(14) Hypothalamus & Limbic System
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Does the hypothalamus make up the ventral or dorsal part of the diencephalon?
ventral
The hypothalamus forms the floor and lower part of the wall of which ventricle?
3rd ventricle
What is the main function of the hypothalamus?
maintain homeostasis
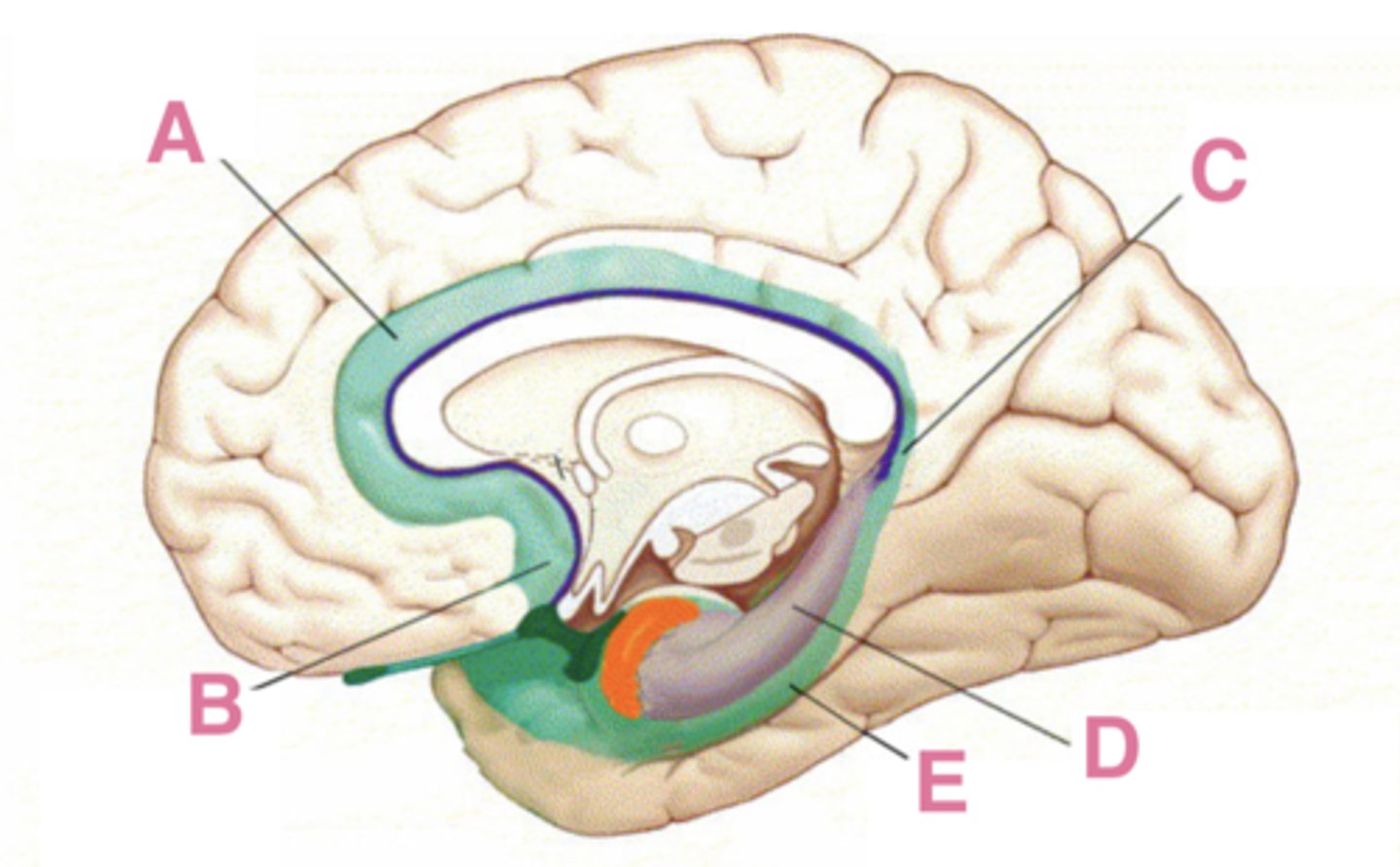
The limbic system is a term that was originally used to describe the limbic lobe, which includes what 5 areas?
subcallosal area, cingulate gyrus, isthmus of the cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, hippocampal formation
A
cingulate gyrus
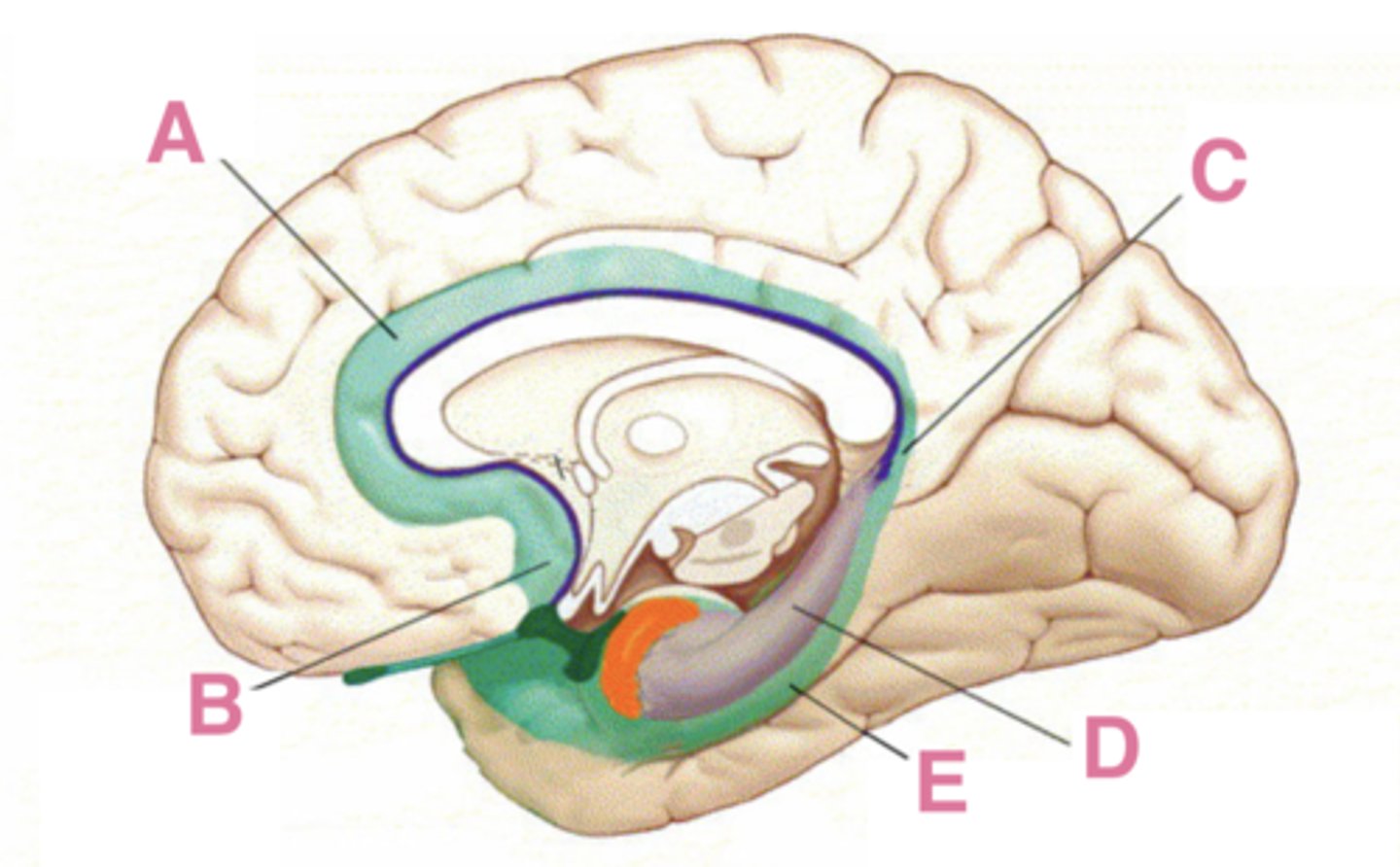
B
subcallosal area
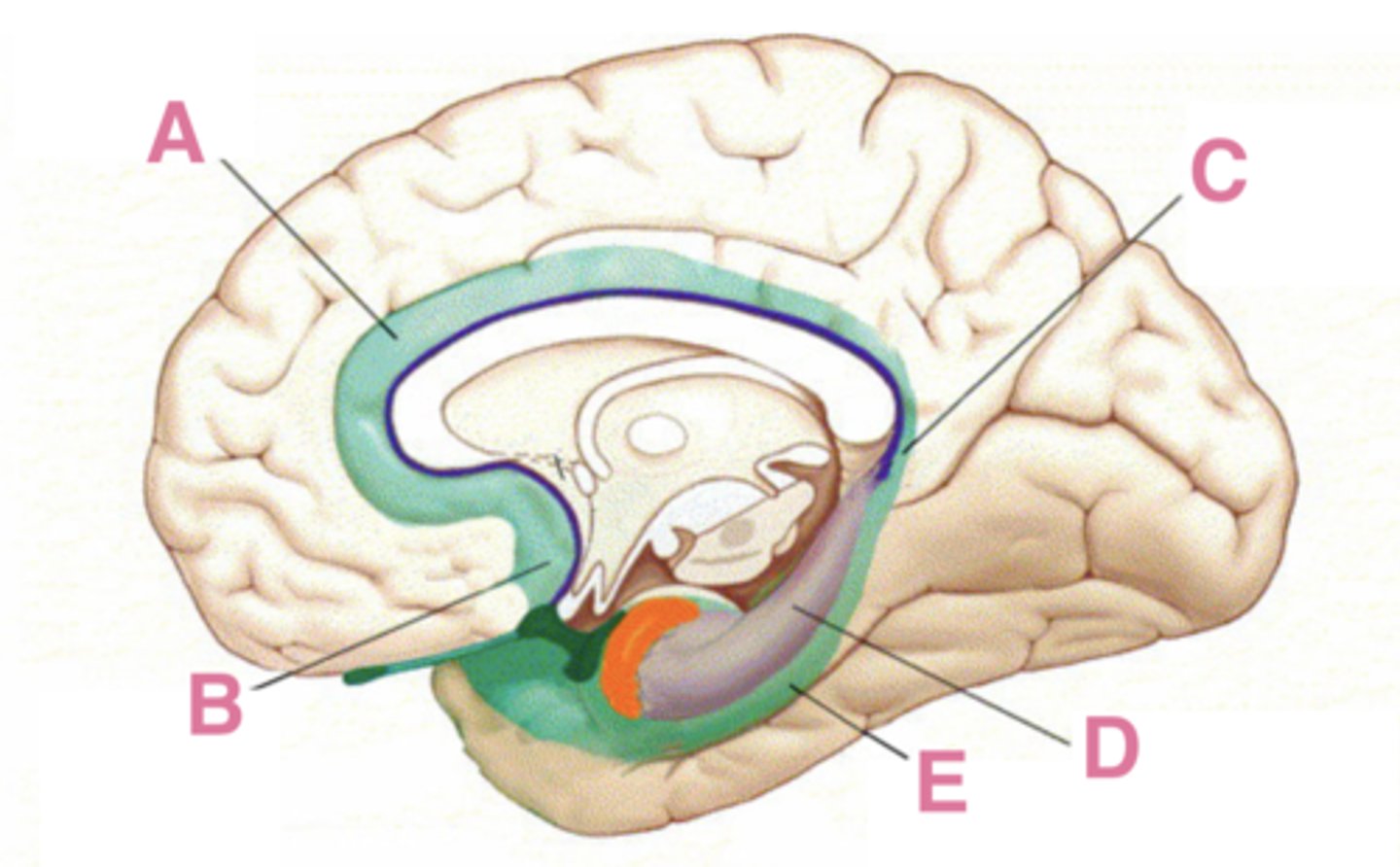
C
isthmus of the cingulate gyrus
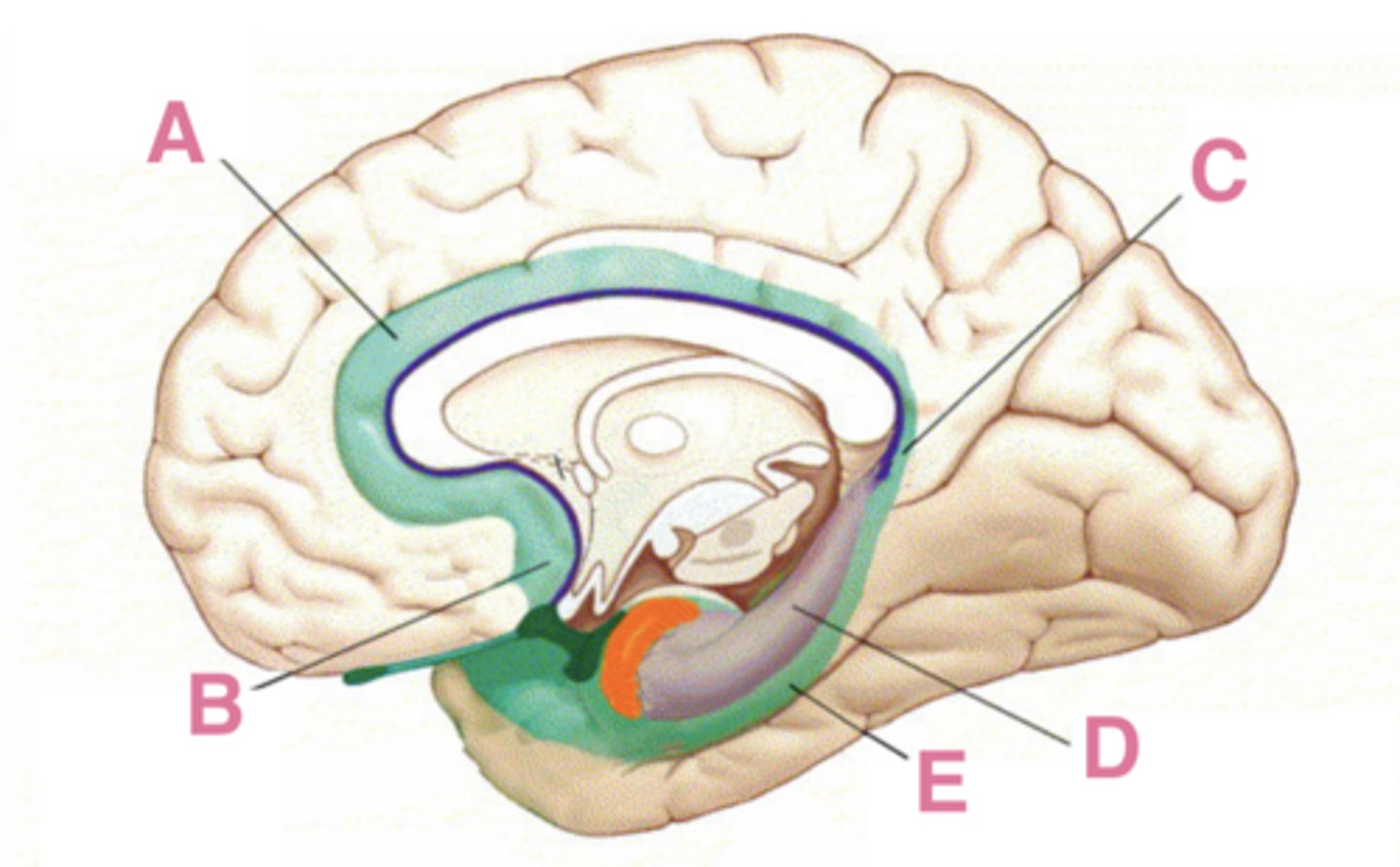
D
hippocampus
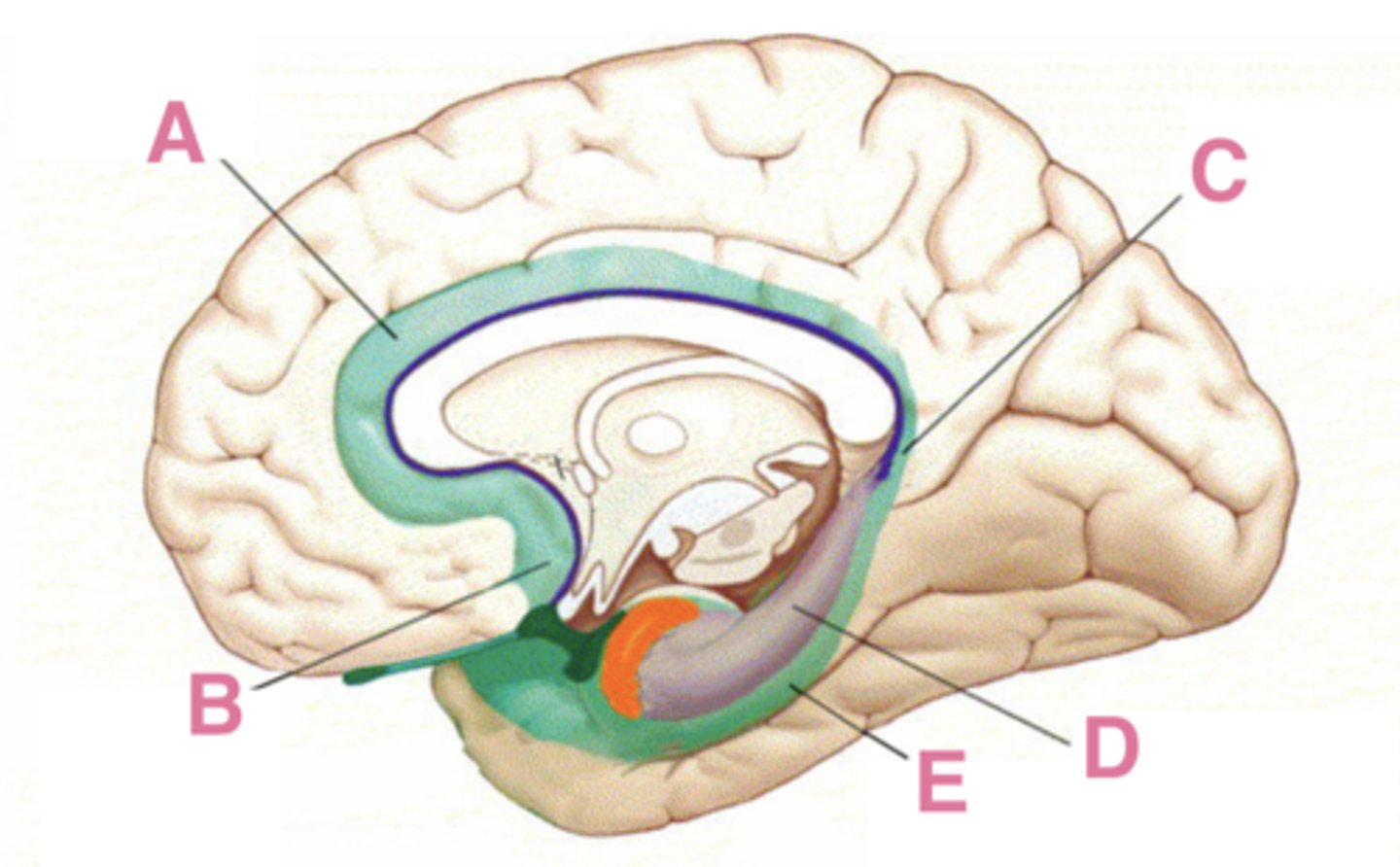
E
parahippocampus
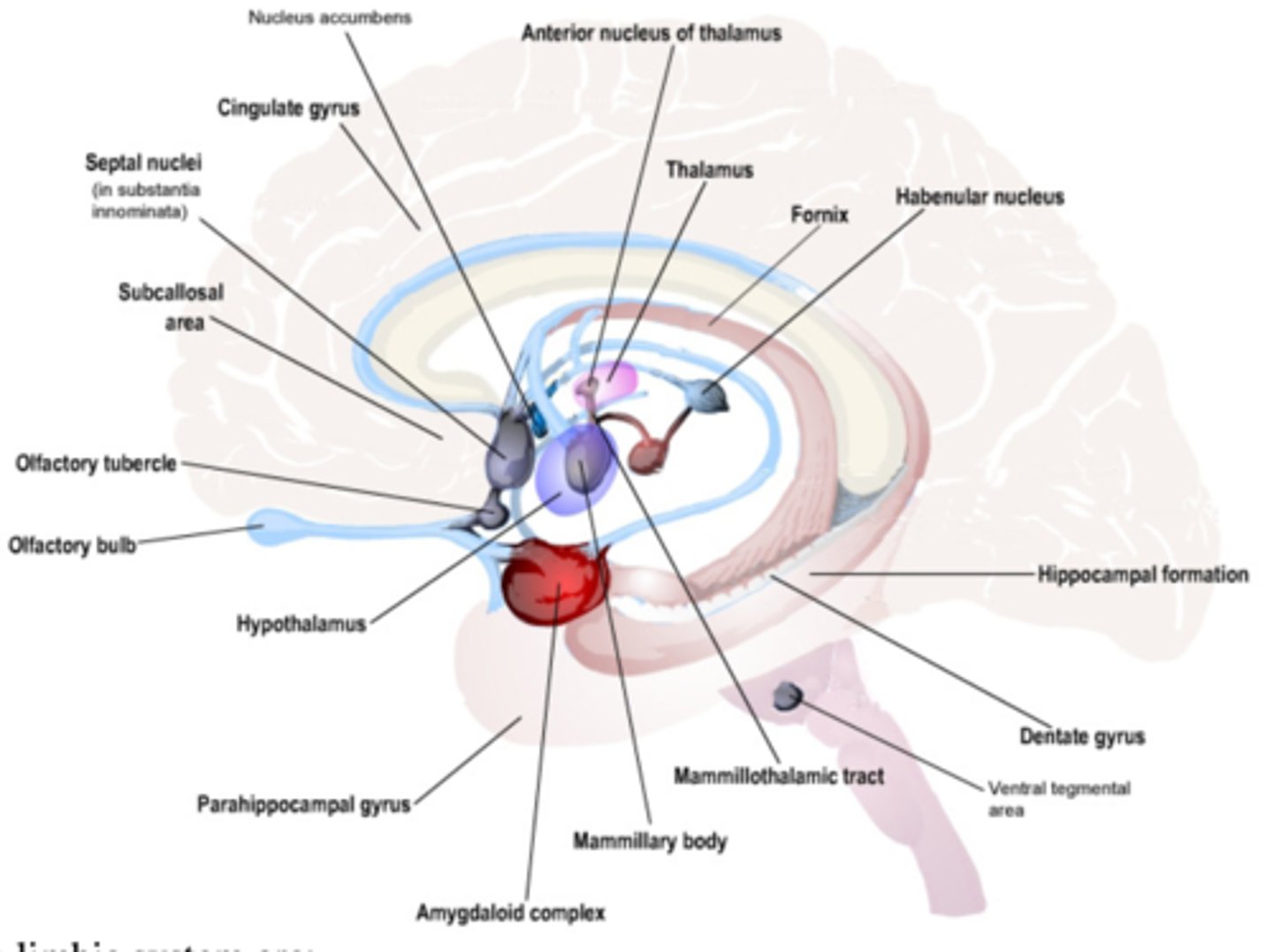
The limbic system is modernly used to describe a more encompassing concept that includes a variety of nuclei and pathways that seem to be functionally related. These areas deal with what 3 sensations?
olfaction, emotional responses, memory
(it's basically the bridge between the thinking and automatic parts of the brain)
Overall, what 3 things are included in the limbic system?
all of the limbic lobe, many subcortical nuclei, several white matter structures
area related to the limbic system in that it appears to be the site of conscious feelings (like empathy, love, and beauty) and self- awareness (e.g., metacognition)
insula
What is the lateral boundary of the hypothalamus?
internal capsule
What is the medial boundary of the hypothalamus?
3rd ventricle
outpocketing of the hypothalamus in front of the maxillary bodies
tuber cinereum
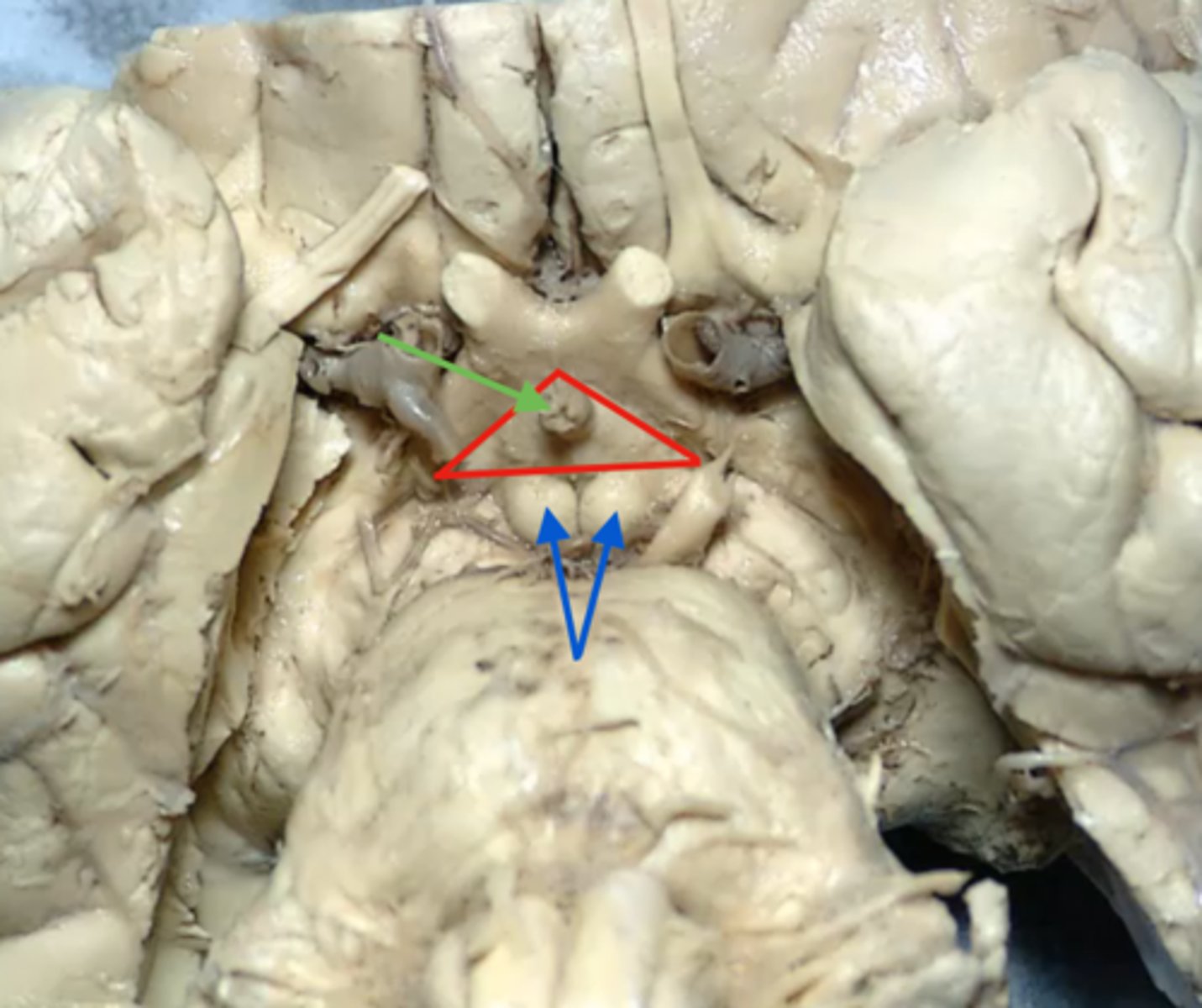
most inferiorly projecting portion of the tuber cinereum of the hypothalamus, which is continuous with the hypophyseal infundibulum
median eminence
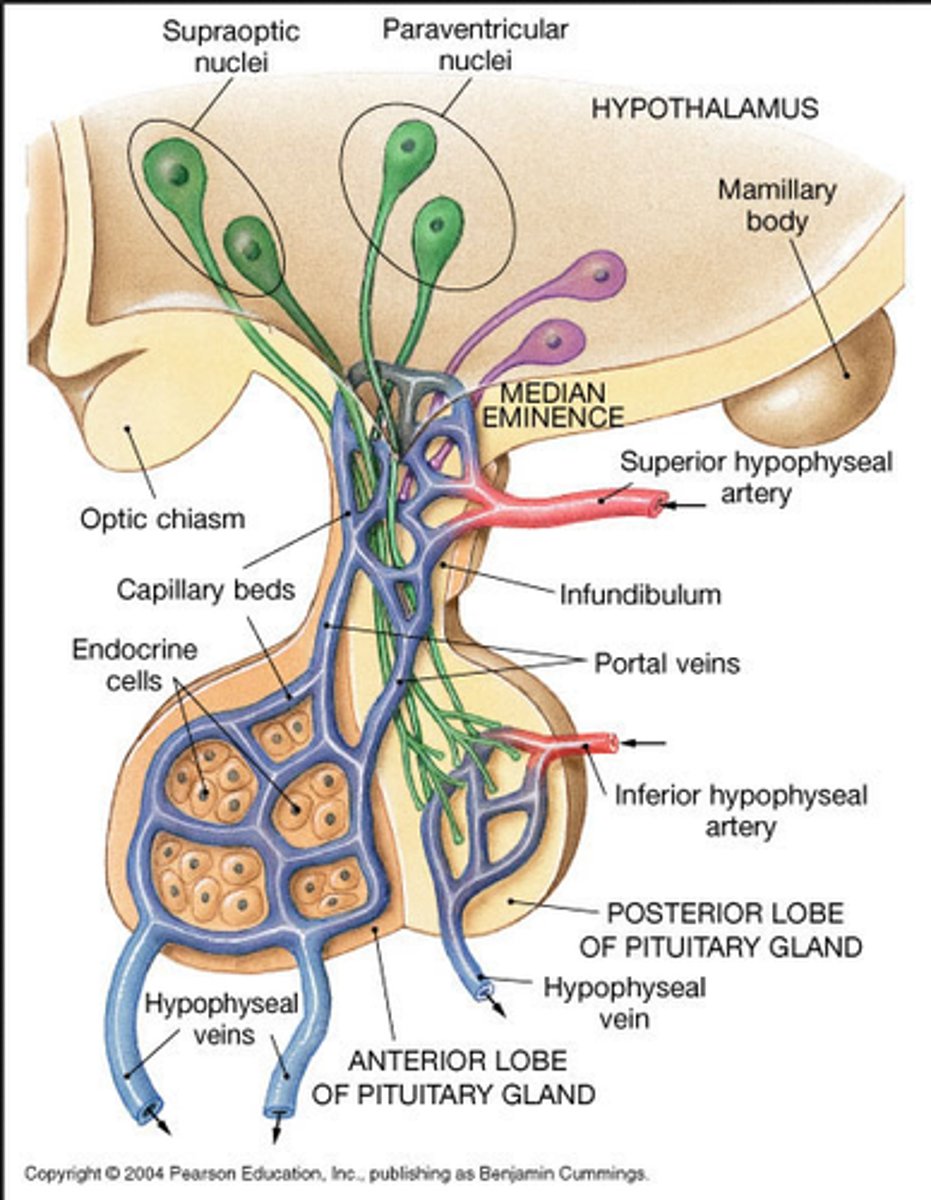
What attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland?
median eminence
What are the 3 parts of the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)?
pars distalis, pars intermedia, pars tuberalis
What are the 2 parts of the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)?
pars nervosa, infundibulum
What part of the pituitary gland attaches to the median eminence of the hypothalamus?
infundibulum
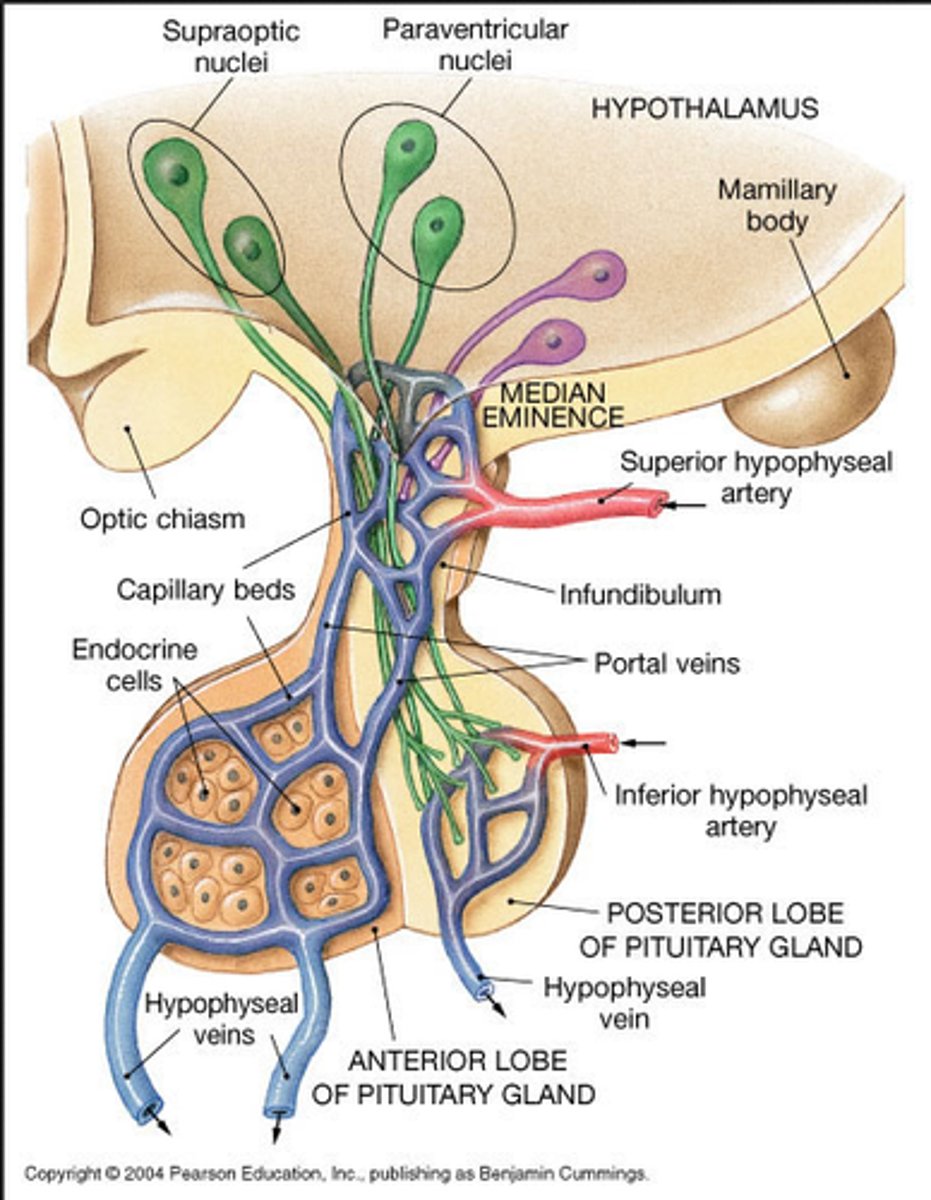
parasympathetic center that is especially involved in producing heat loss (when the body is too warm); also helps control the anterior pituitary via releasing and inhibiting factors
preoptic nucleus
parasympathetic center that is especially involved in producing heat loss (when the body is too warm)
anterior nucleus
fever-producing products of certain bacterial decomposition that appear to work by inhibiting the anterior hypothalamus (preoptic and/or anterior nuclei)
**reduces the function of the mechanisms involved in heat loss, and the body temperature goes up
pyrogens
Which two hypothalamic nuclei do pyrogens affect?
preoptic, anterior
sympathetic center that is especially involved in conserving heat (when the body is too cold)
posterior nucleus
feeding center, such that when stimulated (e.g., experimentally with an electric current) feeding occurs
**if this nucleus has a lesion (e.g., experimentally), the animal will refuse to eat and even starve itself
lateral nucleus
satiety center, such that when stimulated (e.g., experimentally with an electric current) feeding stops
**if this nucleus has a lesion (e.g., experimentally), the animal will increase its feeding behavior and become morbidly obese
ventromedial nucleus
hypothalamic nucleus that contains osmoreceptors for controlling thirst and also produces vasopressin (ADH) and oxytocin for release into the blood from the posterior pituitary gland
supraoptic nucleus
hypothalamic nucleus that produces vasopressin (ADH) and oxytocin for release into the blood from the posterior pituitary gland
**also the site of the vast majority of central autonomic neuron cell bodies that will project to synapse on preganglionic autonomic neurons, which represents how the “higher centers” have input to and control the autonomic nervous system
paraventricular nucleus
major output pathway of the hypothalamus that descends through the periaqueductal gray matter of the midbrain, white matter near the 4th ventricle, and lateral funiculus in the spinal cord
**nerve fibers of neurons with their cell bodies in the paraventricular nucleus run through here
dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
hypothalamic nucleus that helps mediate circadian rhythms by receiving direct retinal input and connecting to the pineal gland
suprachiasmatic nucleus
emotional center such that when stimulated (e.g., experimentally with an electric current) a behavior known as sham rage occurs
dorsomedial nucleus
hypothalamic nucleus that exhibits the main control of the anterior pituitary via releasing and inhibiting factors
arcuate nucleus
hypothalamic nuclei that usually consist of multiple small clusters of neuron cell bodies which help control the anterior pituitary via releasing and/or inhibiting factors
tuberal nuclei
memory center that is the main terminus of the fornix and is the
source of fibers to the anterior nucleus of the thalamus
also connects to the reticular formation and helps regulate a variety of autonomic behaviors
mamillary nucleus (body)
Is the preoptic nucleus a sympathetic or parasympathetic center?
parasympathetic
What is the main function of the preoptic nucleus?
heat loss (when the body is too warm)
Is the anterior nucleus a sympathetic or parasympathetic center?
parasympathetic center
What is the main function of the anterior nucleus?
heat loss (when the body is too warm)
Is the posterior nucleus a sympathetic or parasympathetic center?
sympathetic
What is the main function of the posterior nucleus?
heat conservation (when the body is too cold)
Is the lateral nucleus a feeding or satiety center?
feeding
What is the main function of the lateral nucleus?
induces feeding
Is the ventromedial nucleus a feeding or satiety center?
satiety
What is the main function of the ventromedial nucleus?
stops feeding
What is the main function of the supraoptic nucleus? (2)
controls thirst, produces ADH and oxytocin
What is the main function of the paraventricular nucleus?
produces ADH and oxytocin
What is the main function of the suprachiasmatic nucleus?
mediates circadian rhythms
What kind of center is the dorsomedial nucleus?
emotional center
What is the main function of the dorsomedial nucleus?
controls aggression
(can induce sham rage when stimulated)
What is the main function of the arcuate nucleus?
controls anterior pituitary via releasing and inhibiting factors
What is the main function of the tuberal nuclei?
help control anterior pituitary via releasing and inhibiting factors
What kind of center is the mamillary nucleus?
memory
(part of the circuit of Papez)
What is the main function of the mamillary nucleus? (2)
memory, regulate autonomic behaviors
Which hypothalamic nucleus exhibits the MAIN control over the anterior pituitary gland?
arcuate nucleus
Which nucleus is the source of fibers to the anterior nucleus of the thalamus?
mamillary nucleus
(mamillothalamic tract)
Where are the cell bodies found for neurons that run through the dorsal longitudinal fasciculus?
paraventricular nucleus
Where does the hypothalamus receive most of its input?
other limbic centers, reticular formation
Where does the hypothalamus send most of its output?
pituitary gland, reticular formation, autonomic nuclei
What are the 3 parts of the hippocampal formation found on the superior aspect of the parahippocampal gyrus?
subiculum, hippocampus, dentate gyrus
cerebral cortical transitional area between 3-layered hippocampus and 5-layered entorhinal cortex (of the parahippocampal gyrus)
**represents the main route of info INTO the hippocampus (from the parahippocampus)
subiculum
3-layered cerebral cortical region with a characteristic C-shape that helps in processing memories
hippocampus
3-layered cerebral cortical region that is arranged with the hippocampus such that they intertwine
dentate gyrus
white matter that represents the innermost region of hippocampus that borders on the lateral ventricle, consisting of many axons of neurons in the hippocampus that form the fimbria
**represents the main route of info OUT OF the hippocampus
alveus
What cognitive process is the hippocampal formation involved in?
short term memory
white matter pathway that runs mostly between the hippocampus and the mamillary bodies
starts as a pair of crura that project as fimbrae and curve posteriorly and superiorly around the posterior part of the thalamus; also has a body that divides into columns and end in the mamillary bodies
fornix
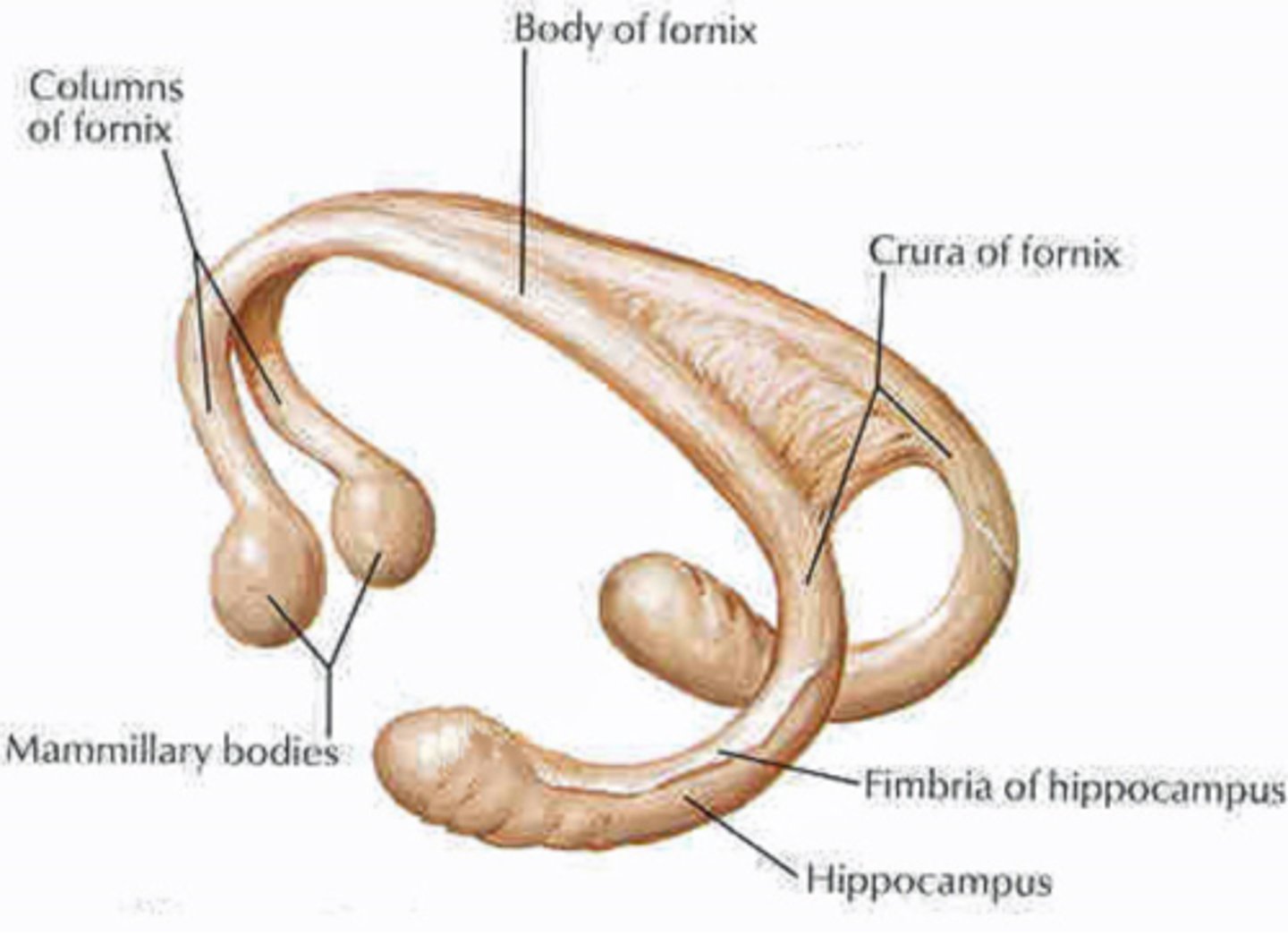
The body of the fornix helps form the medial walls of what ventricle?
lateral ventricles
The body of the fornix helps form the roof of what ventricle?
3rd ventricle
fibers that run in the columns of the fornix and curve posteriorly to end in the mamillary bodies
postcommissural fibers
Circuit of Papez 1a: What structure does information leave from at the beginning of the circuit of Papez?
hippocampus
Circuit of Papez 1b: What kind of information initially leaves from the hippocampus at the beginning of the circuit of Papez?
short term memory
Circuit of Papez 2: Information about short term memory leaves the hippocampus via what structure?
alveus
Circuit of Papez 3: Information leaves the hippocampus via the alveus and enters what other structure?
fornix
Circuit of Papez 4: Where does the fornix deliver the information that it receives?
mamillary bodies
Circuit of Papez 5: The mamillary bodies, after receiving information about short term memory from the fornix, gives rise to the mamillothalamic tract that takes that info to what specific collection of cell bodies?
anterior nucleus (of the thalamus)
Circuit of Papez 6: From the anterior nucleus of the thalamus, the information goes via the thalamocortical tract to what structure in the cerebral cortex?
cingulate gyrus
Circuit of Papez 7: After information reaches the cingulate gyrus from the thalamocortical tract, where is the information sent? (specific cortex + general structure)
entorhinal cortex of parahippocampal gyrus
Circuit of Papez 8: The entorhinal cortex of the parahippocampal gyrus sends the information it receives to which structure to finish the circuit?
hippocampus
(back to where we began)
What is the order of structures in the circuit of Papez? (8)
hippocampus, fornix, mamillary bodies, mamillothalamic tract, anterior nucleus, thalamocortical tract, entorhinal cortex, hippocampus
What is the main function of the circuit of Papez?
consolidate long term memories
Problems with the circuit of Papez usually lead to what general type of condition?
anterograde amnesia
(inability to form new memories)
model of memory consolidation in which synaptic activity causes the postsynaptic cell to change the presynaptic cell to release more neurotransmitter by releasing nitric oxide that diffuses (backwards) across the synaptic cleft from the postsynaptic cell to the presynaptic cell
these brief, sustained increases in synaptic activity increase the probability that future synaptic activity will take place, causing stimuli and responses to be paired in the process and thus resulting in memory
long term potentiation
Which neurotransmitter is released in the circuit of Papez?
glutamate
How does Alzheimer disease affect the circuit of Papez?
interferes with entorhinal cortex
How does Korsakoff syndrome affect the circuit of Papez?
**results from prolonged thiamine (B1) deficiency
affects mamillary bodies and fornix
group of neuron cell bodies in the rostromedial portion of the limbic lobe that receives input from a wide range of somatosensory, visual, and visceral (including olfactory) sources
output goes mainly to the hypothalamus and other limbic structures, visceral nuclei of the brain stem, and (indirectly) the cerebral cortex
amygdala (or amygdaloid complex)
Where does the amygdala receive its input?
different somatosensory, visual, and visceral sources
Where does the amygdala send its output?
hypothalamus, brain stem nuclei, cerebral cortex
What are the main functions of the amygdala? (2)
memory, emotion
What four base emotions/sensations is the amygdala responsible for?
food, fear, fight, sex
True or false: Injuries involving the amygdala and hippocampus result in more memory loss
than those involving only the hippocampus.
true
In Klüver-Bucy syndrome, which involves bilateral temporal lobe lesions (including the amygdaloid complex), what 4 signs/symptoms classically occur?
visual agnosia, hyperorality, placidity, hyperphagia
Where does the nucleus accumbens receive its input?
amygdala, hippocampus, brain stem
Where does the nucleus accumbens send its output?
hypothalamus, brain stem nuclei
What is the main function of the nucleus accumbens?
feeling of gratification