"Lipids" 6th Week - BIOCHEMISTRY (1styr-2ndsem-Midterms)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:28 PM on 3/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
1
New cards
**Lipids**
* Are a heterogenous group of compounds including: fats, oils, steroids, waxes, and related compound
* Are transported in the blood combined with proteins in lipoprotein particles
* Are transported in the blood combined with proteins in lipoprotein particles
2
New cards
**Common properties of lipids**
a. Relatively insoluble in water
b. Soluble in nonpolar solvents such as ether and chloroform
\
b. Soluble in nonpolar solvents such as ether and chloroform
\
3
New cards
**Simple lipids, Complex lipids, and Derived lipids**
What are the types of lipids?
4
New cards
**Simple lipids**
* Fats
* Waxes
* Waxes
5
New cards
**Complex lipids**
Are esters of fatty acids which always contain:
* An alcohol
* One or more fatty acids
* Other groups
* An alcohol
* One or more fatty acids
* Other groups
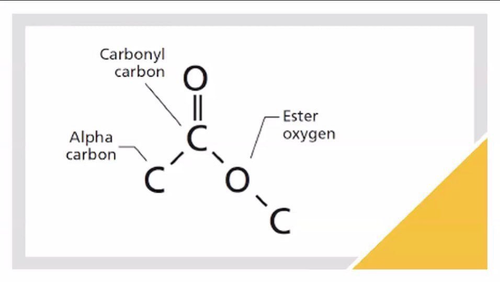
6
New cards
**Ester**
An any class of organic compounds that react with water to produce alcohols and organic or inorganic acids
7
New cards
**Phospholipids, Glycolipids, and other Complex lipids**
What are the 3 types of Complex lipids?
8
New cards
**Derived lipids**
* Are formed from the hydrolysis of both simple and complex lipids
* May act as precursor lipids in the formation of simple and complex lipids
* Include fatty acids, glycerol, steroids, other alcohols, fatty aldehydes, ketone bodies, hydrocarbons, lipid-soluble vitamins and micronutrients, and hormones
* May act as precursor lipids in the formation of simple and complex lipids
* Include fatty acids, glycerol, steroids, other alcohols, fatty aldehydes, ketone bodies, hydrocarbons, lipid-soluble vitamins and micronutrients, and hormones
9
New cards
**Fats**
Are important dietary constituents
\
Contains:
* Essential fatty acids
* Fats-soluble vitamins (e.g., vit A/D/E/K)
* Other lipophilic micronutrients
\
Contains:
* Essential fatty acids
* Fats-soluble vitamins (e.g., vit A/D/E/K)
* Other lipophilic micronutrients
10
New cards
**1 gram carbohydrate**
= 4 calories
11
New cards
**1 gram proterin**
= 4 calories
12
New cards
**1 gram fat**
9 calories
13
New cards
**Fats**
* Stored in adipose tissue in the subcutaneous tissue and around certain organs
\
* also serve as thermal insulator
\
* also serve as thermal insulator
14
New cards
**Waxes**
* Are esters of fatty acids with higher molecular weight monohydric alcohols
\
* consist of long-chain fatty acid linked through an ester oxygen to a long-chain alcohol
\
* completely water-insoluble and generally solid at biological temperatures
\
* function as water repellants on the leaves of some plants, on feathers, and on the cuticles of certain insects
\
* consist of long-chain fatty acid linked through an ester oxygen to a long-chain alcohol
\
* completely water-insoluble and generally solid at biological temperatures
\
* function as water repellants on the leaves of some plants, on feathers, and on the cuticles of certain insects
15
New cards
**Wax production**
Associated with the sebaceous glands of the skin
16
New cards
**Wax esters**
Composition of human sebum
17
New cards
**Complex lipids**
* Phospholipds
* Glycolipids
* other complex lipids
* Glycolipids
* other complex lipids
18
New cards
**Phospholipids**
Contain phosphoric residue
19
New cards
**Choline**
Phospholipid that have nitrogen-containing bases
20
New cards
**Glycerophospholipids**
Phospholipids that contain alcohol as glycerol
21
New cards
**Sphingophospholipids**
phospholipids that contain amino group as sphingosine
22
New cards
**Glycolipids**
Glycosphingolipids
* contain a fatty acid, sphingosine, and carbohydrate
* contain a fatty acid, sphingosine, and carbohydrate
23
New cards
**Complex lipids**
* Sulfolipids
* Amino lipids
* Liporoteins
* Amino lipids
* Liporoteins
24
New cards
**Neutral lipids**
These are uncharged lipids
\
* acylglycerols (glycerides)
* cholesterol
* cholesteryl esters
\
* acylglycerols (glycerides)
* cholesterol
* cholesteryl esters
25
New cards
**Derived lipids**
* Occur in the body as 90% esters and unesterified form
\
* are also structural components of membrane lipids such as phospholipids
\
* are also precursors of the hormone-like prostoglandins
\
* are also structural components of membrane lipids such as phospholipids
\
* are also precursors of the hormone-like prostoglandins
26
New cards
**Fatty acid esters**
* TAG
* cholesteryl esters
* phospholipds
* cholesteryl esters
* phospholipds
27
New cards
**Fatty acid unesterified**
Free fatty acids
28
New cards
**TAGs**
* Esterified FAs stored in white adipose tissue
\
* serve as the major energy reserve of the body
\
* serve as the major energy reserve of the body
29
New cards
**Alterations in fatty acid metabolism**
Are associated with obesity and diabetes
30
New cards
**Tissues**
**liver**
**musles**
**liver**
**musles**
Areas where FAs provide energy
31
New cards
**Liver**
Area where FAs provide the substrate for ketone body synthesis
32
New cards
**3 systems in naming fatty acids**
* Delta nomenclature
* Omega nomenclature
* Common anmes
* Omega nomenclature
* Common anmes
33
New cards
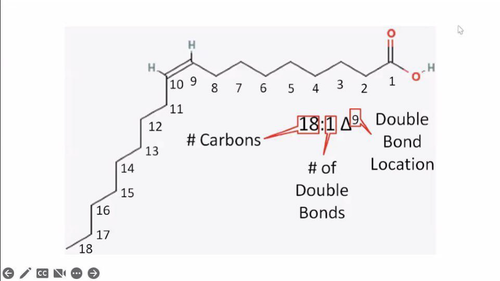
**Delta nomenclature**
Identify 3 things:
number of carbons in fatty acid
number of double bonds
number of carbons are counted from the carboxylic acid end to the first carbon with double bonds
\
use the delta symbol
\
applies to naming unsaturated fatty acids
number of carbons in fatty acid
number of double bonds
number of carbons are counted from the carboxylic acid end to the first carbon with double bonds
\
use the delta symbol
\
applies to naming unsaturated fatty acids
34
New cards
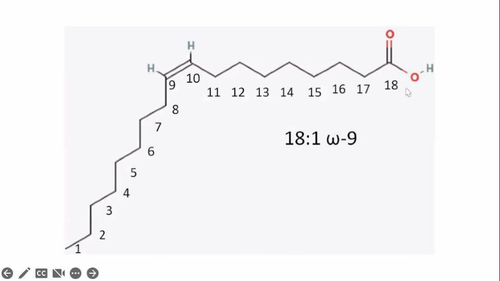
**Omega nomenclature**
Identify 3 things:
number of carbons in the fatty acid
number of double bonds
number of carbons are counted from the methyl end instead of the carboxylic acid end
\
use the omega symbol (w) or for (n) for unsaturated FAs
\
applies to naming unsaturated fatty acids
number of carbons in the fatty acid
number of double bonds
number of carbons are counted from the methyl end instead of the carboxylic acid end
\
use the omega symbol (w) or for (n) for unsaturated FAs
\
applies to naming unsaturated fatty acids
35
New cards
**Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA)**
De
36
New cards
Stearic Acid (Octadecanoic Acid)
Omega 18:0
37
New cards
Arachidic acid
Omega Name: 20:0
38
New cards
Lignoceric acid
Omega Name: 24:0
39
New cards
Oleic acid
Omega Name 18:1 (n-9)
40
New cards
Linoleic acid
Omega Name: 8:2 (n-6)
41
New cards
Alpha-linoleic acid
Omega Name: 18:3 (n-3)
42
New cards
Unsaturated acids
End in -enoic
ex: octadecenoic acid (oleic acid, C18)
ex: octadecenoic acid (oleic acid, C18)
43
New cards
Saturated acids
End in -anoic ex: octanoic acid (C8)
44
New cards
Saturated fatty acids
Butyric acid; caproic acid; caprylic acid
45
New cards
Butyric acid
Butanoic acid; 4:0
46
New cards
CAPROIC acid
Hexanoic acid; 6:0
47
New cards
Caprylic acid
Octanoic acid 8:0
48
New cards
False
**T/F**: Proteins are composed of heterogenous biomolecules
49
New cards
False
**T/F**: Carbohydrates are composed of heterogenous biomolecules
50
New cards
**Lipids**
A family of structurally diverse compounds whose similarity is only their water-solubility / immiscibility.
51
New cards
Fatty Acids
Simple, linear carboxylic acids
52
New cards
Saturated fatty acids
Contains single bonds only
Good Stacking
Solids at room temp
Have relatively high melting points
Good Stacking
Solids at room temp
Have relatively high melting points
53
New cards
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Contains at least one double bond
Less stacking because of kinks
Have relatively low melting points
Less stacking because of kinks
Have relatively low melting points
54
New cards
Short-Chain FA
Composed of 2 to 6 carbons
55
New cards
Medium-Chain FA
Composed of 8 to 14 carbons
56
New cards
Long-Chain FA
Composed of at least 16 carbons
57
New cards
Very Long Chain FA
Composed of at least 22 carbons
58
New cards
Caproic Acid
Name of 6-carbon saturated fatty acid
59
New cards
Caprylic Acid
Name of 8-carbon saturated fatty acid
60
New cards
Capric Acid
Name of 10-carbon saturated fatty acid
61
New cards
Lauric Acid
Name of 12-carbon saturated fatty acid
62
New cards
Myristic Acid
Name of 14-carbon saturated fatty acid
63
New cards
Palmitic Acid
Name of 16-carbon saturated fatty acid
64
New cards
Stearic Acid
Name of 18-carbon saturated fatty acid
65
New cards
Arachidic Acid
Name of 20-carbon saturated fatty acid
66
New cards
Behenic Acid
Name of 22-carbon saturated fatty acid
67
New cards
Lignoceric Acid
Name of 24-carbon saturated fatty acid
68
New cards
a-Linolenic acid
Cervonic acid (docosahexaenoic acid) - DHA
Timnodonic acid (eicosapentaenoic acid)
Cervonic acid (docosahexaenoic acid) - DHA
Timnodonic acid (eicosapentaenoic acid)
Which of the following are examples of **ω-3** fatty acids?
\
a-Linolenic acid
Arachidonic acid
Cervonic acid (docosahexaenoic acid) - DHA
Elaidic acid
Linoleic acid
Oleic acid
Timnodonic acid (eicosapentaenoic acid)
\
a-Linolenic acid
Arachidonic acid
Cervonic acid (docosahexaenoic acid) - DHA
Elaidic acid
Linoleic acid
Oleic acid
Timnodonic acid (eicosapentaenoic acid)
69
New cards
Arachidonic acid
Linoleic acid
Linoleic acid
Which of the following are examples of **ω-6** fatty acids?
\
a-Linolenic acid
Arachidonic acid
Cervonic acid (docosahexaenoic acid) - DHA
Elaidic acid
Linoleic acid
Oleic acid
Timnodonic acid (eicosapentaenoic acid)
\
a-Linolenic acid
Arachidonic acid
Cervonic acid (docosahexaenoic acid) - DHA
Elaidic acid
Linoleic acid
Oleic acid
Timnodonic acid (eicosapentaenoic acid)
70
New cards
Elaidic acid
Oleic acid
Oleic acid
Which of the following are examples of **ω-9** fatty acids?
\
a-Linolenic acid
Arachidonic acid
Cervonic acid (docosahexaenoic acid) - DHA
Elaidic acid
Linoleic acid
Oleic acid
Timnodonic acid (eicosapentaenoic acid)
\
a-Linolenic acid
Arachidonic acid
Cervonic acid (docosahexaenoic acid) - DHA
Elaidic acid
Linoleic acid
Oleic acid
Timnodonic acid (eicosapentaenoic acid)
71
New cards
1 glycerol + 3 Fatty Acid
Structure of triglycerides
72
New cards
Storage lipids
Function of triglycerides
73
New cards
1 glycerol + 2 FA + 1 phosphate with alcohol as head group
Structure of glycerophospholipids / phospholipids
74
New cards
Membrane lipids
Function of glycerophospholipids / phospholipids
75
New cards
**None**
Head of Phosphatidic Acid
76
New cards
**Choline**
Head of Phosphatidylcholine (PC)
77
New cards
**Serine**
Head of Phosphatidylserine (PS)
78
New cards
**Ethanolamine**
Head of Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)
79
New cards
**Inositol**
Head of Phosphatidylinositol (PI)
80
New cards
**Sphingosine + 1 FA + monosaccharide / oligosaccharide**
Structure of sphingolipids
81
New cards
**Sphingosine + 1 FA + phosphate + alcohol**
Structure of glycosphingolipids
82
New cards
**Saponification**
A reaction of fatty acids where a triglyceride and a strong base is mixed together to form a fatty acid salt or soap
83
New cards
**Rancidification**
A reaction of fatty acids where there is a complete or incomplete autooxidation of a fatty acid.
84
New cards
**Hydrogenation**
A reaction of fatty acids used to prolong the shelf life of unsaturated fatty acids,
85
New cards
**None**
Head of ceramide
86
New cards
**Glu / Gal**
Head of cerebroside
87
New cards
**Oligosaccharide**
Head of globoside
88
New cards
**Polysaccharide (with sialic acid)**
Head of ganglioside
89
New cards
**Phosphate & Choline**
Head of sphingomyelin
90
New cards
**Waxes**
Pliable, water-repelling substances used for repelling water and protecting surfaces
91
New cards
**I and IV**
Which are unsaturated fatty acids?
I. Arachidonic acid
II. Caproic acid
III. Palmitic acid
IV. Linoleic acid
\
A. I and II
B. II and III
C. I and IV
D. IV only
I. Arachidonic acid
II. Caproic acid
III. Palmitic acid
IV. Linoleic acid
\
A. I and II
B. II and III
C. I and IV
D. IV only
92
New cards
**None of the choices**
In which of the following properties are unsaturated fatty acids greater than saturated fatty acids?
A. Melting point
B. Van der Waals forces
C. Compactness
D. None of the choices
A. Melting point
B. Van der Waals forces
C. Compactness
D. None of the choices
93
New cards
**Vitamin A**
Deficiency of this fat-soluble vitamin may lead to night blindness and xerophthalmia
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin D
C. Vitamin E
D. Vitamin K
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin D
C. Vitamin E
D. Vitamin K
94
New cards
**HDL**
Which of the following has the capability to reduce plasma cholesterol?
A. VLDL
B. chylomicrons
C. LDL
D. HDL
A. VLDL
B. chylomicrons
C. LDL
D. HDL
95
New cards
**Acrolein Test**
Which of the following tests is used to test for glycerol?
a. Acrolein Test
b. Ammonium Molydate Test
c. Lieberman Burchard Test
d. Osmic acid Test
e. Salkowski Test
a. Acrolein Test
b. Ammonium Molydate Test
c. Lieberman Burchard Test
d. Osmic acid Test
e. Salkowski Test
96
New cards
**Heating the sample**
Reagent used in Acrolein Test
97
New cards
**Acid/burnt odor of acrolein (propenal)**
Visible positive result of Acrolein Test
98
New cards
**Ammonium Molydate Test**
Which of the following tests is used to test for phosphate?
a. Acrolein Test
b. Ammonium Molydate Test
c. Lieberman Burchard Test
d. Osmic acid Test
e. Salkowski Test
a. Acrolein Test
b. Ammonium Molydate Test
c. Lieberman Burchard Test
d. Osmic acid Test
e. Salkowski Test
99
New cards
**Ammonium molybdate**
Reagent used in Ammonium Molybdate Test
100
New cards
**Yellow ppt**
Visible positive result of Ammonium Molybdate Test