Lecture 4: Intro to Lab Testing
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Reasons to Order Lab Test
Screen
Diagnose
Manage Therapy
Prognosis
Osler’s Rule
If patient < 50 y/o, look for one etiology/one disease to explain all abnormal lab results
“Gold standard” test
Recognized best methodology against which new tests are compared
Test Accuracy
Test measures the true amount of a substance in a sample
Test Precision
Degree that result is consistently reproducible
Preanalytic events that compromise test results
Hemolysis #1 cause of rejection
Misidentification
Handling
Physiologic/biologic variation
Drugs & other interfering substances such as Biotin supplements (interfere with TSH, Troponin, T3-T4, Vit D levels, etc. in immunoassays)
Meals, hydration
Analytic events that compromise test results
Testing inaccuracies in the lab, e.g., bad reagents, bad instrument, etc.)
Rare
Postanalytic events that compromise test results
Errors in preparing or transmitting reports → result assigned to wrong patient or switched with another patient
Age-related variation in children
↑ Blood Lymphocyte count over adult range
↑ Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in children & teens above adult from osteoblasts in active growth plates
Age-related variation in elderly
Albumin, total protein decrease starting mid-adult
GFR decreased
Creatinine decreased (lower muscle mass)
Muscle-related enzymes (AST, CPK) decreased (lower muscle mass)
Lymphocytes reduced
What common hormone shows a marked diurnal variation?
Cortisol highest in morning
Nicotine/tobacco smoke affects
↑ glucose, catecholamines, cortisol, free fatty acids; neutrophils; carboxyhemoglobin (Hb + CO due to carbon monoxide); ↑ CEA (Carcinoembryonic antigen)
Alcohol affects
↑ GGT (gamma glutamyl transferase) & Triglycerides
Caffeine affects
↑ catecholamines, glucose
Exercise/physical training/exertion affects
Strenuous exercise (post-marathon, etc.): ↑ muscle enzymes AST, CK, LD & ↑ lactic acid
Well-trained athletes: ↓ glucose, WBCs, baseline CK
↑ bilirubin (hemolysis during exercise), ↑ BUN (due to high-protein diet; dehydration)
“Normal range”/Reference range
Values falling within 2 Standard Deviations from test mean
95% will have a result in the “normal range
2.5% will have a result above the “normal range” & 2.5% below
True positive (TP)
Positive result in patient with a certain disease/condition
True negative (TN)
Negative result in a patient who is without the disease
False positive (FP)
Positive result in a patient without disease
False negative (FN)
Negative result in a patient who has a disease
Ulysses Syndrome
The ill effects of extensive diagnostic investigations conducted because of a false-positive result during routine laboratory screening
Sensitivity
True Positives/(True Positives + False Negatives)
Specificity
True Negatives/(True Negatives + False Positives)
Lower the prevalence
Higher the False positive rate
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen)
Made in Liver from Ammonia and excreted via Kidneys
Sensitive marker of decreased glomerular filtration (GFR)
↑ BUN & Creatinine = Azotemia (urea and nitrogen in blood)
↑ in renal disease & Poor renal perfusion (dehydration, shock, heart failure, etc.)
↑ in Catabolic states (fever, burns, diabetes, intense exercise)
↑ in GI bleeding due to digestion of blood into proteins & ↑ BUN production
Creatinine
Catabolic end-product skeletal muscle Creatine (stores energy to make ATP)
Production is constant & proportional to muscle mass
Excreted by kidney: Indirect measurement of glomerular filtration (GFR)
Bilirubin
Waste product created from breakdown of Hemoglobin
Initially made in Unconjugated form (Indirect), then Conjugated in the liver (Direct bilirubin) & excreted via the bile ducts into GI tract
Prehepatic (unconjugated) hyperbilirubinemia is due to hemolysis
Intrahepatic (liver disease) as hepatitis, cirrhosis; liver failure: ↑ may be a mix of Unconjugated & Conjugated bilirubin
Posthepatic: due to large bile duct obstruction, as from gallstone (↑ Conjugated form)
AST (Aspartate aminotransferase)
Widely distributed; mitochondria & cytosol
Elevated in: Liver (hepatocyte) injury (“hepatitis”)
Skeletal muscle injury
ALT (Alanine aminotransferase)
In the cytosol
Elevated in: Liver injury
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
Major source is from the Hepatobiliary system in cholestatic liver disease
Other from Bones of growing children & teenagers
Placenta (rises in pregnancy)
Minor sources: intestine, kidneys
Creatine Kinase (CK)/ Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK)
Total CK elevated in:
Skeletal muscle injury: trauma, intense exercise, Statin (drug) therapy; hypothyroidism; myositis; rhabdomyolysis
Myocardial infarction
Stroke/brain trauma
Globulins
Total Protein - Albumin
Albumin
Made in the Liver
Maintains oncotic pressure
Albumin decreased:
Impaired synthesis: malnutrition, malabsorption, hepatic disease
Increased loss: renal disease with proteinuria (particularly nephrotic syndrome), protein-losing gastroenteropathy
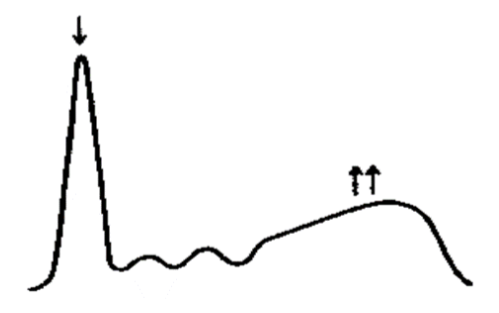
Polyclonal Gammopathy: chronic infection or inflammation
Decreased albumin
Polyclonal increase in γ globulins
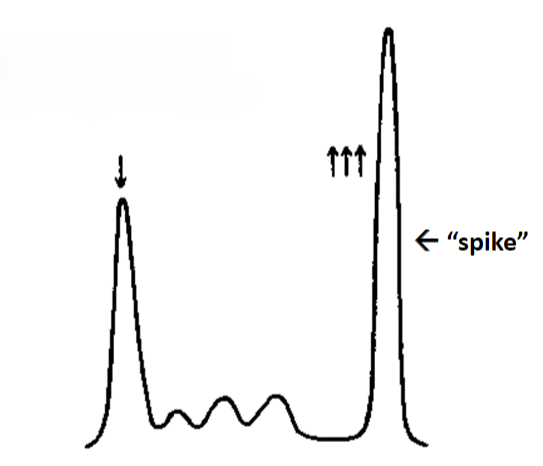
Monoclonal Gammopathy: neoplastic plasma cell proliferation
“Monoclonal spike” potentially Malignant Multiple Myeloma
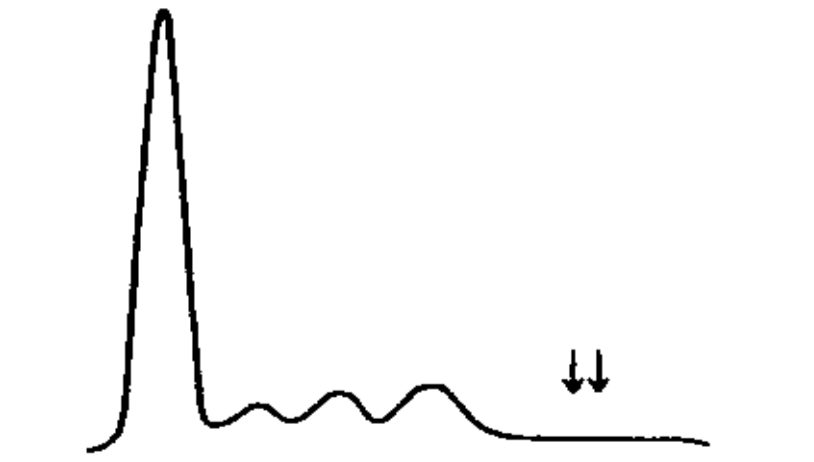
Hypogammaglobulinemia (or Agammaglobulinemia)
Indicative of B-cell immunodeficiency, congenital or acquired
Patient is at increased risk for pyogenic infections
Acute phase response
Inflammation (infectious or noninfectious, acute or chronic)
even if localized, if associated with significant production of inflammatory cell Cytokines (mainly TNF, IL-1, IL-6), may induce systemic reactions called Acute-phase response
Manifestations include Fever (>100°F; >38°C), production of acute-phase proteins (mainly by the Liver), Leukocytosis, & in cases of extreme cytokine production, Shock
Common Acute Phase Reactants (APR)
C-reactive protein
General scavenger molecule
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
Speed of fall of RBCs in a column of blood in mm/hr
ESR is a nonspecific indicator of inflammation
Procalcitonin
More severe the stimulus, the higher the elevations
Less than lower limit: bacterial infection is unlikely
Low level: localized infection or autoimmunity
High level: strongly favors severe bacterial infection
Also used to monitor effectiveness of Antibiotic Rx
An increase in what analyte implies systemic hypoperfusion?
Lactic Acid (Lactate) as an indicator of Shock
Lactate rises with all causes of systemic hypoperfusion