Early embryology and brachial arch development
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
morula
After fertilization, there is the proliferative phase, in which the zygote initially undergoes a series of rapid divisions that lead to the formation of a ball of cells called __.
Morula
A solid ball of cells that makes up an embryo; in humans, this stage occurs within four days of fertilization.
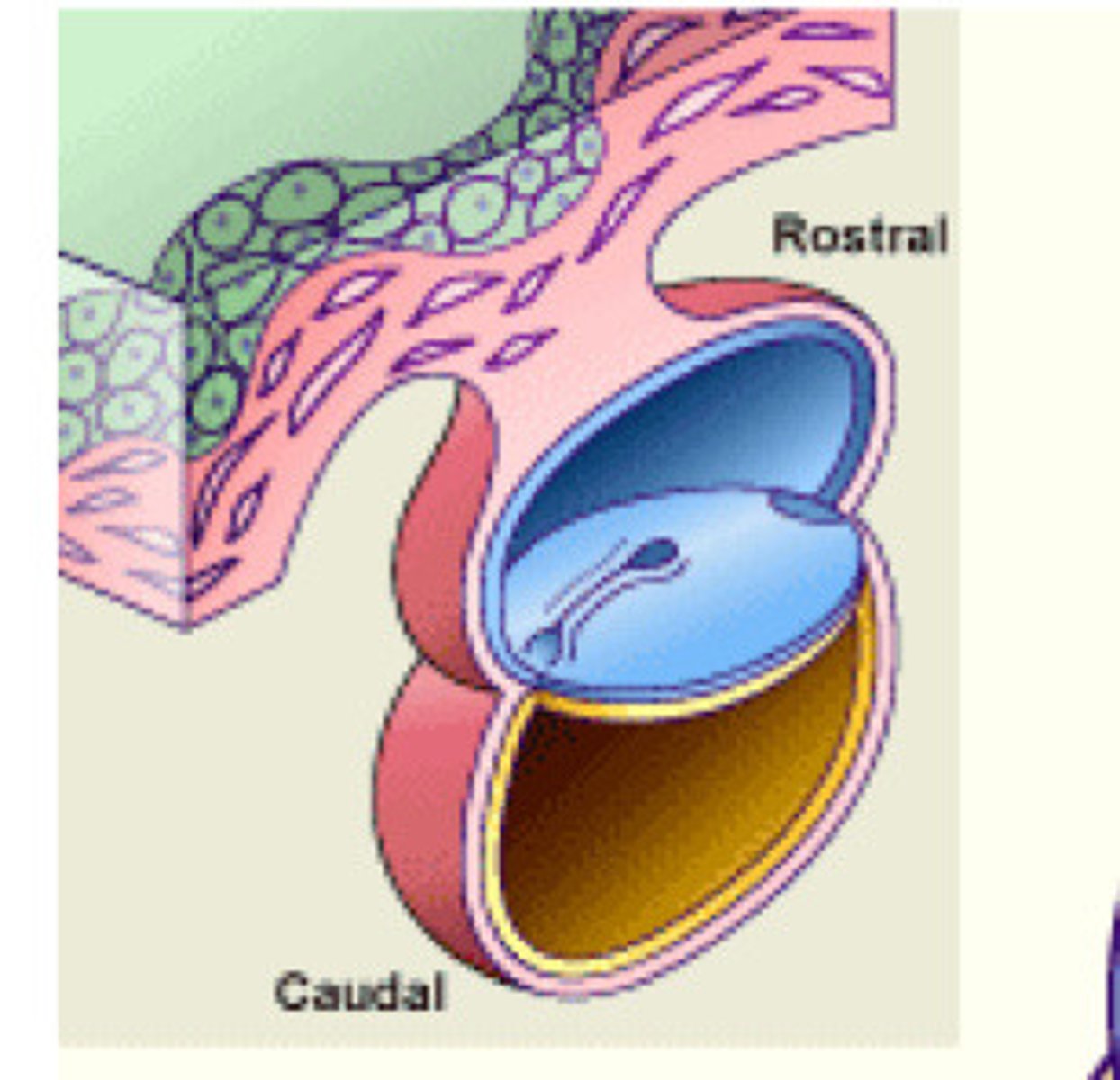
Trophoblast
outer cells of the blastocyst that secrete enzymes that allow implantation
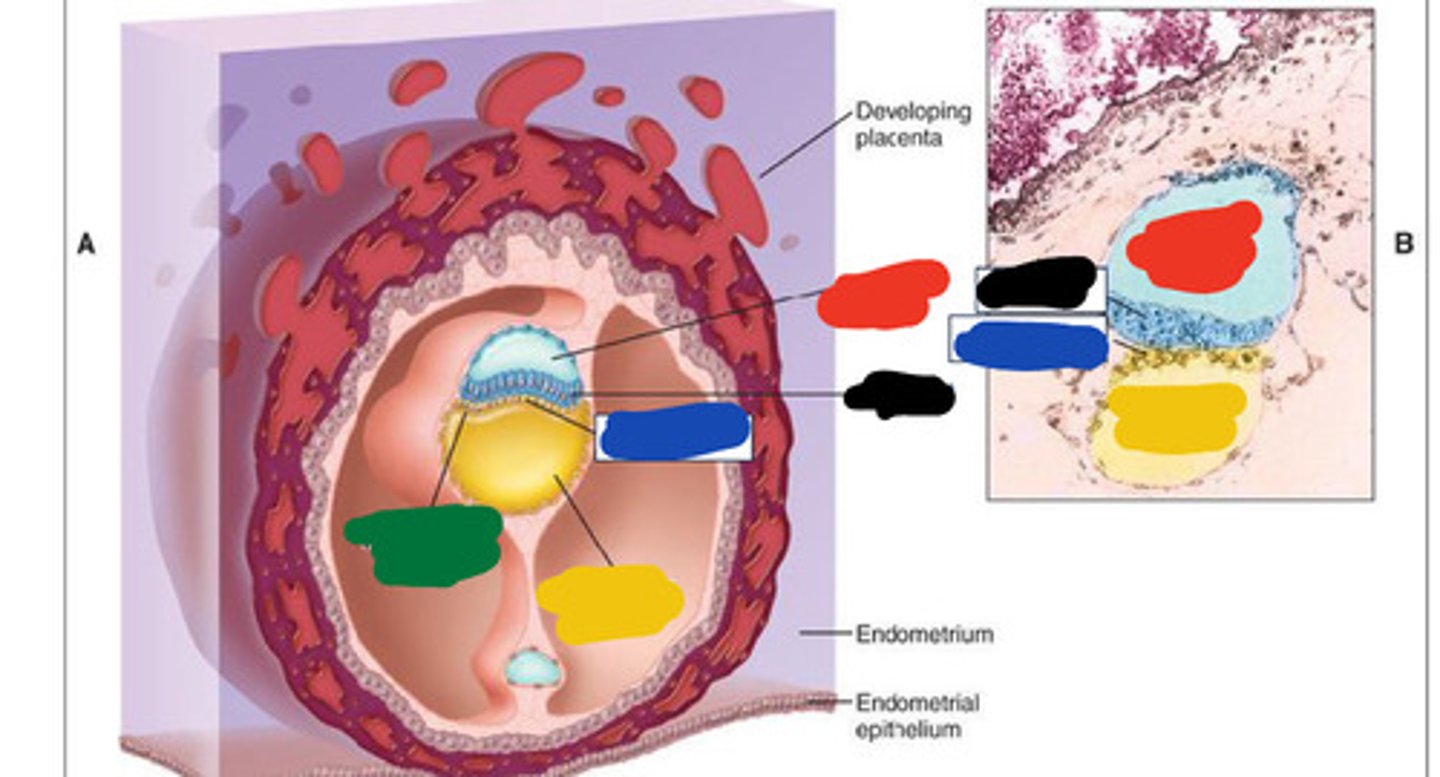
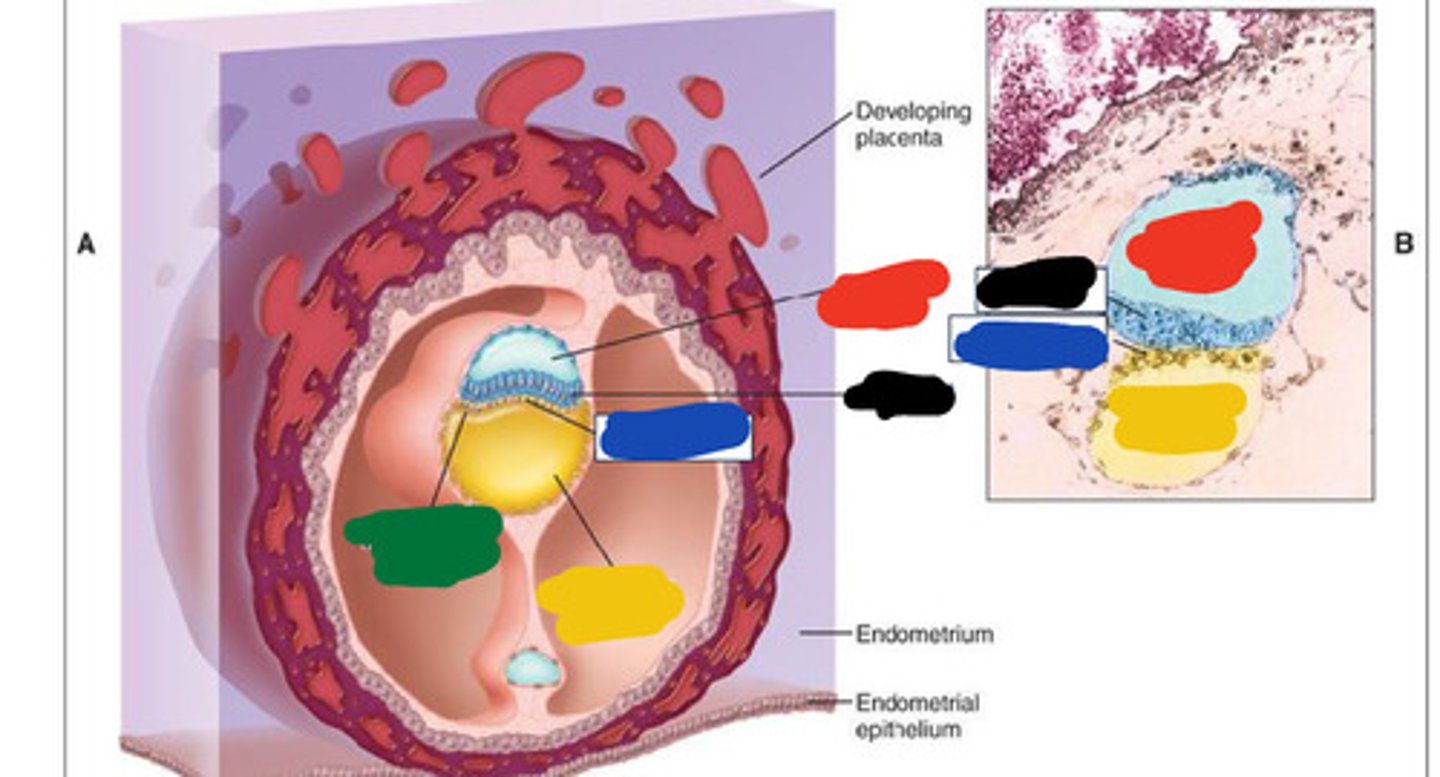
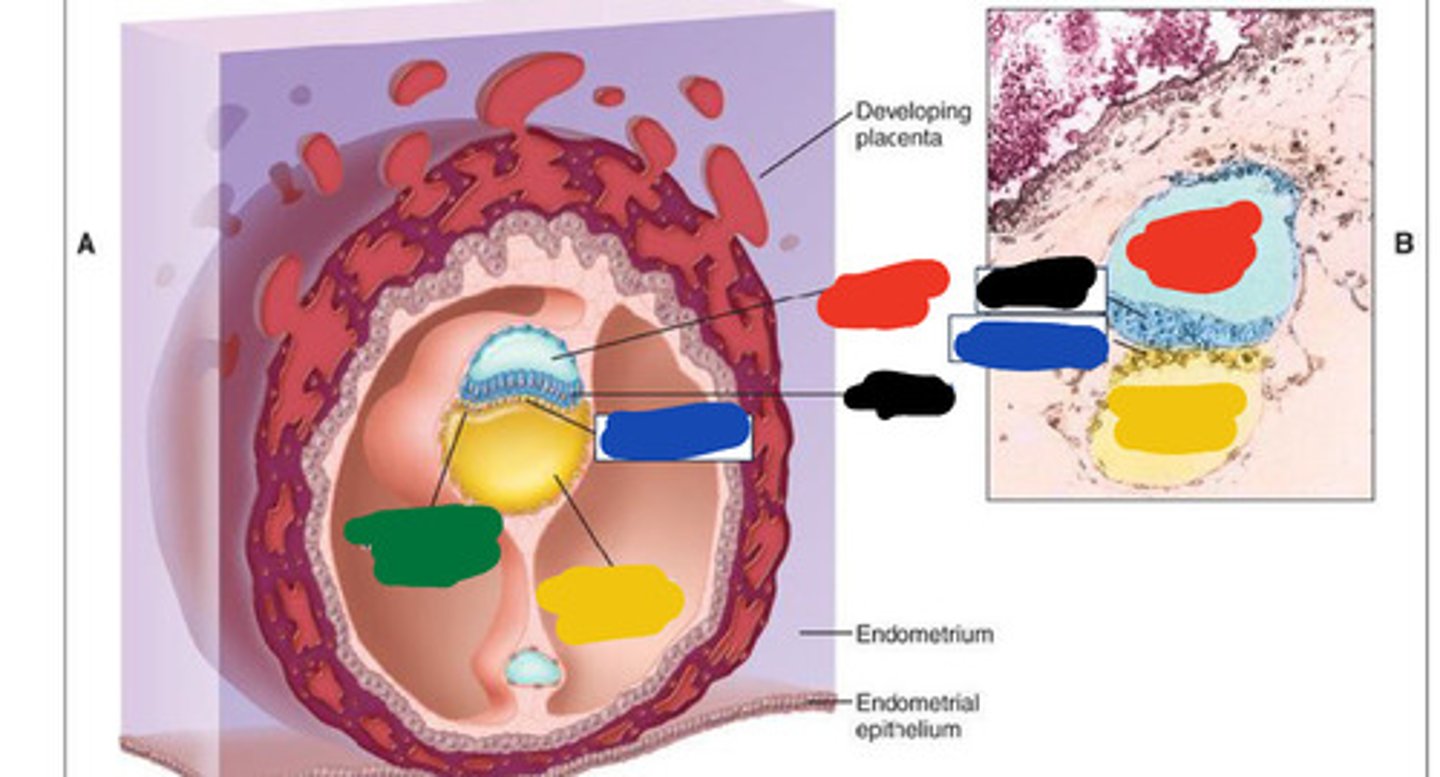
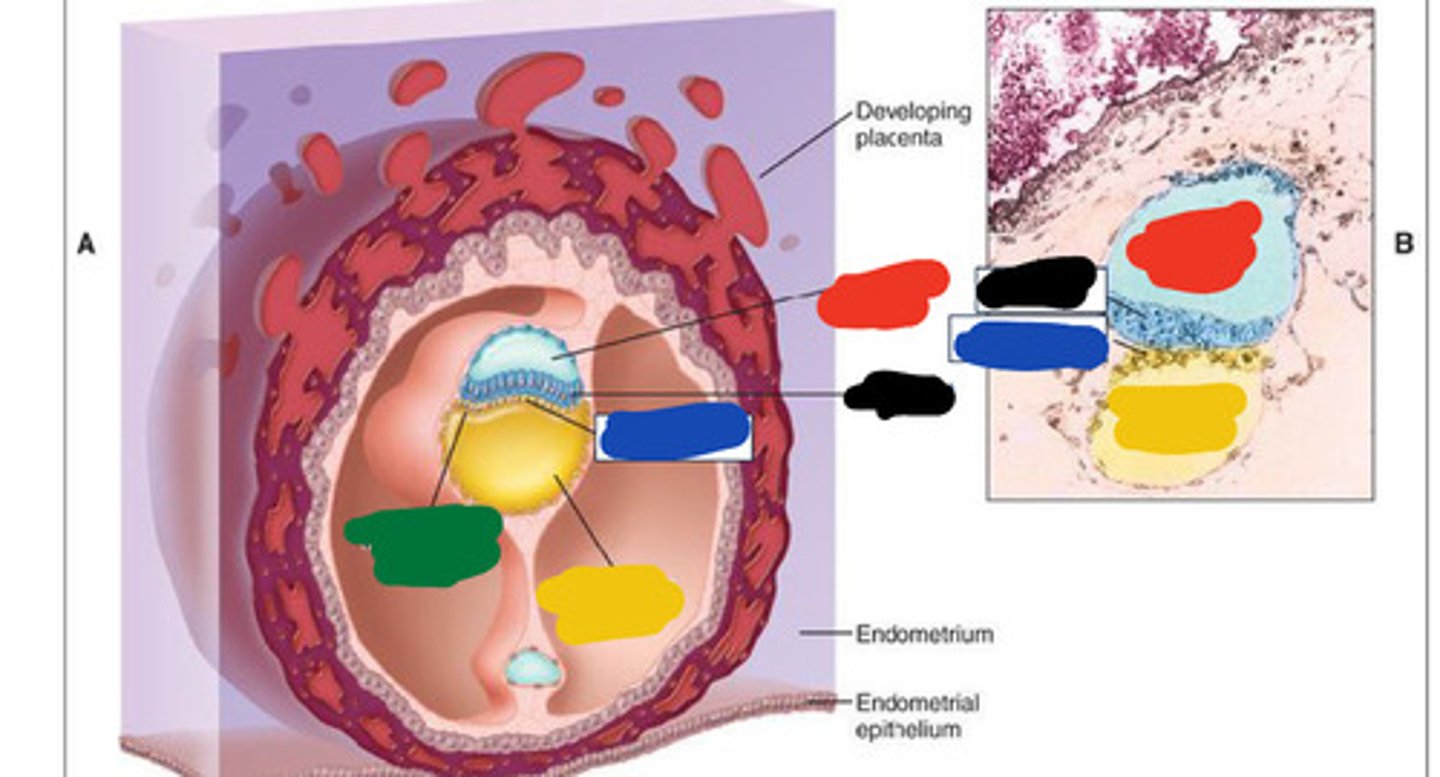
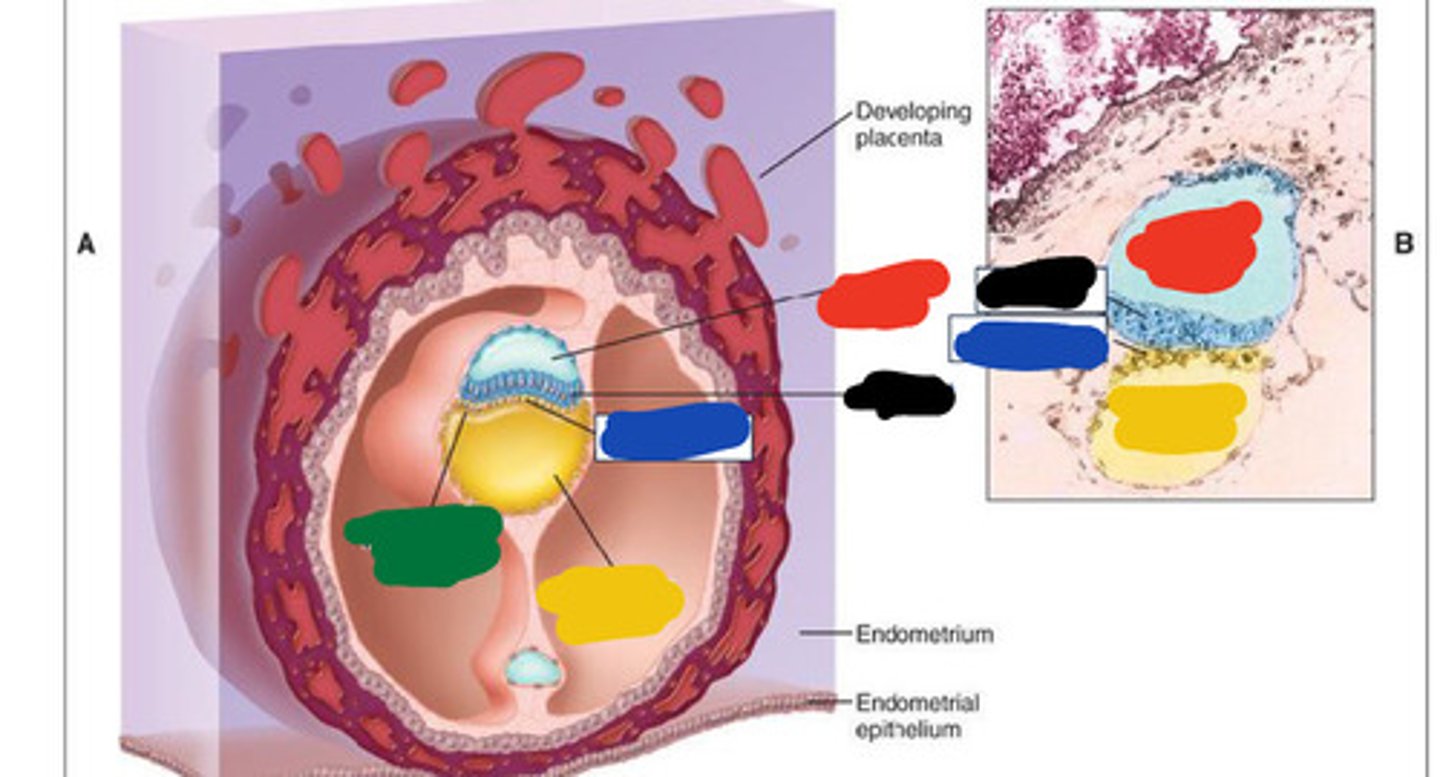
Black
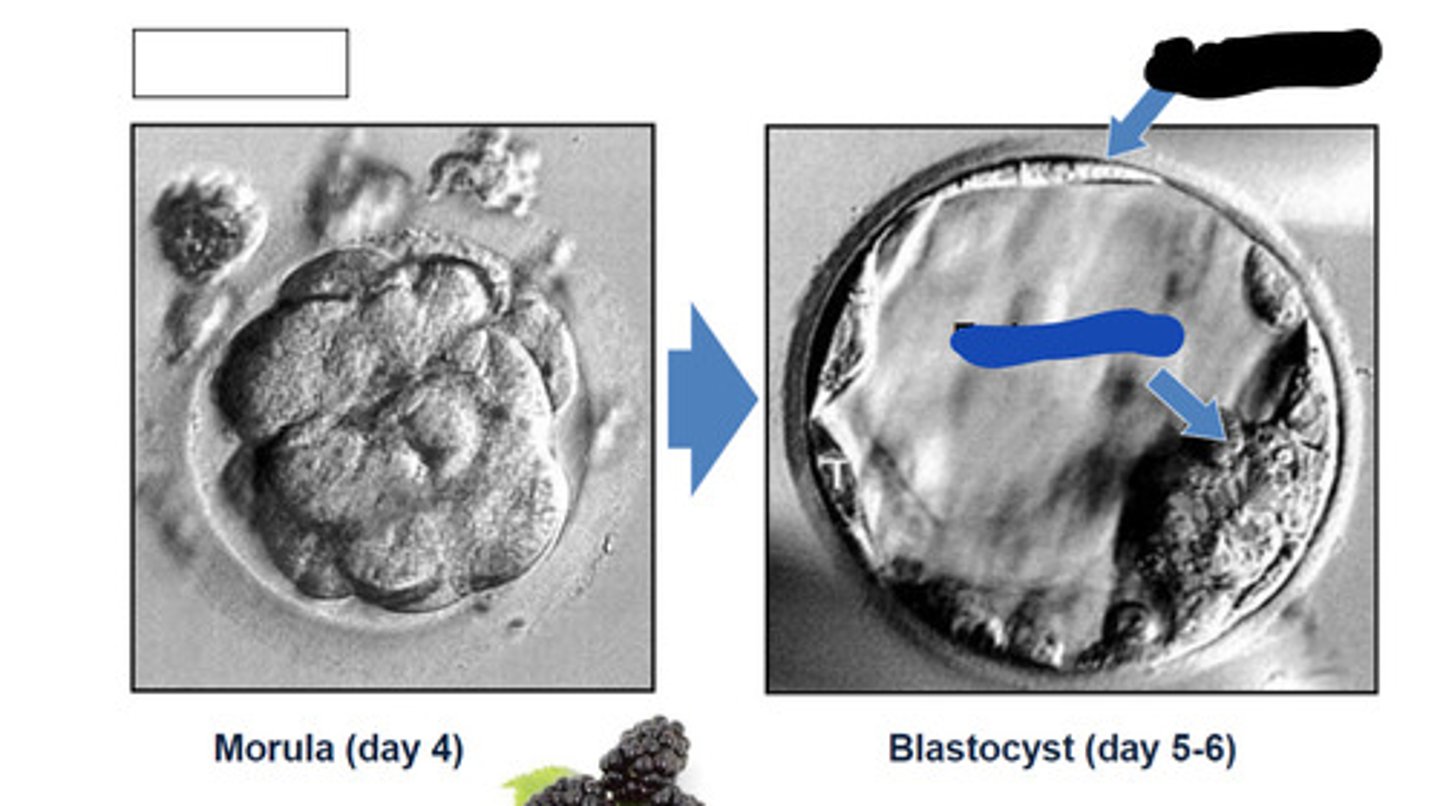
Embryoblast
The inner cell mass of the blastocyst, which is the developing human organism.
Blue
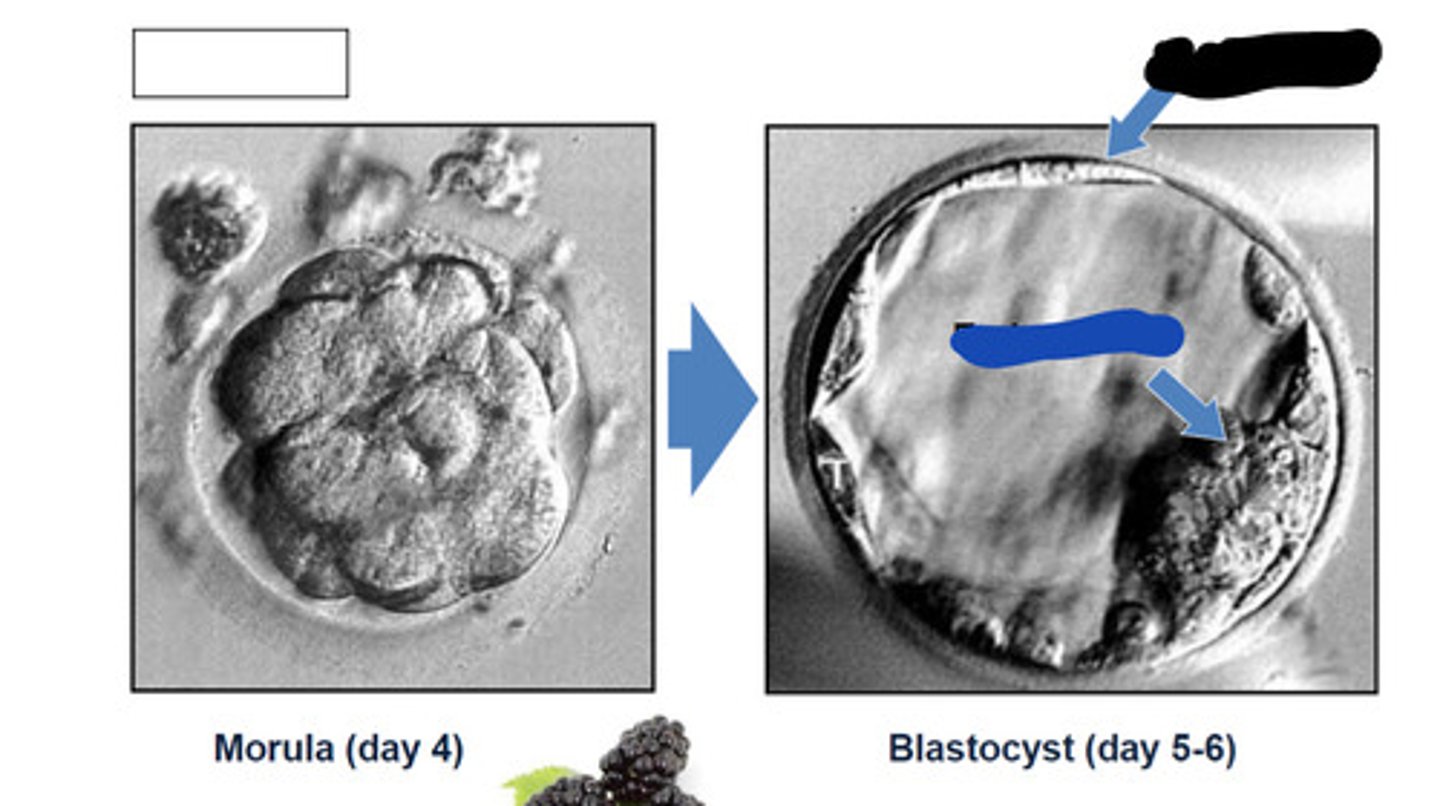
4
What day does morula show
5-6
What day does blastocyst show
Blastocele
fluid filled cavity in blastocyst
Endometrium
inner lining of the uterus
Black
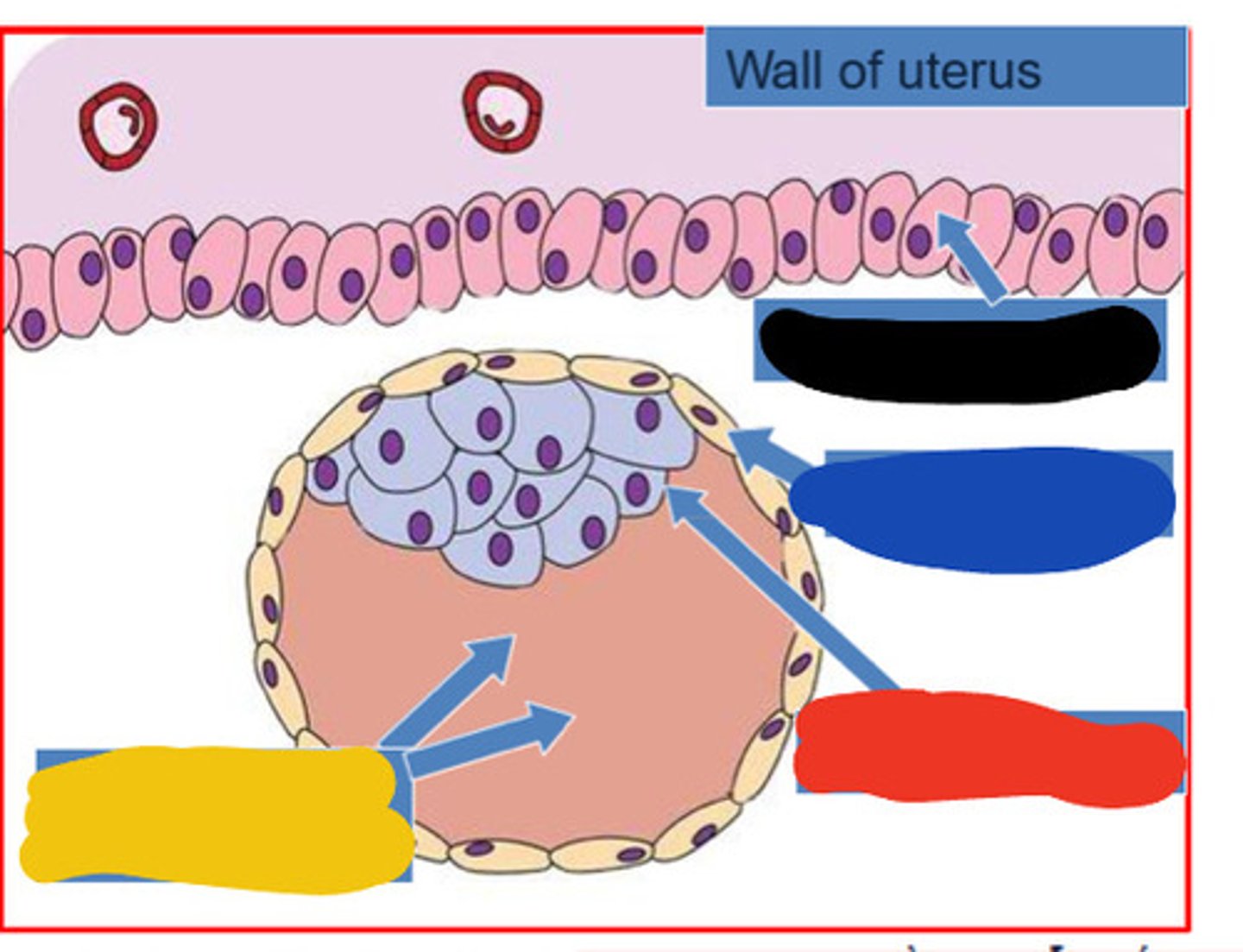
Trophoblast
Blue
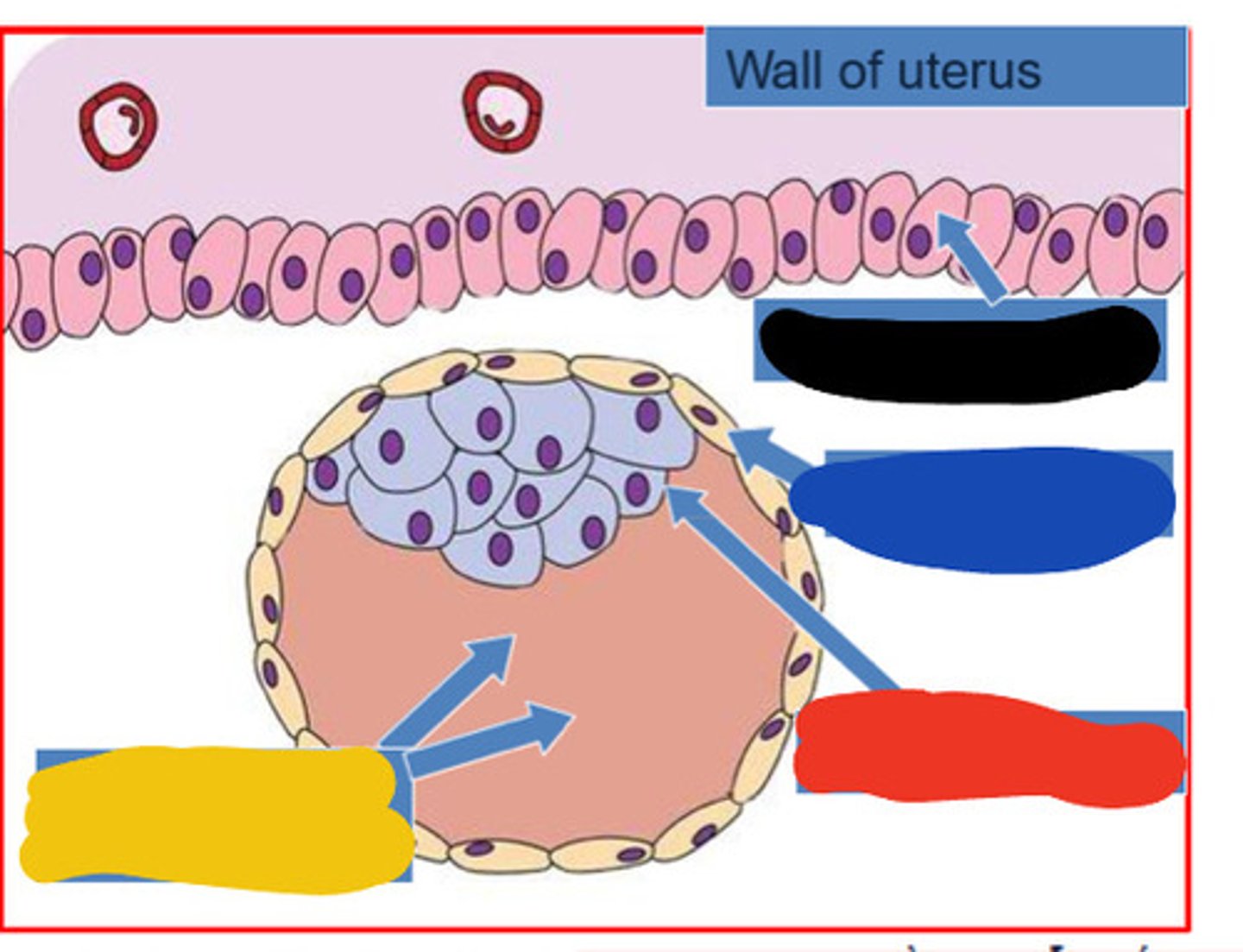
Embryoblast
Red
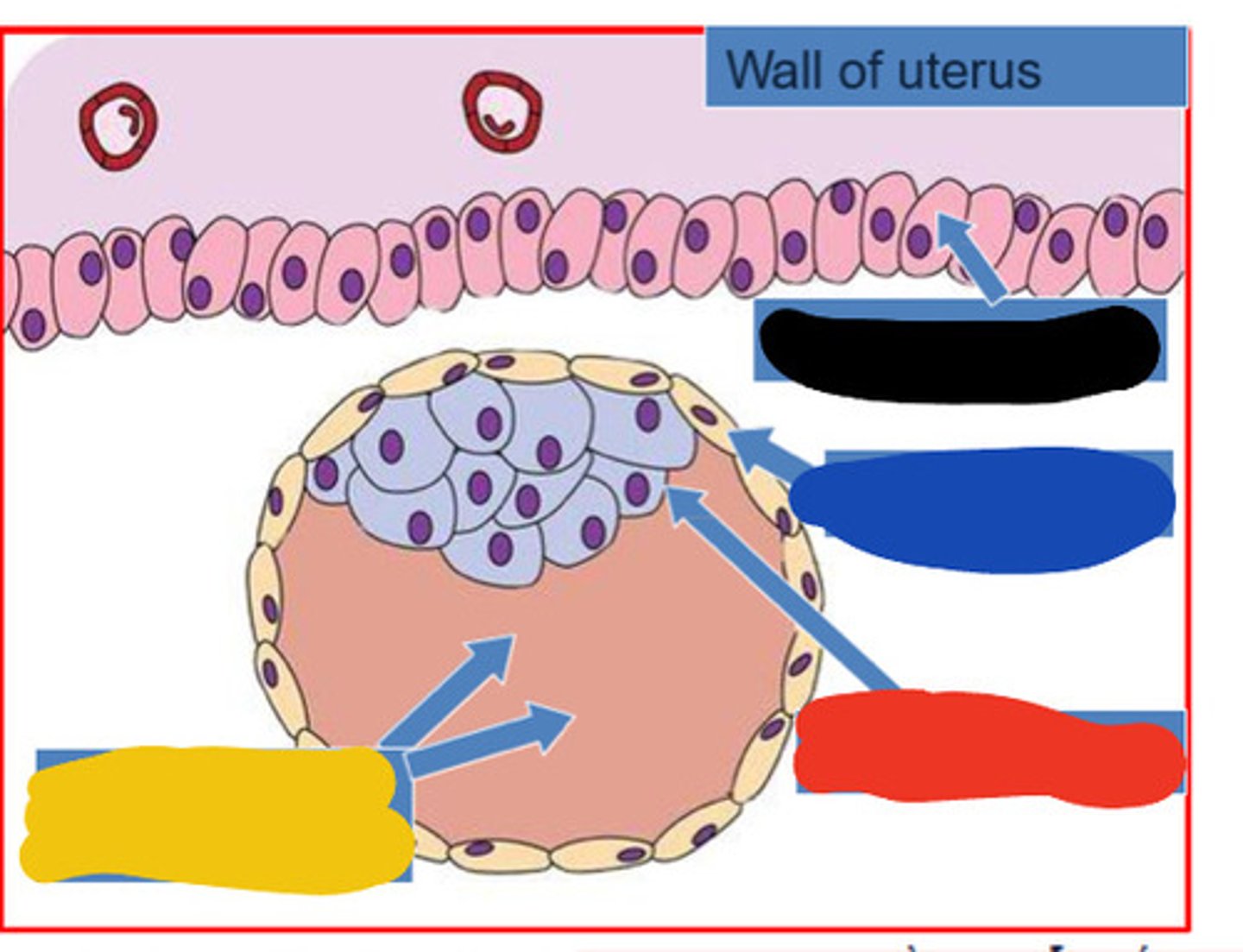
Blastocoele
Yellow
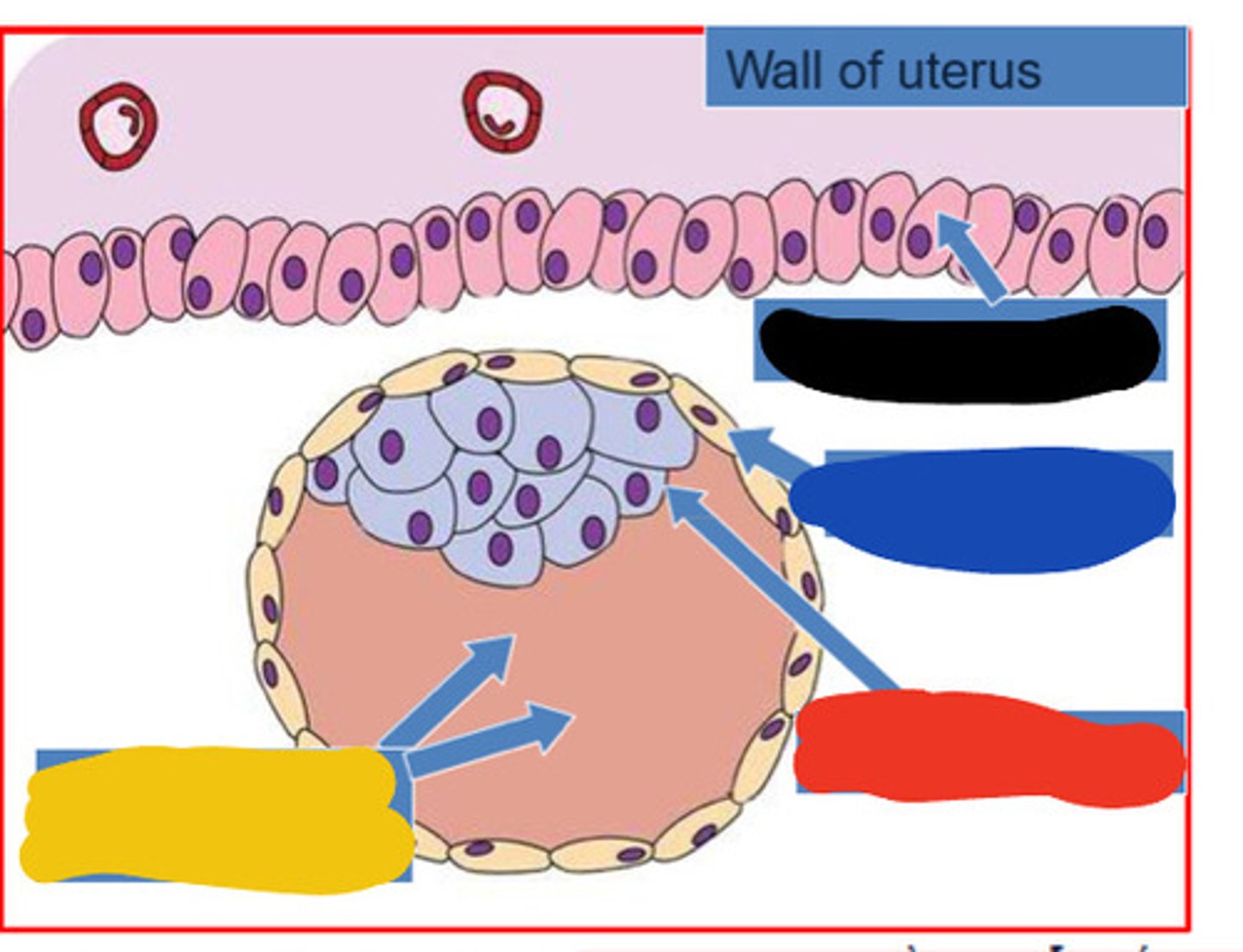
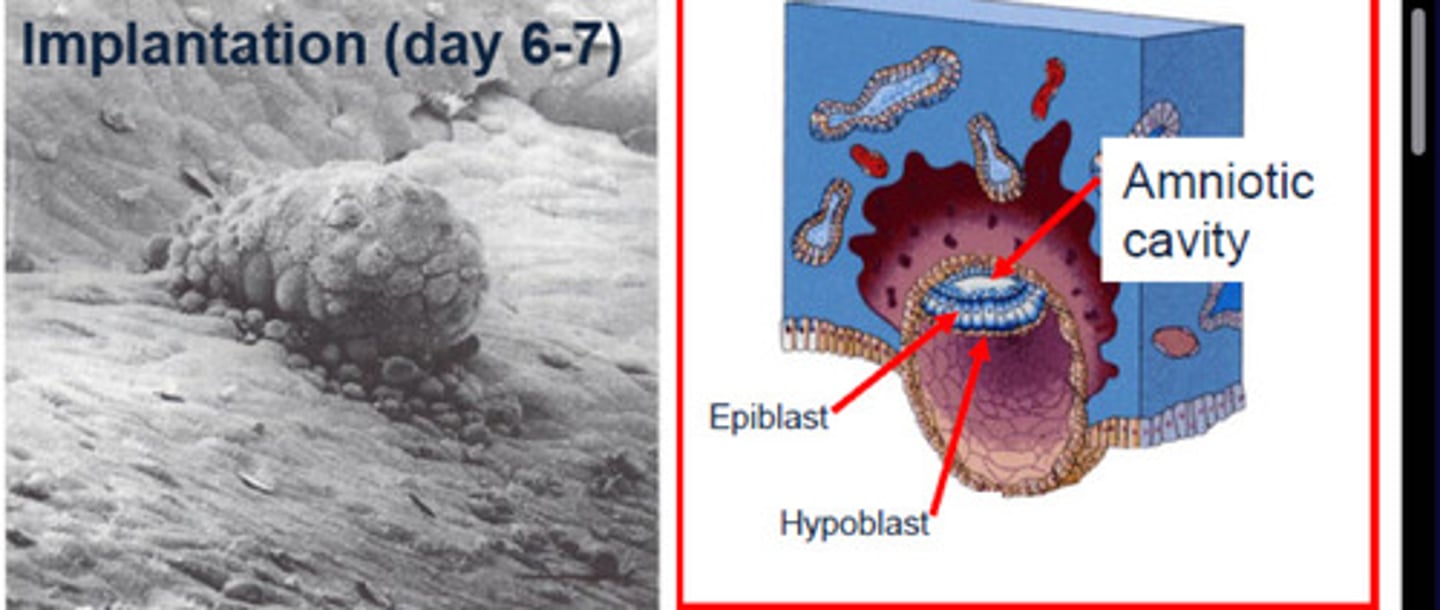
Implantation of blastocyst
6 days after conception
bilaminar disc
two-layered disc (epiblasts and hypoblasts) that forms from the inner cell mass at around day 8-14
Epiblast
the SIMPLE COLUMNAR outermost layer of an embryo before it differentiates into ectoderm and mesoderm.
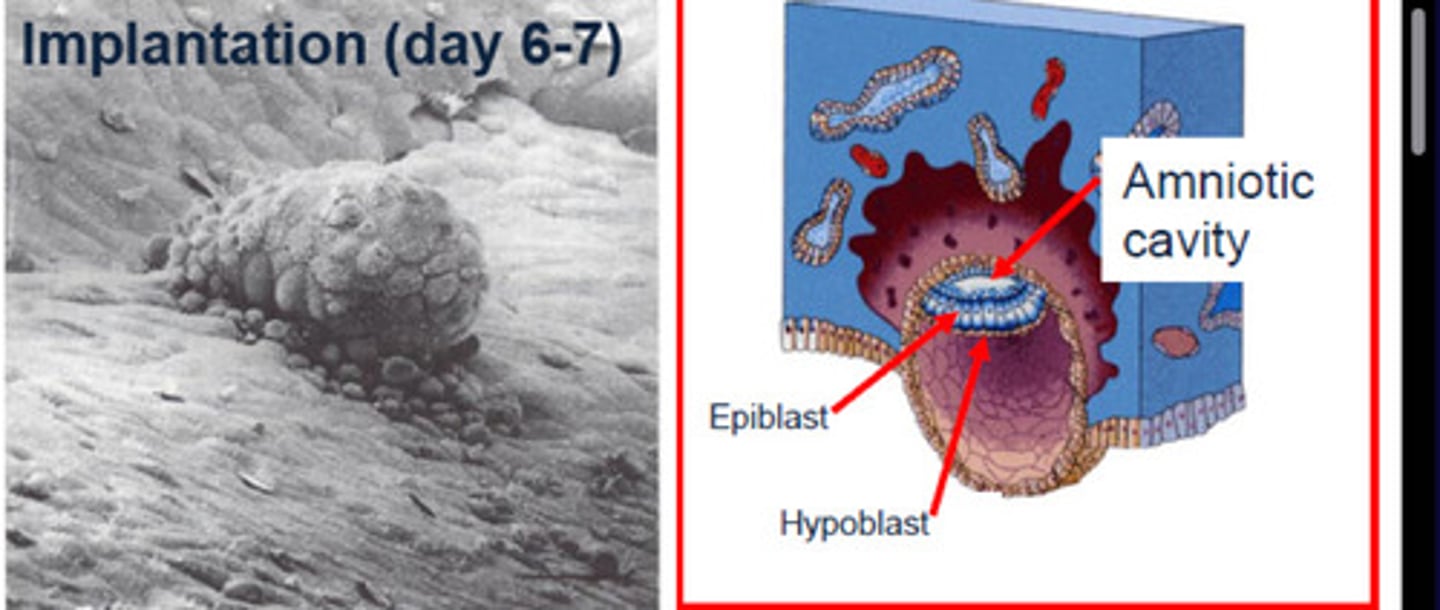
Hypoblast
layer of SIMPLE CUBOIDAL cells facing the blastocyst cavity
Prochordal plate
area where the epiblast and hypoblast fuse (axis of the embryo); future site of the mouth (1-2nd weeks)
1-2 weeks
How many weeks does the prochordal plate forms
Epiblast
Black
Hypoblast
Blue
Amniotic cavity
Red
Secondary yolk sac
Yellow
Prochordal plate
Green
primary yolk sac
Another name for blastocyst
Amniotic cavity
Fluid-filled cavity facing epiblast layer
Secondary yolk sac
Fluid filled cavity surrounded by Hypoblast
Gastrulation
bilaminar embryonic disc converted to trilaminar disc
Trilaminar disc
First to form, contains ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm
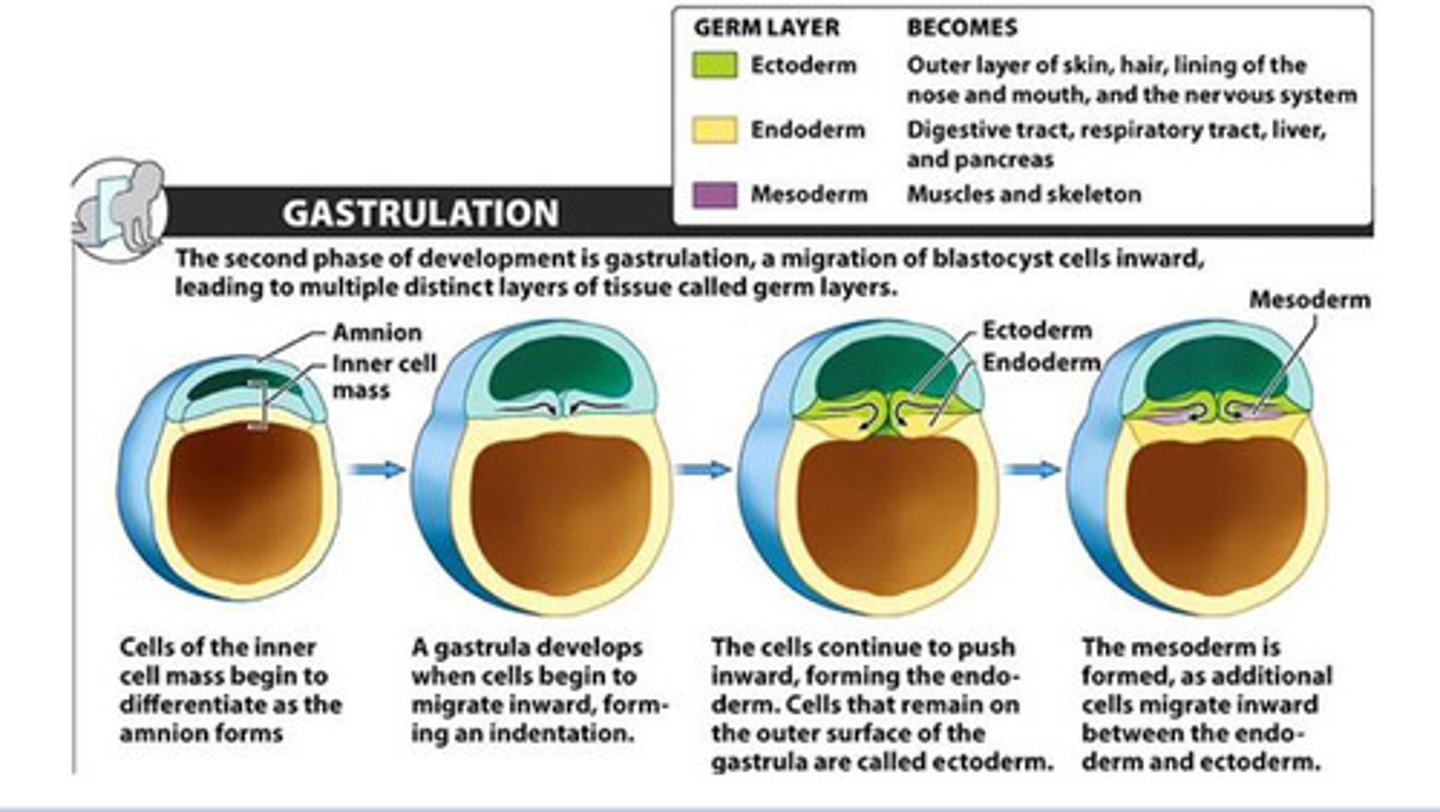
Ectoderm
outermost germ layer; produces sense organs, nerves, and outer layer of skin
Endoderm
Digestive tract, respiratory tract, liver, pancreas,
Mesoderm
Muscles and skeleton
Amnion
Cells of inner cell mass begin to differentiate as __ forms
Gastrula
A __ develops when cells begin to migrate inward forming indentation and push forming the endoderm. Cells on the outside are called ectoderm
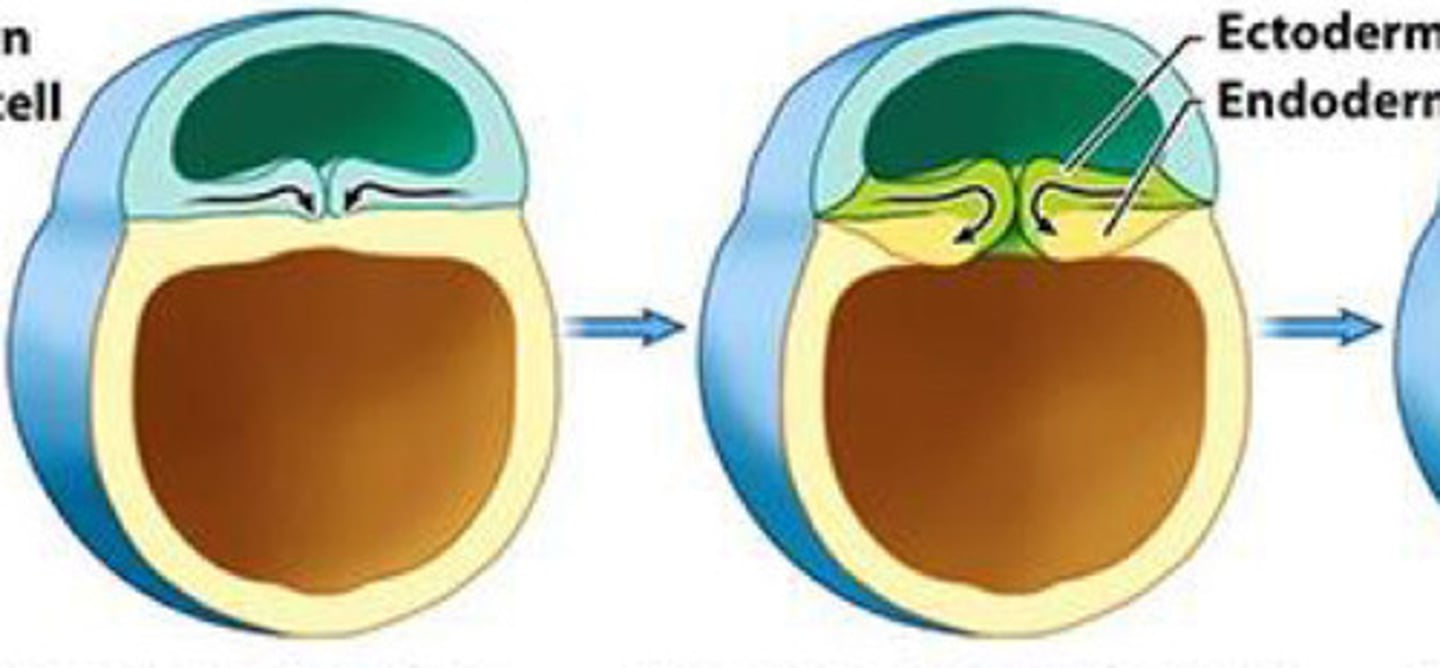
endoderm; ectoderm
A gastrula develops when cells begin to migrate inward forming indentation and push forming the __. Cells on the outside are called __
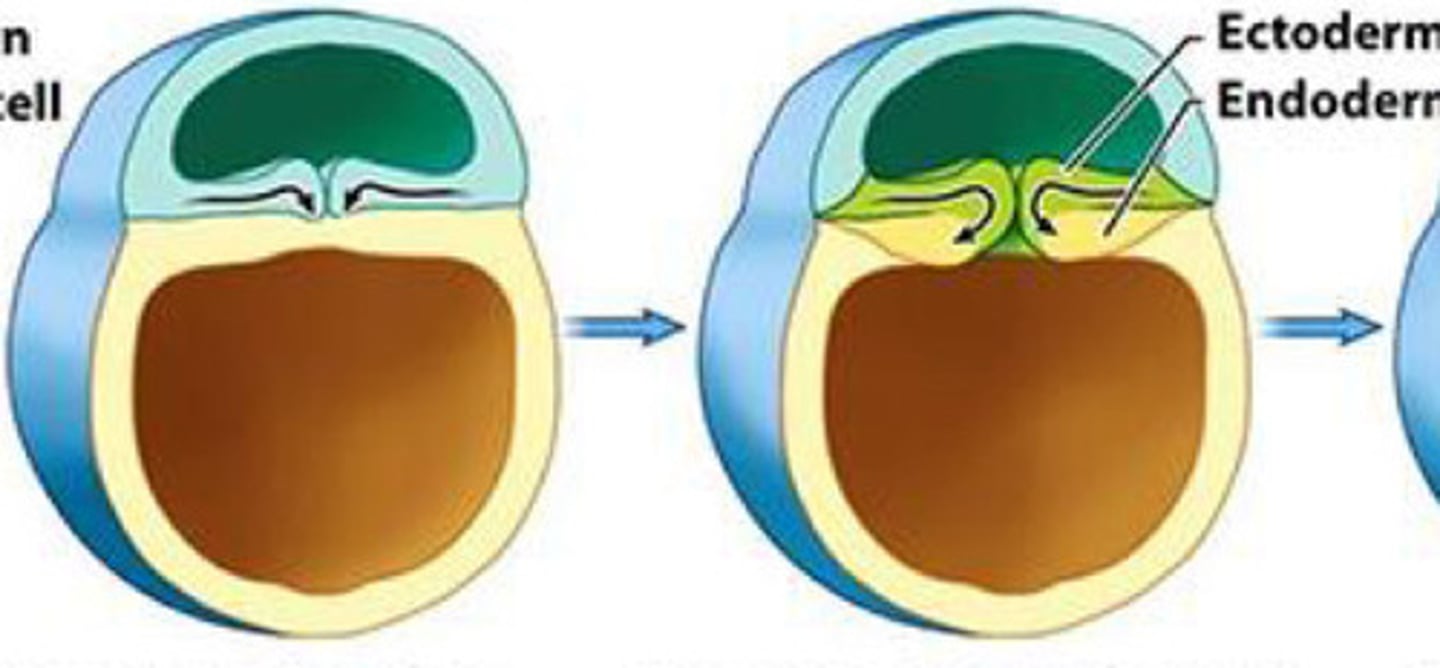
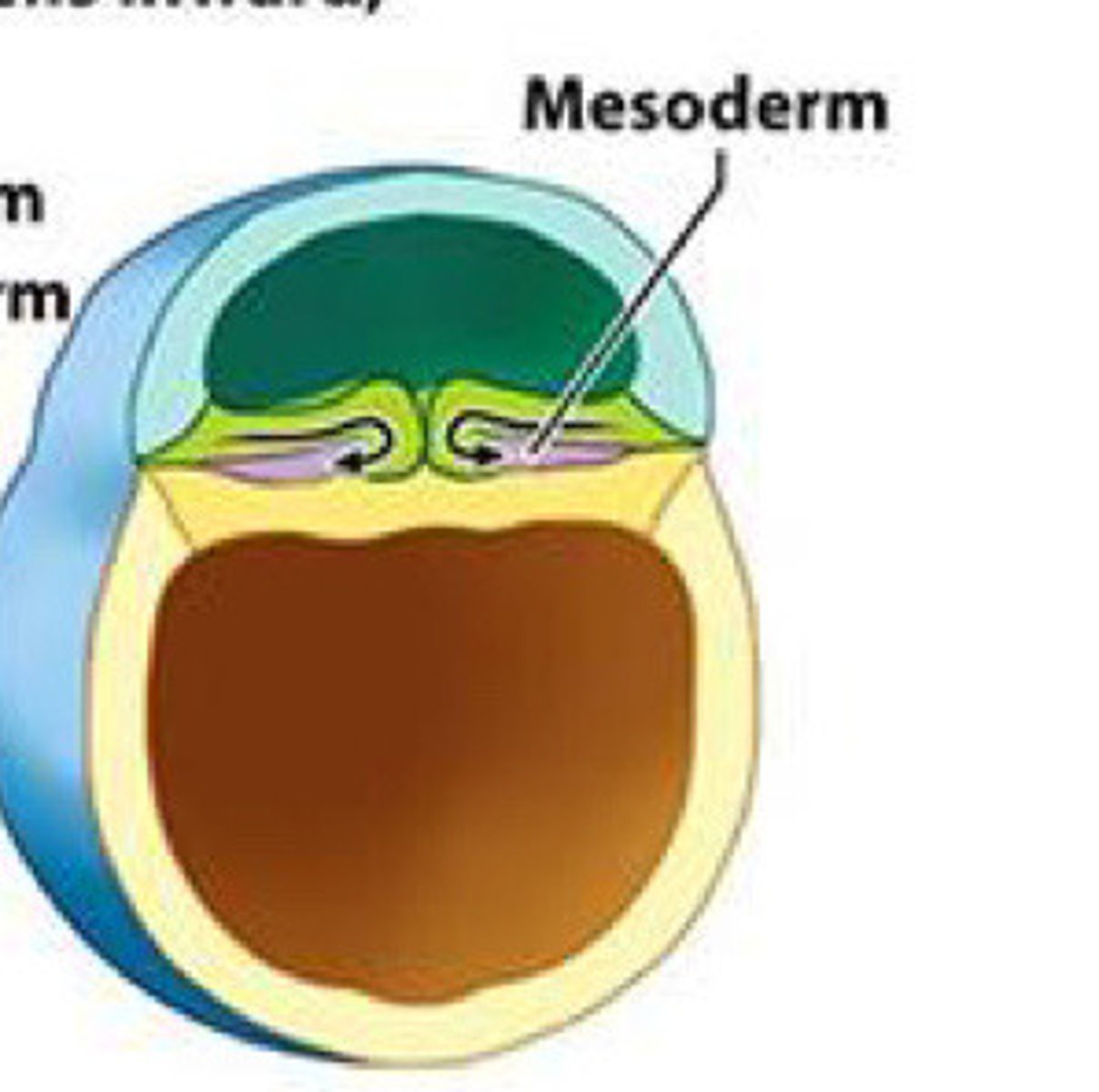
Mesoderm
The __ is formed as additional cells migrate inward between endo and ectoderm
Epiblast; Hypoblast
The three germ layers originate from the __ and not the __
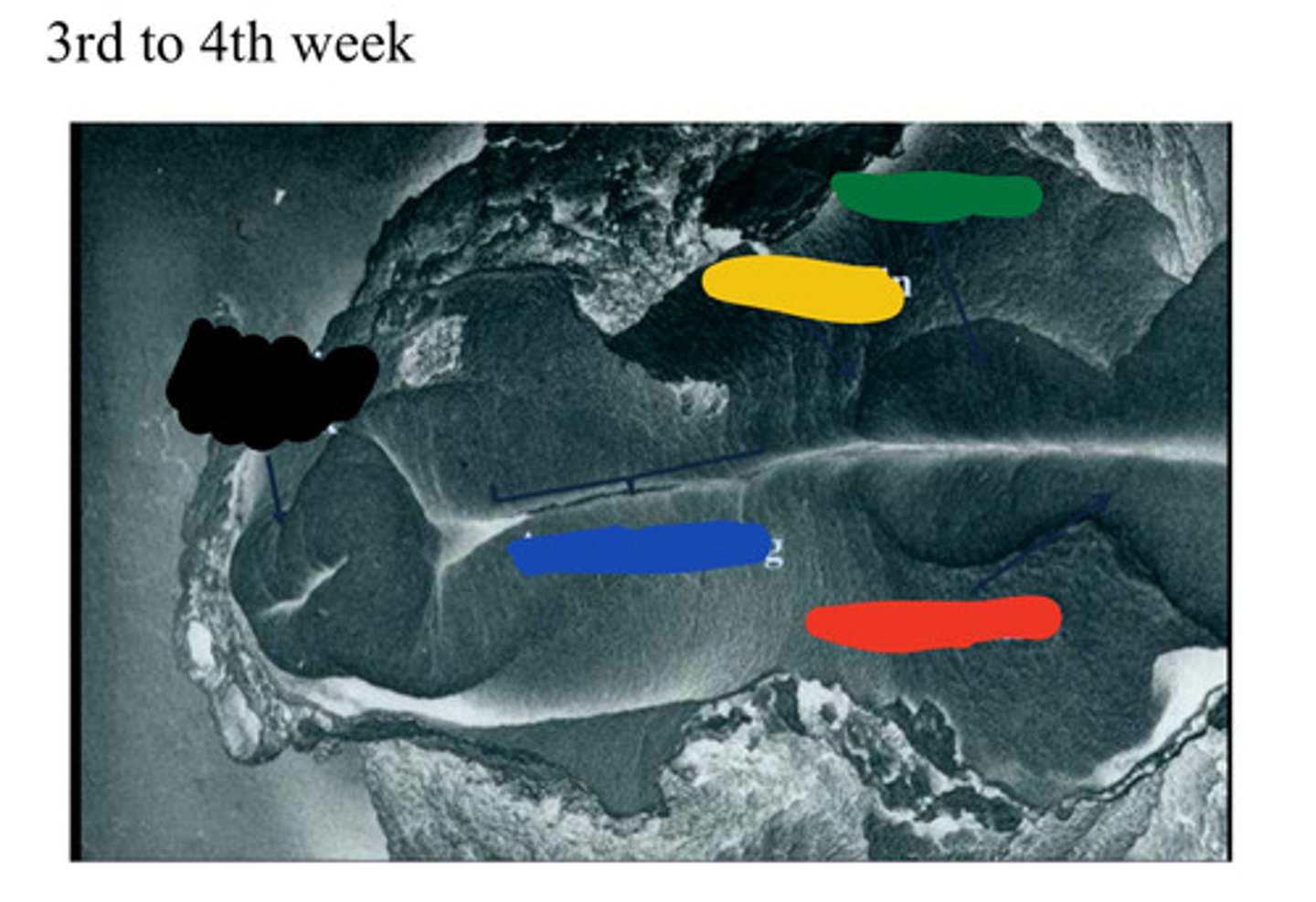
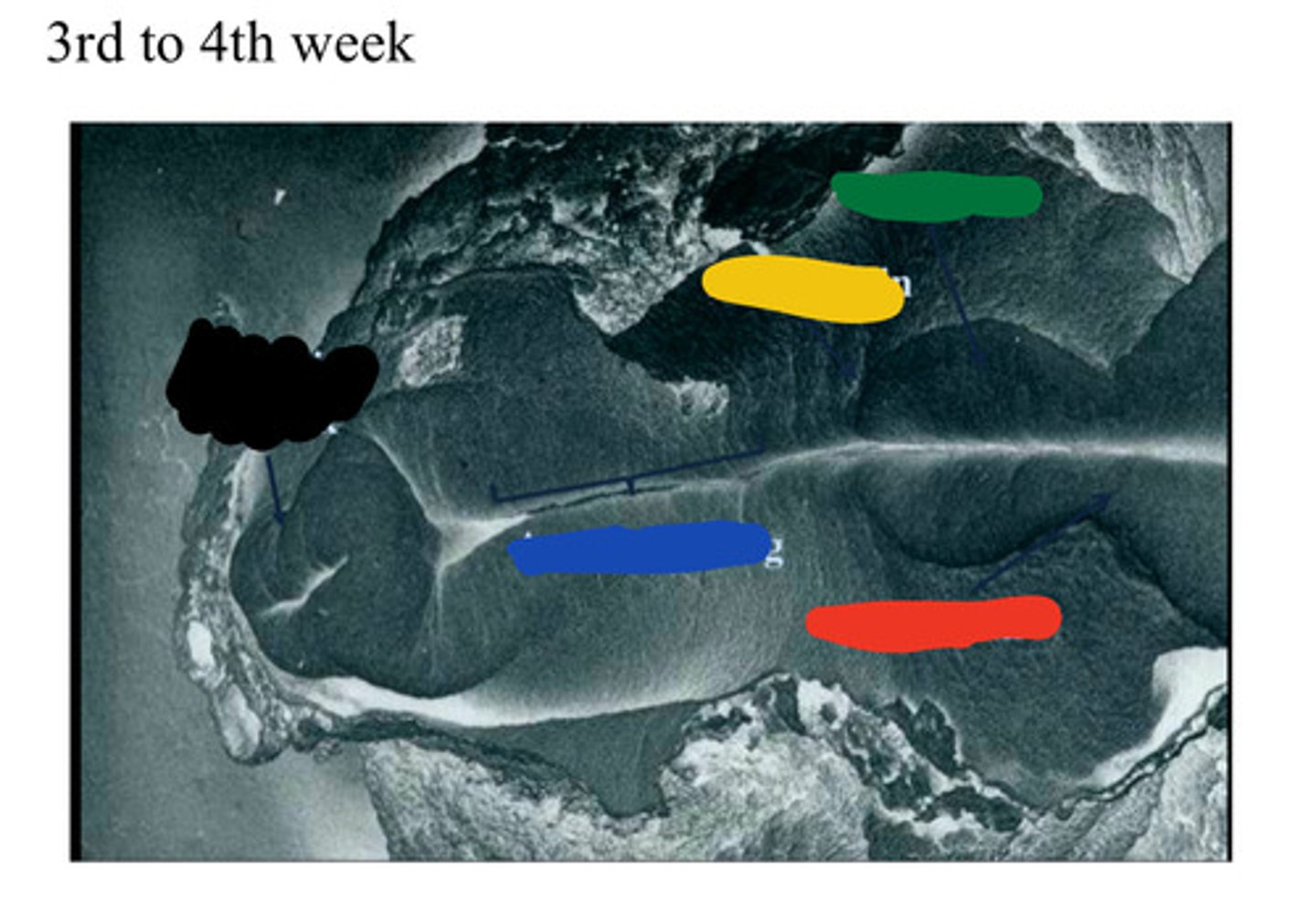
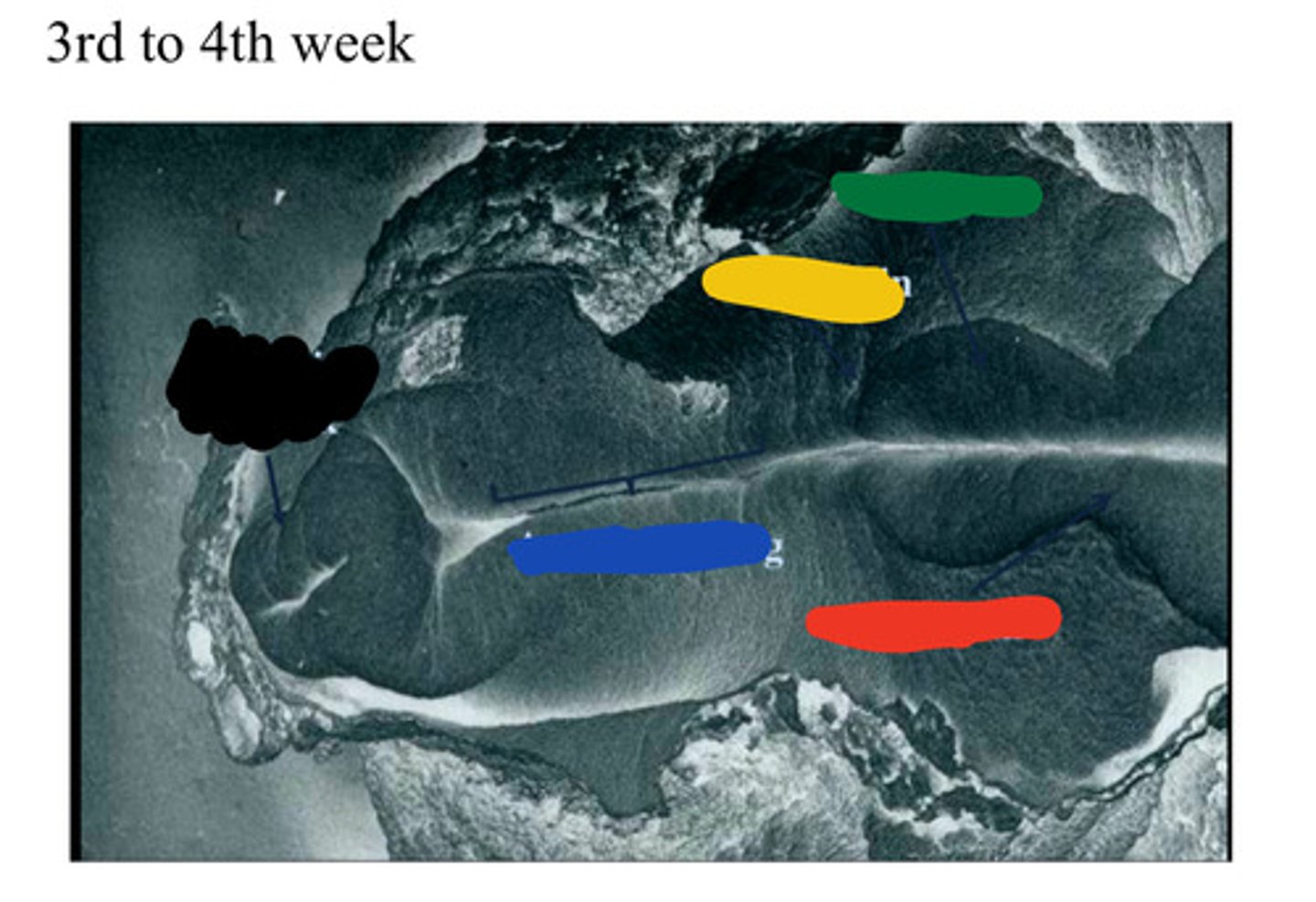
Primitive streak
A groove on the surface of an early avian embryo along the future long axis of the body.
Primitive streak
__ (1) develops along the midline forming a narrow groove.
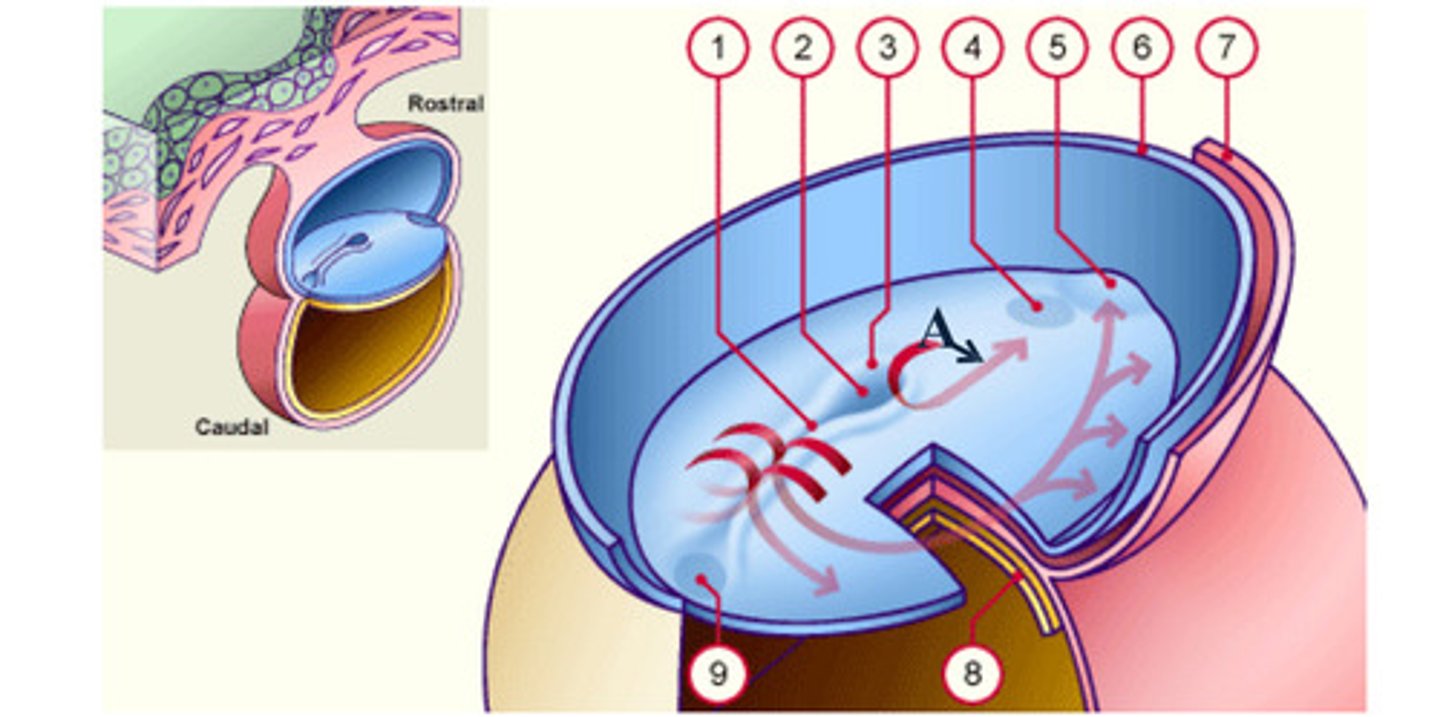
primitive node
The rostral end of the streak finishes in a small depression called __ (3) or pit (2).
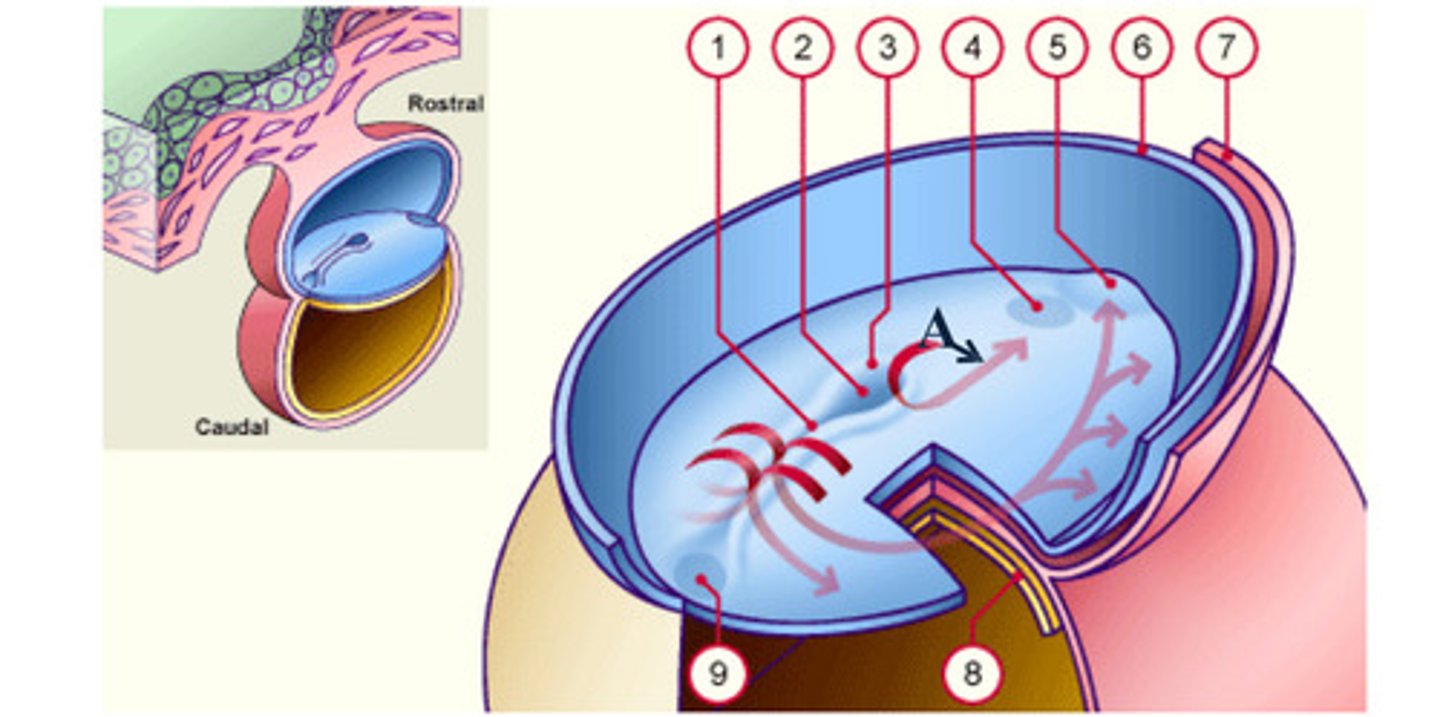
pit
The rostral end of the streak finishes in a small depression called primitive node (3) or __ (2).
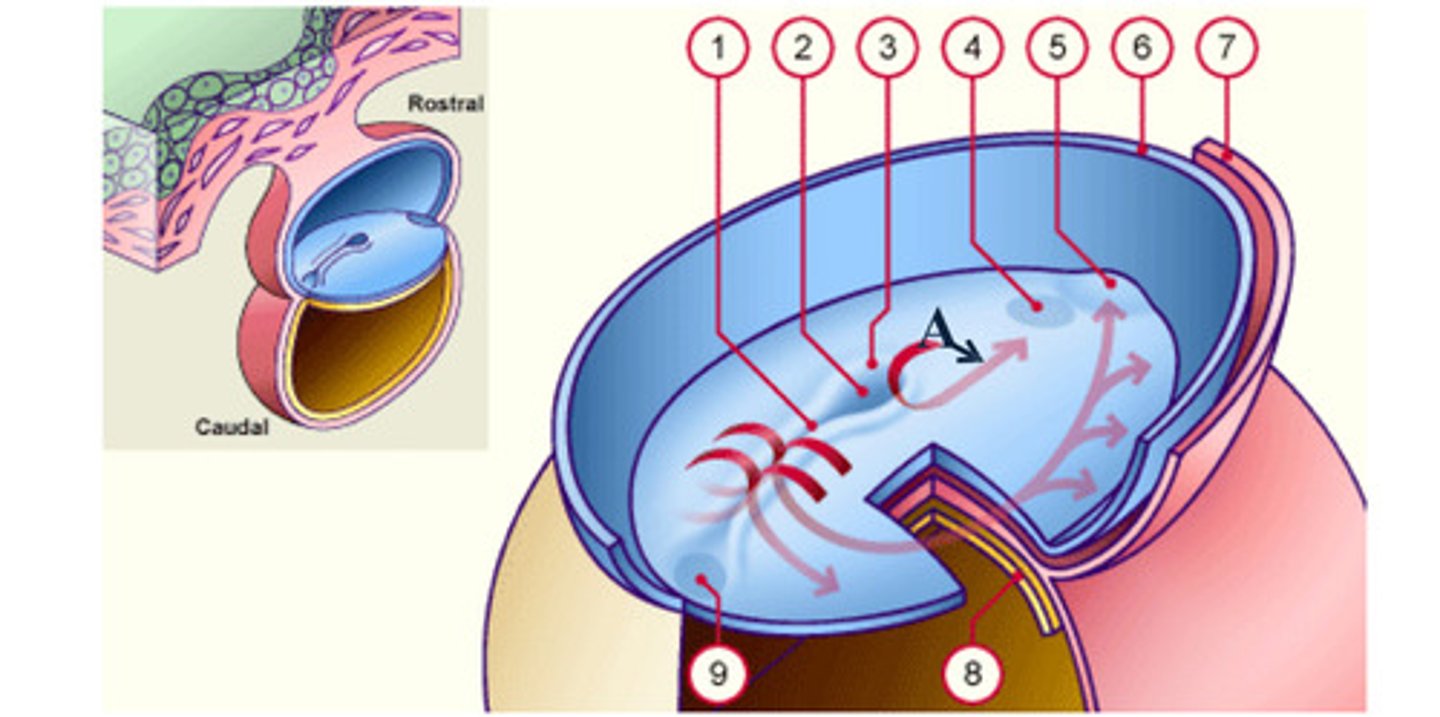
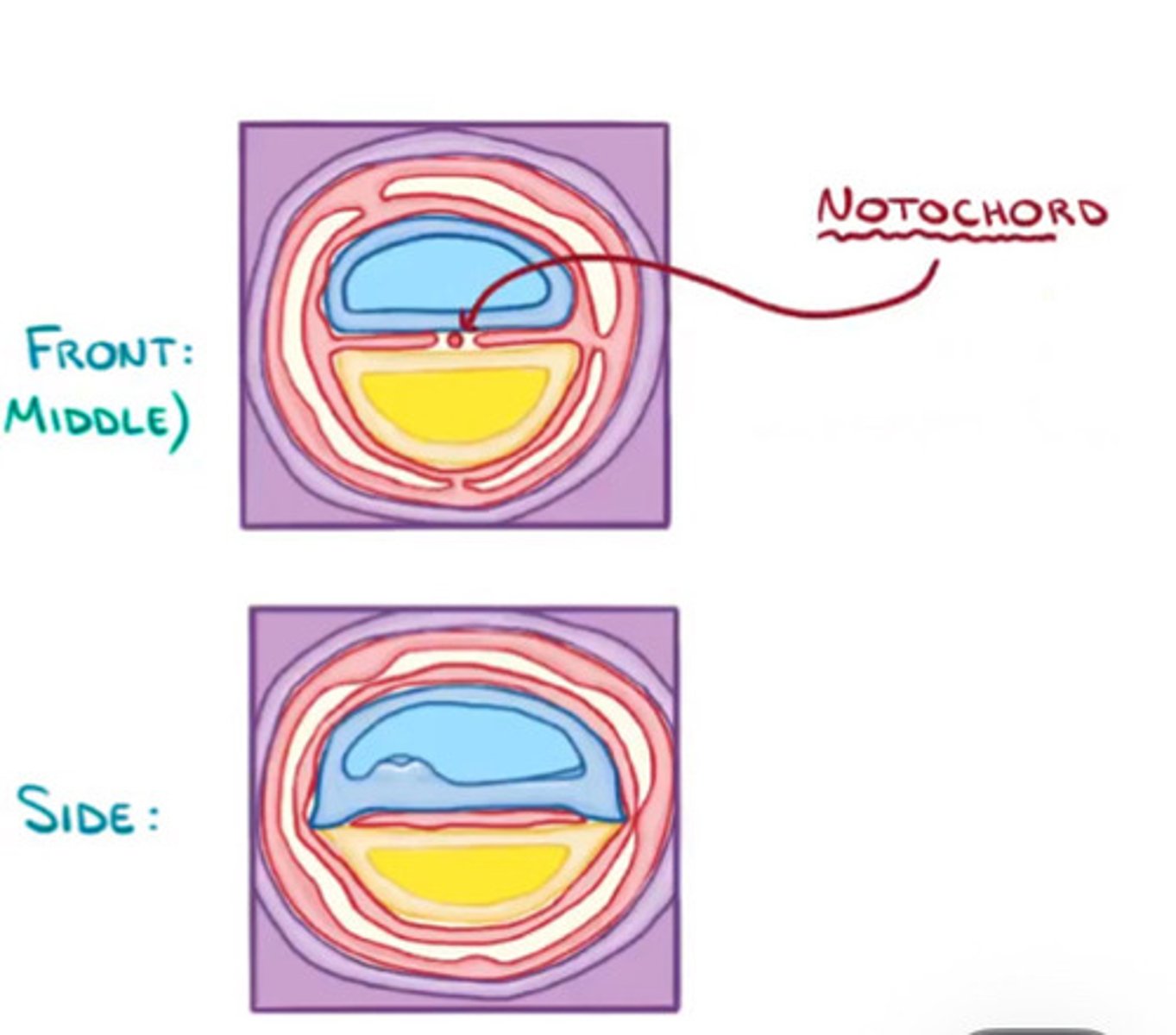
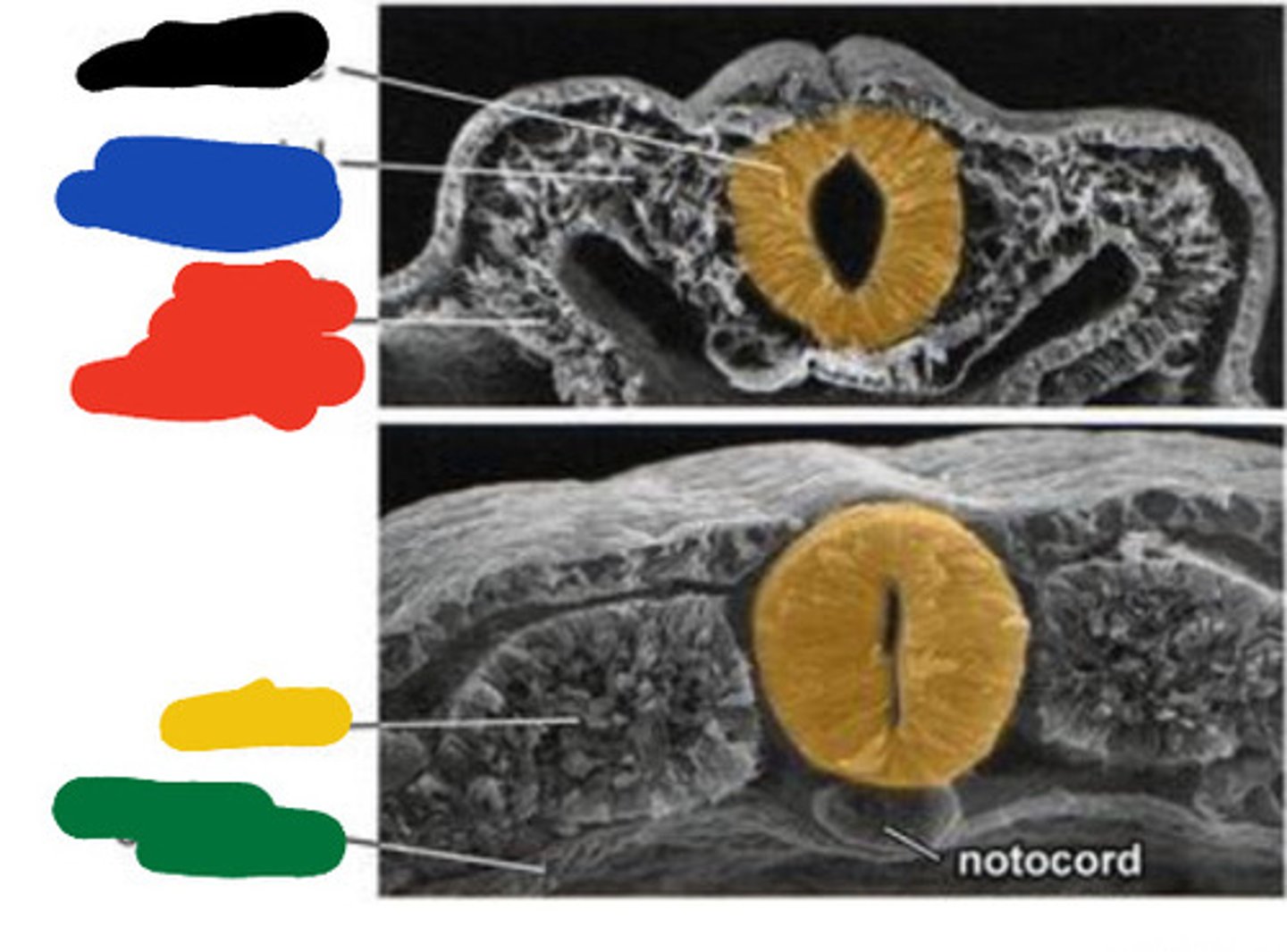
notochord
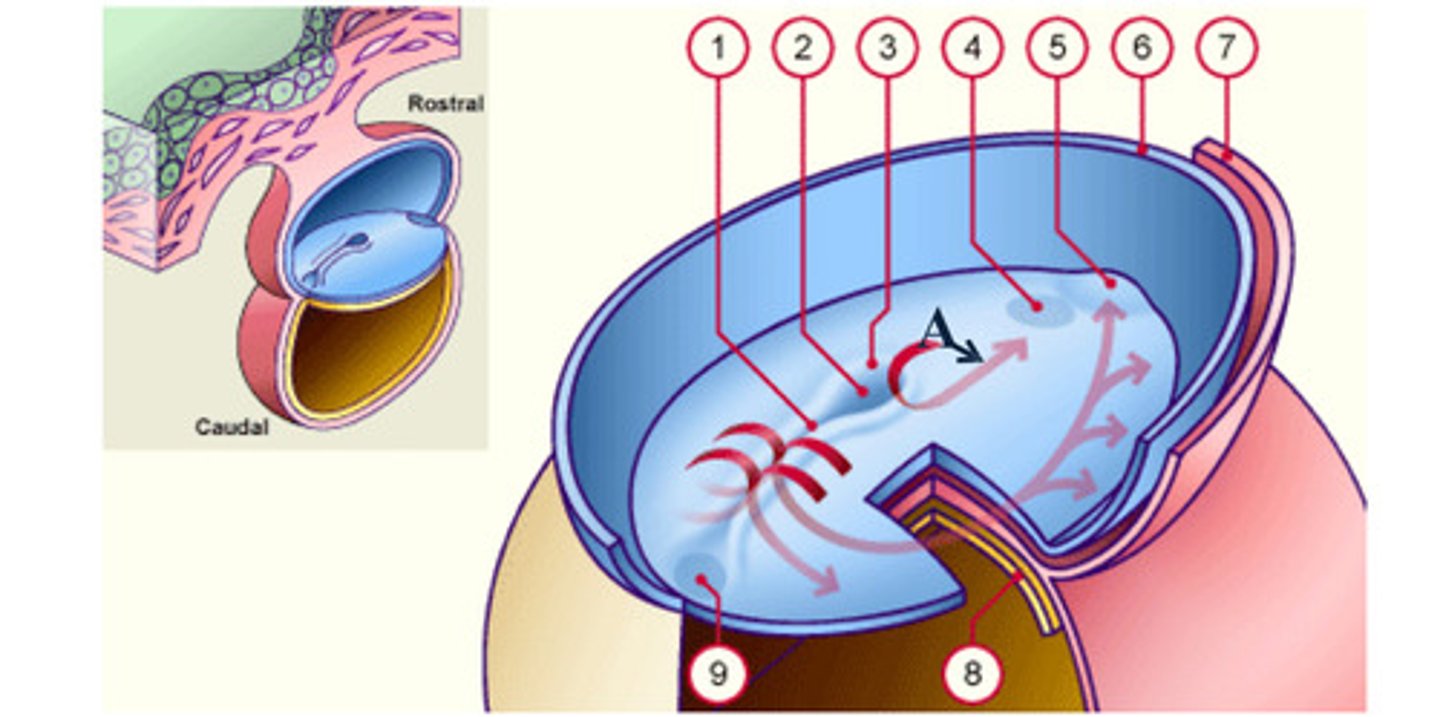
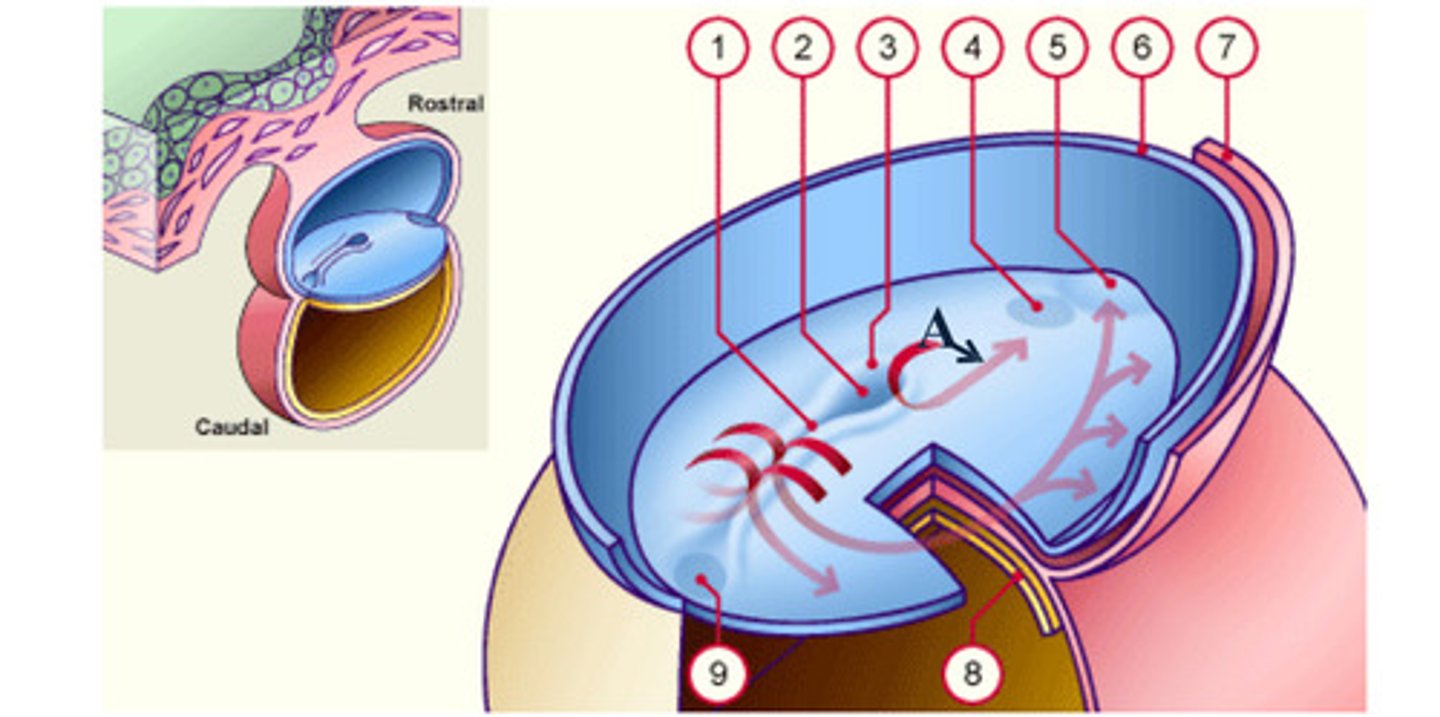
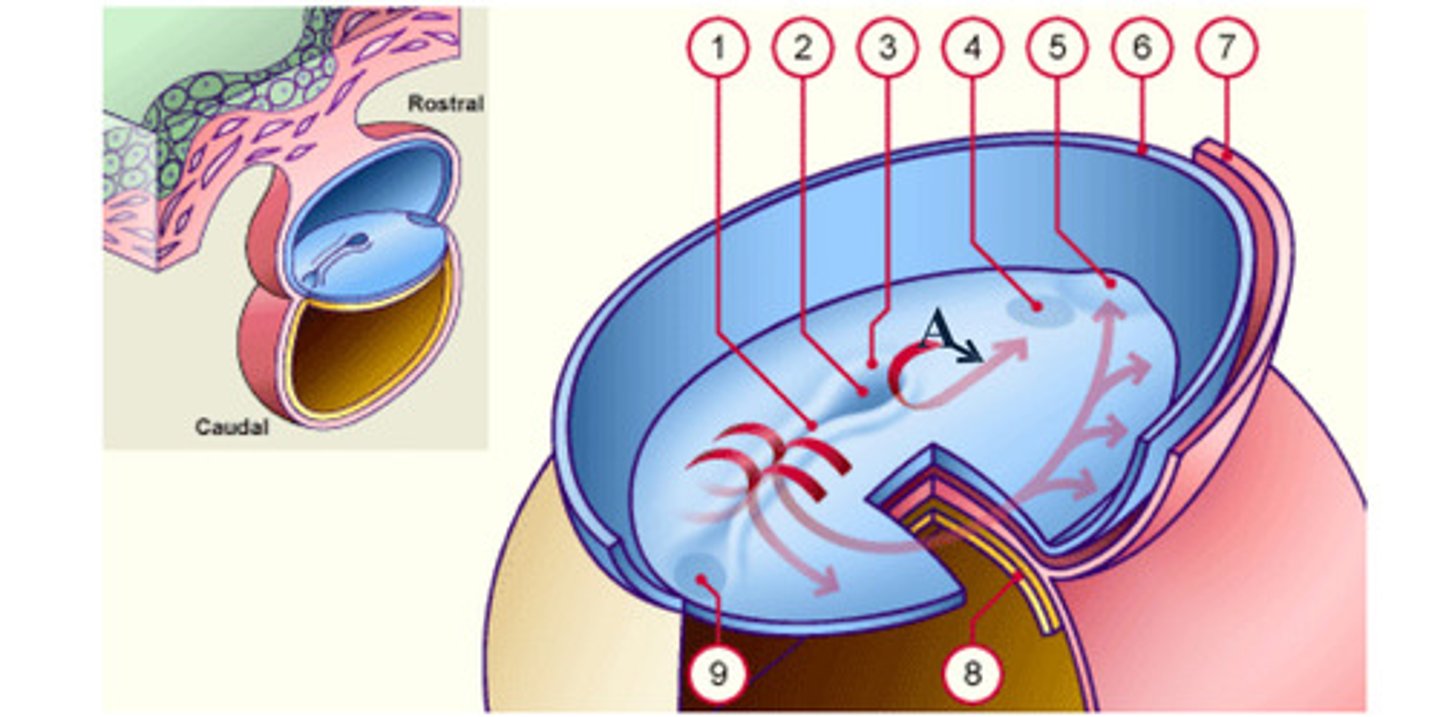
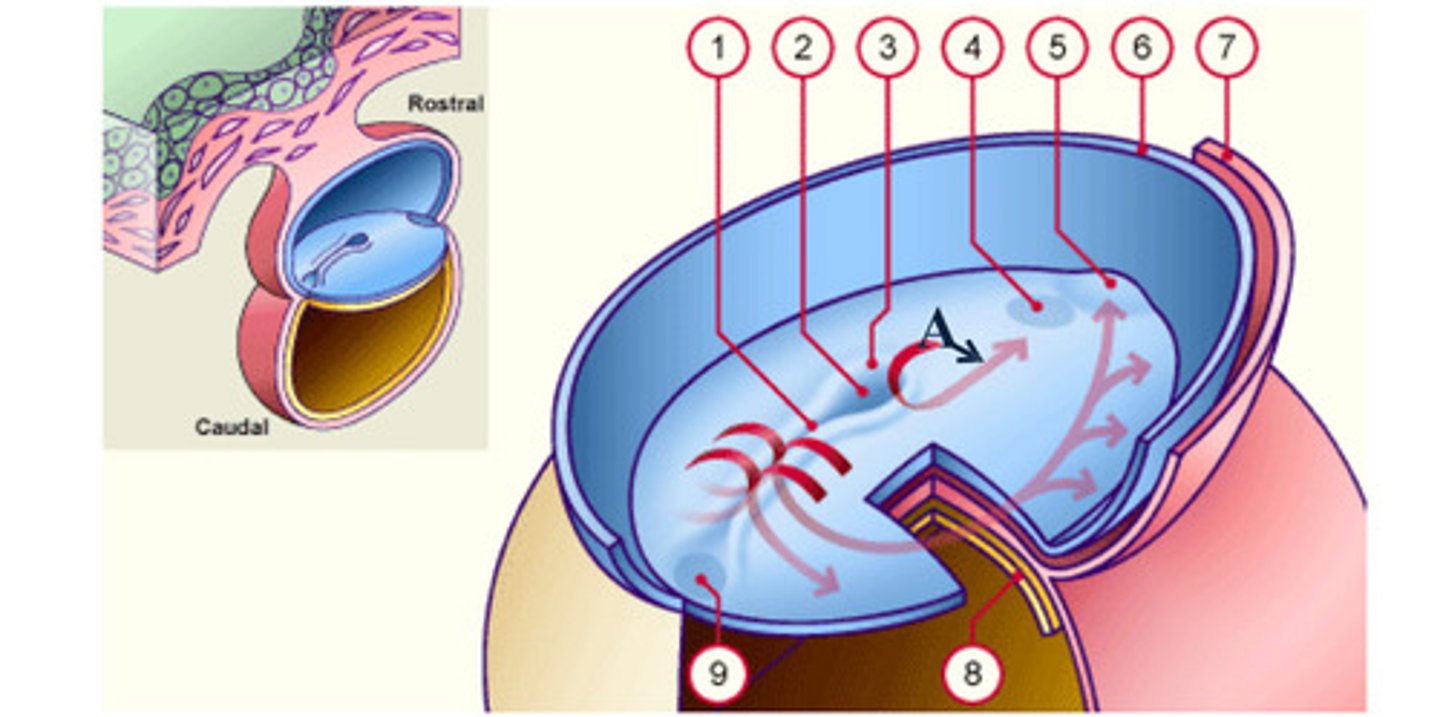
The __ (A), which is mesoderm, extends anteriorly from the primitive pit (2) to the prochordal plate (4).
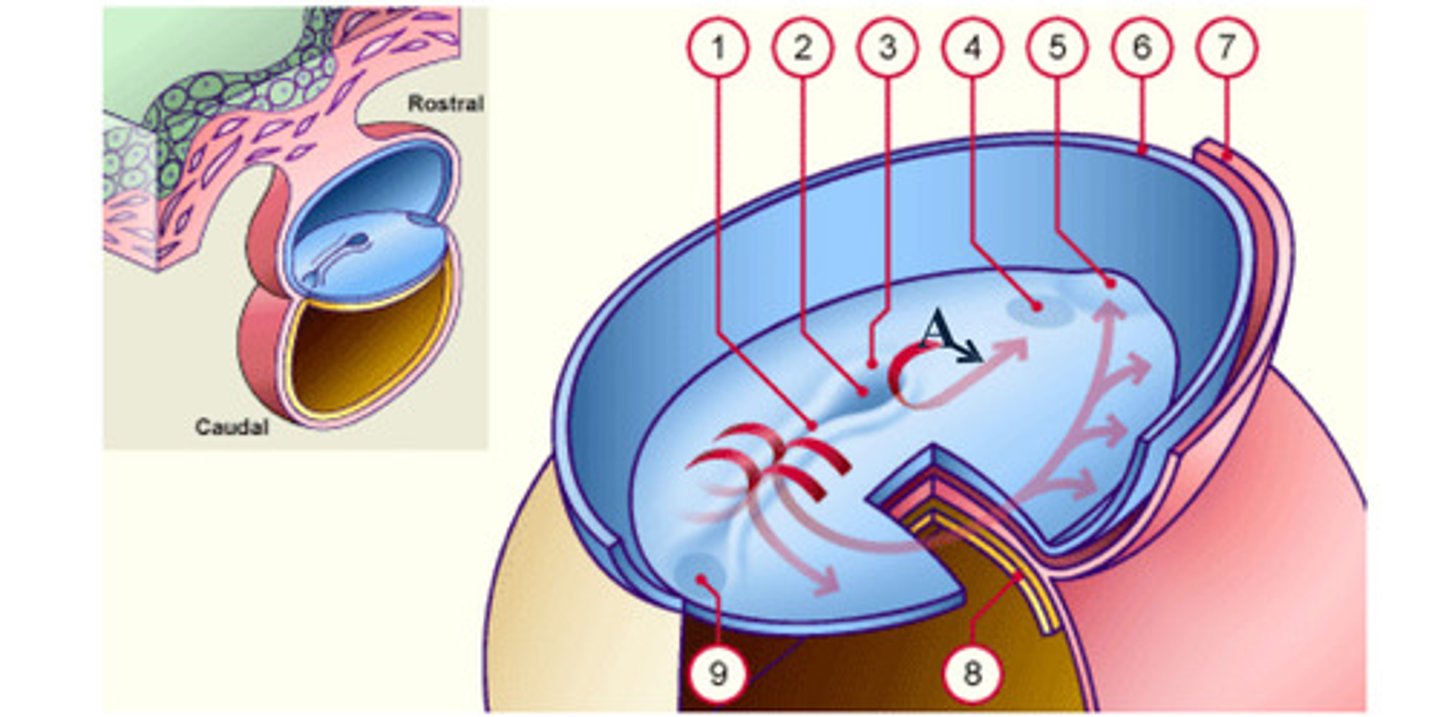
Notochord
A flexible rod that supports a chordate's back
Mesoderm
Notochord is from the
primitive pit
The notochord (A), which is mesoderm, extends anteriorly from the __ (2) to the prochordal plate (4).
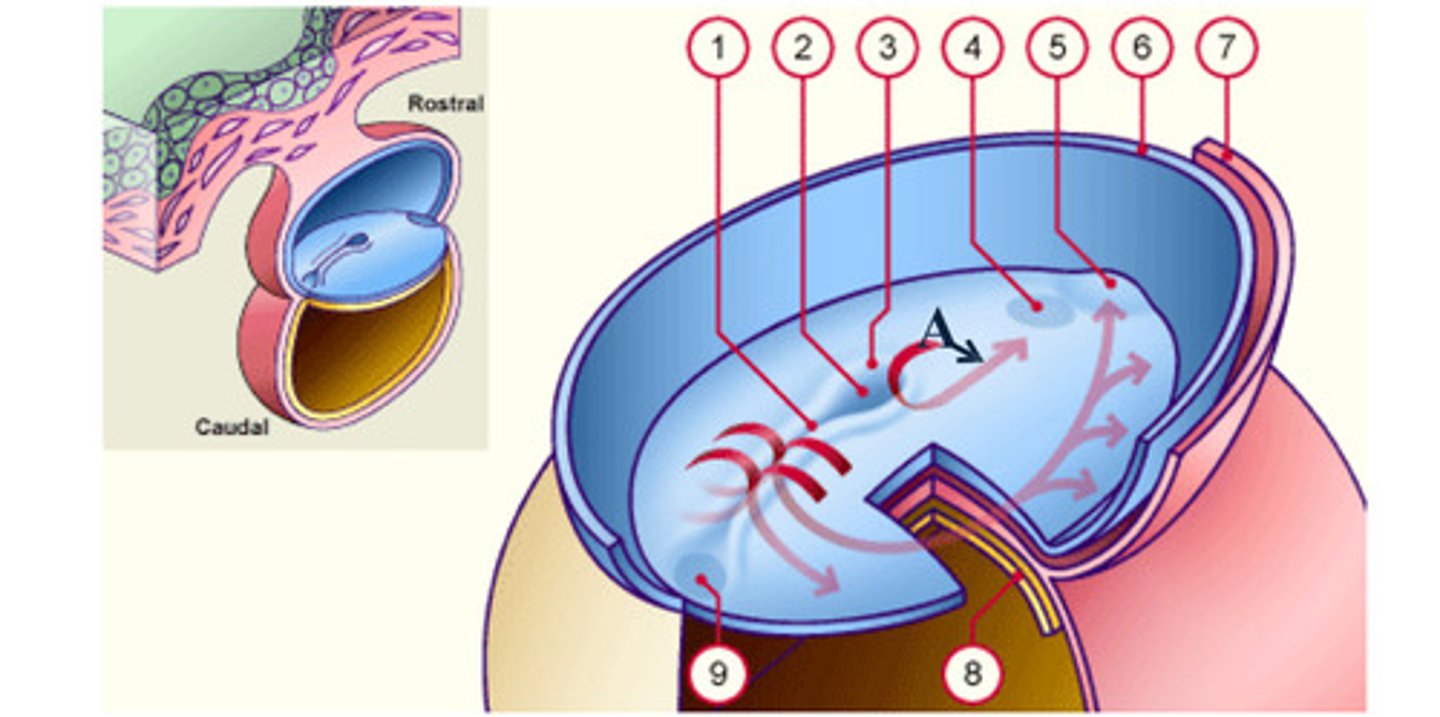
prochordal plate
The notochord (A), which is mesoderm, extends anteriorly from the primitive pit (2) to the __ (4).
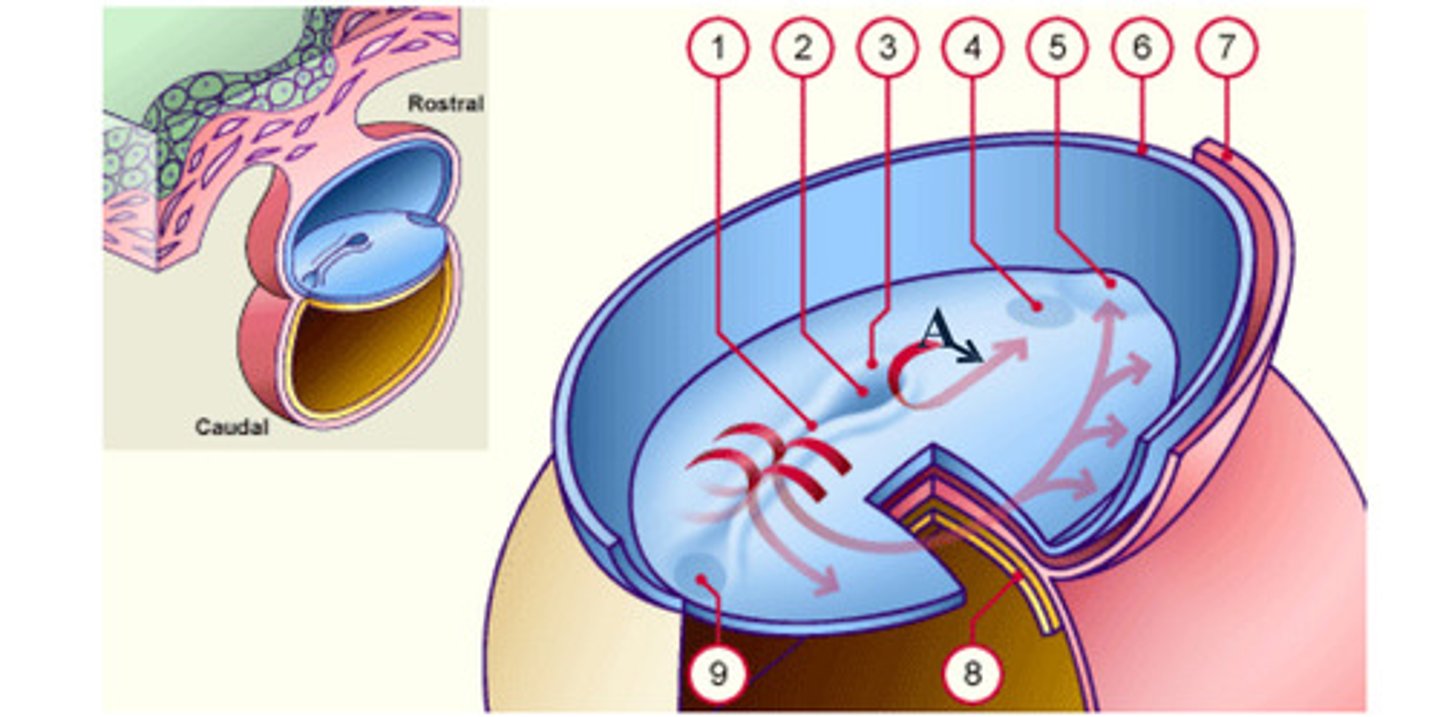
separate
As a result of the cell migrations, the notochord/ mesoderm completely __ the ectoderm from endoderm, except in the prochordal (4) and cecal (9) plates.
prochordal; cecal
As a result of the cell migrations, the notochord/ mesoderm completely separate the ectoderm from endoderm, except in the __ (4) and __ (9) plates.
Cecal plate
Fusion area at the tail end of the embryo. (9)
prochordal plate
area where the epiblast and hypoblast fuse; future site of the mouth (4)
Primitive pit
Depression in primitive node (2)
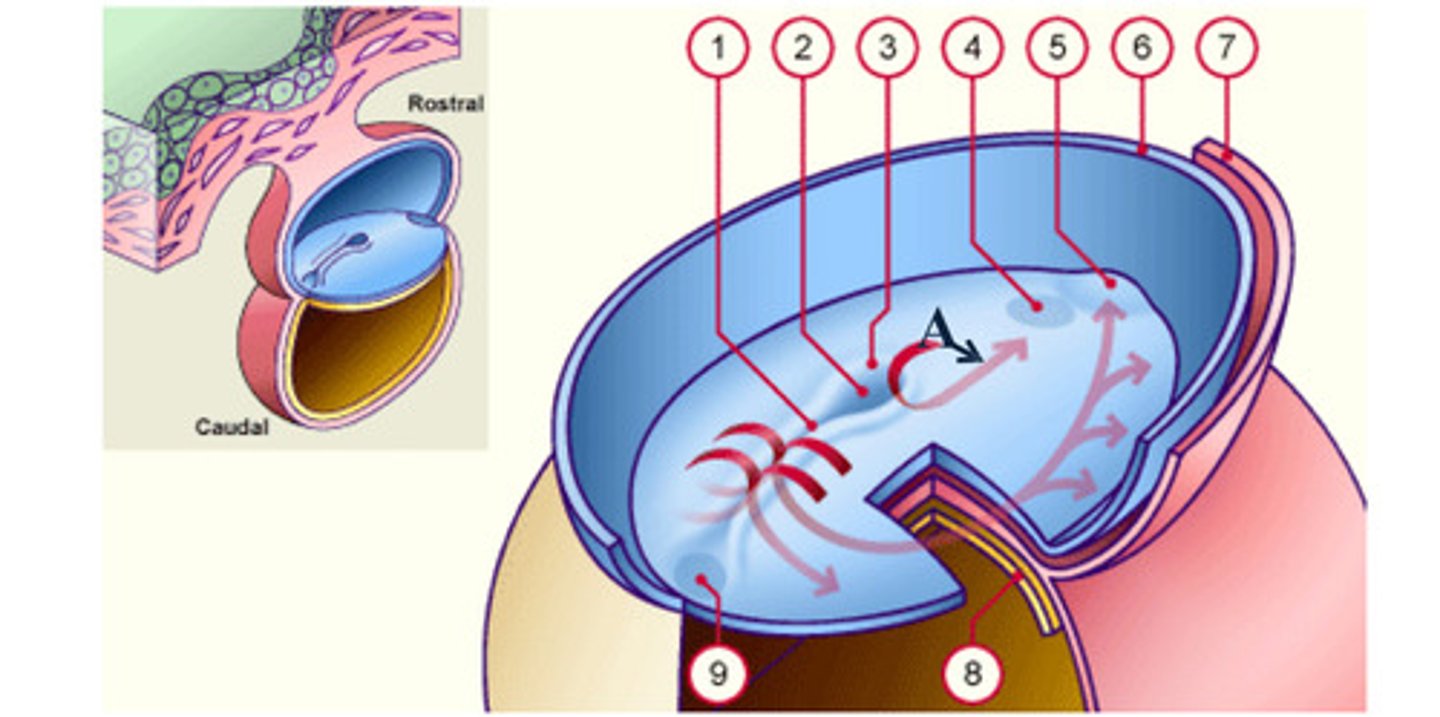
cardiac plate
Cells that accumulate anterior to the prochordal plate give rise to the __ (5).
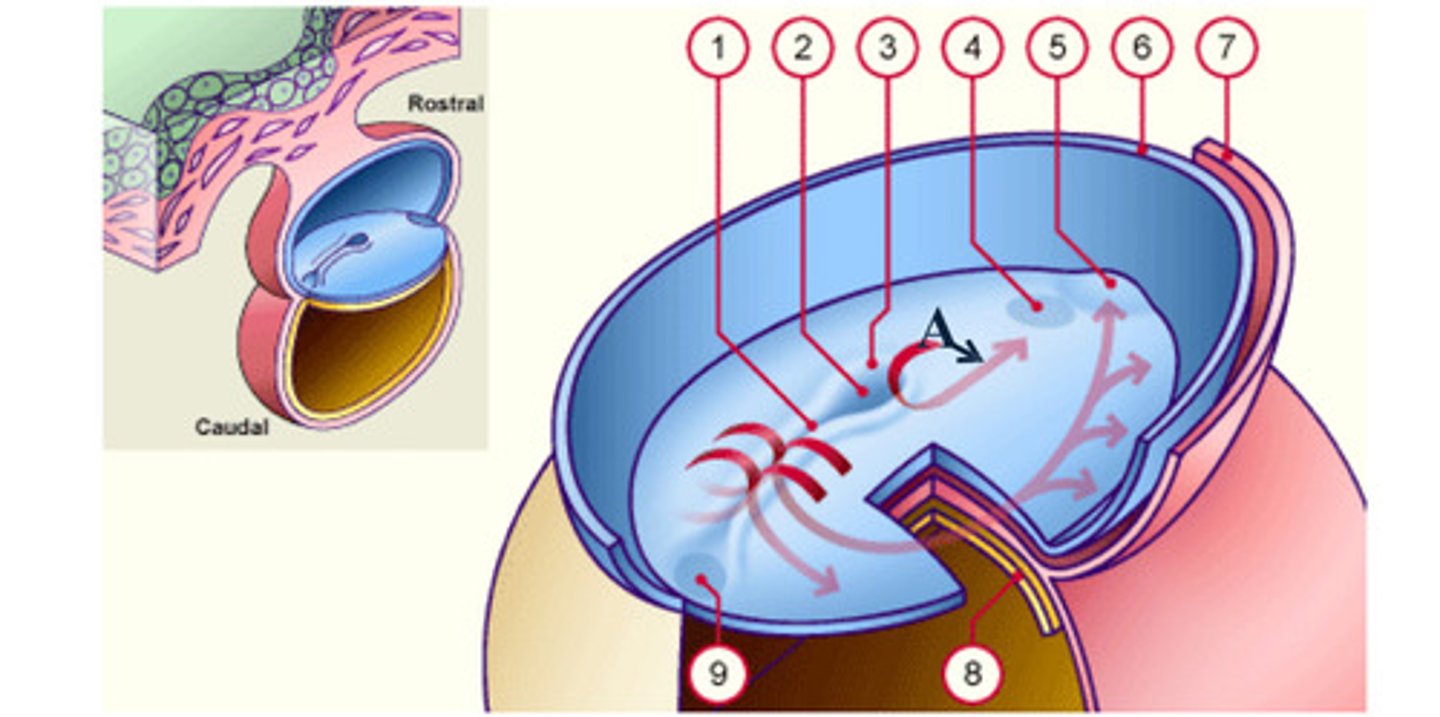
Cardiac plate
early development: the mesodermal cells continue to spread forward on each side of the notochord and prochordal plate. mesodermal cells that accumulate anterior to the prochordal plate give rise to the ______ _____ which will form the heart (5)
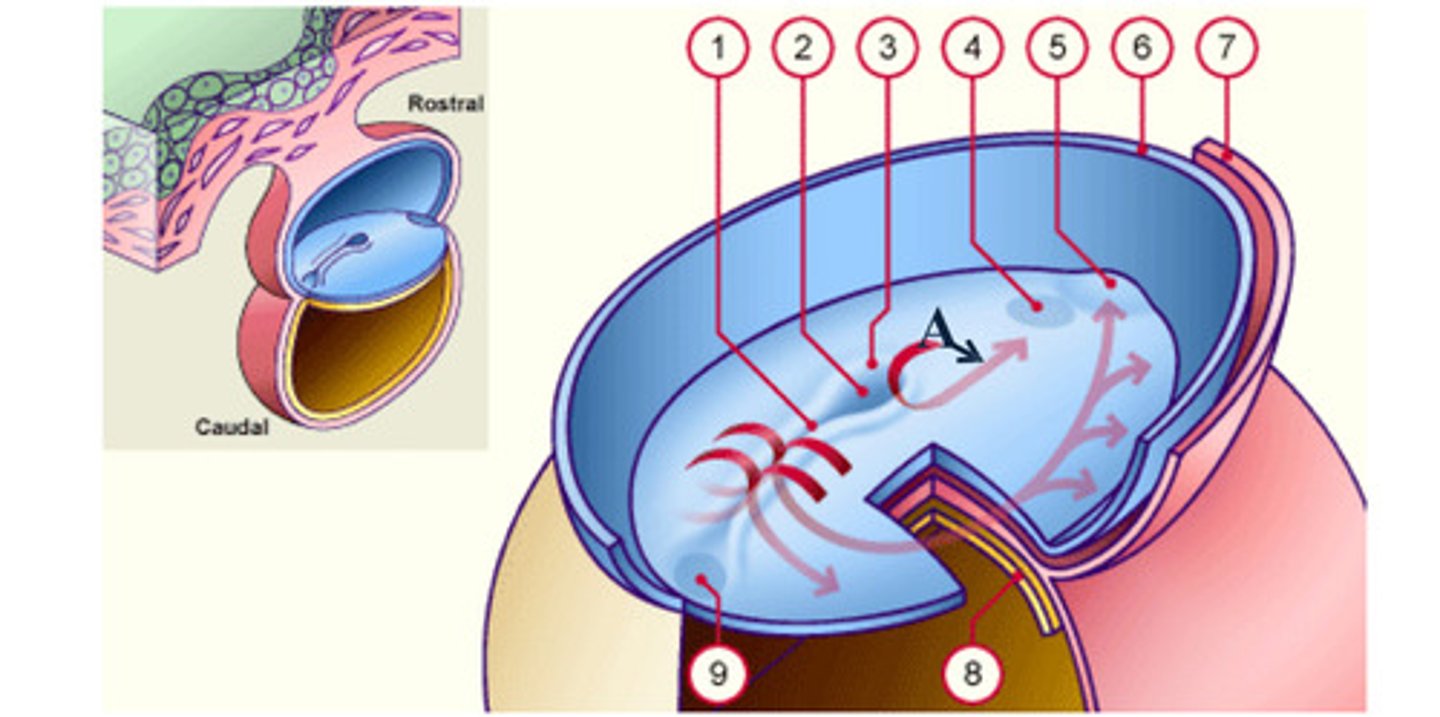
Rostral
toward the forehead or nose
Caudal
toward the tail
3-4 weeks
How many weeks for notochord formation begins
Notochord
Transient embryonic structure formed by condensed cells of the mesoderm layer
Embryo folding
Notochord influences the
Sonic hedgehog protein
Cells secrete ___ which difuses from notochord and help cells to know where they are in a 3D space
neurulation
The notochord extends from the primitive pit to the prochordal plate and starts the process of __
neurulation
development of the nervous system
Sonic hedgehog (Shh)
A secreted protein of the hedgehog family that plays a range of roles during development. For example it is involved in the specification of motor neurons in the developing spinal cord.
3-4 weeks
When does neural tube formation, cephalon folding, and neural crest formation
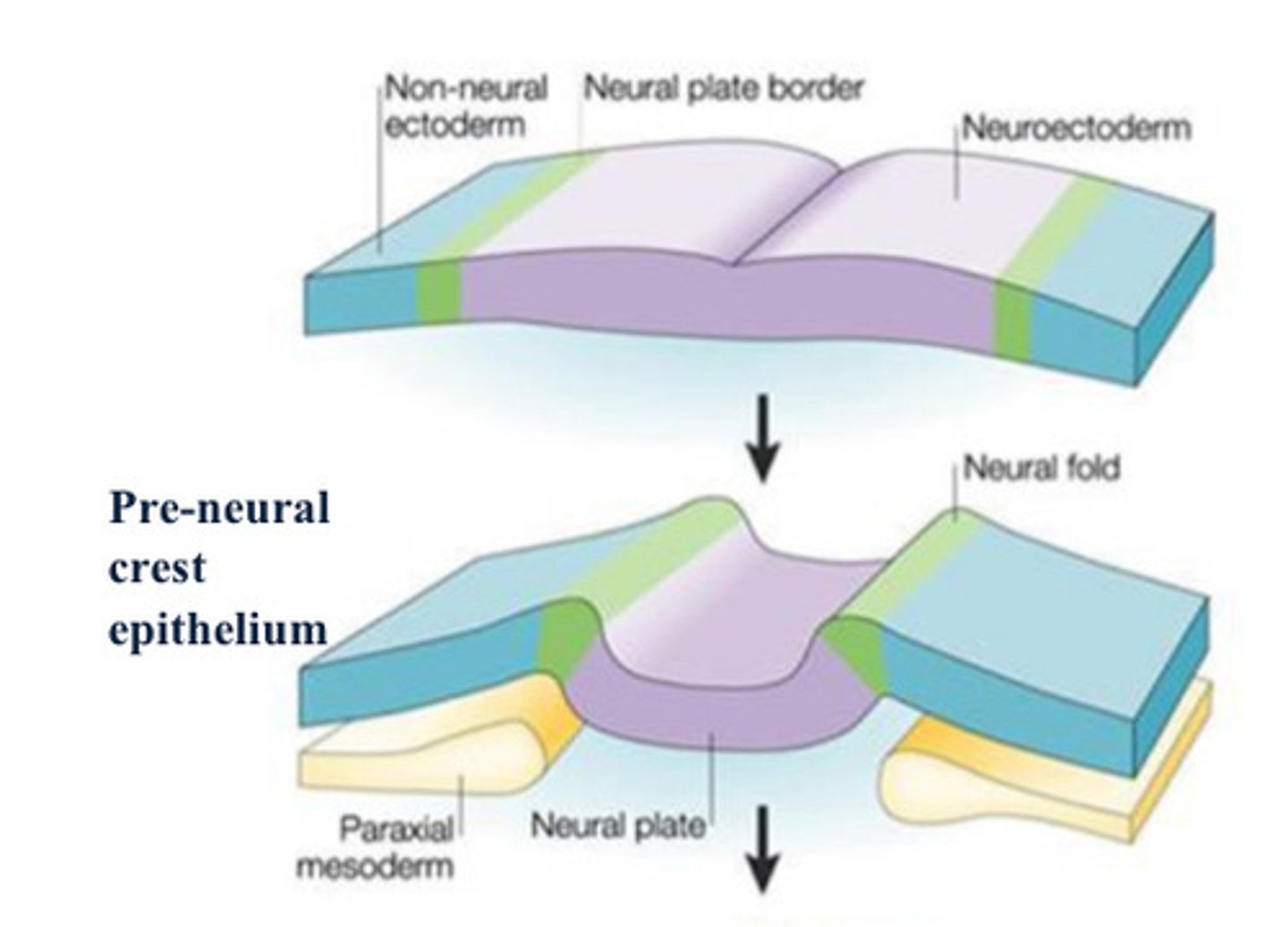
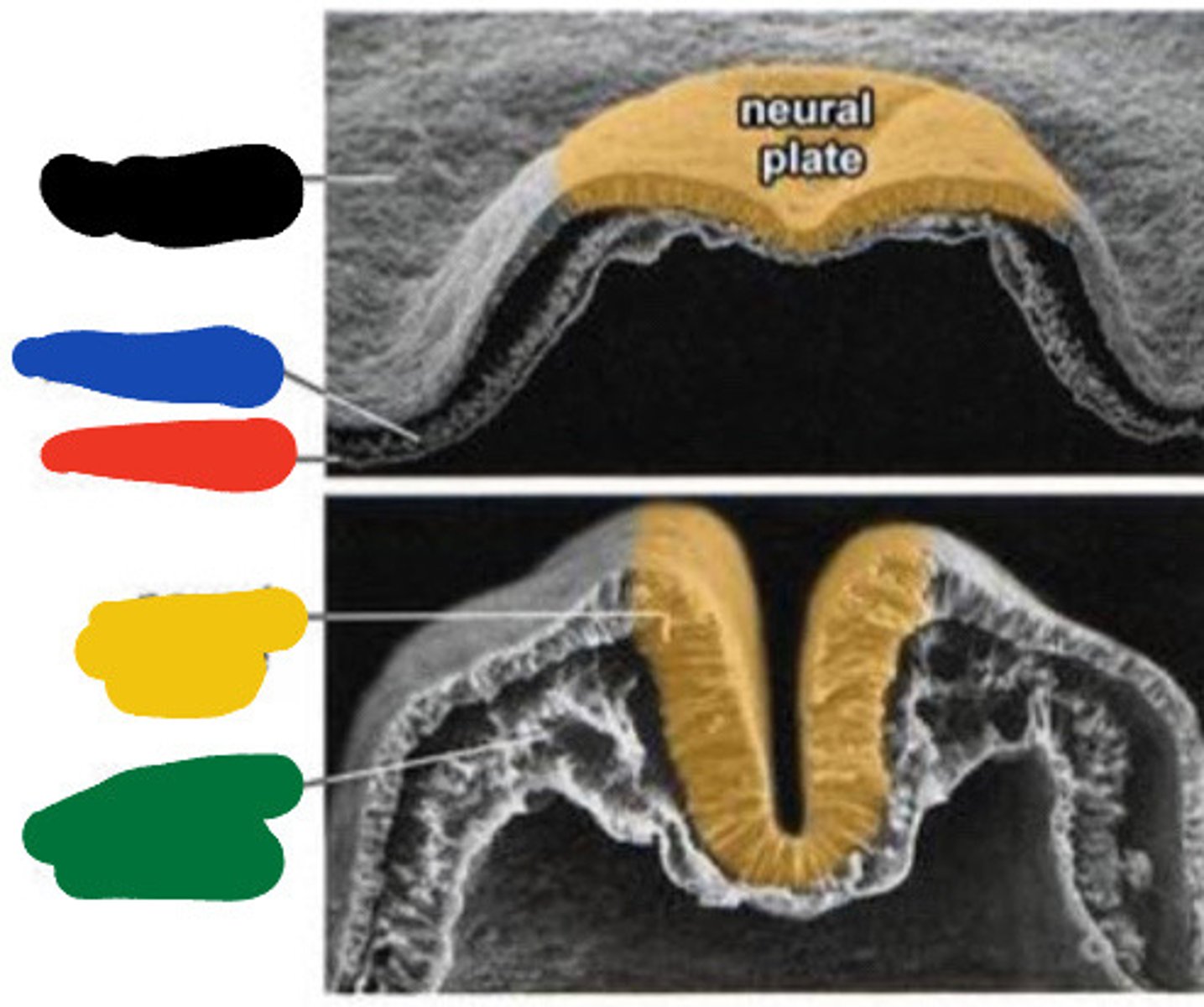
neuroectoderm
The nervous system develops as a
thickening within the ectodermal layer at
the rostral end of the embryo, forming the
neural plate or __.
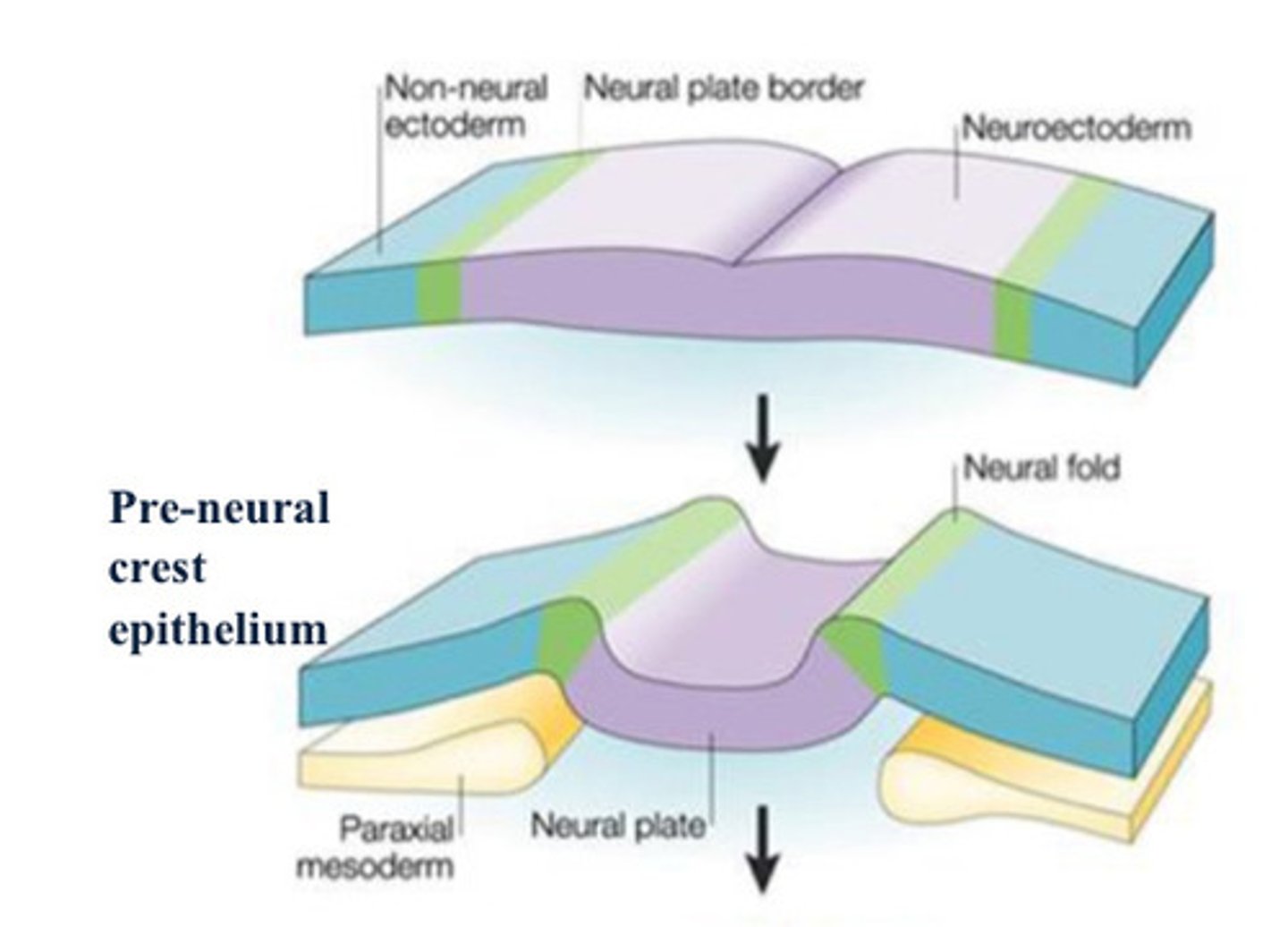
Neural folds
thickening of tissue on either side of neural groove
neural groove
Neural folds delineate a deepening midline
depression (__).
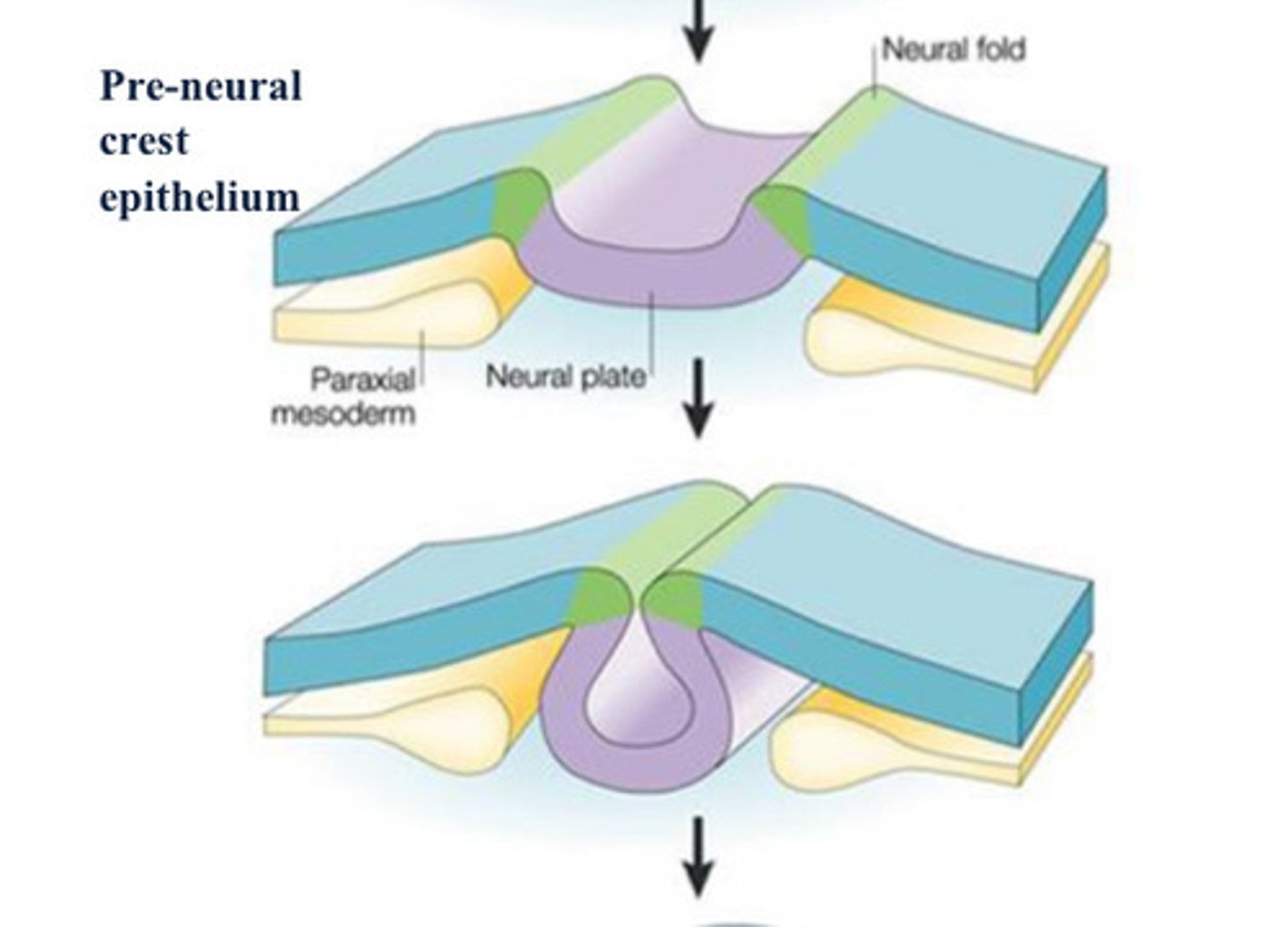
neural tube
Fusion of neural folds occurs in central
body region (__) and then
proceeds cranially and caudally. Forms
anterior and posterior neuropores, when
closed (4th week) the central nervous
system is established.
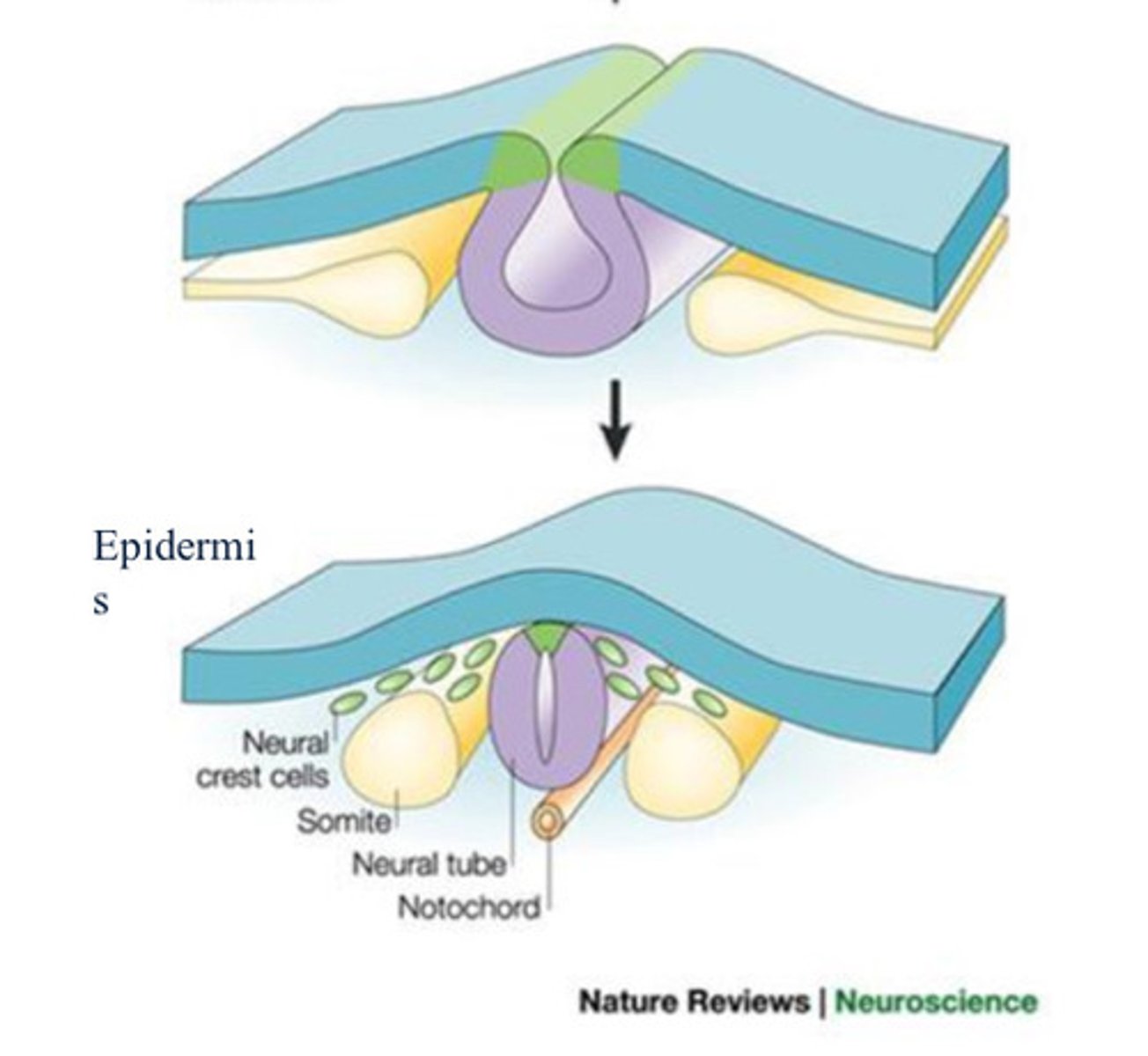
Neural crest cells
Cells at the tip of the neural fold; this group of cells gives rise to many components of the peripheral nervous system.
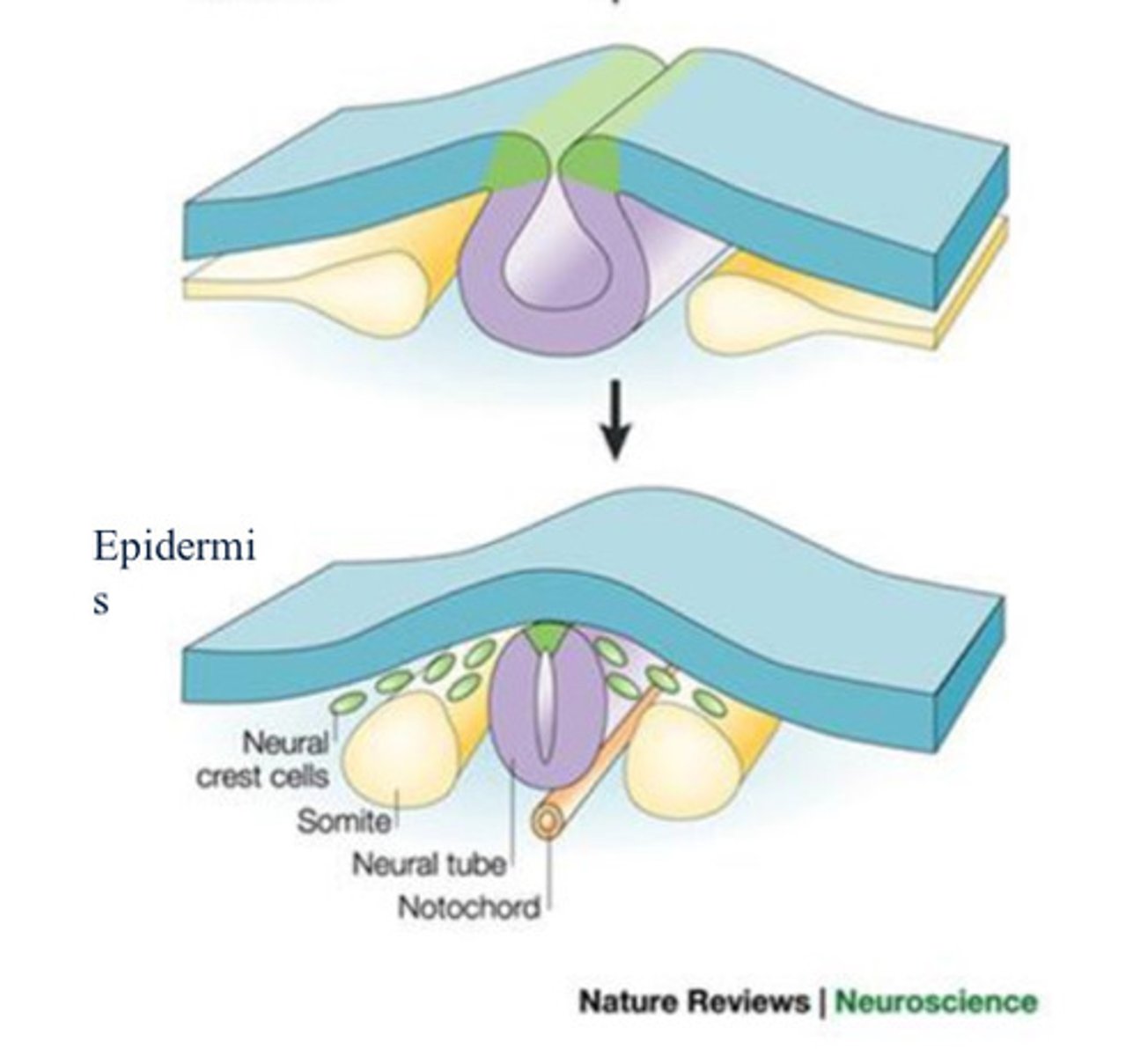
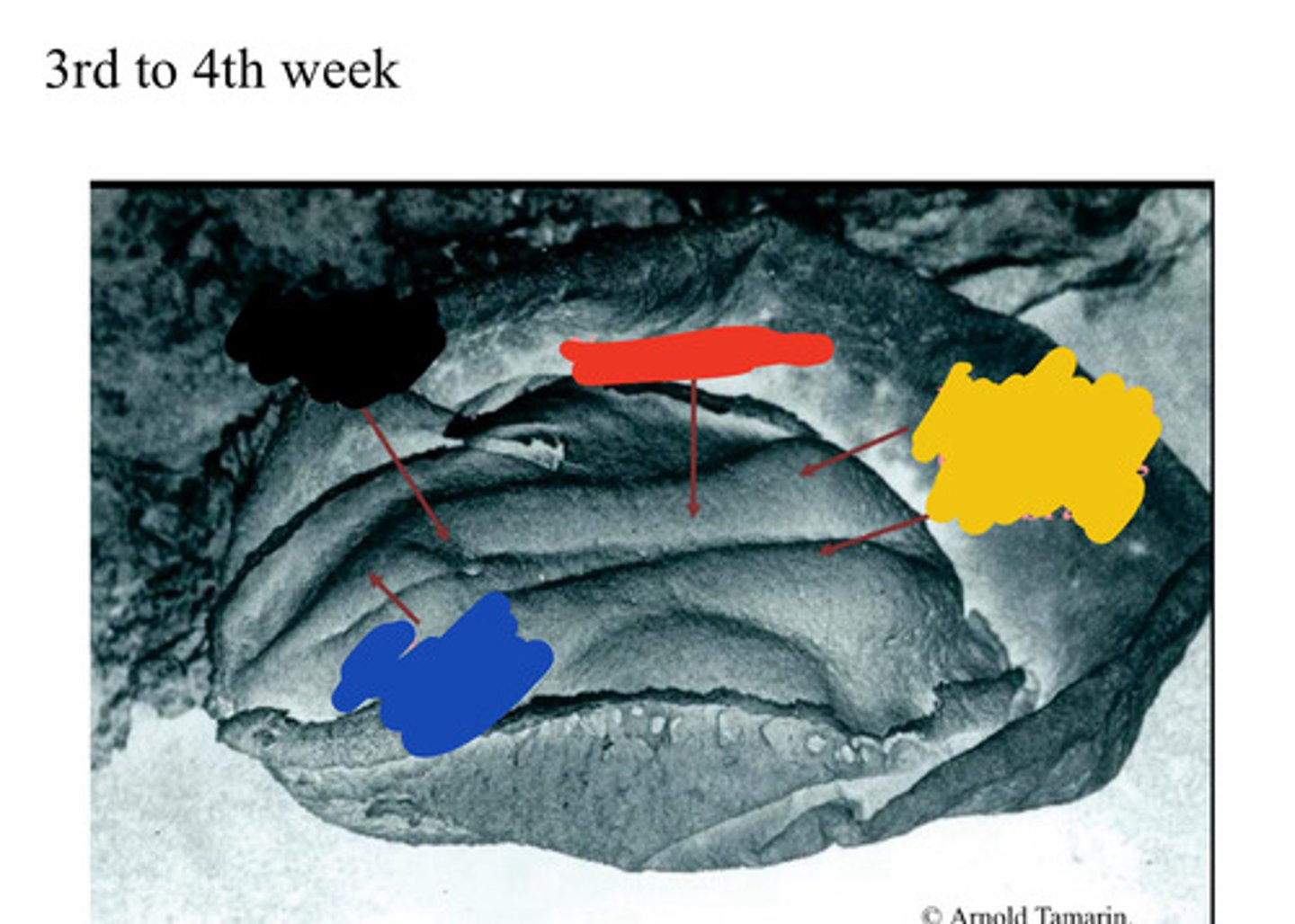
somite
one of the paired, repeating blocks of tissue located on either side of the notochord in the early embryo
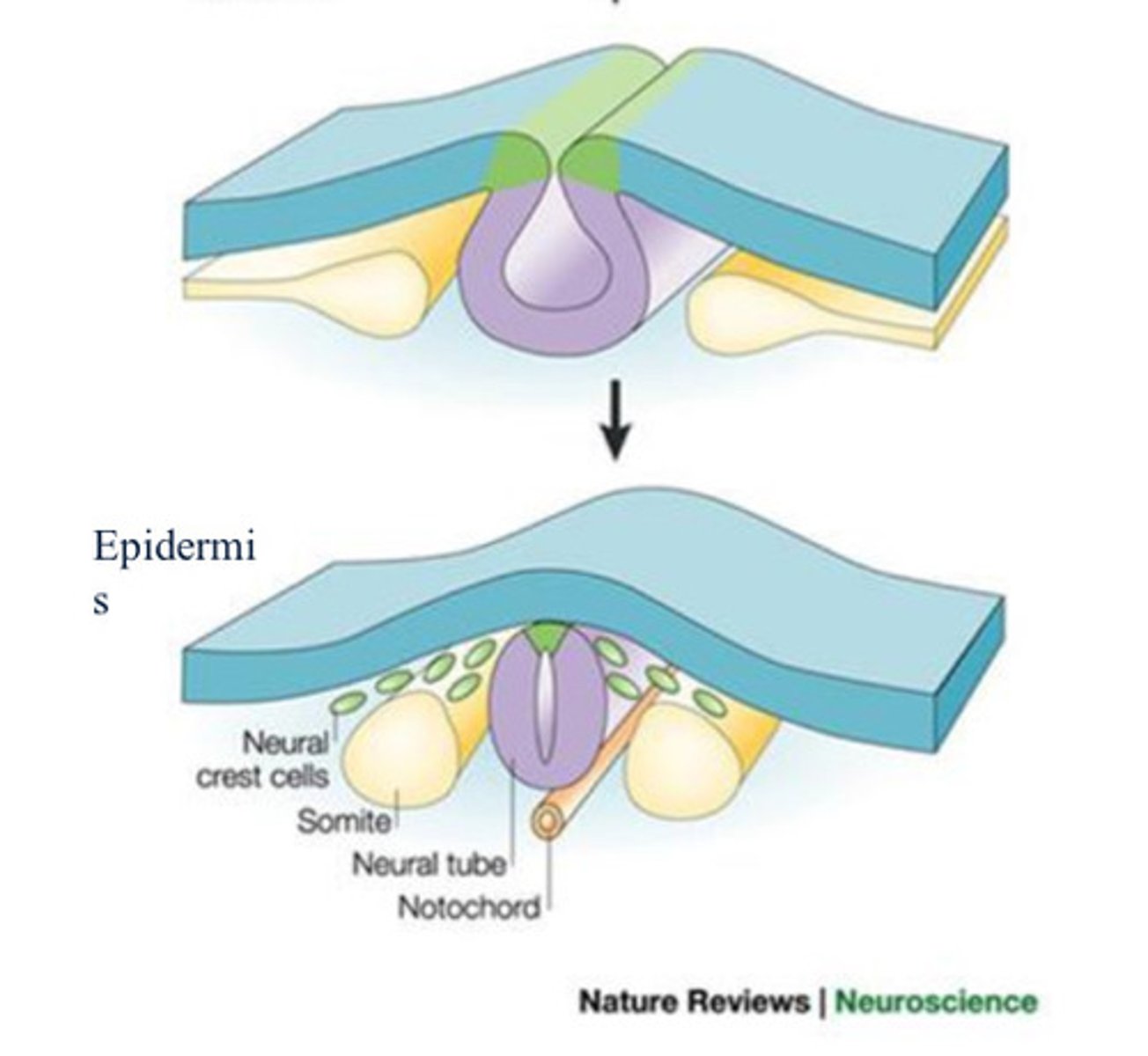
Ectoderm
Nervous system forms from
Paraxial mesoderm
gives rise to somites
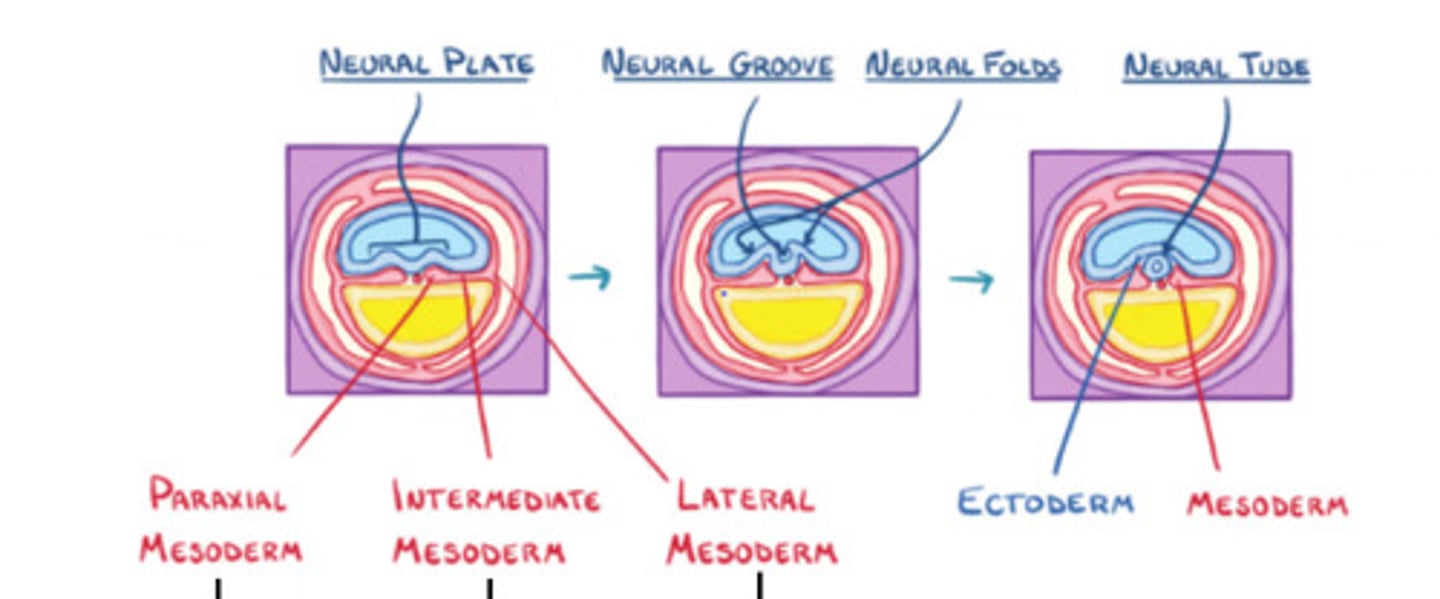
Intermediate mesoderm
forms urogenital system
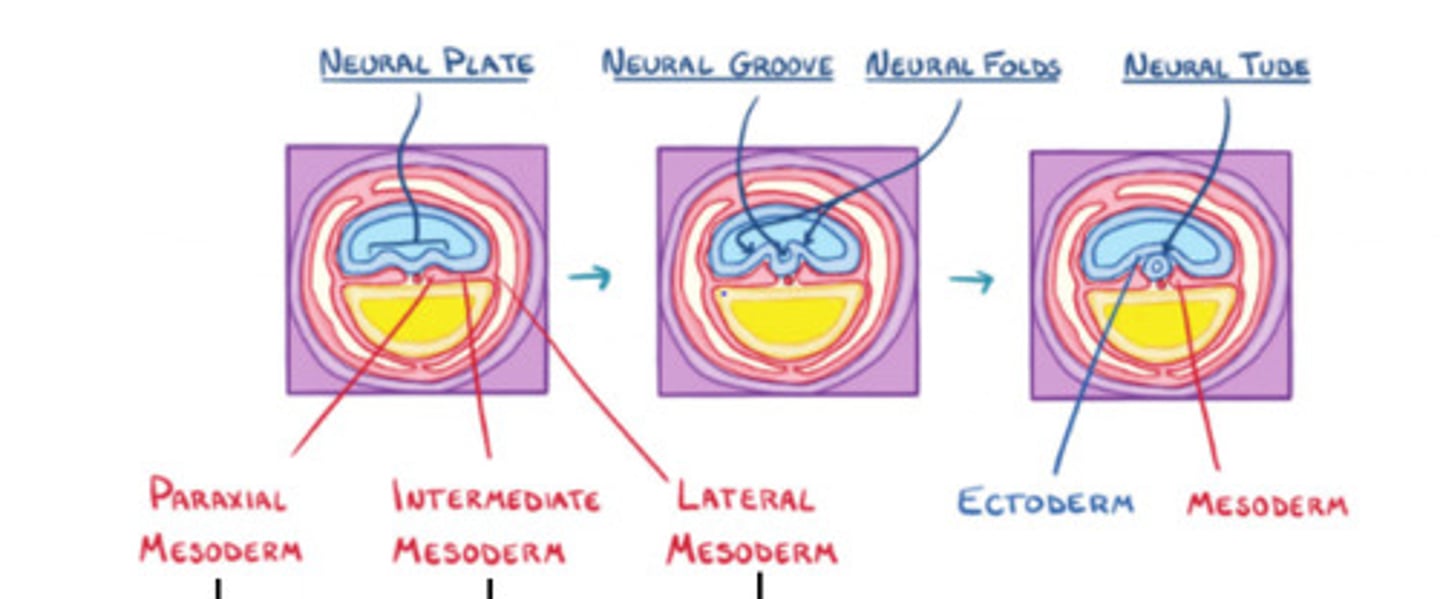
Lateral mesoderm
Connective tissue associated with muscle and viscera, cardiovascular system, blood, etc
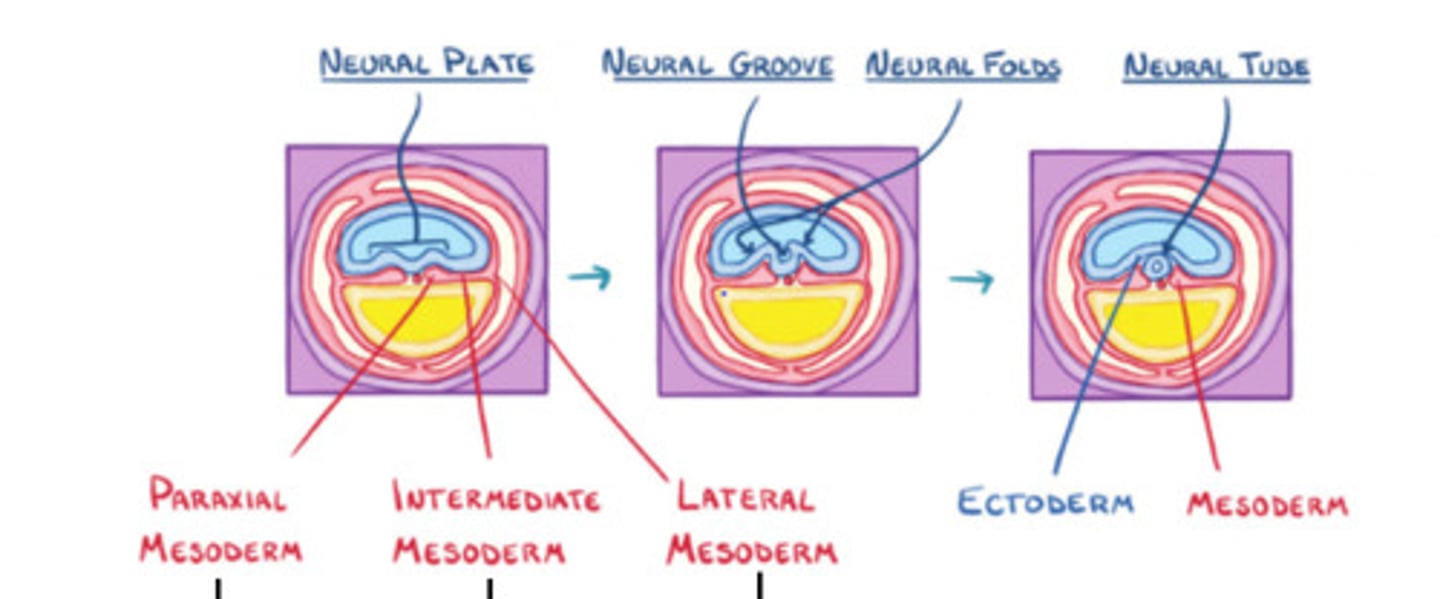
Ectoderm
Black
Mesoderm
Blue
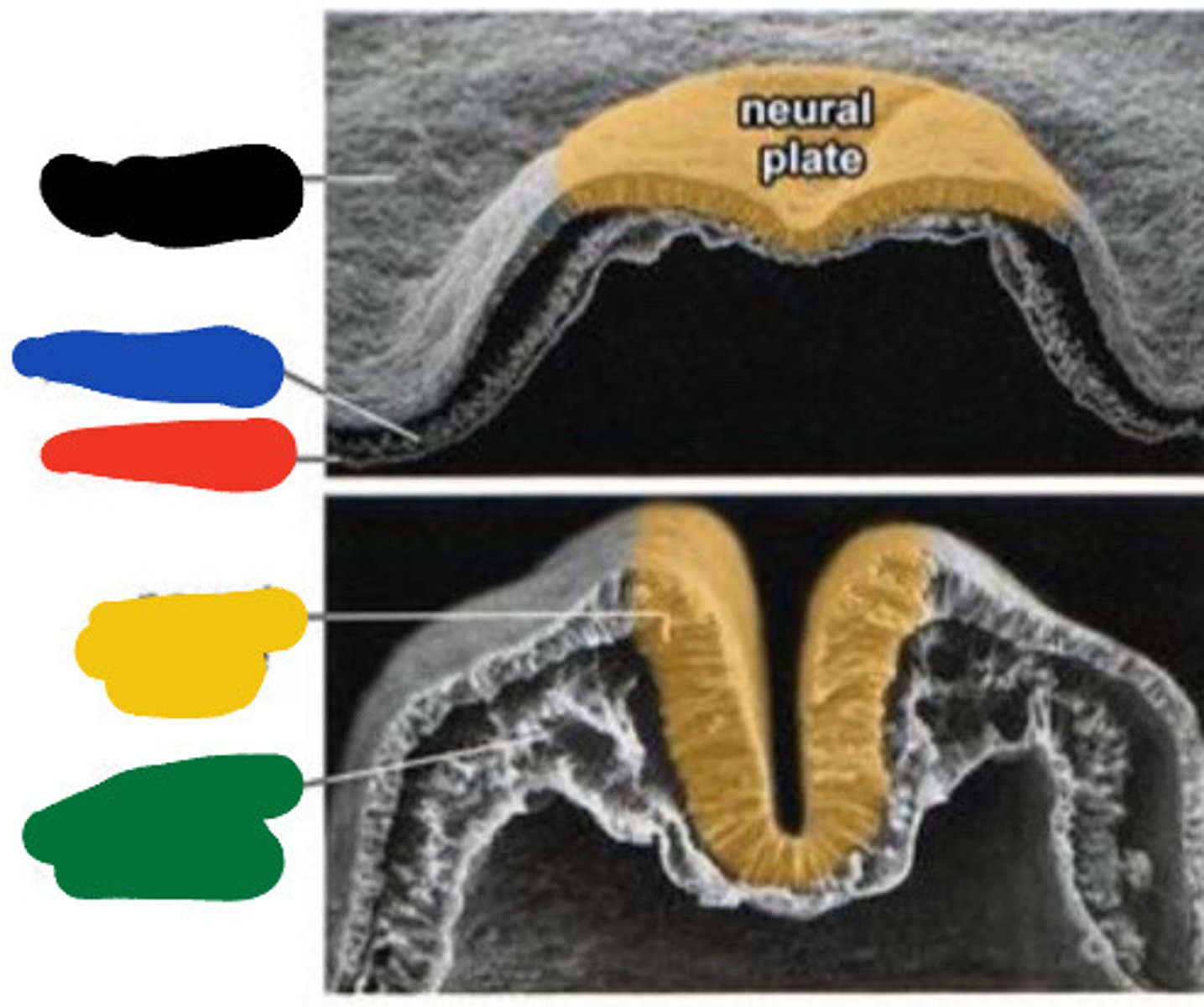
Endoderm
Red
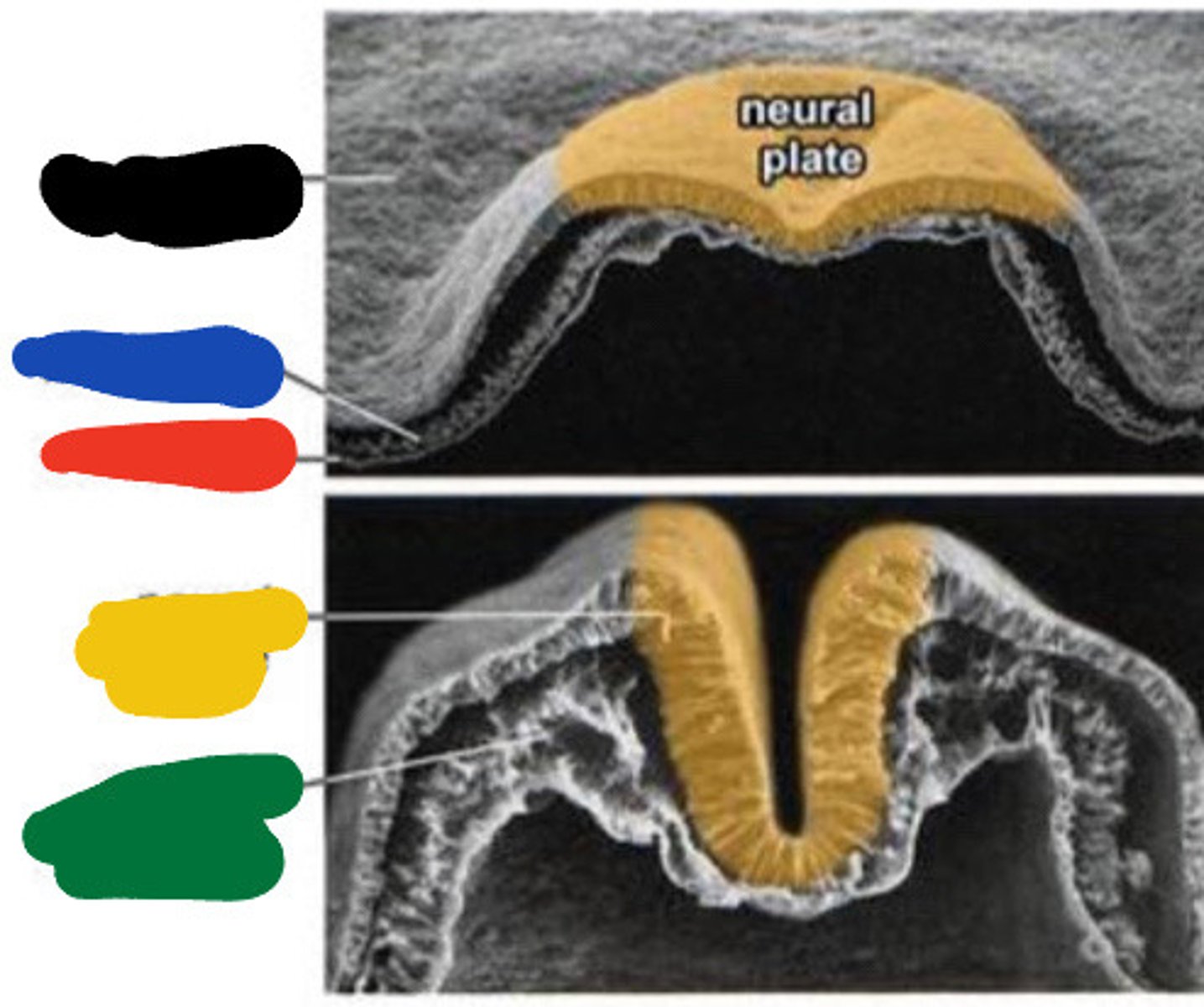
Neural groove
Yellow
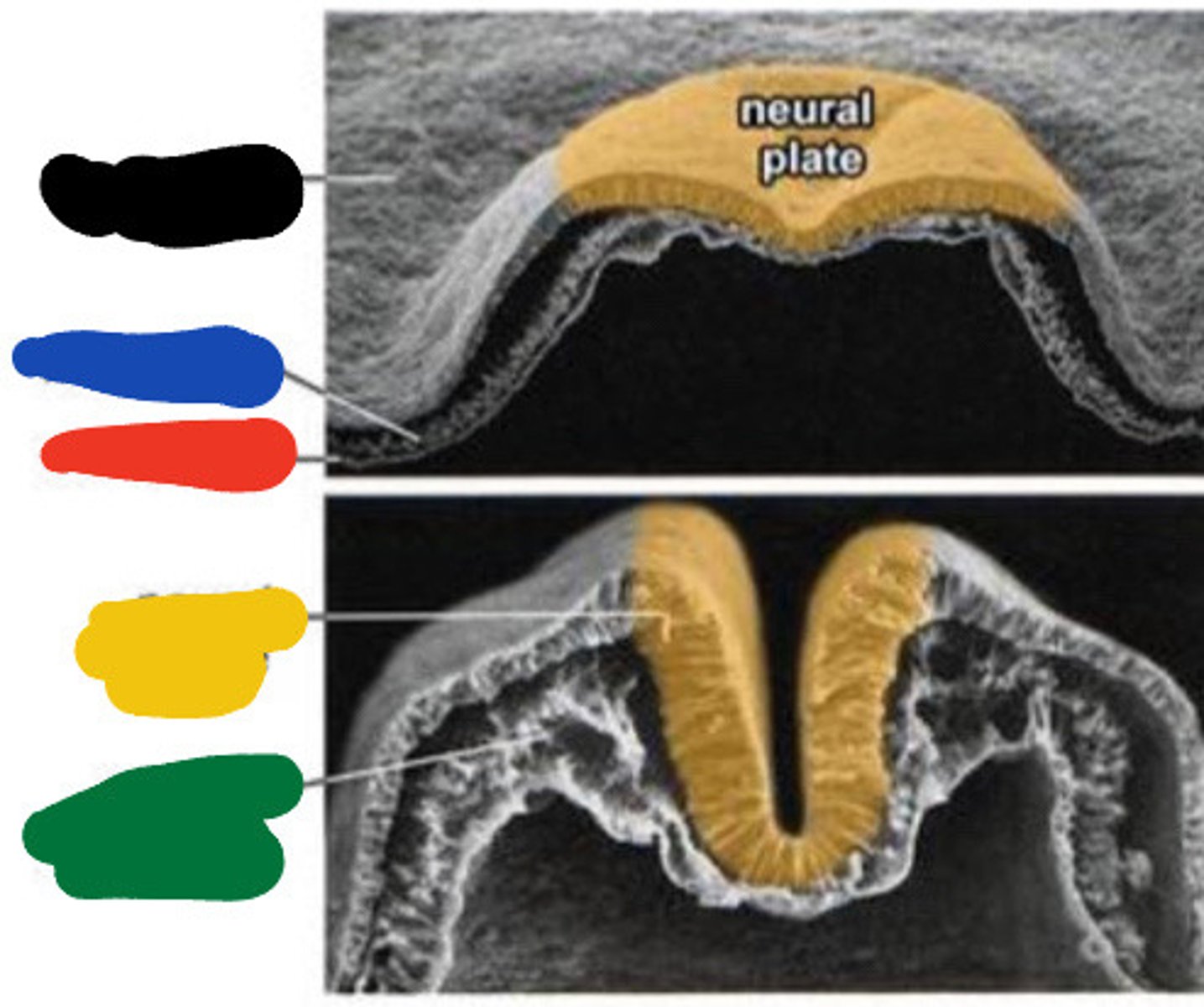
Paraxial mesoderm
Green
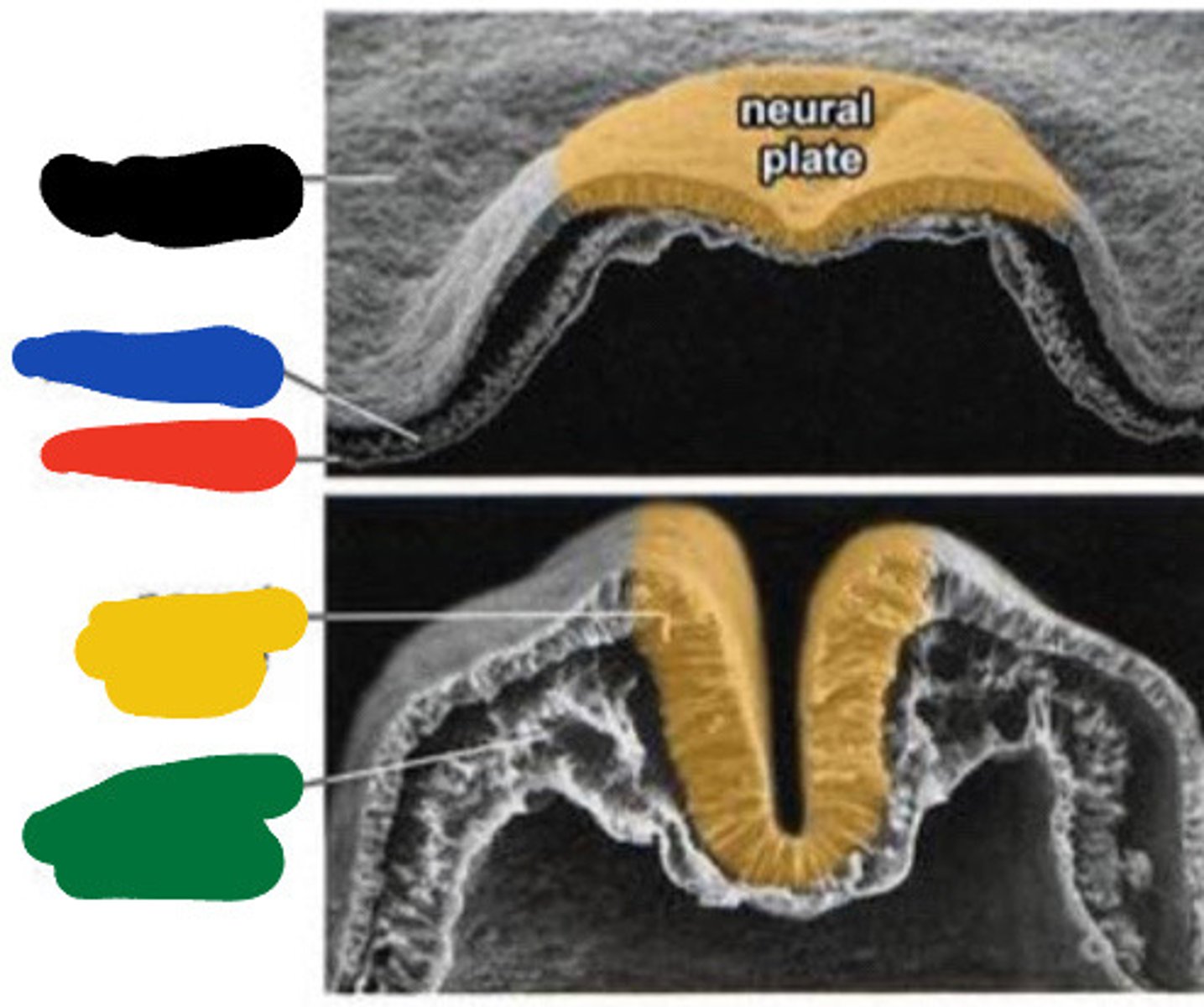
Neural tube
Black
Paraxial mesoderm
Blue
Lateral plate mesoderm
Red
Somite
Yellow
Endoderm
Green
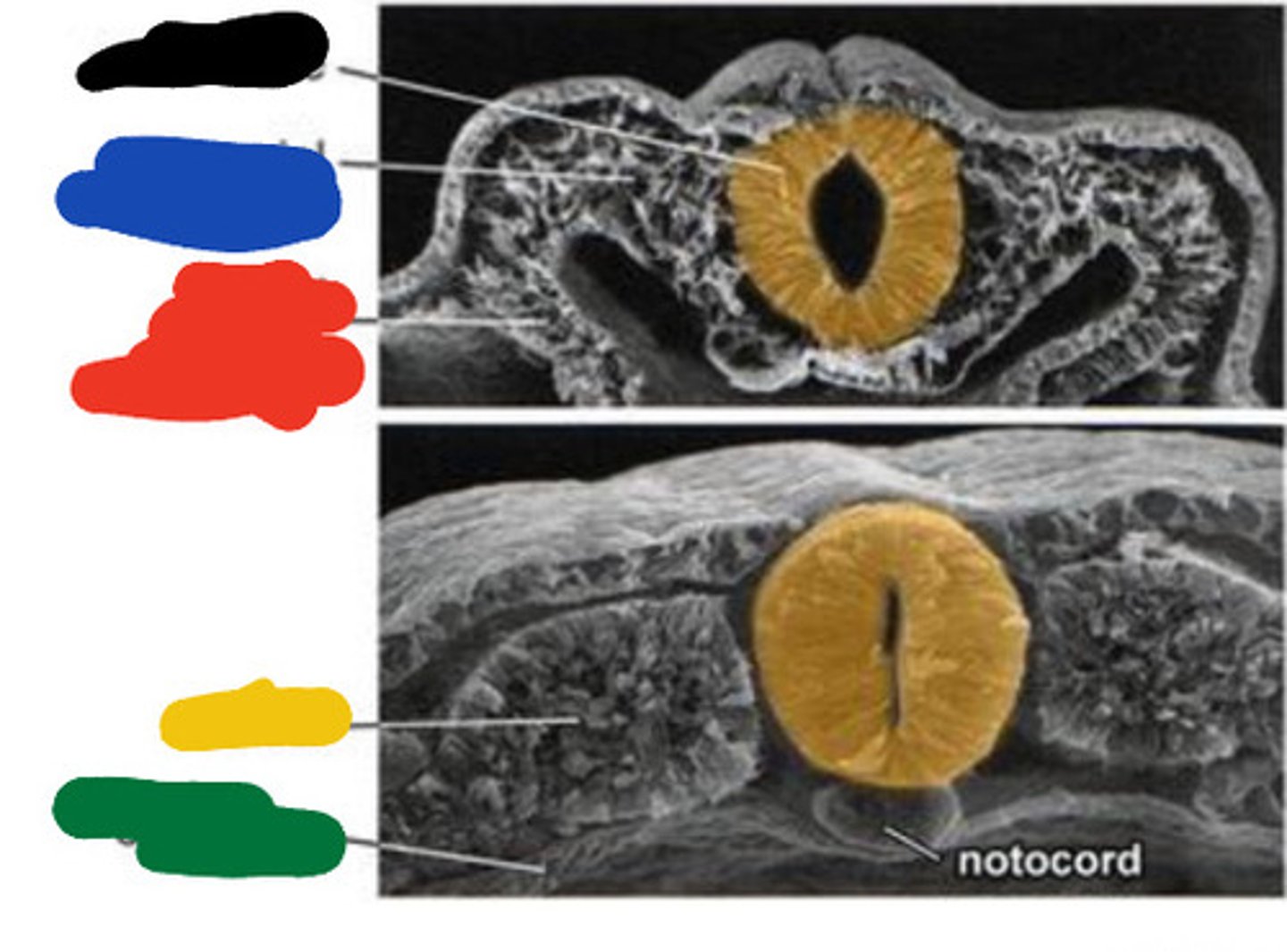
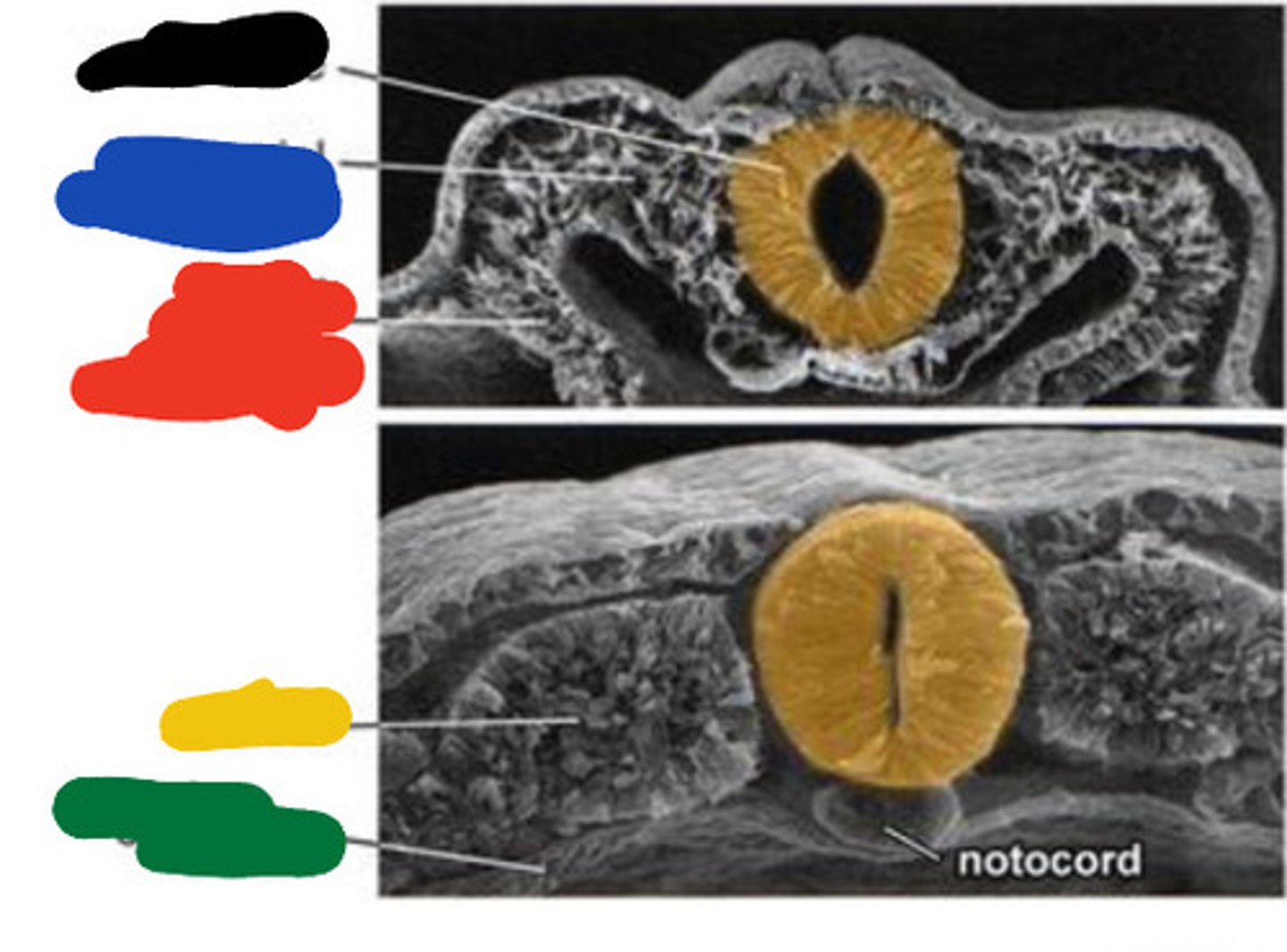
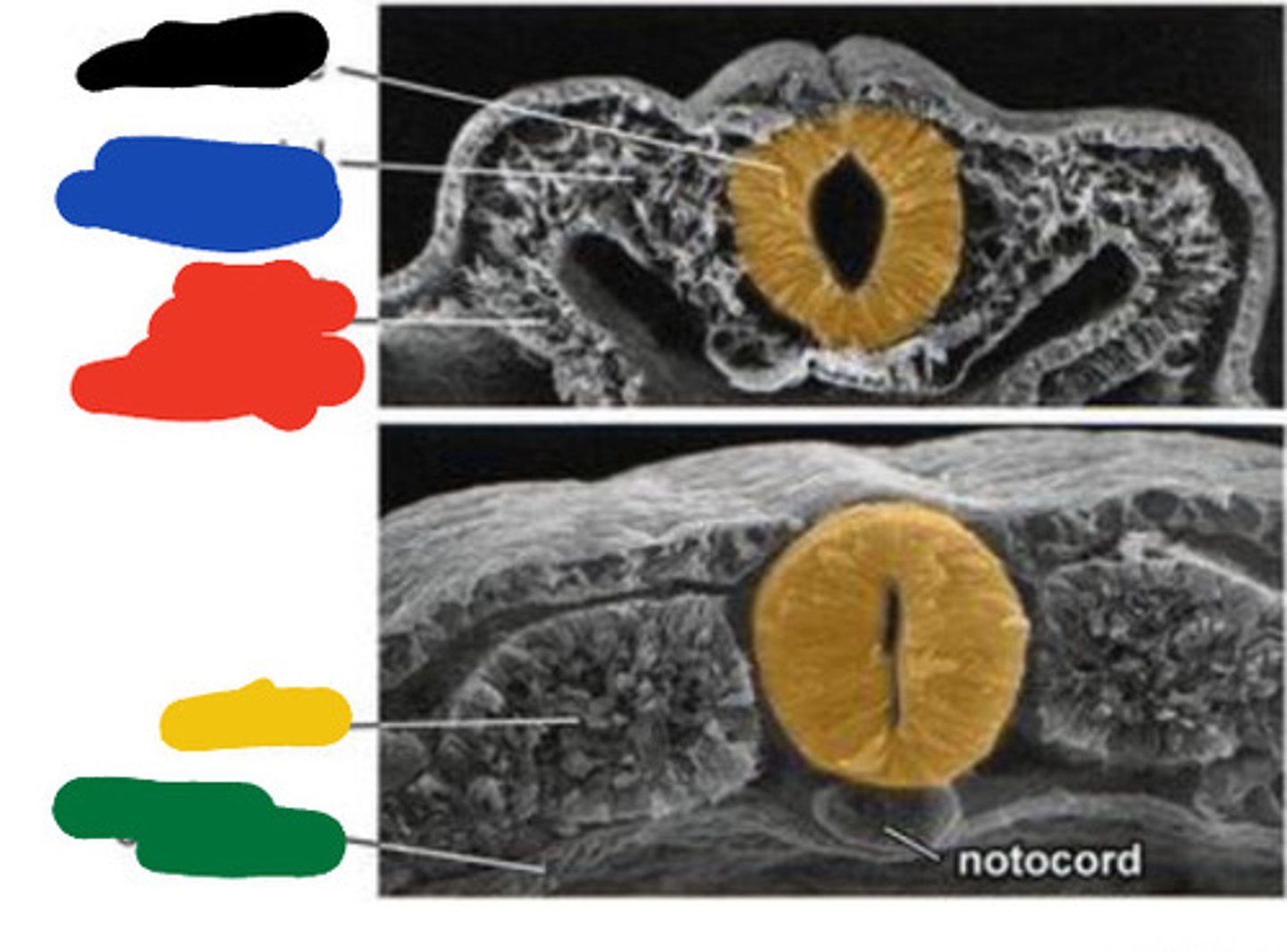
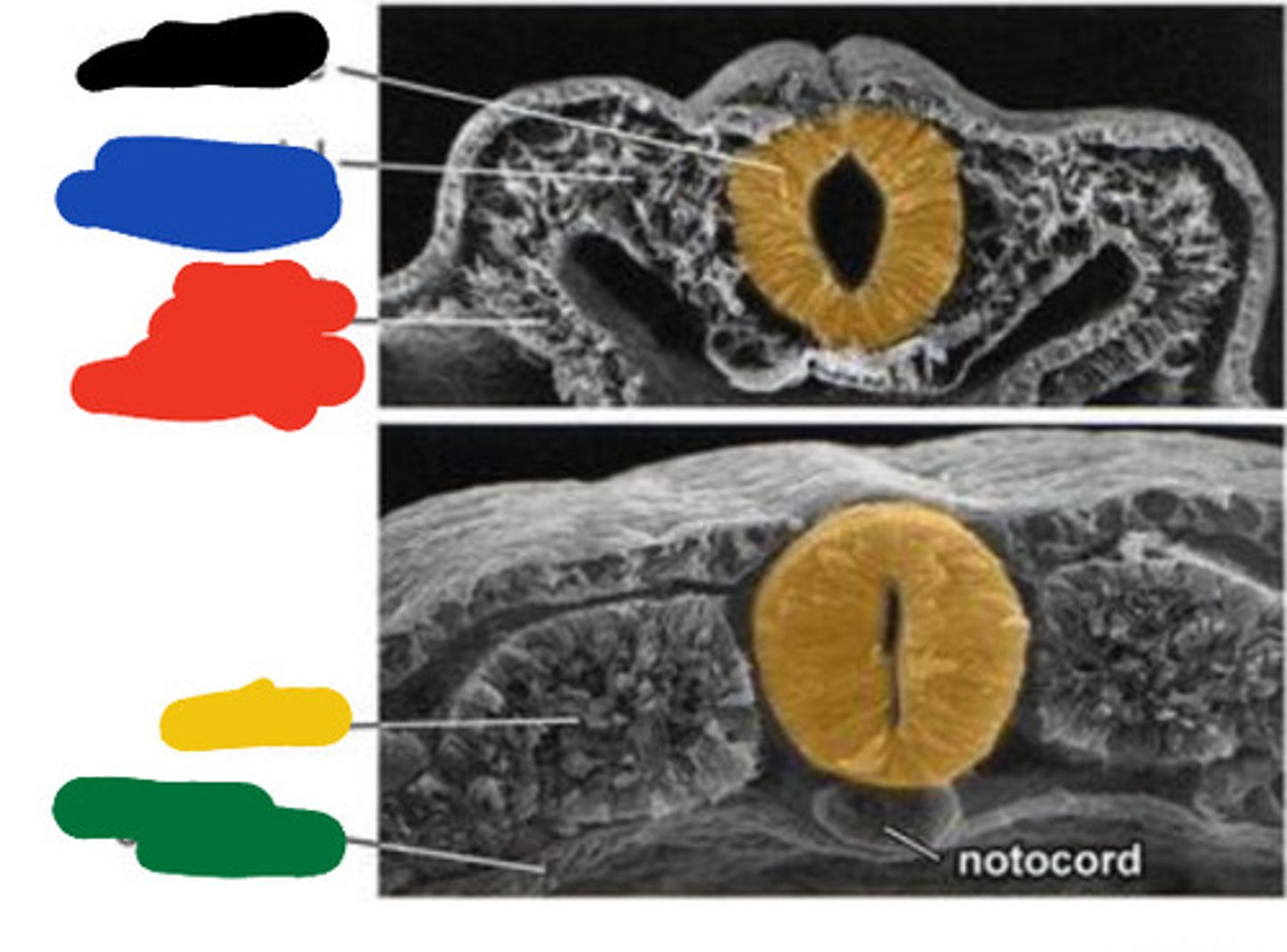
Primitive pit
Black
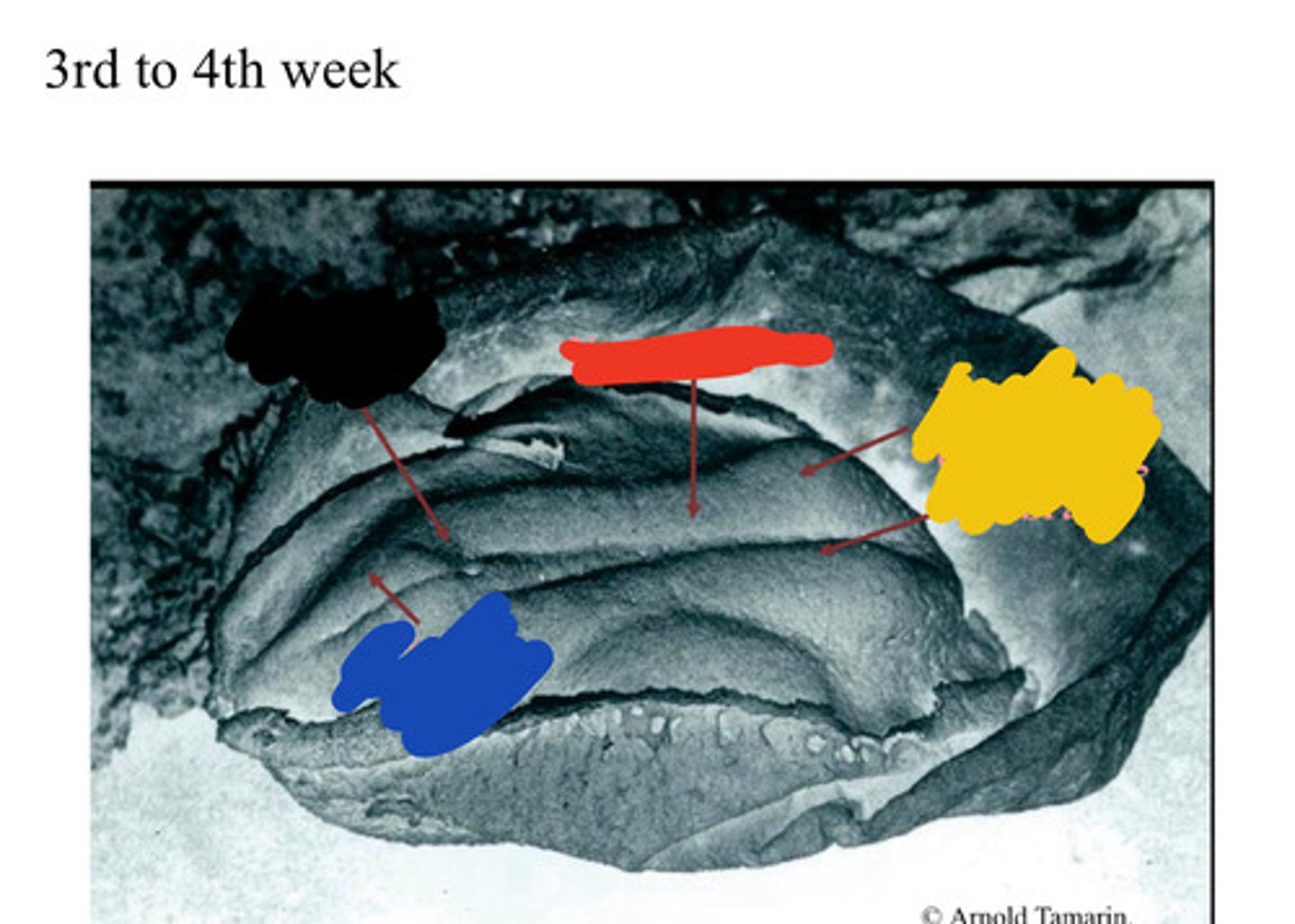
Primitive streak
Blue
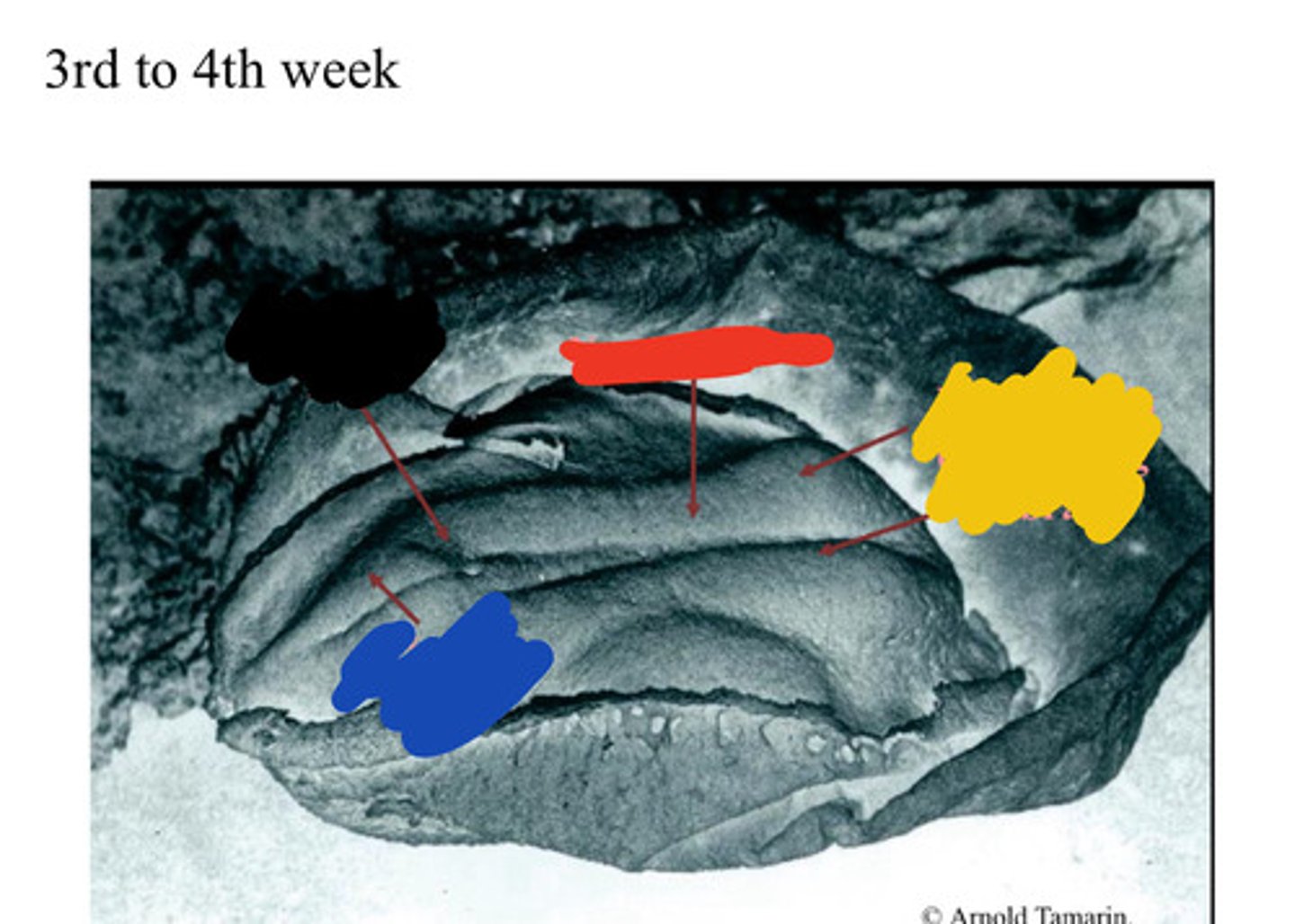
Neural groove
Red
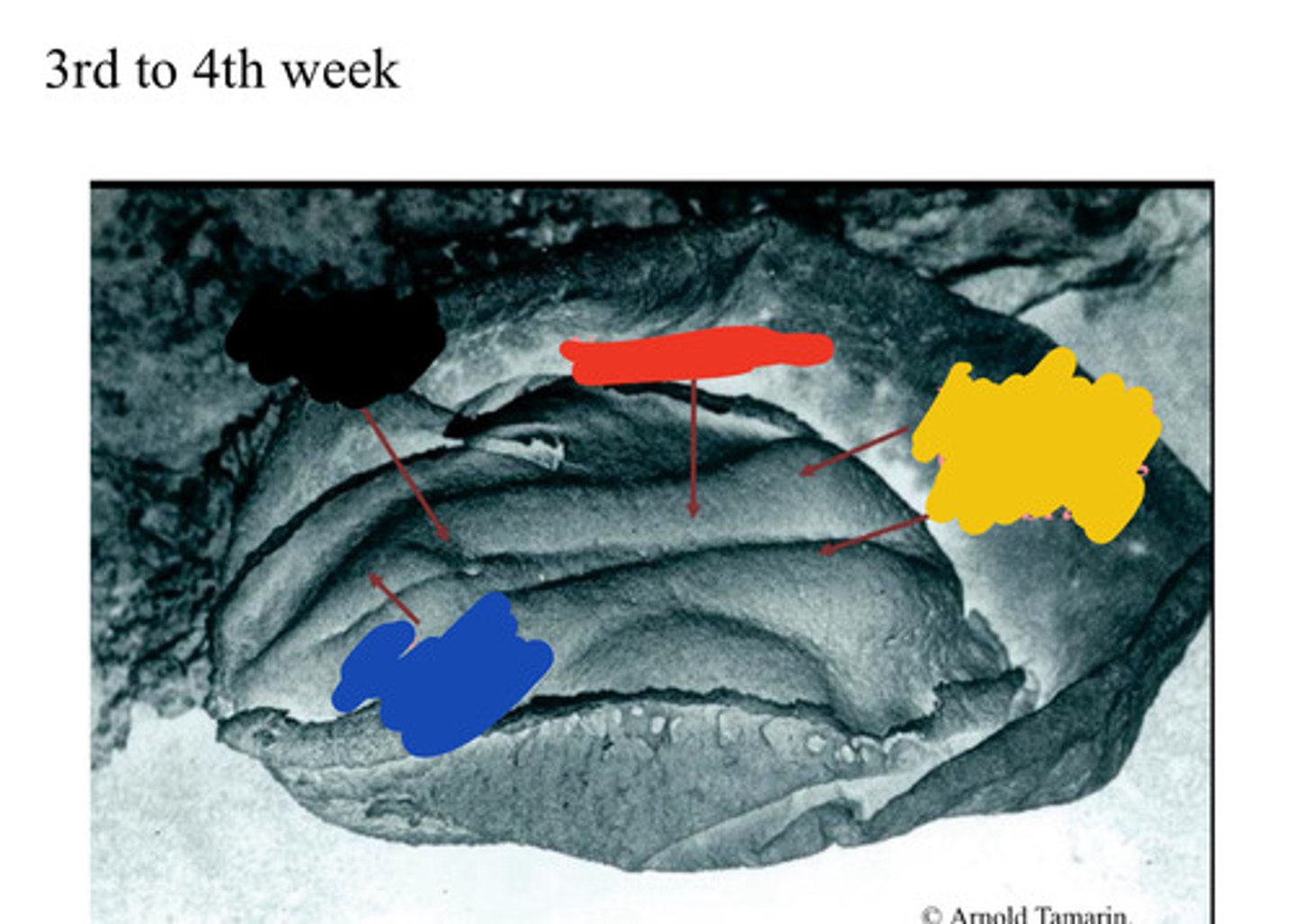
Neural folds
Developing forebrain
Yellow
Primitive streak
Black
Area of closing
Blue
Forebrain
Red
Hind brain
Yellow
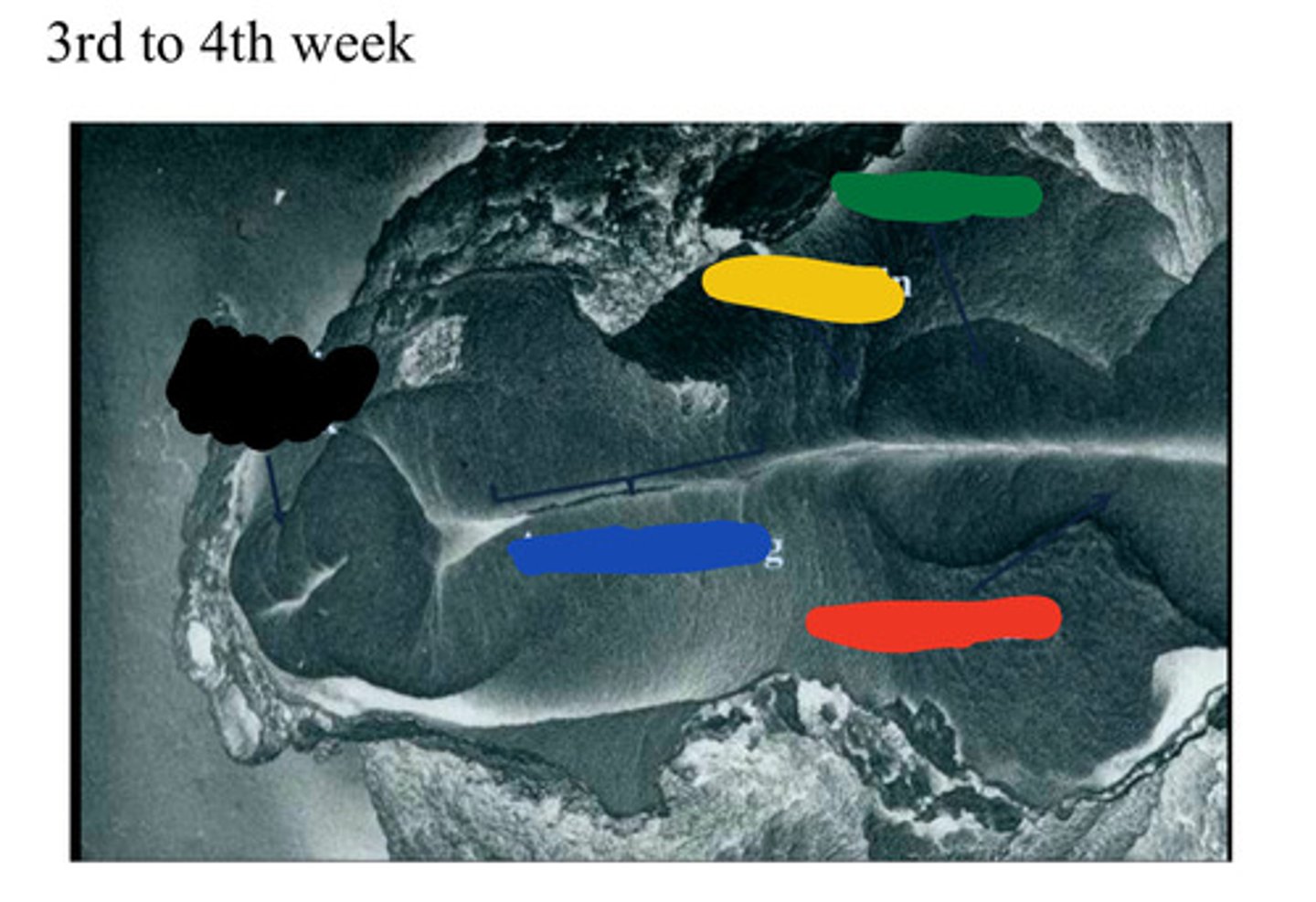
Midbrain
Green
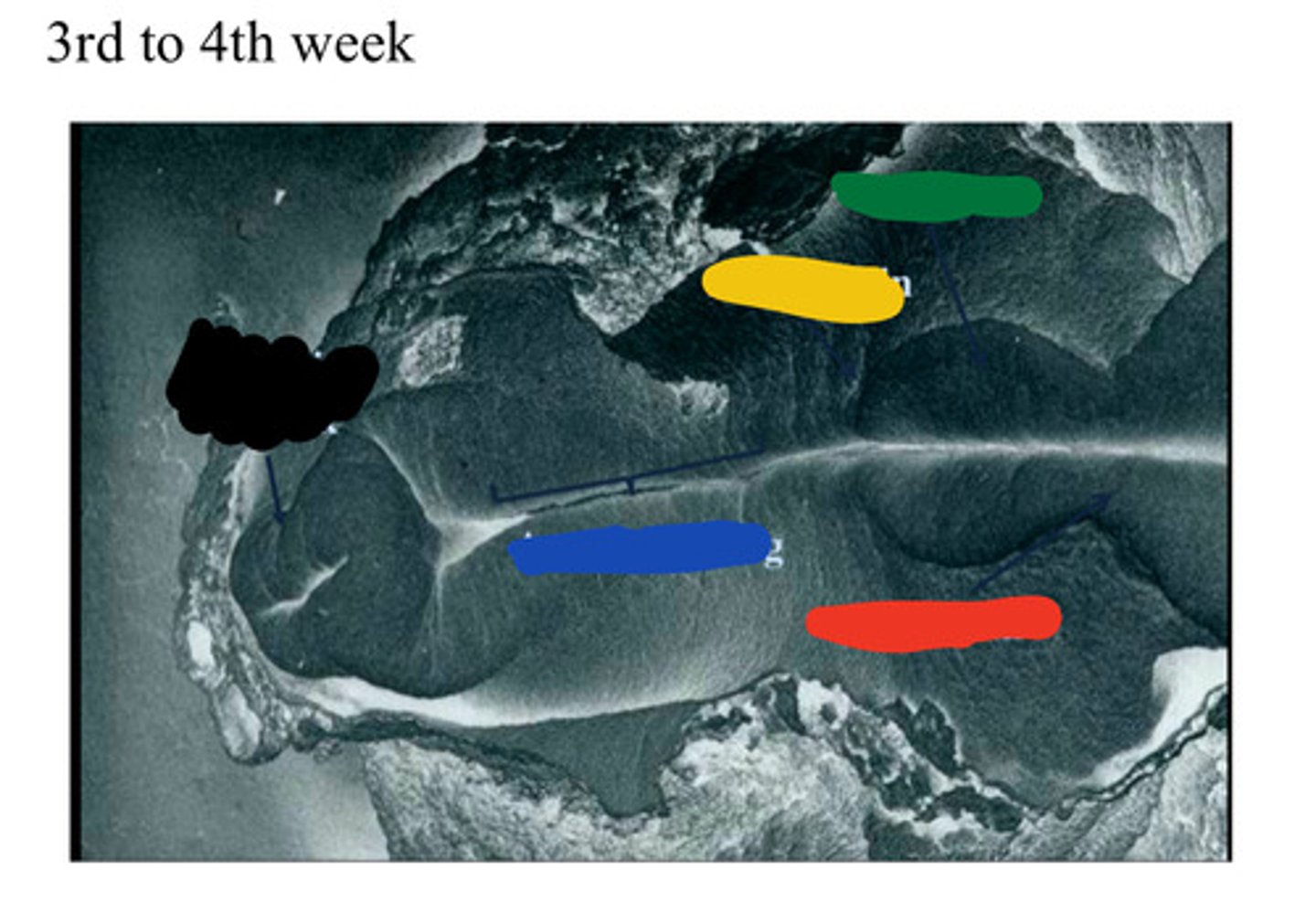
Anencephaly
congenital deformity in which some or all of fetal brain is missing
Spina bifida
a congenital defect that occurs during early pregnancy when the spinal canal fails to close completely around the spinal cord to protect it
Neural tube
Both anencephaly and spina bifida are defects in closure of
stomatodeum
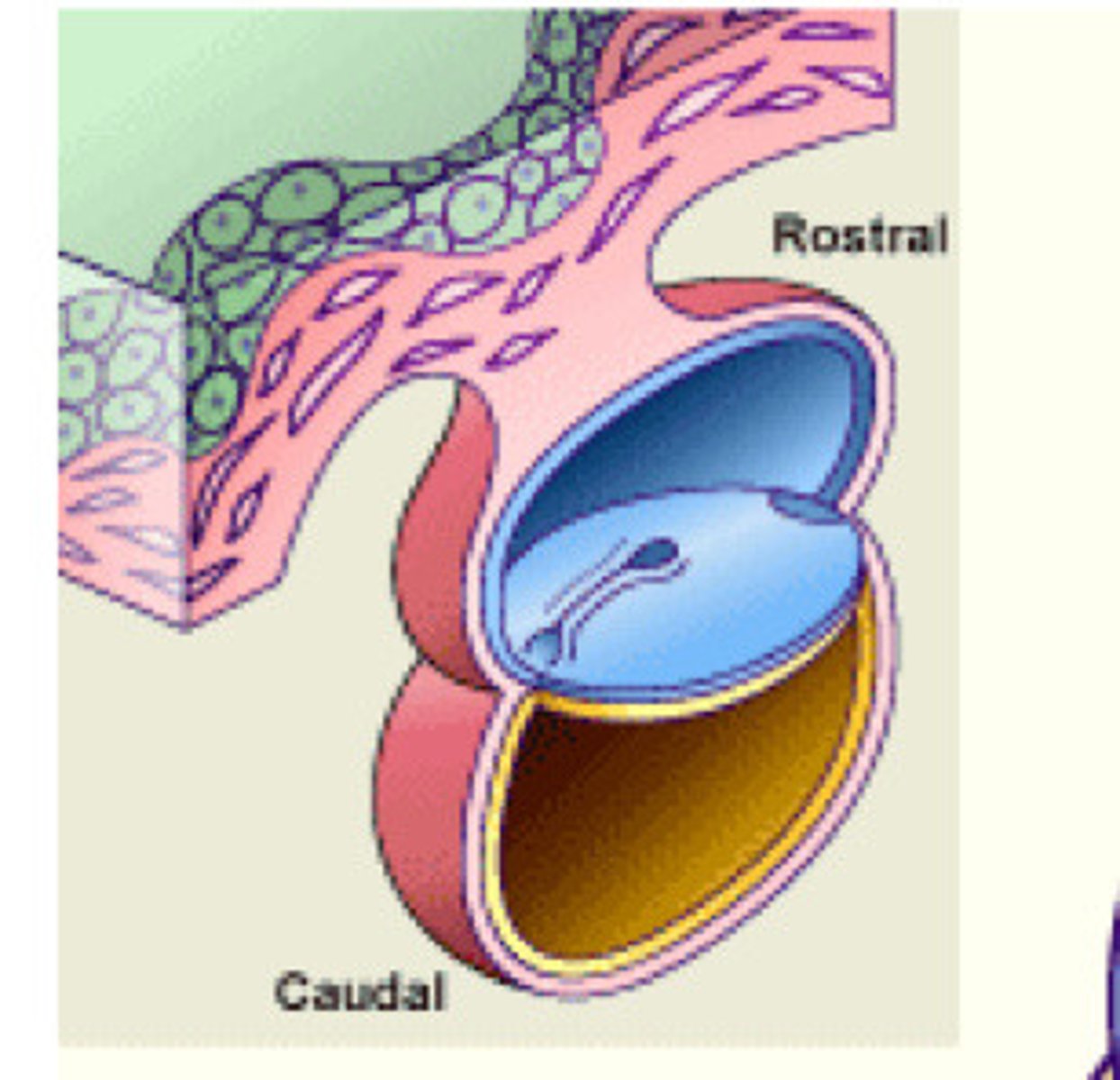
The head fold is critical to the
formation of the primitive oral
cavity (__) and
foregut.
buccopharyngeal membrane
separates the stomatodeum (primitive mouth) and the foregut. It is composed of ectodermal and endodermal tissue
Cephalic folding
Results in head development
Elongation brings only ectoderm
There is no mesoderm above the pituitary stalk
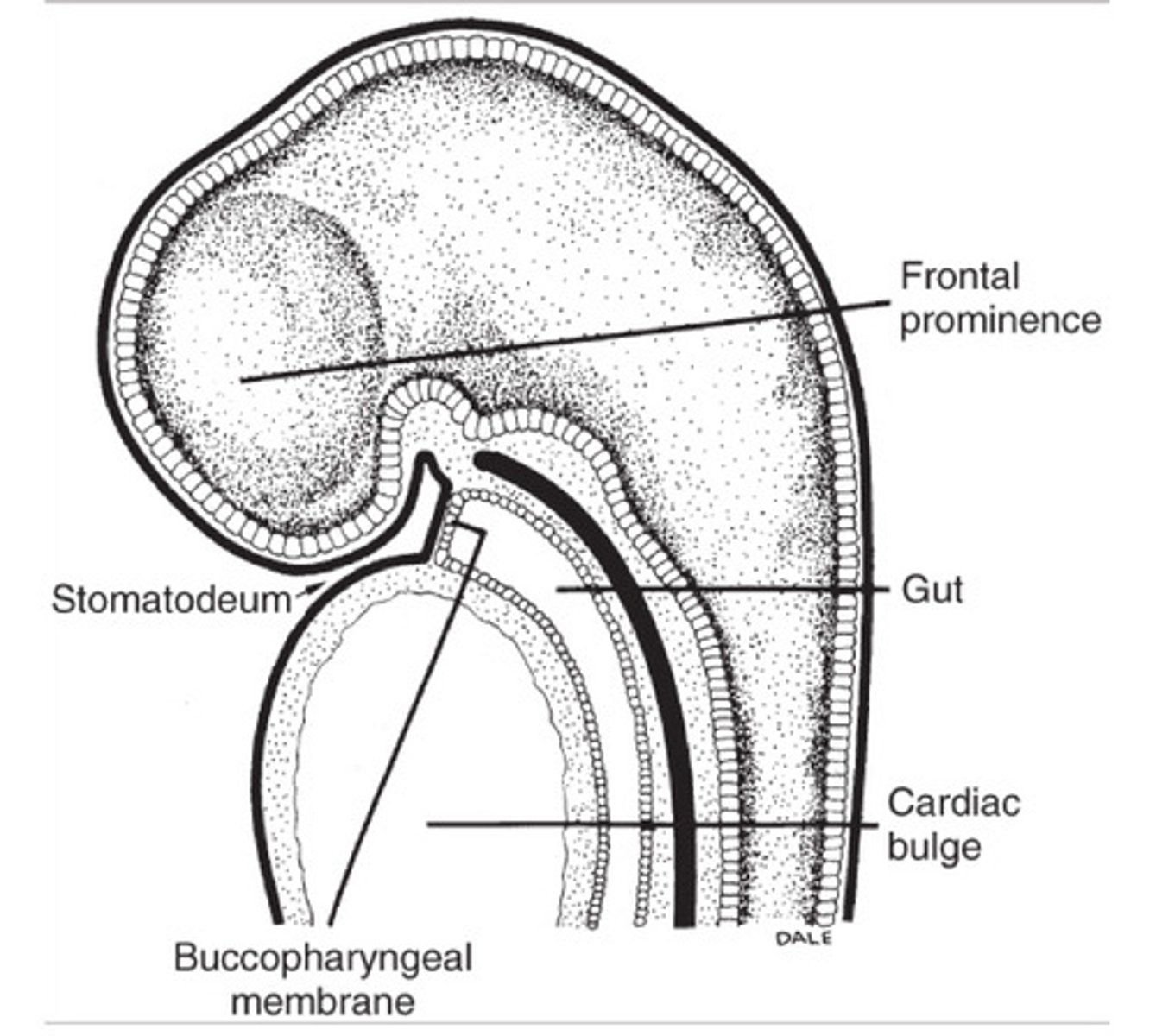
Stomatodeum
primitive oral cavity
Frontal prominence
Bulge in the forehead region that forms the upper facial area in the embryo.
Cardiac bulge
What is the inferior boundary of the stomodeum?
stomatodeum
When the __ is first formed, it is delimited rostrally by the frontal prominence and caudally by the developing cardiac bulge.