OMM IV Midterm Glossary Terms
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Balanced Ligamentous Tension
According to Sutherland’s model, all the joints in the body are balanced ligamentous articular mechanisms. The ligaments provide proprioceptive information that guides the muscle response for positioning the joint, and the ligaments themselves guide the motion of the articular components.
Cerebrospinal fluid, fluctuation of
A description of the hypothesized action of cerebrospinal fluid with regard to the craniosacral mechanism.
Core link
The connection of the spinal dura mater from the occiput at the foramen magnum to the sacrum. It coordinates the synchronous motion of these two structures.
Cranial rhythmic impulse (CRI)
A palpable, rhythmic fluctuation believed to be synchronous with the primary respiratory mechanism.
Craniosacral mechanism
A term used to refer to the anatomical connection between the occiput and the sacrum by the spinal dura mater.
Craniosacral extension
1. Posterior movement of the base of the sacrum in relation to the ilia. (sacrum alone)
2. In Osteopathy in the cranial field, the sacral base moves antero-inferiorly as the sphenobasilar synchondrosis (SBS) descends and flattens during the exhalation phase of the primary respiratory mechanism. (craniosacral)
Craniosacral flexion
1. Anterior movement of sacral base in relation to the ilia. (sacrum alone)
2. In Osteopathy in the cranial field, it is said to occur when the sacral base moves postero-superiorly as the sphenobasilar synchondrosis (SBS) ascends and angulates during the inhalation phase of the primary respiratory mechanism. (craniosacral)
Compression of the fourth ventricle (CV-4)
A cranial technique in which the lateral angles of the occipital squama are manually approximated slightly exaggerating the posterior convexity of the occiput and taking the cranium into sustained extension.
Extrinsic corrective forces
Treatment forces external to the patient that may include operator effort, effect of gravity, mechanical tables, etc.
Exaggeration method
An osteopathic treatment strategy by which the dysfunctional component is carried away from the restrictive barrier and beyond the range of voluntary motion to a point of palpably increased tension.
Facilitated positional release (FPR)
A system of indirect myofascial release treatment. The component region of the body is placed into a neutral position, diminishing tissue and joint tension in all planes, and an activating force (compression or torsion) is added.
Intrinsic corrective forces
Voluntary or involuntary forces from within the patient that assist in the manipulative treatment process.
Inherent motion
Spontaneous motion of every cell, organ, system and their component units within the body.
Isokinetic contraction
1. A concentric contraction against resistance in which the angular change of joint motion is at the same rate.
2. The counterforce is less than the patient force.
Isokinetic exercise
Exercise using a constant speed of movement of the body part.
Membranous balance
The ideal physiologic state of harmonious equilibrium in the tension of the dura mater of the brain and spinal cord.
NMM-OMM
Certification in Neuromusculoskeletal Medicine and Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine. A certification granted by the American Osteopathic Association through the American Osteopathic Board of NMM & OMM since 1999.
Osteopathy in the Cranial Field (OCF)
A system of diagnosis and treatment by an osteopathic practitioner using the primary respiratory mechanism and balanced membranous tension.
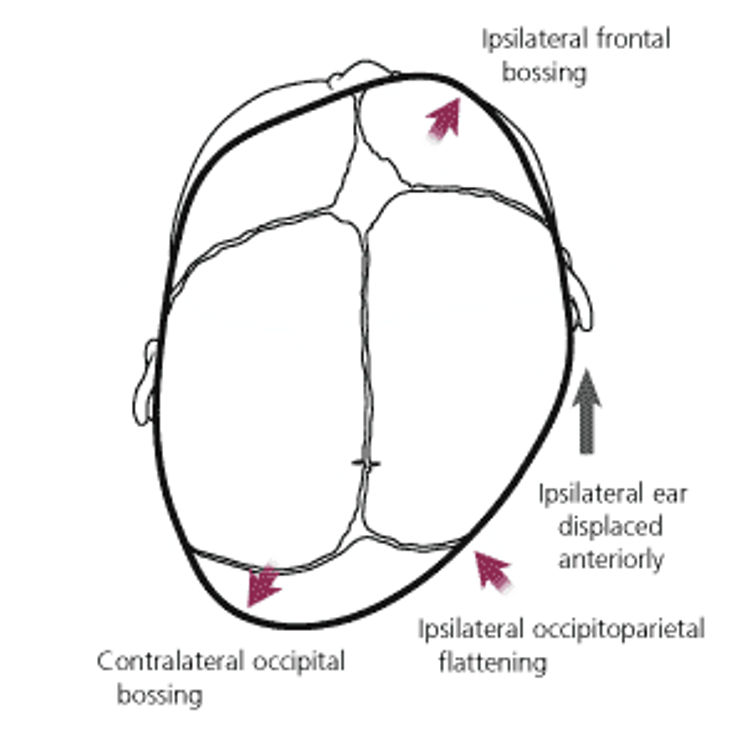
Plagiocephaly
Cosmetic issue. Distortion of the “circular” shape of head that can affect the function of different systems: reflux, recurrent otitis media, strabismus, learning problems
Primary respiratory mechanism
A conceptual model that describes a process involving five interactive, involuntary functions:
The inherent motility of the brain and spinal cord.
Fluctuation of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Mobility of the intracranial and intraspinal membranes.
Articular mobility of the cranial bones.
Mobility of the sacrum between the ilia (pelvic bones) that is interdependent with the motion at the sphenobasilar synchondrosis.
This mechanism refers to the presumed inherent (primordial) driving mechanism of internal respiration as opposed to the cycle of diaphragmatic respiration (inhalation and exhalation). It further refers to the innate interconnected movement of every tissue and structure of the body. Optimal health promotes optimal function and the inherent function of this interdependent movement can be negatively altered by trauma, disease states or other pathology.
Reciprocal tension membrane
The intracranial and spinal dural membrane including the falx cerebri, falx cerebelli, tentorium and spinal dura.
Scaphocephaly
Also called scaphoid head or hatchet head, it is a transverse compression of the cranium with a resultant mid-sagittal ridge.
SBS compression
Somatic dysfunction in which the basisphenoid and basiocciput are held forced together
SBS lateral strain
Sphenoid and occiput have rotated in the same direction around parallel vertical axes. These SBS strains are named for the position of the basisphenoid, right or left.
SBS sidebending-rotation
Sphenoid and occiput have rotated in opposite directions around parallel vertical axes and rotate in the same direction around an anterior-posterior A-P axis. They are named for the convexity, right or left.
SBS torsion
Sphenoid and occiput have rotated in opposite directions around an anterior-posterior (A-P) axis. It is named for the high greater wing of the sphenoid, right or left.
SBS vertical strain
Sphenoid and occiput have rotated in the same direction around parallel transverse axes. It is named for the position of the basisphenoid, superior or inferior.
Still point
A term used to identify and describe the temporary cessation of the rhythmic motion of the primary respiratory mechanism. It may occur during osteopathic manipulative treatment when a point of balanced membranous or ligamentous tension is achieved.
Springing technique
A low velocity/moderate amplitude technique where the restrictive barrier is engaged repeatedly to produce an increased freedom of motion.
Traube-Herring-Mayer wave
An oscillation that has been measured in association with blood pressure, heart rate, cardiac contractility, pulmonary blood flow, cerebral blood flow and movement of the cerebrospinal fluid, and peripheral blood flow including venous volume and thermal regulation. This whole-body phenomenon, which exhibits a rate typically slightly less than and independent of respiration, bears a striking resemblance to the primary respiratory mechanism.
Toggle technique
Short lever technique using compression and shearing forces.
V-spread
A technique using forces transmitted across the diameter of the skull to accomplish sutural gapping.