Chapter 2 AP Micro
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
economic systems
a particular set of institutional arrangements and a coordinating mechanism to respond to the economizing problem
differences of economic systems
who owns the factors of production (resources)
the method used to coordinate, motivate, and direct economic actively
Laissez-Faire Caplitalism
very limited government involvement
limited to: protecting private property and establishing a legal government (enforce contracts, market interactions)
proponents argue
government will be corrupter by special interest if it is involved in the economy: benefits special interests
government should only prevent people and firms from coercing one another; protection only; leads to mutually beneficial transactions
never been tried: every government has been more involved
Command System (Communism or Socialism)
government owns most resources
central economic plan set and enforced by the government
production goals, resource distribution, consumer vs. capital balance
not as prevalent anymore
market system (capitalism or mixed economy)
private sector: private ownership of resources, uses markets, businesses make individual decisions for their own benefit, participants act in their own self-interest, profit motivates innovation
government: economic initiatives (unemployment/inflation), rules for economic activity, provides goods and services, modifies income
private property
characteristic of the market system
private (non-governmental) ownership of resources
can do what they want with them
encourages cooperation (mutually agreeable transaction), investment, innovation, exchange, maintenance of property, economic growth
intellectual property (patents and copyrights)
freedom of enterprise and change
characteristic of the market system
enterprise: private sector can obtain and use resources to produce what they want and sell products as they want
choice: entities can use or dispose of resources and money as they want
can by anything you’re qualified to be
can spend on what you want
self-interest
characteristic of the market system
each country pursues its own goal
maximize profit
directs economy
competition
characteristic of the market system
2+ entities pursuing the same goal or resource
diffuses economic power: limits abuse of power
free to enter or leave market
markets and prices
characteristic of the market system
any mechanism that brings buyers and sells together
prices are determined by a combination of firms and consumers: dollar voting
technology and capital goods
characteristic of the market system
new innovations produce profit for the innovator
inspires new technology and capital: keep what you make
specialization
characteristic of the market system
use of resources to make a particular or a few things
exchange them for other goods/services
division of labor
uses different abilities: promotes efficiency
fosters learning by doing: develops skill and technique
saves time: no shifting from one task to another
geographic specialization: use particular land resources efficiently
use of money
characteristic of the market system
medium of exchange: buys what’s needed/wanted and simplifies trade: no bartering
can be anything agreed upon
active, but limited, government
characteristic of the market system
government is active but within prescribed limits
five fundamental questions
what will be produced?
whatever makes a profit: consumers ultimately decide →dollar voting, directs resources to successful products/industries
how will the goods and services by produced?
combination of resources that produces a lowest cost per unit: maximizes profit, promotes efficiency
who will get the output?
whoever is willing and able to pay: dependent on income and prices
how will the system accommodate change?
self-interest will direct firms towards profit: moves resource allocation, ultimately consumers decide
how will the systems promote progress?
desires: more output, higher standard of living
technological advance: creative destruction- new methods will wipe out companies that don’t change
capital accumulation: companies dollar vote for resources, including capital
dollar voting
consumers have full power to choose
consumer purchasing decisions act as "votes," determining which products and firms succeed or fail in a market economy
by buying specific goods, consumers signal demand, prompting firms to produce more of what is favored, thus dictating resource allocation and shaping corporate behavior
Adam Smith’s “The Wealth of Nations”
the individual self-interest of firms and resource provides will promote public welfare: new products, technologies, techniques
competition makes businesses responsive to consumers
efficiency: meets the wants of society, new was equals more profit
incentives: profit as a motivator
freedom: can do what you want
Demise of the Command Systems
why didn't they work
coordination problem: tried to make decisions for entities, too much or too little produced, failure to meet targets in one industries effects others, lack of variety
quality was success gauge: often at an economic loss, changed by how things were produced (weight vs. number)
incentive problem: meeting quota was all that mattered (shortages or surpluses), no reward for success/punishment for “failure”
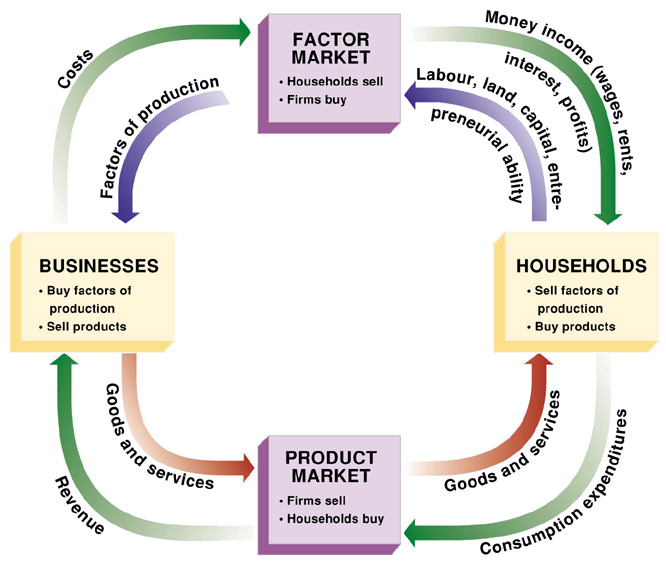
households
part of the circular flow model
one or more people occupying a unit of housing
buy goods and services
provide resources
businesses
part of circular flow model
buy resources
provide goods and services
sole proprietorship business
owned and operated by one person
+: decision making control
-: limited funding; unlimited liability
partnership business
two or more individuals own and operate business
+: increased funding; some specialization
-: still limited funding; unlimited liability; shared decision making
cooperation business
legal entity that can acquire resources, own assets, produce and sell products, incure debts, extend credit, sue and be sued
+: limited liability; funding
-: principle-agent problem
produce market
part of circular flow model
mechanisms selling goods and services
resource market
part of circular flow model
mechanisms selling land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial skill
circular flow diagram
how the market deals with risk
profit system: the desire for profit and the fear of loss pushes people and firms to manage risk
shielding employees and suppliers from business risk: contracts with employees and other businesses must be honored (even if you’re operating at a loss)
dealing with losses: cannot choose if losses continue, don’t have to share profits
benefits of restricting businesses risk to owners:
attracting inputs- resource providers sell resources without worrying about profits
focusing attention- attention is paid to managing risk: avoid losses