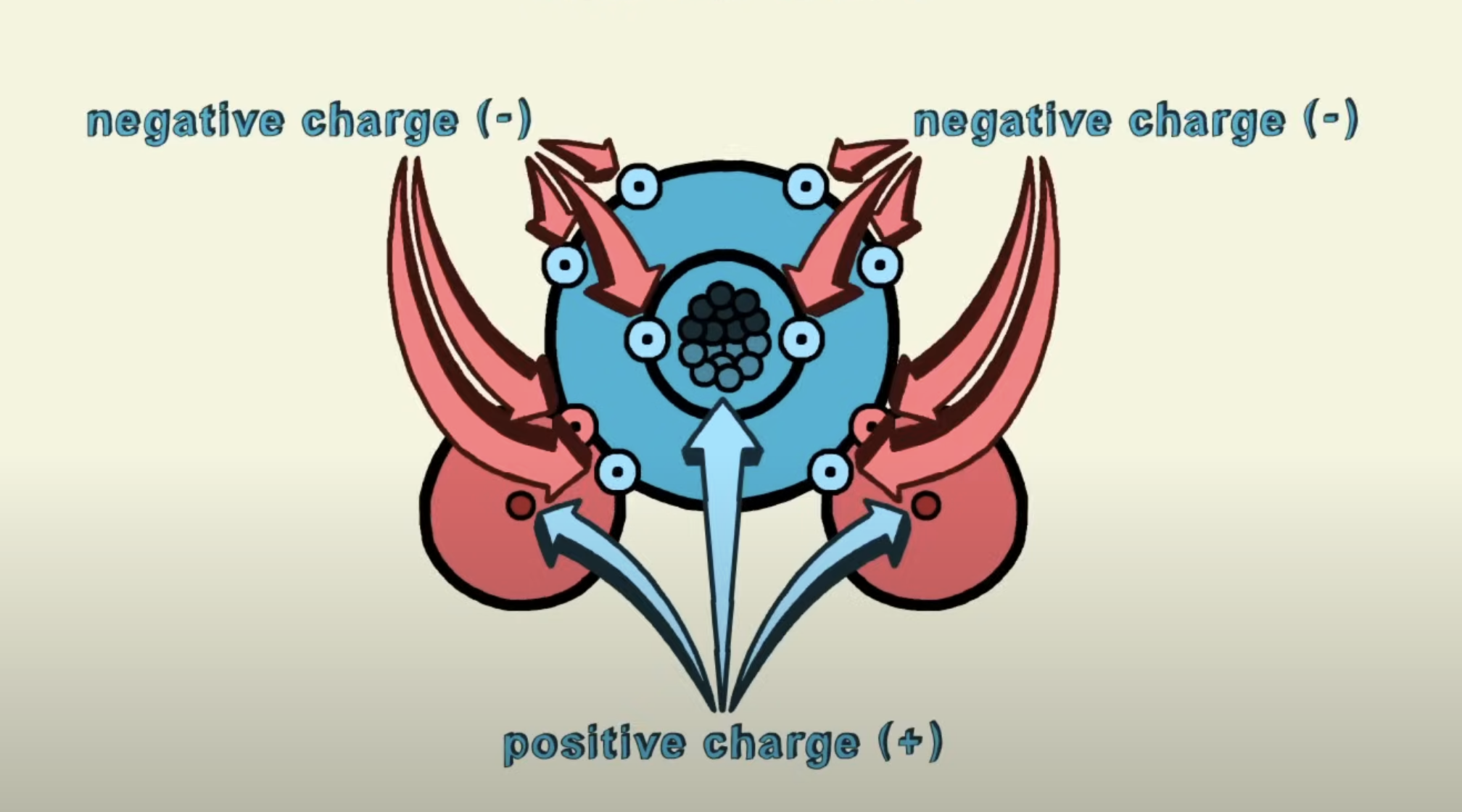
Water molecules Joined by covalent bonding, but due to their electrons of not being shared equally, creating a polar covalent bond.
Hydrogen is the slightly more positive charge and the oxygen is the slightly more negative charge.
Hydrogen and oxygen atoms are joined by covalent bonds where electrons are shared
Electrons are not shared equally -> therefore creates a polar covalent bond
This results in a slightly positive charge for the hydrogen atoms and a slightly negative charge for the oxygen atom
This is why water is a polar molecule: it has different charges at the end
Although water molecules have only slight charges, their opposite charges still attract to each other to form a hydrogen bond
Each hydrogen bond in weak but have lots of them in volume of water
Polar Covalent bond
A bond where electrons are unequally distributed between two atoms, causing a charge imbalance.
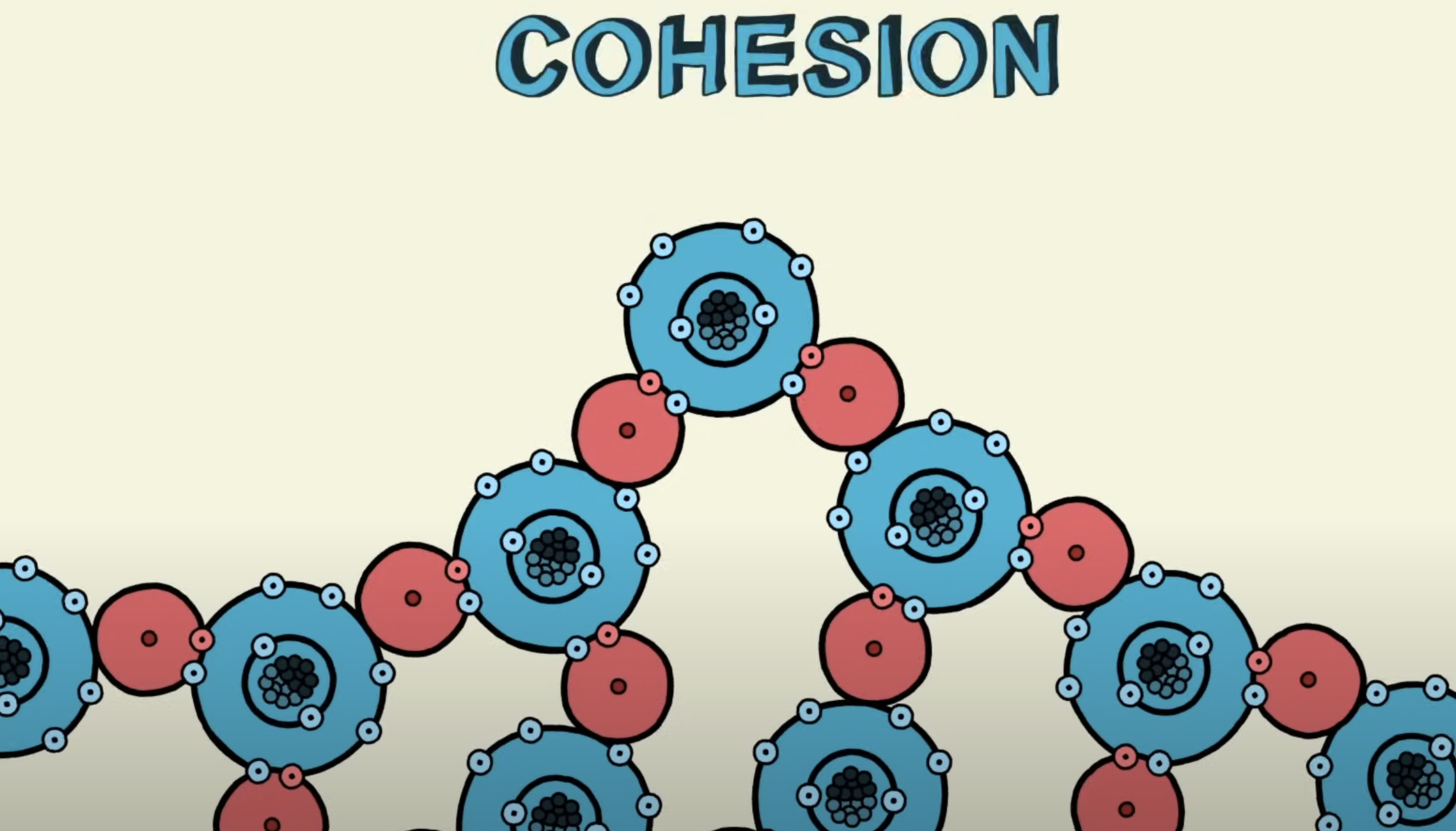
Cohesion
Occurs when similar type of molecules stick to each other
Refers to when the molecules stick to each other (when due to hydrogen bonding)
Allows the water to transport in the plants (water in plants is transformed through interconnected tubes called xylem)
Can withstand the force of gravity and transport water and nutrients upwards against it (called mass transport)
Are able to transport (在植物那上升) as the water is being pulled up by evaporation from the leaves
Enable surface tension
Causes the surface of the water to behave like a stretched membrane which can support small objects (虫子在水上)
Objects break through when many hydrogen bonds are broken
(石头打破张力?)
A water molecule is able to stick to other water molecules via the formation of hydrogen bonds
Water molecules stick together because of hydrogen bonds, which makes the surface of the water slightly stretchy. This is called surface tension.
The high surface tension of water makes it sufficiently dense for certain smaller organisms to move along its surface

Adhesion
A water molecule is able to stick to other polar or charged molecules via the formation of polar associations
Helps water move through narrow tubes by capillary action. This attraction helps water move upward against gravity.
Allows water to move through narrow spaces
E.g. pores in soil or the microscopic channels in plant cell walls
Allows water to move through the pores between soil particles, distributing water and nutrients throughout the soil and providing moisture to plant roots
Responsible for the movement of water and nutrients between cells, allowing the plant to transport these essential substances to where they are needed.
The strength of the capillary action will be dependent on the diameter of the pore through which the water moves (smaller diameter = more action)
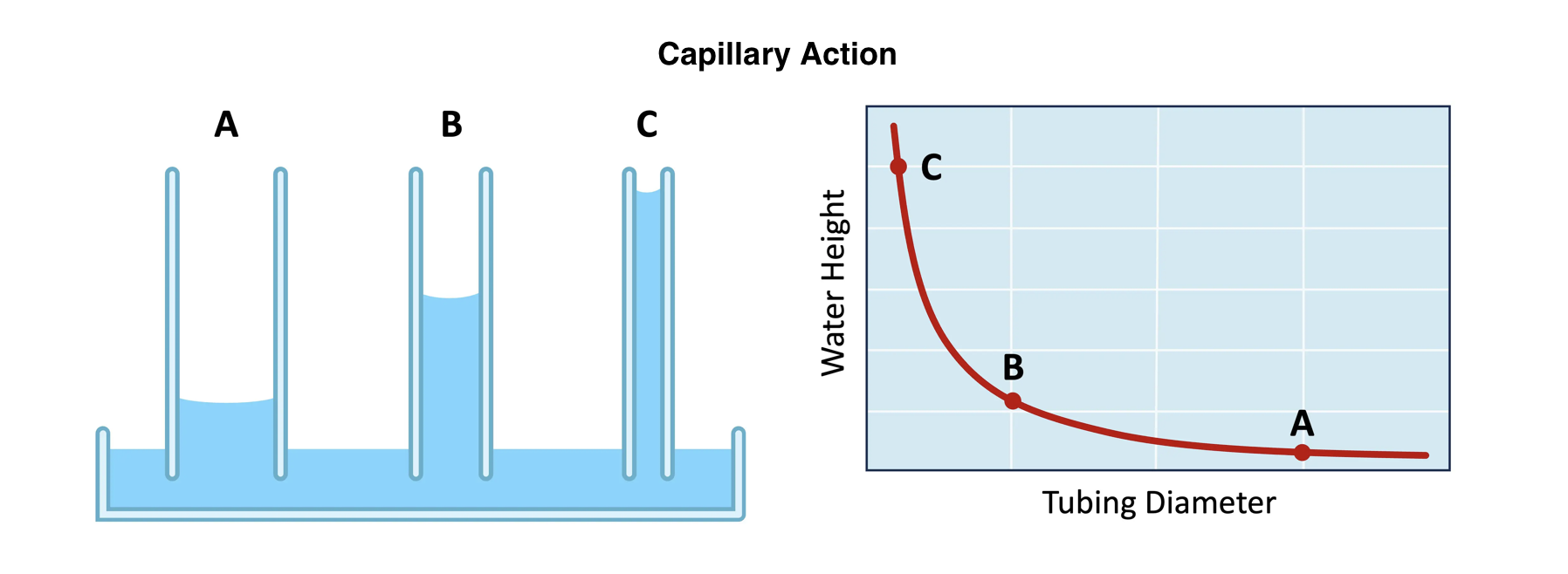
Capillary action
Capillary action refers to the ability of water to move upward through narrow spaces, such as the tiny tubes (xylem vessels) in plant stems.
Cohesion:
The attraction between water molecules, which allows them to stick together.
Adhesion
The attraction of water molecules to the walls of the xylem vessels, which helps water "climb" up the stem
The type of soil will influence the strength of the capillary action, affecting the efficacy of agricultural practices
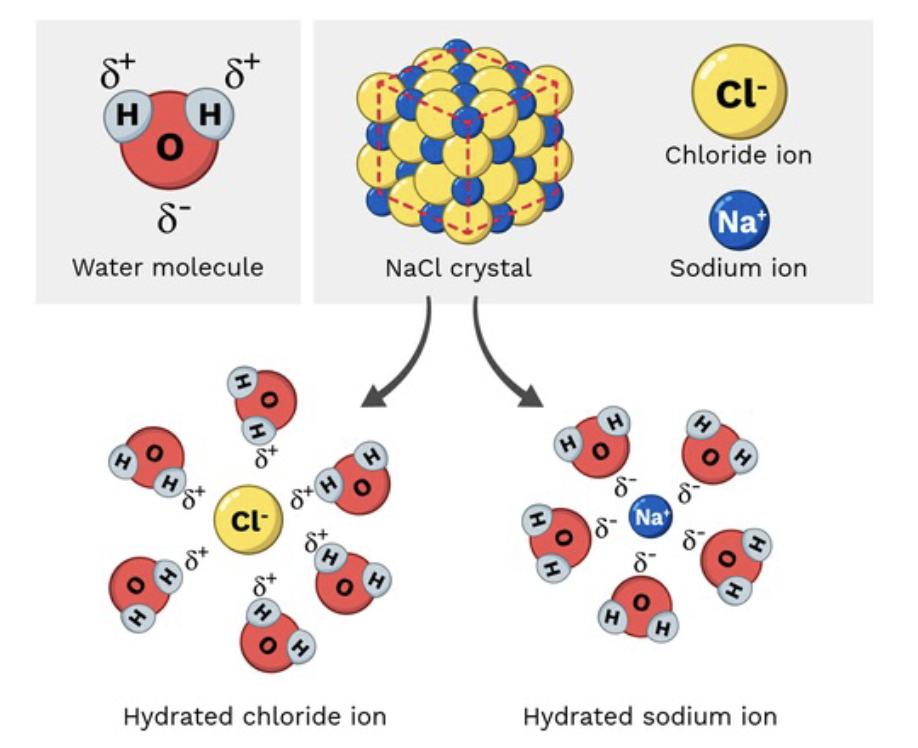
Hydrophilic ("water-loving,")
Any Polar molecules and charged ions could dissolve in water.
Water forms around charged molecules to keep them dissolved.
Polar: (have regions of partial positive and negative charges due to uneven electron distribution, but they are neutral overall)
Salt
Sugar
Charged ion: (atoms or molecules with a full positive or negative charge)
δ
When there is an extremely small particle
Aqueous solution
Water that contains one or more dissolved substance that substances can move and interact
The cytoplasm in cells is an aqueous solution with a mix of dissolved substances that substances can move in and interact.
Enzymes are found in the cytoplasm which help catalyse chemical reactions. All the reactions that occur are known as metabolism.
Metabolism
(新陈代谢)
The sum of reaction in the body that provides energy for each cell within the body with energy.
Transportation of Plant
Use xylem and phloem to move substances in aqueous solutions.
Transportation of Animals
Use blood to transport various substances.
Soluble: Ionic compounds (e.g., sodium chloride), amino acids, glucose.
Slightly Soluble: Oxygen, carried by hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Insoluble: Fats and oils.
Hydrophobic
Substances like fat/water are water hating, and are insoluble in the water. This happens as they are nonpolar or has no charge.
The hydrophobic and insoluble nature of molecules like fats and oils is essential for their function within cells. This characteristic allows them to form cell membranes and store energy efficiently without dissolving in the cell's aqueous environment.
Lipids can create a barrier that separates the inside of the cell or organelle from the outside environment.
Steroid hormones are derived from cholesterol. They include hormones like testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol. Their hydrophobic nature allows them to easily cross the hydrophobic lipid bilayer of the cell membrane.
Fat-soluble vitamins: Vitamins A, D, E, and K are all fat-soluble vitamins that are hydrophobic and insoluble in water. These vitamins are essential for various biological processes, such as vision, bone health, and blood clotting.
Glucose
Polar due to hydroxyl groups (OH groups) Which cause water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with
Amino Acid
Whether an amino acid is hydrophilic (water-loving) or not depends on its R-group (the side chain). Some R-groups are charged, some are polar, and some are nonpolar. Because amino acids can form zwitterions (molecules with both positive and negative charges), all amino acids dissolve in water to some extent, but how well they dissolve depends on the R-group.
Cholesterol
The entire structure is nonpolar/without a charge, except on OH group. This provides a small amount of polarity, but not sufficient (in relation to size of the molecule).
Fat & Lipids
Entirely, Absolutely non polar
Oxygen
Entirely non-polar as a molecule, solubility depends on the temperature (hot water - better solubility).
Sodium chloride
Polar molecule due to cations (Nat) & anion (Cl) which are held together by an ionic bond. The ions are surrounded by polar water molecules when dissolved in water.
Sodium chloride is table salt. It is a polar molecule because it is made up of positive sodium ions (Na+) and negative chloride ions (Cl-). When it dissolves in water, these ions are surrounded by water molecules.
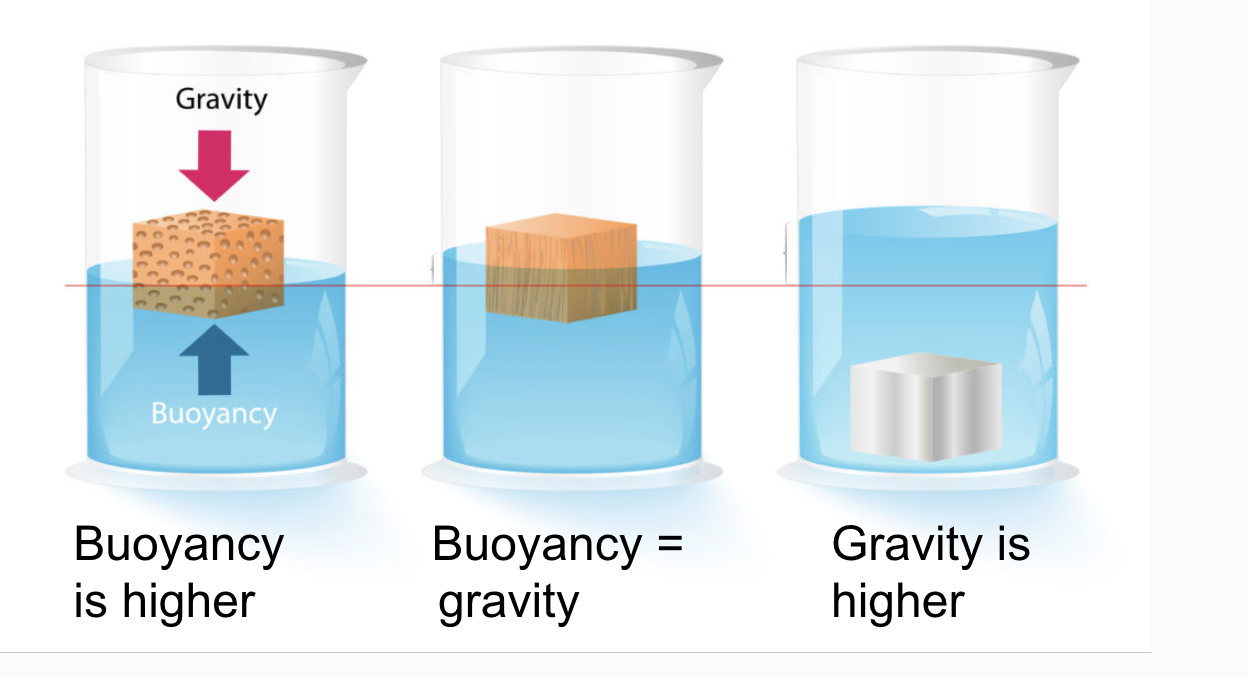
Buoyancy
Upwards force of the water allows floating
Viscosity
Thickness of a liquid which determines how easily it can flow
Water becomes less viscous when it heats up
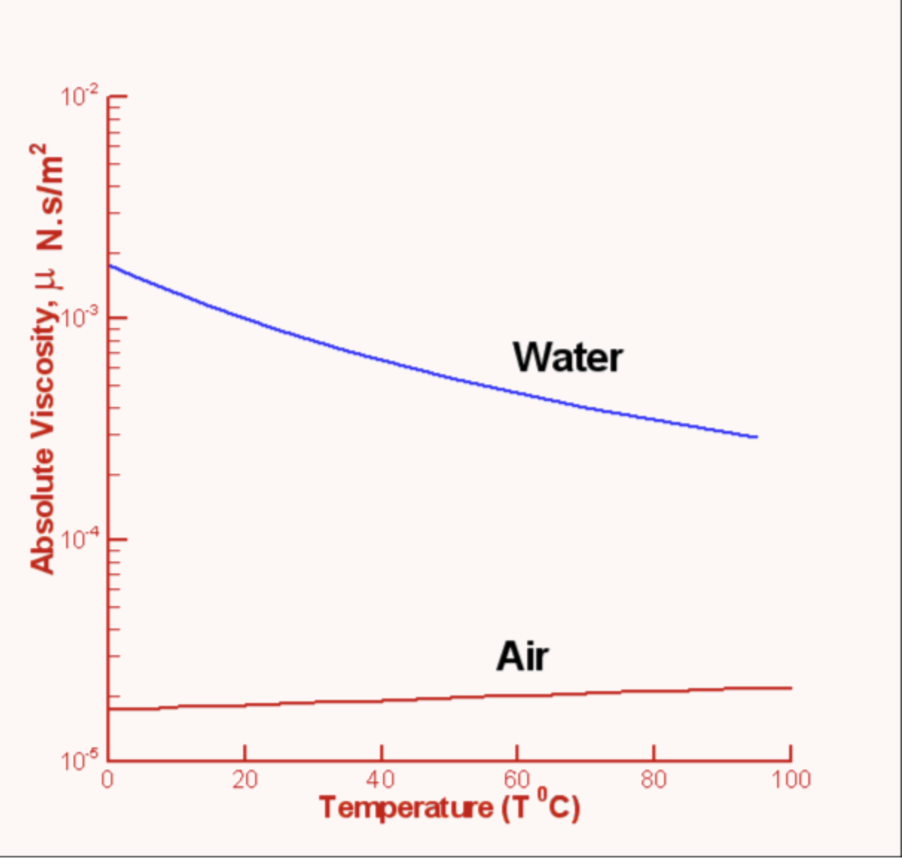
Thermal conductivity
Heat can be transferred through water more easily as the temperature increases
Heat can pass through water quicker than in air as the particles collide more easily in water
Specific heat capacity
The amount of heat that must be added to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an increase of one unit in temperature.
But Water can absorb a lot of heat before changing state.
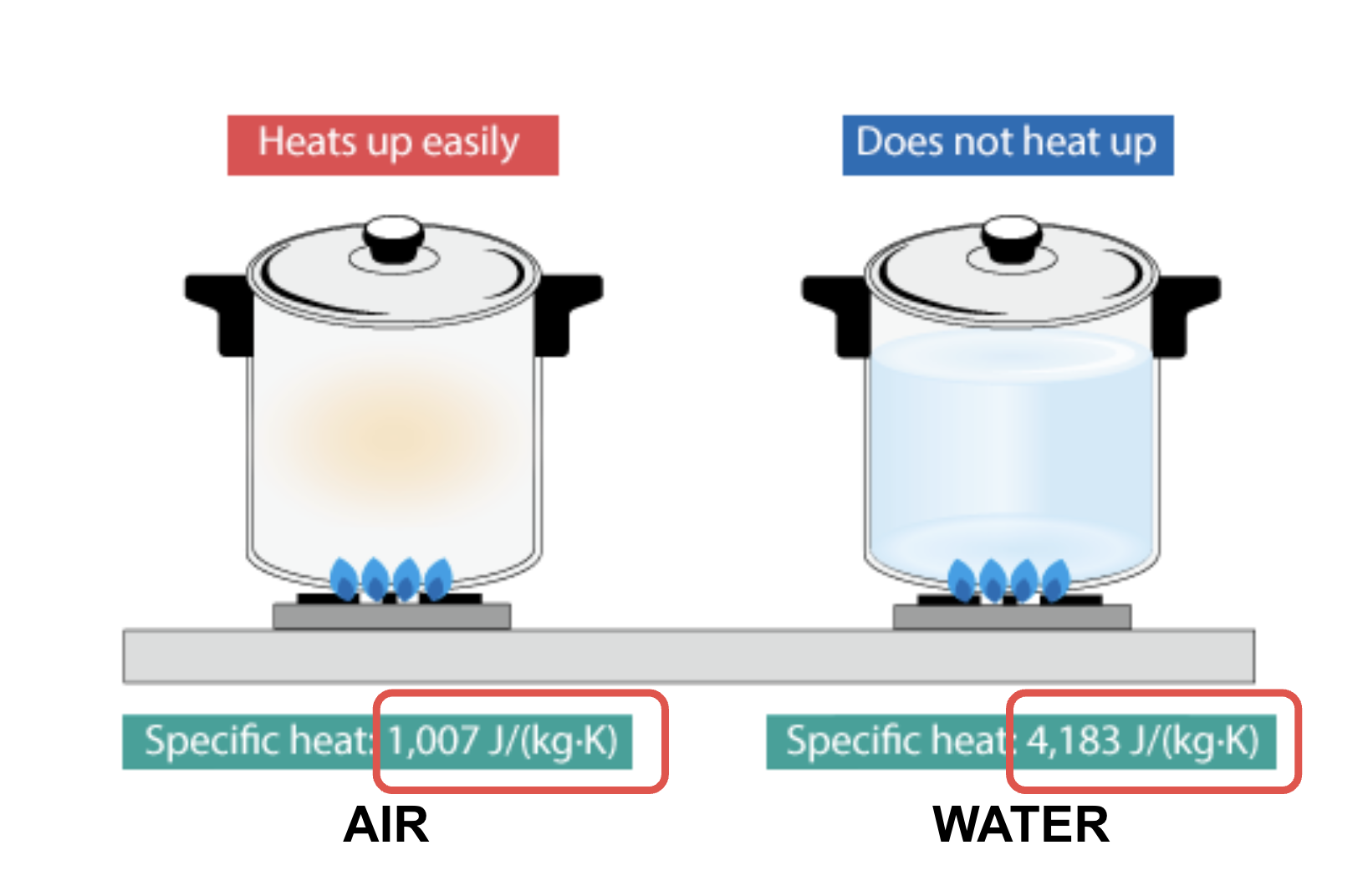
Substances
Need to be transported in plants and animals
Plants transport them in aqueous solutions in xylem and phloem tubes
In animals, blood transport a wide range of substances including soluble and insoluble substances
Soluble
Ionic compounds like sodium chloride, amino acids, glucose
Slightly soluble
Oxygen, but need to be carried by hemoglobin on red blood cells to increase the amount transported
Insoluble
Fat and oil
Hydrophobic
Specific heat capacity
Water can absorb a lot of heat bzaoefore changing state
Physical properties of water
Buoyancy
Viscosity
Thermal conductivity
Specific heat capacity