module 3: heart and blood vessels
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
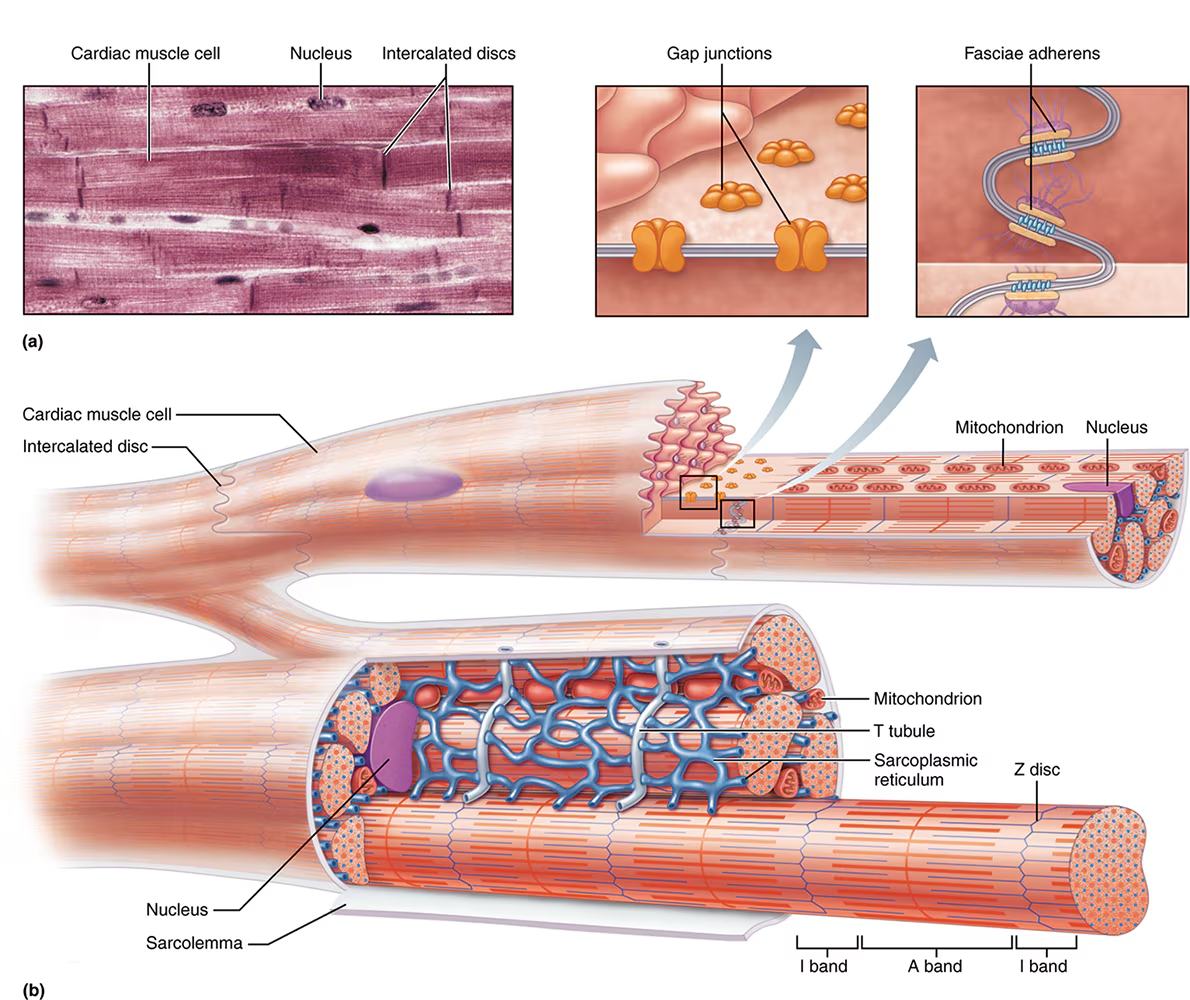
what are intercalated discs? what 2 regions are within the discs?
Intercalated discs are junctions that joint sarcolemma’s together like interlocking fingers, they contain 2 regions:
fasciae adherens
gap junctions
what is the function of the fasciae adherens within intercalated discs?
desmosome-like junctions: long, strong stitches
physically bind cells together
transmit the contractile force to adjacent cells
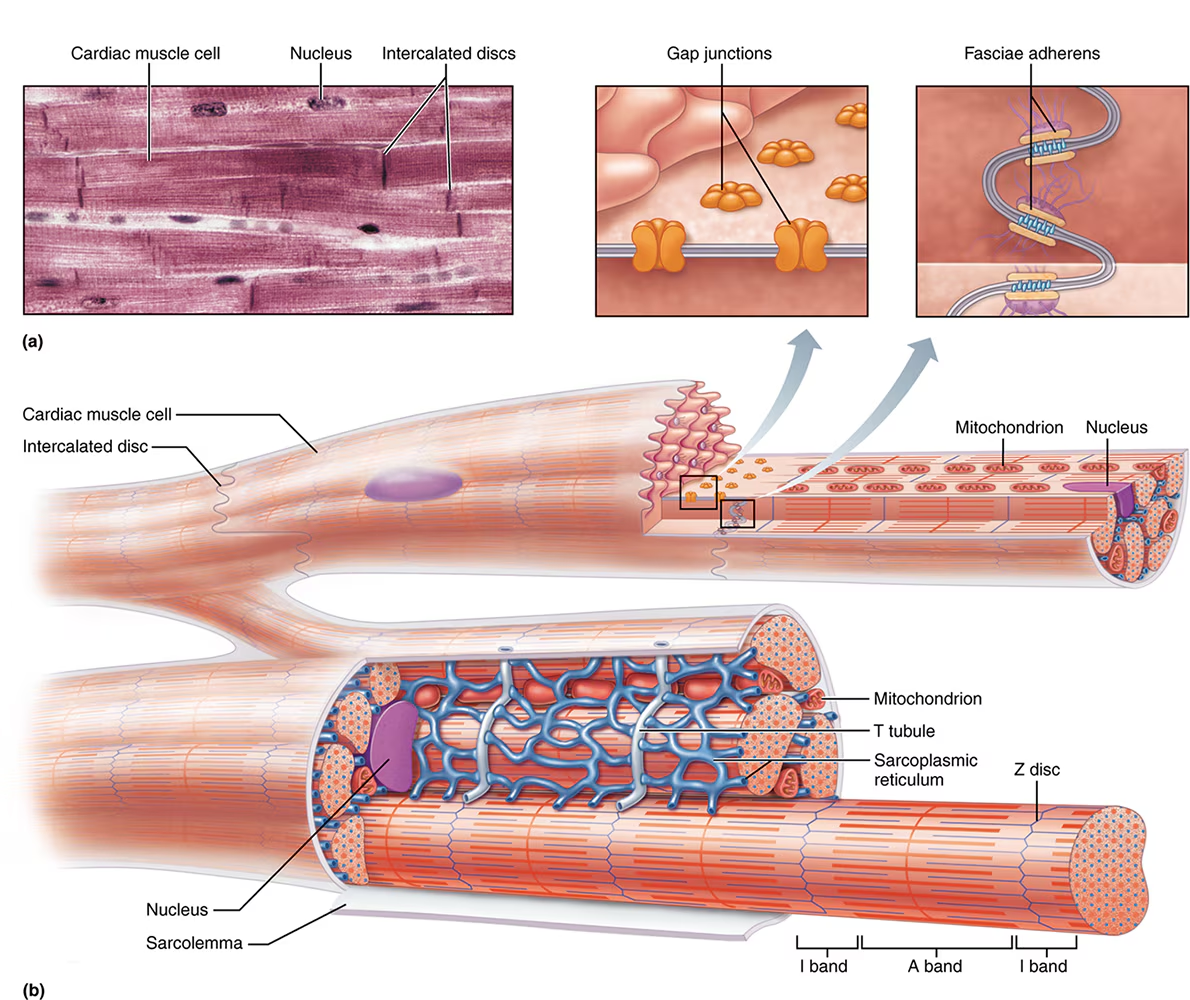
what is the function of the gap junctions within intercalated discs?
small channels made of connexons
allow passage of ions between cells: “"cell to cell communication”
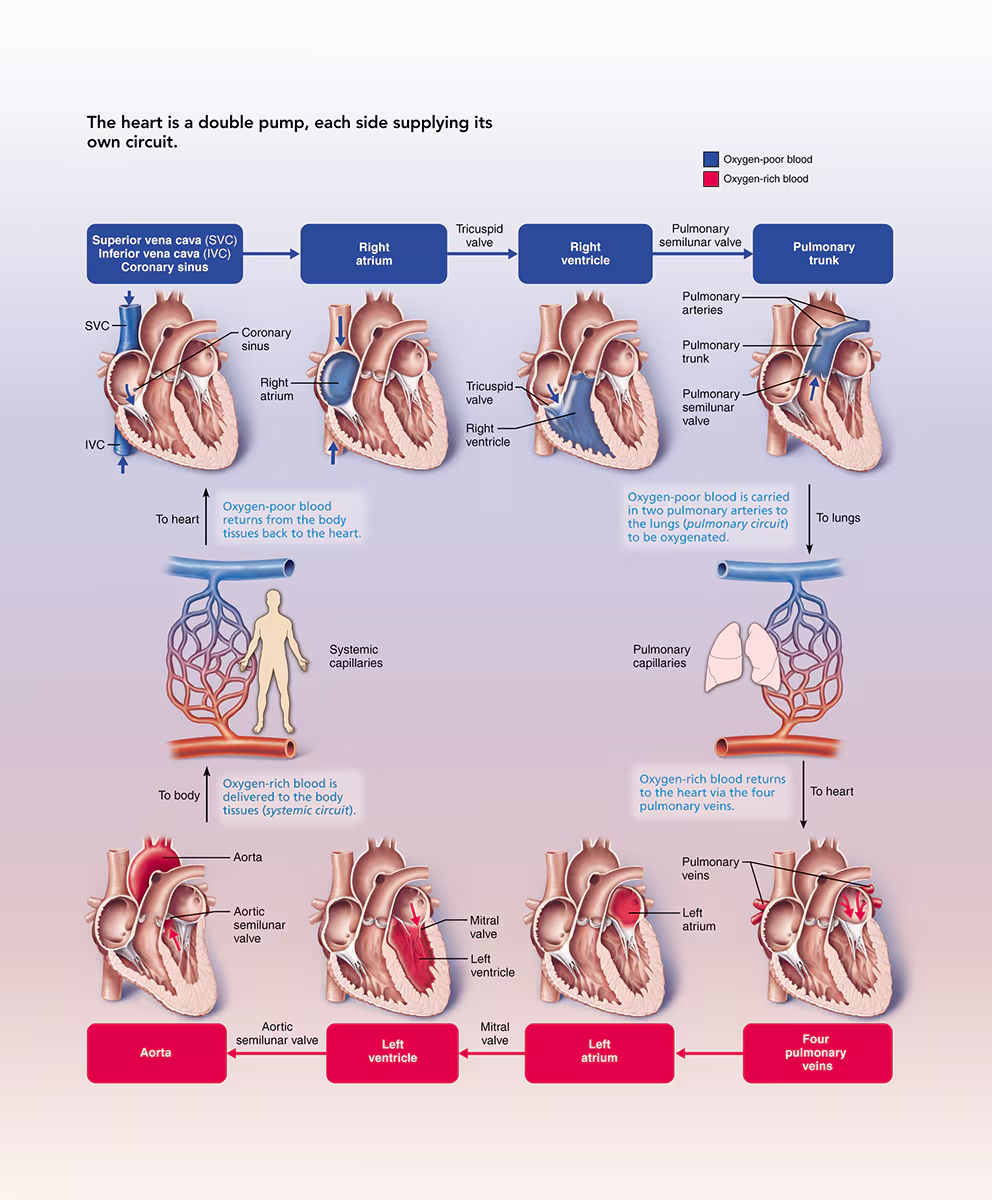
Flow of Blood (where is blood oxygenated/deoxygenated)
SVC / IVC / Coronary Sinus
Right atrium → tricuspid valves
Right ventricle → pulmonary semilunar valve
Pulmonary trunk / artery
Lung / pulmonary capillaries → back to the heart / pulmonary veins
Left atrium → mitral / bicuspid valve
Left ventricle (strongest chamber) → aortic semilunar valve
aorta → body
Arrhythmias: what is tachycardia and bradycardia (include bpm)?
Tachycardia: heart beats too fast (>100bpm)
Bradycardia” heart beats too slow (<60bpm)
Arrhythmias (variation from normal heart rhythm): what is atrial fibrillation?
random signals originating from the AV node
cause ventricles to contract quickly and irregularly
can form clots, which can break off, reach the brain, and cause strokes
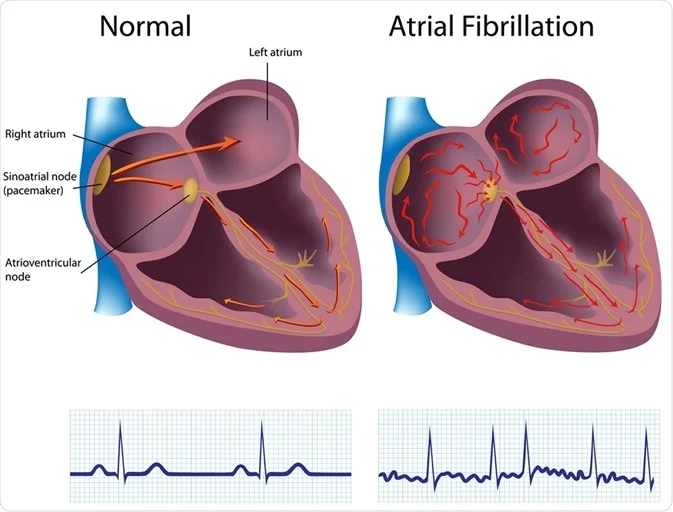
Arrhythmias (variation from normal heart rhythm): what is ventricular fibrillation? what causes this?
irregular beats originating w/i the ventricles
ventricles are unable to pump blood (quivering)
results in cardiac arrest
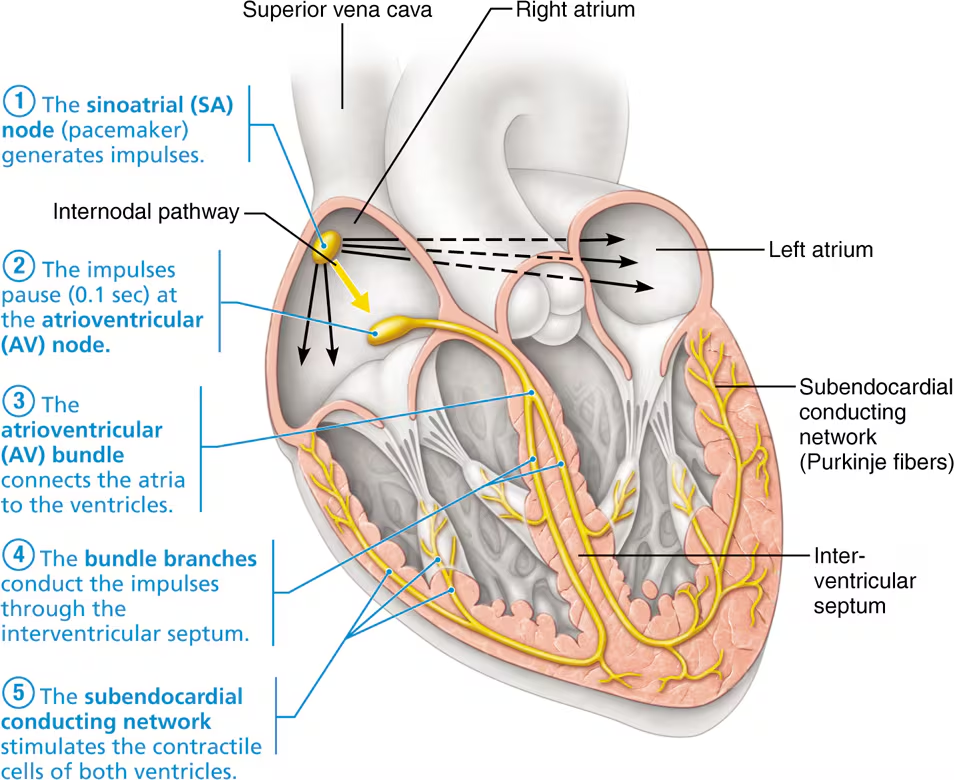
what is the conducting system? does it depend on extrinsic nerve impulses?
Conducting system: specialized cardiac muscle cells that carry impulses throughout the heart
does not depend on extrinsic nerve impulses, functions independently
what is the order of the conducting system pathway (5 components)?
SA node
AV node
AV bundle
bundle branches
purkinje fiber (subendocardial conducting network)
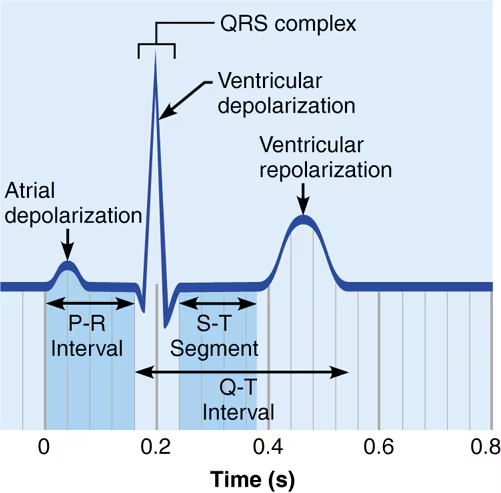
describe the 3 structures represented on an EKG, what does each represent?
P wave: atria contract (depolarize)
QRS complex: atria recharge (repolarization not visible, hidden by the spike) and ventricles contract (depolarize)
T wave: ventricles relax and recharge (repolarize)
heart sounds: lub-dup sound is made by what?
sound of valves closing
first sound: name and what causes it?
Lub (S1)
AV valves close (mitral & tricuspid)
ventricles start to squeeze
second sound: name and what causes it?
Dub (S2)
semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonary) close
ventricles begin to relax
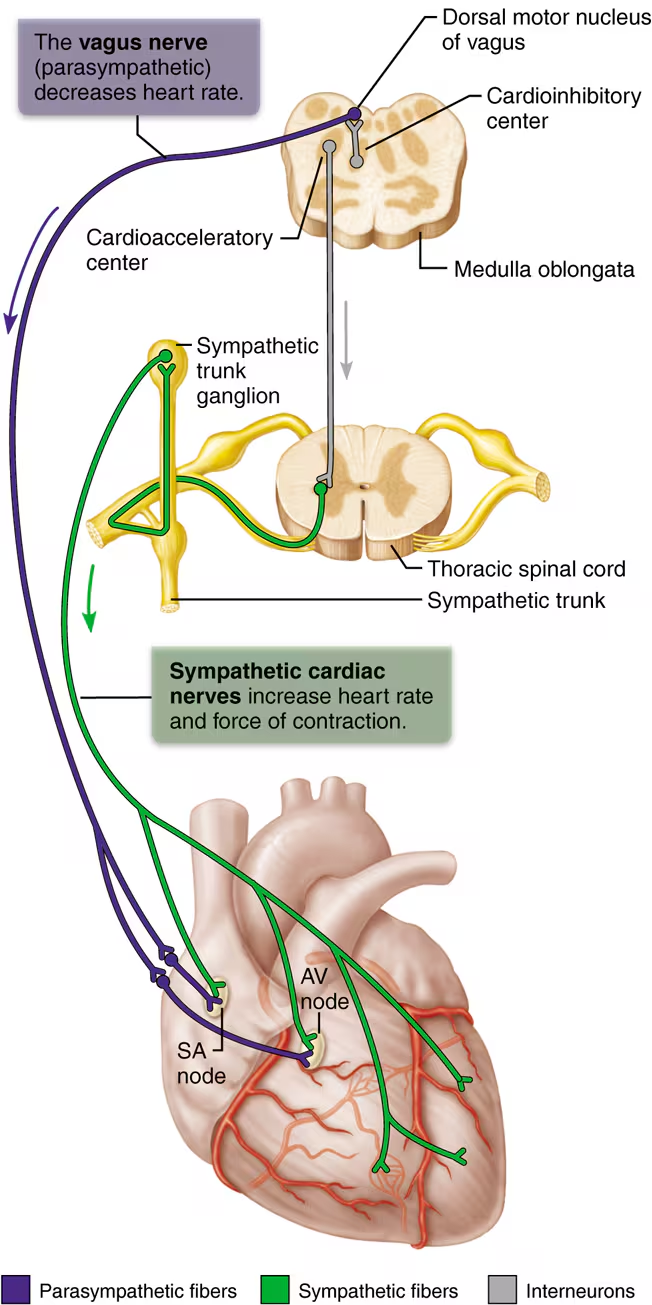
what controls heart rate? this can be altered by which 2 extrinsic neural controls?
SA node, sets the hearts inherent rate of contraction
Parasympathetic nerves: decreases HR (i.e. rest and digest)
Sympathetic nerves: increase HR and strength of contraction (i.e. fight or flight, emotion, exercise)
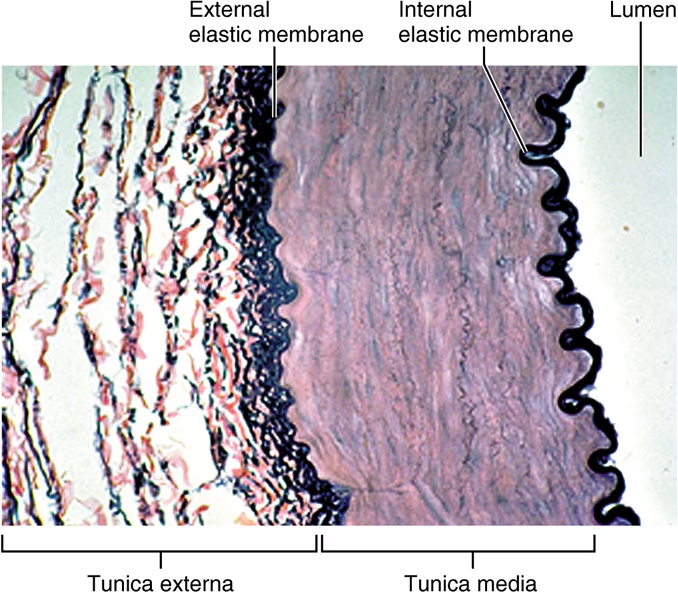
describe the 3 tunics that form the wall of blood vessels. what is the blood-filled space of a vessel called?
Tunica intima (deepest)
Contains simple squamous epithelium
Tunica media (functional layer)
contains smooth muscle for vasoconstriction and vasodilation
Tunica externa
composed of connective tissue
Lumen: contains blood
what are the 3 types of arteries?
elastic arteries
muscular (distributing) arteries
arterioles
Elastic arteries are the largest arteries, they contain a lot of (_) to help (_)?
a.k.a. conducting arteries because they are the pathway for blood leaving the heart
High amount of elastin to help soften the surge of blood pressure
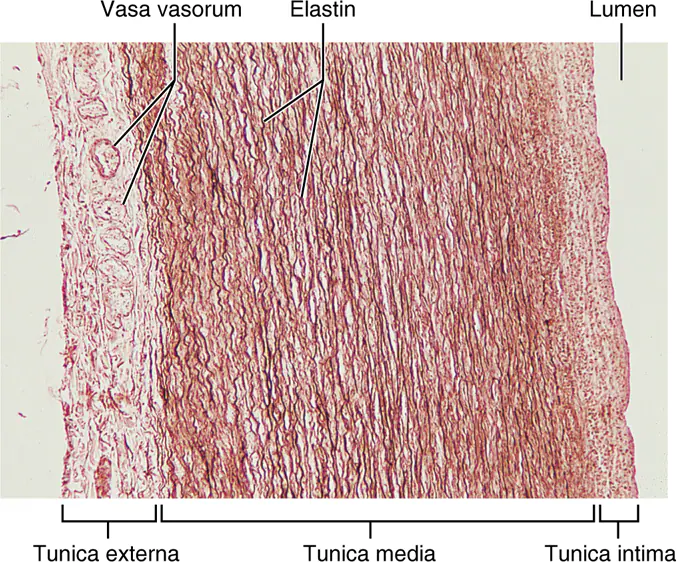
Muscular (distributing) arteries
function??
structure??
a.k.a named arteries
distribute blood to body regions and organs
thicker tunica media than elastic arteries
improved constriction/dilation
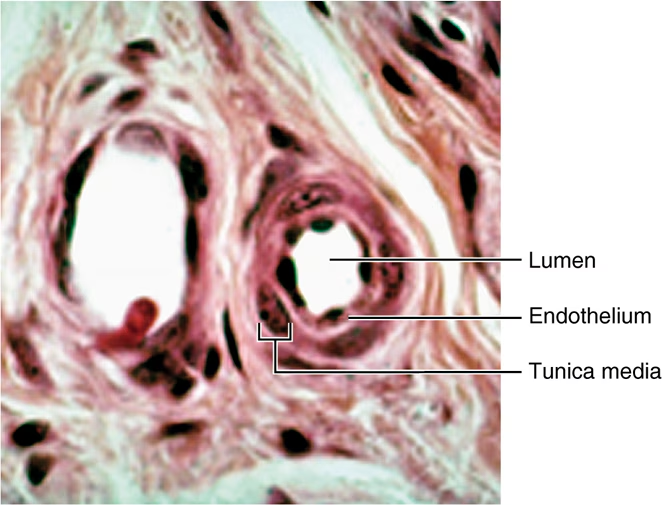
Arterioles are known as…?
These can be controlled by an intristic factor like…?
Smallest arteries (some only possess smooth muscle)
sympathetic NS
fight-or-flight triggers vasocontraction
increases BP and makes skin pale
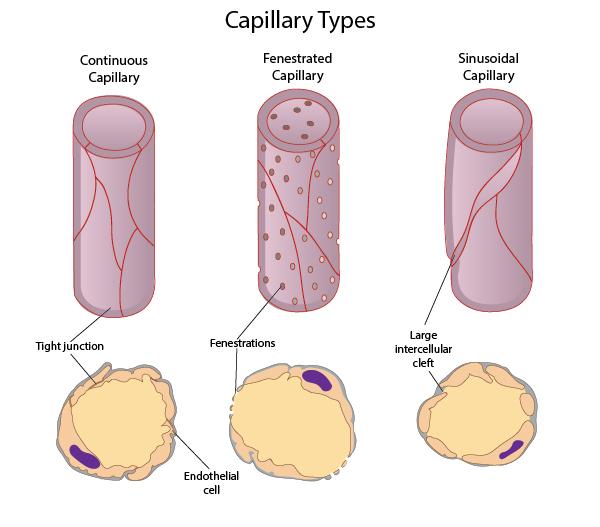
capillaries are the smallest blood vessels, for this reason RBCs pass through in (_). what are 4 site-specific function of capillaries?
Red blood cells pass through single file
Lungs: exchange O2 and CO2
Small intestines: receive nutrients
Endocrine glands: receive hormones
Kidneys: remove nitrogenous wastes
capillaries are the smallest blood vessels, what are the 3 types and their permeability?
Continuous: least permeable (most common)
Fenestrated: semi-permeable
Sinusoidal: most permeable
what 4 locations lack capillaries, meaning they are avascular?
epithelium
cartilage
cornea
lens
describe the size of venules. venules join the form what?
smallest veins
venules join to form veins
what are 4 key structural differences between veins and arteries?
Arteries // veins
Thicker walls // thinner walls
Thicker tunica media: more smooth muscle
Smaller, round lumens // wide, flattened lumens
No valves // have valves
Pulmonary circuit
direction of flow?
Heart → lungs
to oxygenate blood
Systemic circuit
Heart → Body (back to heart)
Oxygenate tissues
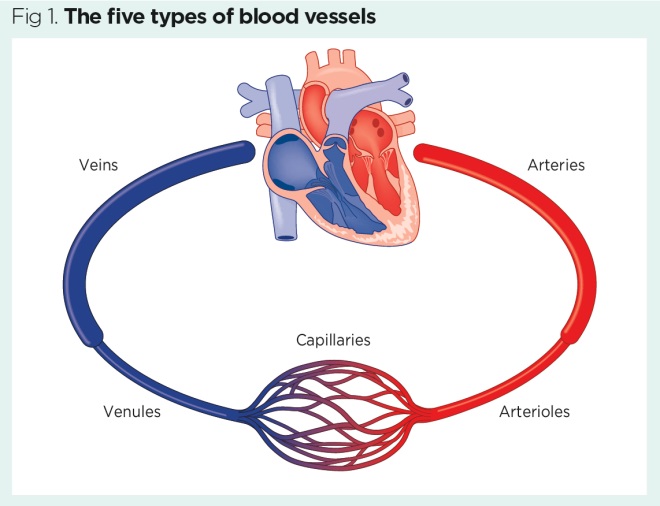
Flow of blood through blood vessels. 6 steps, 5 types of blood vessels
Heart → arteries
Arteries → arterioles
arterioles → capillaries
capillaries → venules
venules → veins
veins → heart