FRSC Fire and Explosion Investigations
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Fire Def
Transformation process by which O2 is united with another substance to produce heat and light
Oxidation def
Combustion of O2 with other substances to produce new products
Fast oxidation example + equation
Methane and O2
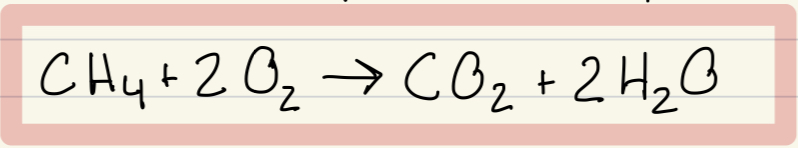
Slow oxidation example + equation
Rust

Why is the oxidation of iron//rust a slow reaction?
The electrons can’t vibrate as fast because iron is solid. When something like methane is oxidizing the reaction is faster because the electrons in gas vibrate more quickly
Energy def + examples
The ability/potential of a system or materia to do work
radiant
Thermal
Light
Mechanical
Nuclear
Electrical
Chemical
U get the idea
Where does the quantity of heat from a chemical reaction come from?
The breaking and formation of chemical bonds
Endothermic reaction + examples
Breaking of chemical bonds by absorption of energy
photosynthesis
Dissolving salt in water
Exothermic reactions + examples
Release of energy, typically as heat or light into the surroundings causing the temperature to increase
rusting
Campfire
Water and acid reaction
Freezing water into ice
When chemical bonds are formed, energy is____. This is an ____ reaction.
Released/liberated
Exothermic reaction
Combustion is a combination of what 3 things?
Oxygen, heat, and fuel
Energy barrier def
All reactions require an input of energy to start them
The _____ the energy barrier, the ____ energy is required to initiate the reaction
Higher
More
If iron + O2 has a low energy barrier and gasoline + O2 has a high energy barrier what is needed to cause a fast oxidation reaction
High temperature ! Must be applied to start the oxidation of the fuel
Ignition temperature
The temperature that the fuel must be raised to in order to exceed the energy barrier
Chain Reaction
Once combustion starts, enough heat is liberated to keep the reaction going by itself. The fire absorbs part of its own liberated heat to generate even more heat
Factors of influence for the rate of collision
Physical state of fuel → must be gaseous to support a flaming fire so that the molecules can collide frequently enough → high rates of collision
Temperature
Flashpoint def
The lowest temperature at which a liquid gives off sufficient vapor to form a mixture with air that will support combustion
3 requirements to initiate and sustain combustion
A fuel must be present
O2 must be available in sufficient quantities to combine with the fuel
Heat must be applied to initiate the combustion and sufficient heat must be generated to sustain the reaction
Heat transfer is critical in fire investigations as it explains how fire spreads. What 3 modes are there?
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
Conduction def
Heat travels through direct contact of solids to spread the fire or damage structures
The heat travels from HOT areas to COLD areas
Convection def
Heat transfer in fluids where the heated fluid rises and cooler fluid sinks, creating a continuous circulation loop
Ex. Boiling water
Radiation def
Transfer of heat energy from a heated surface to a cooler surface by electromagnetic radiation
Ex. Space heaters
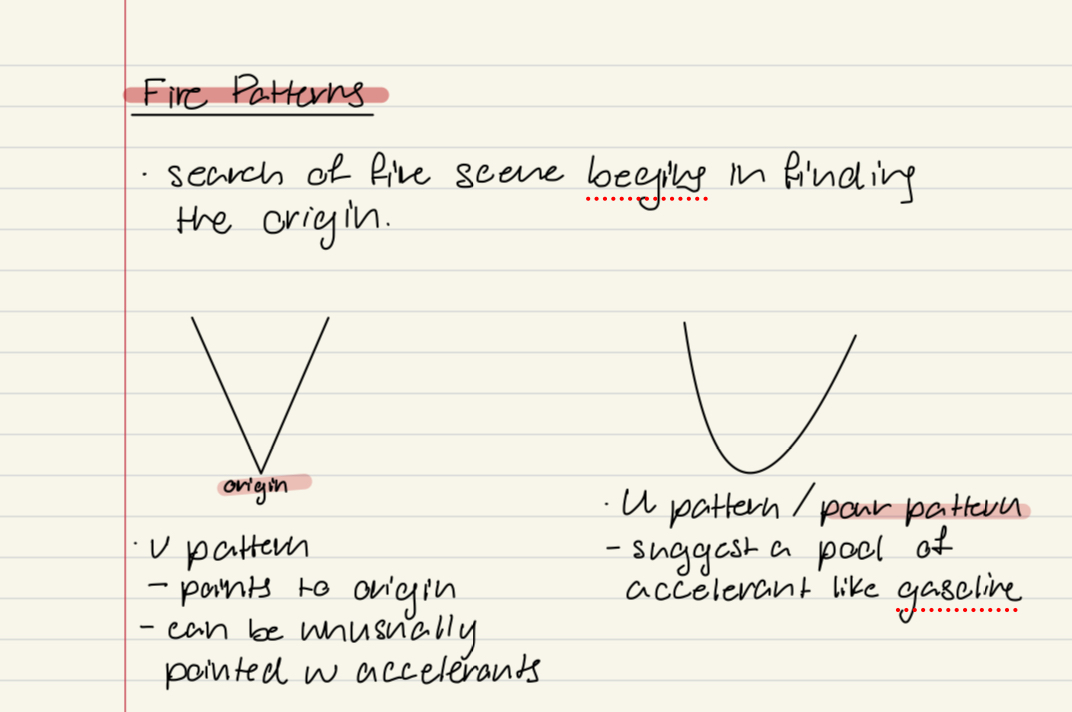
Where do searches of fire investigations begin
Finding the origin
Pour patterns
V patterns
points to the origin
Can be unusually pointed with accelerants
U pattern
“pour pattern”
Suggests a pool of accelerant like gasoline
Fires tend to move upward, so the probable origin point will be at the lowest point with the mose intense characteristics of burning
Hydrocarbon detection
Good screening tool for checking suspect samples
Where are samples of fire evidence kept
Airtight containers to prevent loss of evidence
Headspace vapor
