Foundations of Medical Science - PA614
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts from the Foundations of Medical Science course PA614 at Brenau University, focusing on metabolism, physiology, biochemistry, and the role of different molecules in human health.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What does catabolism refer to in metabolism?
Energy-releasing decomposition reactions that produce smaller molecules and release useful energy.
What is anabolism?
Energy-storing synthesis reactions that require energy input and produce larger molecules like glycogen, protein, or fat.
What is the first law of thermodynamics as it relates to metabolism?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
What is the Gibbs Free Energy (G)?
It represents the usable energy in a system, with energy always lost as heat in chemical transformations.
Define a molecule and the types of bonds they can form.
A molecule is made up of two or more chemically bonded atoms, which can form covalent, ionic, or hydrogen bonds.
What are the primary functions of proteins in the body?
Proteins serve as structural components, enzymes, and are involved in transport and signaling.
What is the significance of ATP in cellular metabolism?
ATP is the primary energy carrier in cells, storing energy in its covalent bonds.
What is glycolysis?
A metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, producing a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
What are three important monosaccharides?
Glucose, galactose, and fructose.
What is the role of insulin in carbohydrate metabolism?
Insulin regulates blood glucose levels and promotes glucose uptake by cells.
Explain the process of transamination in amino acid metabolism.
Transamination exchanges amino groups between amino acids and α-keto acids, forming new amino acids.
What is lipogenesis?
The metabolic process through which excess carbohydrates or fatty acids are converted into fat.
Name the three ketone bodies produced during ketogenesis.
Acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate.
What are the two primary pathways for amino acid catabolism?
Deamination and transamination.
What happens during oxidative phosphorylation?
Electrons are transferred through the electron transport chain, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
What is gluconeogenesis?
The metabolic pathway that generates glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates.
Describe the function of coenzymes.
Coenzymes assist enzymes in catalyzing biochemical reactions and often transport electrons.
What is the primary storage form of carbohydrates in the body?
Glycogen.
What is the difference between a molecule and a compound?
A molecule is two or more atoms chemically bonded, while a compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements.
What is the first law of thermodynamics as it relates to metabolism?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Define a molecule and the types of bonds they can form.
A molecule is made up of 2 or more chemically bonded atoms, which can form covalent, ionic, or hydrogen bonds.
What are the primary functions of proteins in the body?
Proteins serve as structural components, enzymes, and are involved in transport and signaling.
What is the role of insulin in carbohydrate metabolism?
Insulin regulates blood glucose levels and promotes glucose uptake by cells.
Explain the process of transamination in amino acid metabolism.
Transamination exchanges amino groups between amino acids and α-keto acids, forming new amino acids.
What are the 2 primary pathways for amino acid catabolism?
Deamination and transamination.
What happens during oxidative phosphorylation?
Electrons are transferred through the electron transport chain, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
Describe the function of coenzymes.
Coenzymes assist enzymes in catalyzing biochemical reactions and often transport electrons.
What is the primary storage form of carbohydrates in the body?
Glycogen.
What is the difference between a molecule and a compound?
A molecule is 2 or more atoms chemically bonded, while a compound is a molecule that contains at least 2 different elements.
Describe the first step of glycolysis.
Glucose is phosphorylated by the enzyme hexokinase to form glucose-6-phosphate, consuming 1 molecule of ATP.
Describe the second step of glycolysis.
Glucose-6-phosphate is rearranged into fructose-6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucose isomerase.
Describe the third step of glycolysis.
Fructose-6-phosphate is phosphorylated by the enzyme phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) to form fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, consuming 1 molecule of ATP.
Describe the fourth step of glycolysis.
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is split by the enzyme aldolase into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P).
Describe the fifth step of glycolysis.
The enzyme triose phosphate isomerase converts DHAP into a second molecule of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P).
Describe the sixth step of glycolysis.
Each G3P is oxidized and phosphorylated by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, producing 2 molecules of NADH.
Describe the seventh step of glycolysis.
The enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase transfers a phosphate group from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP, forming 3-phosphoglycerate and producing 2 molecules of ATP.
Describe the eighth step of glycolysis.
The enzyme phosphoglycerate mutase relocates the phosphate group in 3-phosphoglycerate to form 2-phosphoglycerate.
Describe the ninth step of glycolysis.
The enzyme enolase removes a water molecule from 2-phosphoglycerate to create phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP).
Describe the tenth step of glycolysis.
The enzyme pyruvate kinase transfers a phosphate group from PEP to ADP, forming pyruvate and producing 2 molecules of ATP.
What is the Lactic Acid Cycle (Cori Cycle)?
A metabolic pathway in which lactate produced by anaerobic glycolysis in muscles moves to the liver, is converted to glucose, and then returns to the muscles.
Describe the conversion of pyruvate during the Lactic Acid Cycle in muscles.
Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is reduced to lactate by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, regenerating NAD+ to sustain glycolysis.
What happens to lactate in the liver during the Lactic Acid Cycle?
Lactate is oxidized back to pyruvate and subsequently converted into glucose via gluconeogenesis.This glucose can then be released into the bloodstream or used for energy in the muscles.
What is the net energy cost of the Lactic Acid Cycle?
The cycle consumes 6 ATP in the liver but only produces 2 ATP in the muscle, resulting in a net cost of 4 ATP.
What is the primary location of the electron transport chain (ETC) in eukaryotes?
The inner mitochondrial membrane (cristae).
What are the primary electron donors for the electron transport chain?
NADH and FADH_{2}, which are produced during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
Describe the function of the complexes in the electron transport chain.
The complexes pass electrons down a series of redox reactions, using the released energy to pump protons (H^{+}) from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space.
What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, and what does it form?
Oxygen and it forms water (H2O) as a byproduct.
What is the role of ATP synthase in oxidative phosphorylation?
It utilizes the proton-motive force created by the H^{+} gradient to catalyze the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (P_{i}).
How many major protein complexes are involved in the electron transport chain?
There are 4 major complexes: Complex I (NADH dehydrogenase), Complex II (Succinate dehydrogenase), Complex III (Cytochrome bc_{1} complex), and Complex IV (Cytochrome c oxidase).
Explain the concept of chemiosmosis in the electron transport chain.
Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions (protons) across a semipermeable membrane down their electrochemical gradient to generate chemical energy in the form of ATP.
What is step 1 of the kreb cycle?
Oxaloacetate becomes citrate
This step combines a two-carbon with a four-carbon molecule to form the six-carbon citrate molecule and releasing the coenzyme. This is done with the help of enzyme citrate synthase
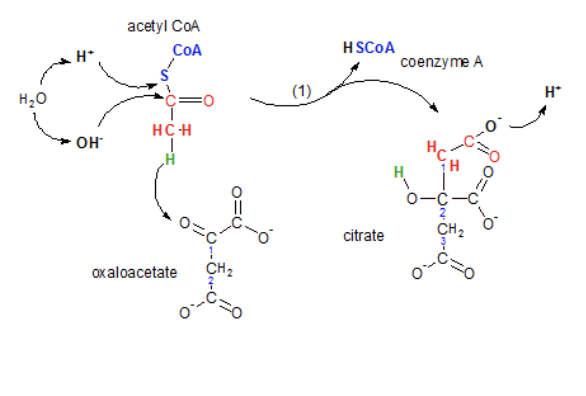
What is step 2 of the kreb cycle?
Citrate becomes isocitrate
Isomerization rearranges the atoms within the molecule changing it’s structure
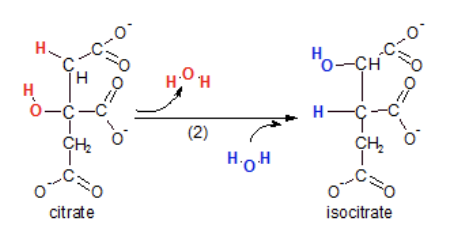
What is step 3 of the kreb cycle?
Isocitrate becomes a-ketogluterate
Decarboxylation releases carbon dioxide creating an a-ketogluterate. The reactant is also oxidized and NADH is produced
Enzyme involved is isocitrate dehydrogenase and at this point we have 2 net ATP and 6 net NADH + H+ (was previously 4 NADH)

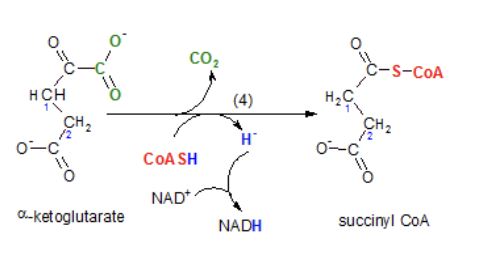
What is step 4 of the kreb cycle?
a-ketoglutarate becomes succinyl CoA
Decarboxylation releases a second carbon dioxide. This reactant is also oxidized again and NADH is produced. Coenzyme A is attached to the substrate.
8 Net NADH
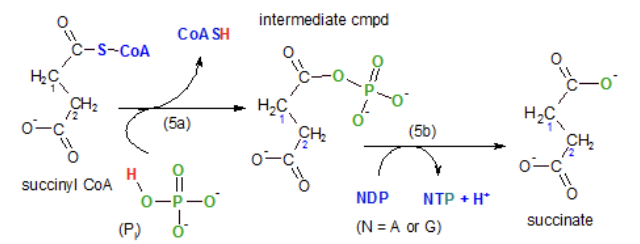
What is step 5 of the kreb cycle?
Succinyl CoA becomes succinate
A phosphate group replaces the coenzyme then it leaves the substrate becoming attached to a nucleotide diphosphate, either ADP or GDP. The triphosphate form is produced
Net ATP becomes 4
What is step 6 of the kreb cycle?
Succinate is dehydrogenates to become fumarate. The substrate is oxidized FADH2 (2 are created).
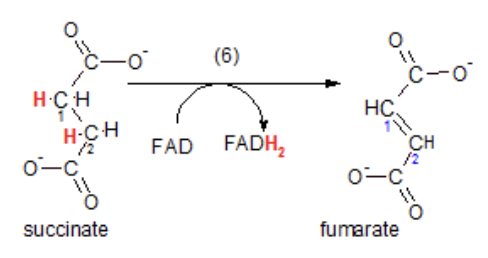
What is step 7 of the kreb cycle?
Fumarate is hydrated to become malate
‘The substrate is hydrated

What is step 8 of the kreb cycle?
Malate is dehydrogenated to become oxaloacetate via malate dehydrogenase.
The substrate is oxidized producing NADH and regenerating the oxaloacetate molecule
Net ATP= 4
Net NADH= 10
Net FADH= 2
What is the end product of glycolysis?
The production of two three-carbon pyruvate molecules, which become 2 acetyle-CoA molecules that can enter the kreb cycle. 2 NADH are also produced.
Metabolites at the end of the glycolysis and citric acid cycle for each glucose molecule?
CO2- 0 from glycolysis, 2 from intermediate step, and 4 from cycle= 6
ATP- 2 from glycolysis, 0 from intermediate step, and 2 from cycle= 4
NADH- 2 from glycolysis, 2 from intermediate step, and 6 from cycle= 10
FADH2- 2 from cycle totals= 2